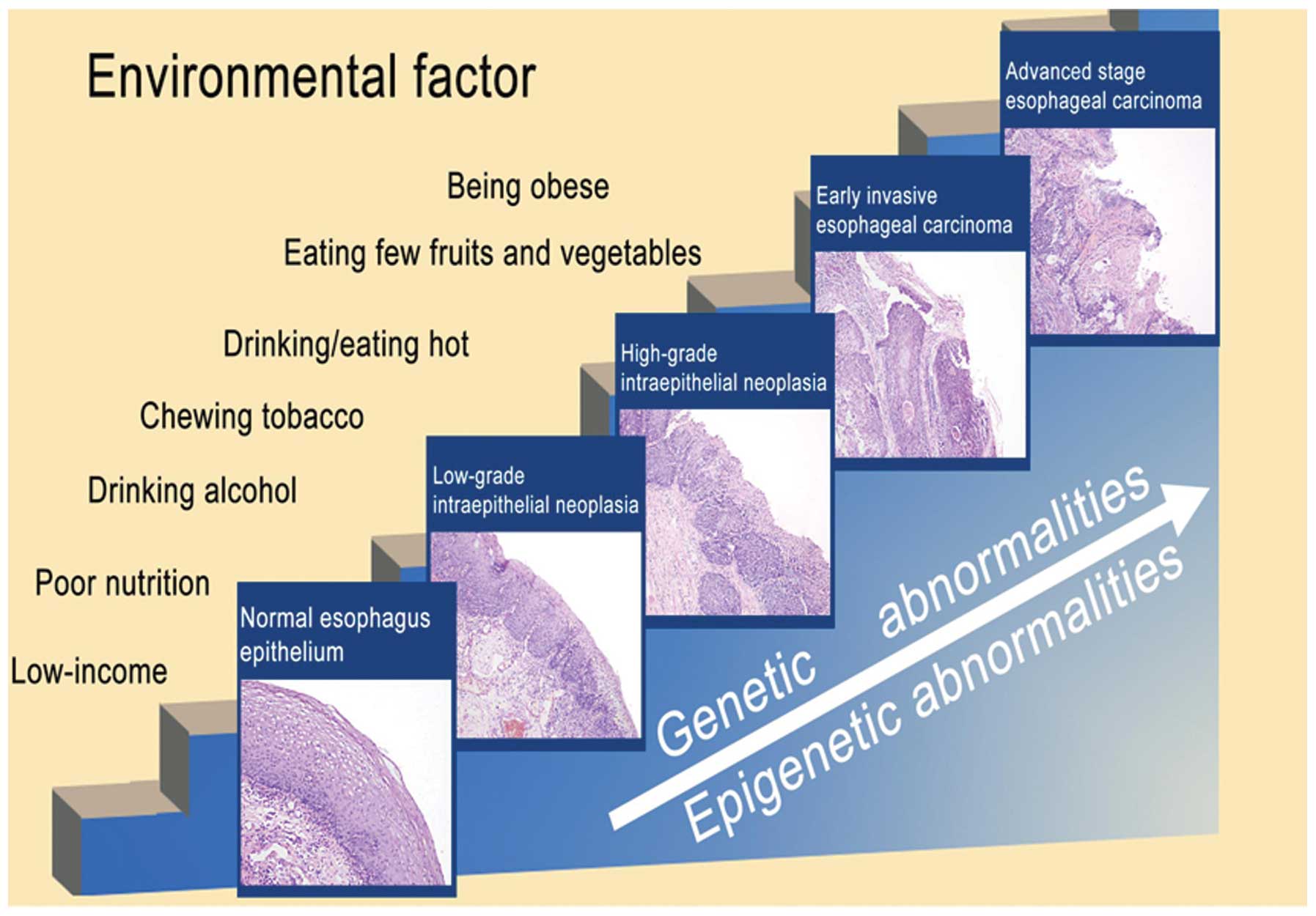
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tischoff I and Tannapfel A: Barrett’s
esophagus: can biomarkers predict progression to malignancy? Expert
Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2:653–663. 2008.
