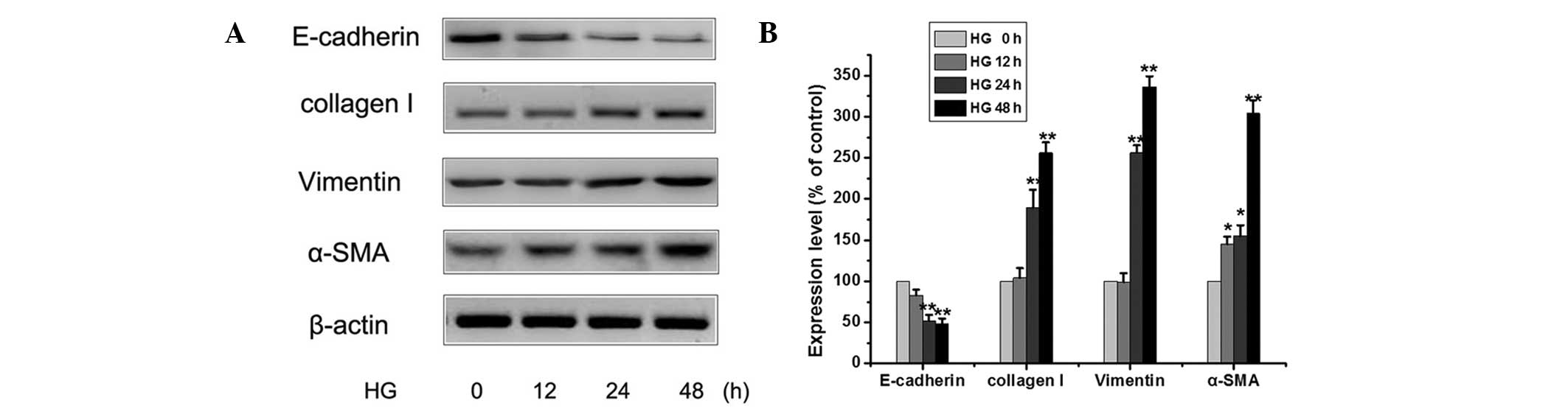
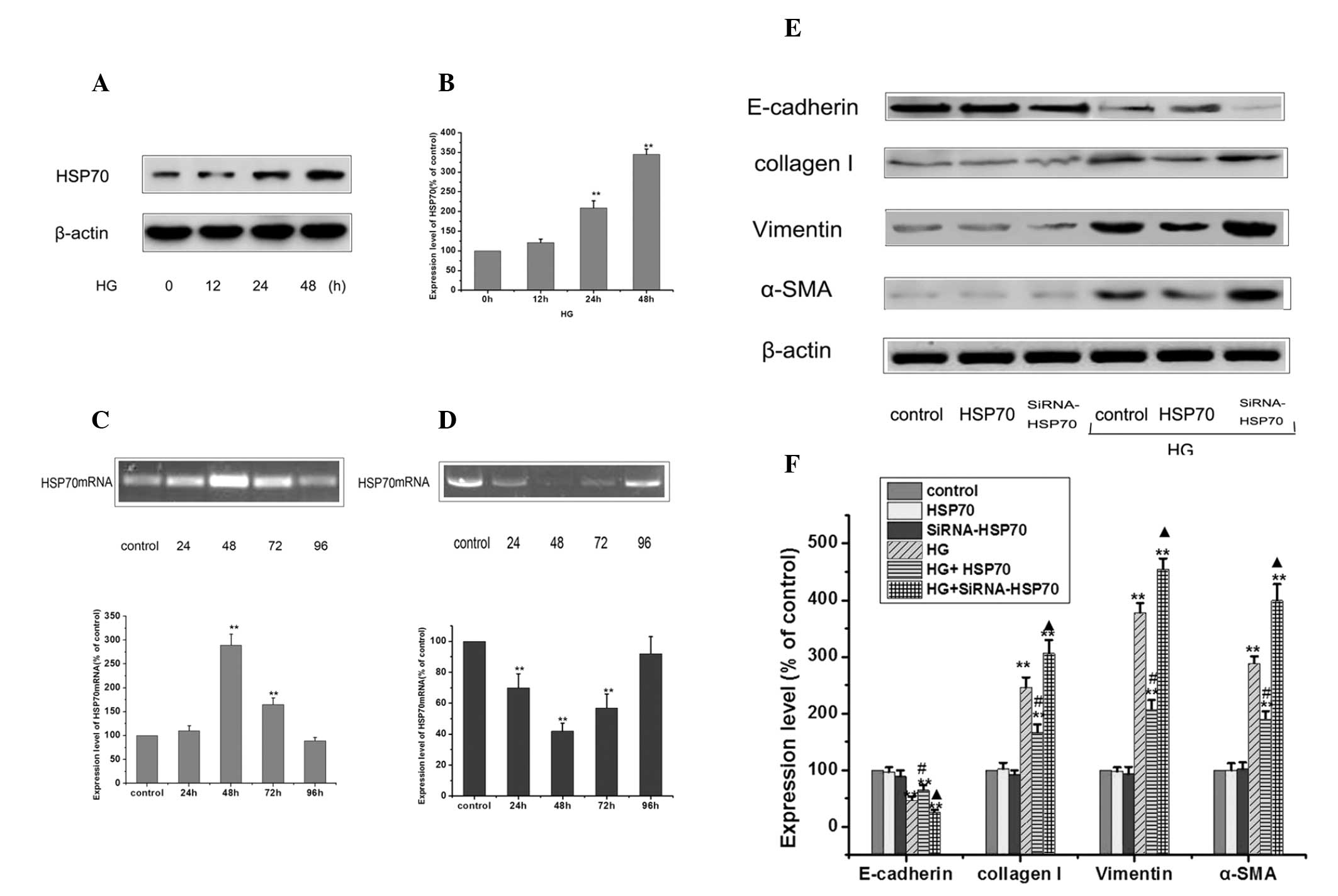
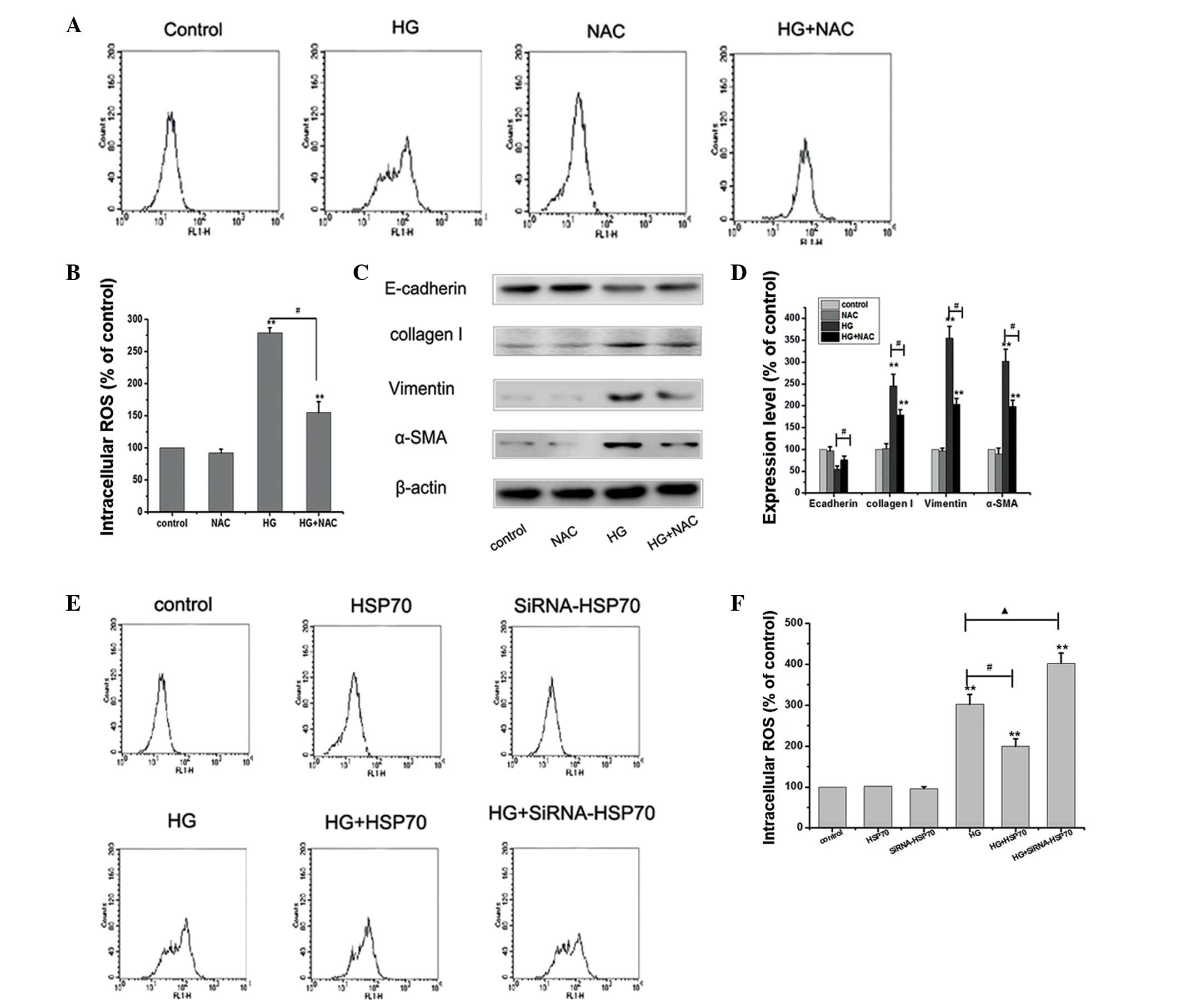
|
1
|
Jager KJ, van Dijk PC, Dekker FW, Stengel
B, Simpson K and Briggs JD; ERA-EDTA Registry Committee. The
epidemic of aging in renal replacement therapy: an update on
elderly patients and their outcomes. Clin Nephrol. 60:352–360.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee YJ and Han HJ: Troglitazone
ameliorates high glucose-induced EMT and dysfunction of SGLTs
through PI3K/Akt, GSK-3β, Snail1, and β-catenin in renal proximal
tubule cells. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 5:F1263–F1275.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Alisson-Silva F, Freire-de-Lima L, Donadio
JL, Lucena MC, Penha L, Sá-Diniz JN, Dias WB and Todeschini AR:
Increase of O-glycosylated oncofetal fibronectin in high
glucose-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition of cultured human
epithelial cells. PLoS One. 8:e604712013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Naber HP, Drabsch Y, Snaar-Jagalska BE,
ten Dijke P and van Laar T: Snail and Slug, key regulators of
TGF-β-induced EMT, are sufficient for the induction of single-cell
invasion. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 435:58–63. 2013.
|
|
5
|
Lu X and Kakkar V: The role of heat shock
protein (HSP) in atherosclerosis: Pathophysiology and clinical
opportunities. Curr Med Chem. 17:957–973. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Mayer MP and Bukau B: Hsp70 chaperones:
cellular functions and molecular mechanism. Cell Mol Life Sci.
62:670–684. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chatterjee M, Andrulis M, Stühmer T,
Müller E, Hofmann C, Steinbrunn T, Heimberger T, Schraud H,
Kressmann S, Einsele H and Bargou RC: The PI3K/Akt signaling
pathway regulates the expression of Hsp70, which critically
contributes to Hsp90-chaperone function and tumor cell survival in
multiple myeloma. Haematologica. 98:1132–1141. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mikuriya T, Sugahara K, Takemoto T, Tanaka
K, Takeno K, Shimogori H, Nakai A and Yamashita H:
Geranylgeranylacetone, a heat shock protein inducer, prevents
acoustic injury in the guinea pig. Brain Res. 1065:107–114. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Margetts PJ, Bonniaud P, Liu L, Hoff CM,
Holmes CJ, West-Mays JA and Kelly MM: Transient overexpression of
TGF-{beta}1 induces epithelial mesenchymal transition in the rodent
peritoneum. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:425–436. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rhyu DY, Yang Y, Ha H, et al: Role of
reactive oxygen species in TGF-beta1-induced mitogen-activated
protein kinase activation and epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
renal tubular epithelial cells. J Am Soc Nephrol. 16:667–675. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Grassmann A, Gioberge S, Moeller S and
Brown G: End-stage renal disease: global demographics in 2005 and
observed trends. Artif Organs. 30:895–897. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Fang CC, Huang JW, Shyu RS, Yen CJ, Shiao
CH, Chiang CK, Hu RH and Tsai TJ: Fibrin-induced
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition of peritoneal mesothelial
cells as a mechanism of peritoneal fibrosis: effects of
pentoxifylline. PLoS One. 7:e447652012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Grune T, Catalgol B, Licht A, Ermak G,
Pickering AM, Ngo JK and Davies KJ: HSP70 mediates dissociation and
reassociation of the 26S proteasome during adaptation to oxidative
stress. Free Radic Biol Med. 51:1355–1364. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yao Q, Pawlaczyk K, Ayala ER, Styszynski
A, Breborowicz A, Heimburger O, Qian JQ, Stenvinkel P, Lindholm B
and Axelsson J: The role of the TGF/Smad signaling pathway in
peritoneal fibrosis induced by peritoneal dialysis solutions.
Nephron Exp Nephrol. 109:e71–e78. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Neil JR, Johnson KM, Nemenoff RA and
Schiemann WP: Cox-2 inactivates Smad signaling and enhances EMT
stimulated by TGF-beta through a PGE2-dependent mechanisms.
Carcinogenesis. 29:2227–2235. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Loor G, Kondapalli J, Schriewer JM,
Chandel NS, Vanden Hoek TL and Schumacker PT: Menadione triggers
cell death through ROS-dependent mechanisms involving PARP
activation without requiring apoptosis. Free Radic Biol Med.
49:1925–1936. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Chen Z, Pittman EF, Romaguera J, Fayad L,
Wang M, Neelapu SS, McLaughlin P, Kwak L and McCarty N: Nuclear
translocation of B-cell-specific transcription factor, BACH2,
modulates ROS mediated cytotoxic responses in mantle cell lymphoma.
PLoS One. 8:e691262013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Hu Y, He K, Wang D, Yuan X, Liu Y, Ji H
and Song J: TMEPAI regulates EMT in lung cancer cells by modulating
the ROS and IRS-1 signaling pathways. Carcinogenesis. 34:1764–1772.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Henningsen C, Zahner G and Thaiss F: High
glucose induces type 1 hexokinase gene expression in isolated
glomeruli of diabetic rats and in mesangial cells. Nephron Physiol.
93:p67–p75. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Di Domenico F, Sultana R, Tiu GF, Scheff
NN, Perluigi M, Cini C and Butterfield DA: Protein levels of heat
shock proteins 27, 32, 60, 70, 90 and thioredoxin-1 in amnestic
mild cognitive impairment: an investigation on the role of cellular
stress response in the progression of Alzheimer disease. Brain Res.
1333:72–81. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Scarpeci TE, Zanor MI and Valle EM:
Investigating the role of plant heat shock proteins during
oxidative stress. Plant Signal Behav. 3:856–857. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|