|
|
3
|
Kaneko K, Katagiri A, Konishi K, et al:
Study of p53 gene alteration as a biomarker to evaluate the
malignant risk of Lugol-unstained lesion with non-dysplasia in the
oesophagus. Br J Cancer. 96:492–498. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Shimizu Y, Yoshida T, Kato M, et al:
Low-grade dysplasia component in early invasive squamous cell
carcinoma of the esophagus. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 25:314–318.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Kobayashi M, Kawachi H, Takizawa T, et al:
p53 mutation analysis of low-grade dysplasia and high-grade
dysplasia/carcinoma in situ of the esophagus using laser capture
microdissection. Oncology. 71:237–245. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tao DM, Xu YZ, Gu YK, et al: A study of
the carcinogenesis time and incidence of carcinoma in 46,161 cases
with normal and hyperplastic esophageal epithelia. Cancer Res Prev
Treat. 24:155–156. 1997.(In Chinese).
|
|
7
|
Sugimachi K, Sumiyoshi K, Nozoe T, Yasuda
M, Watanabe M, Kitamura K, Tsutsui S, Mori M and Kuwano H:
Carcinogenesis and histogenesis of esophageal carcinoma. Cancer.
75(Suppl): 1440–1445. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kamangar F, Diaw L, Wei WQ, et al: Serum
pepsinogens and risk of esophageal squamous dysplasia. Int J
Cancer. 124:456–460. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chen W, Abnet CC, Wei WQ, Roth MJ, Lu N,
Taylor PR, Pan QJ, Luo XM, Dawsey SM and Qiao YL: Serum markers as
predictors of esophageal squamous dysplasia and early cancer.
Anticancer Res. 24:3245–3249. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Shamma A, Doki Y, Shiozaki H, Tsujinaka T,
Yamamoto M, Inoue M, Yano M and Monden M: Cyclin D1 overexpression
in esophageal dysplasia: a possible biomarker for carcinogenesis of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oncol. 16:261–266.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang WC, Wu TT, Chandan VS, Lohse CM and
Zhang L: Ki-67 and ProExC are useful immunohistochemical markers in
esophageal squamous intraepithelial neoplasia. Hum Pathol.
42:1430–1437. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Sakamoto K, Fujii T, Kawachi H, Miki Y,
Omura K, Morita K, Kayamori K, Katsube K and Yamaguchi A: Reduction
of NOTCH1 expression pertains to maturation abnormalities of
keratinocytes in squamous neoplasms. Lab Invest. 92:688–702. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
ENCODE Project Consortium. Birney E,
Stamatoyannopoulos JA and Dutta A: Identification and analysis of
functional elements in 1% of the human genome by the ENCODE pilot
project. Nature. 447:799–816. 2007.
|
|
14
|
Kurokawa R, Rosenfeld MG and Glass CK:
Transcriptional regulation through noncoding RNAs and epigenetic
modifications. RNA Biol. 6:233–236. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Moran VA, Perera RJ and Khalil AM:
Emerging functional and mechanistic paradigms of mammalian long
non-coding RNAs. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:6391–6400. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kugel JF and Goodrich JA: Non-coding RNAs:
key regulators of mammalian transcription. Trends Biochem Sci.
37:144–151. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Costa FF: Non-coding RNAs: Meet thy
masters. BioEssays. 32:599–608. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Garzon R, Calin GA and Croce CM: MicroRNAs
in cancer. Annu Rev Med. 60:167–179. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Chen ZL, Zhao XH, Wang JW, et al:
microRNA-92a promotes lymph node metastasis of human esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma via E-cadherin. J Biol Chem.
286:10725–10734. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo Y, Chen Z, Zhang L, et al: Distinctive
microRNA profiles relating to patient survival in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Cancer Res. 68:26–33. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
IAkagi I, Miyashita M, Ishibashi O,
Mishima T, Kikuchi K, Makino H, Nomura T, Hagiwara N, Uchida E and
Takizawa T: Relationship between altered expression levels of
MIR21, MIR143, MIR145, and MIR205 and clinicopathologic features of
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Dis Esophagus. 24:523–530.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hong L, Han Y, Zhang H, Li M, Gong T, Sun
L, Wu K, Zhao Q and Fan D: The prognostic and chemotherapeutic
value of miR-296 in esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg.
251:1056–1063. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tian D, Sun S and Lee JT: The long
noncoding RNA, Jpx, is a molecular switch for X chromosome
inactivation. Cell. 143:390–403. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kretz M, Siprashvili Z, Chu C, et al:
Control of somatic tissue differentiation by the long non-coding
RNA TINCR. Nature. 493:231–235. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kretz M, Webster DE, Flockhart RJ, et al:
Suppression of progenitor differentiation requires the long
noncoding RNA ANCR. Gene Dev. 26:338–343. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Pang KC, Dinger ME, Mercer TR, et al:
Genome-wide identification of long noncoding RNAs in
CD8+T cells. J Immunol. 182:7738–7748. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Aoki K, Harashima A, Sano M, Yokoi T,
Nakamura S, Kibata M and Hirose T: A thymus-specific noncoding RNA,
Thy-ncR1, is a cytoplasmic riboregulator of MFAP4 mRNA in immature
T-cell lines. BMC Mol Bio. 11:992010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Khaitan D, Dinger ME, Mazar J, et al: The
melanoma-upregulated long noncoding RNA SPRY4-IT1 modulates
apoptosis and invasion. Cancer Res. 71:3852–3862. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Du Y, Kong G, You X, et al: Elevation of
highly up-regulated in liver cancer (HULC) by hepatitis B virus X
protein promotes hepatoma cell proliferation via down-regulating
p18. J Biol Chem. 287:26302–26311. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Jin G, Sun J, Isaacs SD, et al: Human
polymorphisms at long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and association
with prostate cancer risk. Carcinogenesis. 32:1655–1659. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gibb EA, Enfield KS, Stewart GL, Lonergan
KM, Chari R, Ng RT, Zhang L, MacAulay CE, Rosin MP and Lam WL: Long
non-coding RNAs are expressed in oral mucosa and altered in oral
premalignant lesions. Oral Oncol. 47:1055–1061. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME, Mariani J, et al:
Noncoding RNAs in long-term memory formation. Neuroscientist.
14:434–445. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Huo JS and Zambidis ET: Pivots of
pluripotency: the roles of non-coding RNA in regulating embryonic
and induced pluripotent stem cells. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1830.2385–2394. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ota T, Suzuki Y, Nishikawa T, et al:
Complete sequencing and characterization of 21,243 full-length
human cDNAs. Nat Genet. 36:40–45. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Sun J, Zhou M, Mao ZT, et al: Systematic
analysis of genomic organization and structure of long non-coding
RNAs in the human genome. FEBS Lett. 587:976–982. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Okazaki Y, Furuno M, Kasukawa T, et al;
FANTOM Consortium; RIKEN Genome Exploration Research Group Phase
I&II Team. Analysis of the mouse transcriptome based on
functional annotation of 60,770 full-length cDNAs. Nature.
420:563–573. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mercer TR, Dinger ME and Mattick JS: Long
non-coding RNAs: insights into functions. Nat Rev Genet.
10:155–159. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Rinn JL and Chang HY: Genome regulation by
long noncoding RNAs. Annu Rev Biochem. 81:145–166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wilusz JE, Sunwoo H and Spector DL: Long
noncoding RNAs: functional surprises from the RNA world. Genes Dev.
23:1494–1504. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Chen FJ, Sun M, Li SQ, et al: Upregulation
of the long non-coding RNA HOTAIR promotes esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma metastasis and poor prognosis. Mol Carcinog. 52:908–915.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
41
|
Cao W, Wu W, Shi F, et al: Integrated
analysis of long noncoding RNA and coding RNA expression in
esophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Genomics.
2013:4805342013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li J, Chen Z, Tian L, et al: LncRNA
profile study reveals a three-lncRNA signature associated with the
survival of patients with oesophageal squamous cell carcinoma. Gut.
Feb 12–2014.(Epub ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
43
|
Hanahan D and Weinberg RA: Hallmarks of
cancer: the next generation. Cell. 144:646–674. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Li SQ, Chen FJ and Cao XF: Distinctive
microRNAs in esophageal tumor: early diagnosis, prognosis judgment,
and tumor treatment. Dis Esophagus. 26:288–298. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Ørom UA, Derrien T, Beringer M, et al:
Long noncoding RNAs with enhancer-like function in human cells.
Cell. 143:46–58. 2010.
|
|
46
|
Wamstad JA, Alexander JM, Truty RM, et al:
Dynamic and coordinated epigenetic regulation of developmental
transitions in the cardiac lineage. Cell. 151:206–220. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Vallot C, Huret C, Lesecque Y, Resch A,
Oudrhiri N, Bennaceur-Griscelli A, Duret L and Rougeulle C: XACT, a
long noncoding transcript coating the active X chromosome in human
pluripotent cells. Nat Genet. 45:239–241. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Redrup L, Branco MR, Perdeaux ER, et al:
The long noncoding RNA Kcnq1ot1 organises a lineage-specific
nuclear domain for epigenetic gene silencing. Development.
136:525–530. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Pasmant E, Sabbagh A, Vidaud M and Bièche
I: ANRIL, a long, noncoding RNA, is an unexpected major hotspot in
GWAS. FASEB J. 25:444–448. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Braconi C, Kogure T, Valeri N, Huang N,
Nuovo G, Costinean S, Negrini M, Miotto E, Croce CM and Patel T:
microRNA-29 can regulate expression of the long non-coding RNA gene
MEG3 in hepatocellular cancer. Oncogene. 30:4750–4756. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Wang J, Liu X, Wu H, Ni P, Gu Z, Qiao Y,
Chen N, Sun F and Fan Q: CREB up-regulates long non-coding RNA,
HULC expression through interaction with microRNA-372 in liver
cancer. Nucleic Acids Res. 38:5366–5383. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Roth C, Stückrath I, Pantel K, et al: Low
levels of cell-free circulating miR-361-3p and miR-625*
as blood-based markers for discriminating malignant from benign
lung tumors. PloS One. 7:e382482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Tanaka H, Nakashiro KI, Oka R, et al:
MicroRNA-361-3p functions as an oncogenic microRNA in human oral
cancer cells. Cancer Res. 71(Suppl 1): 1452011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
54
|
Hughes AH, Sharma G, Roy S, et al:
microRNA expression and mRNA transcripts in clear cell
(conventional) renal cell carcinoma. Lab Invest. 91(Suppl 1s):
199A–200A. 2011.
|
|
55
|
Xiong W, Chen X, Liu F, et al: MiRNA
expression profile of microvesicles derived from K562 cells. Blood
(ASH Annual Meeting Abstracts). 118:44112011.
|
|
56
|
Sultan A, Kiet T, Chan J, et al:
Significance of microRNAs in determining taxane resistance in
ovarian cancer. Gynecol Oncol. 125(Suppl 1): S1312012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
57
|
Miyata H, Doki Y, Shiozaki H, et al:
CDC25B and p53 are independently implicated in radiation
sensitivity for human esophageal cancers. Clin Cancer Res.
6:4859–4865. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
58
|
Xue LY, Hu N, Song YM, et al: Tissue
microarray analysis reveals a tight correlation between protein
expression pattern and progression of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. BMC Cancer. 6:2962006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
59
|
Li JM, Wang J, Liu H, et al: The
expressions of CDC25A and CDC25B in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma and their relationship with cell apoptosis and
proliferation. Tumor. 28:586–590. 2008.(In Chinese).
|
|
60
|
Jiang Y, Liang ZD, Wu TT, et al:
Ataxia-telangiectasia mutated expression is associated with tobacco
smoke exposure in esophageal cancer tissues and benzo[a]pyrene diol
epoxide in cell lines. Int J Cancer. 120:91–95. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
61
|
Wan Y and Wu XY: Expression and clinical
significance of DAPK1 and CD147 in esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma. Zhonghua Zhong Liu Za Zhi. 34:44–48. 2012.(In
Chinese).
|
|
62
|
Daigeler A, Chromik AM, Geisler A, et al:
Synergistic apoptotic effects of taurolidine and TRAIL on squamous
carcinoma cells of the esophagus. Int J Oncol. 32:1205–1220. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
63
|
Fukuda K, Sakakura C, Miyagawa K, et al:
Differential gene expression profiles of radioresistant oesophageal
cancer cell lines established by continuous fractionated
irradiation. Br J Cancer. 91:1543–1550. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|