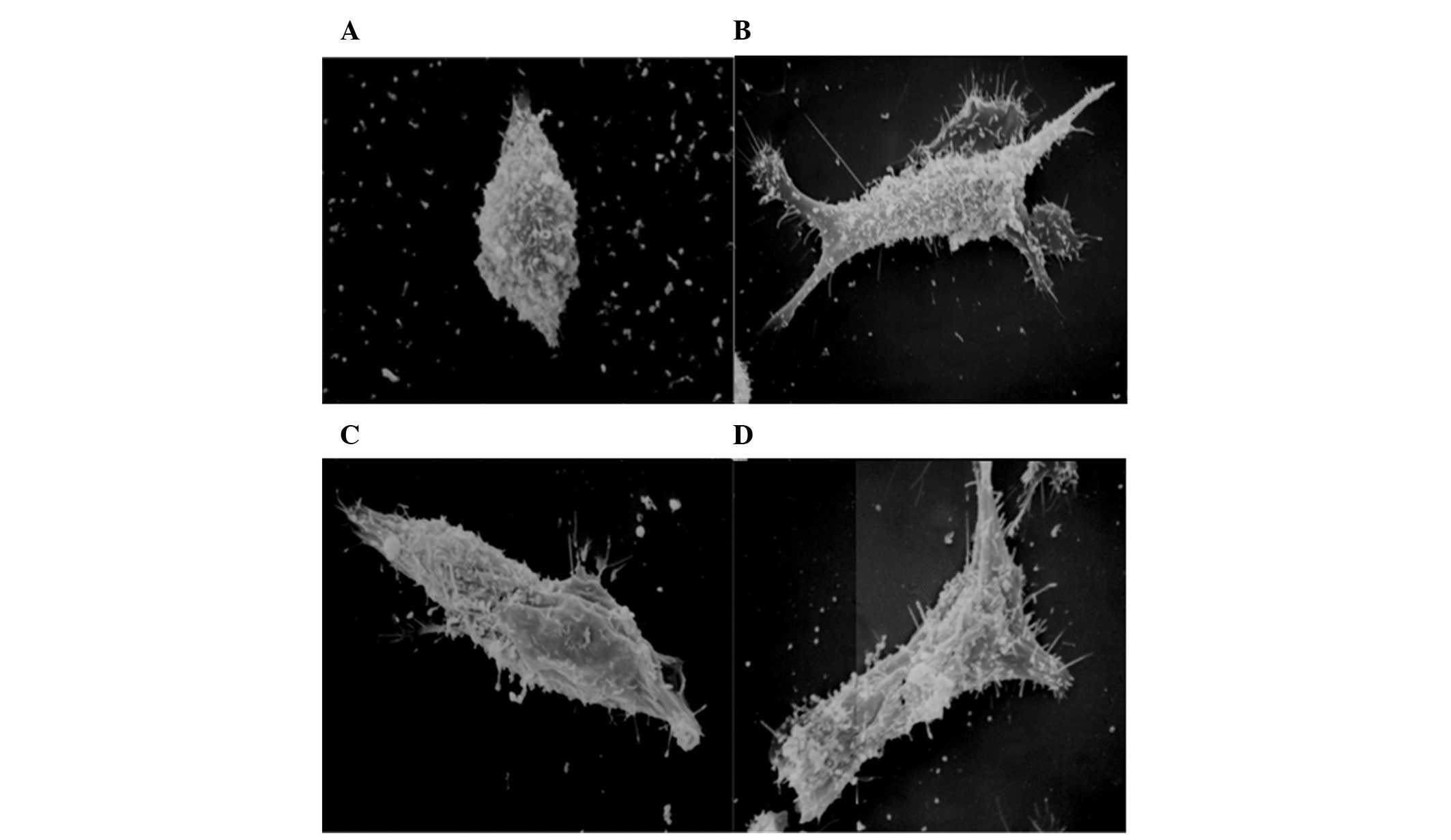
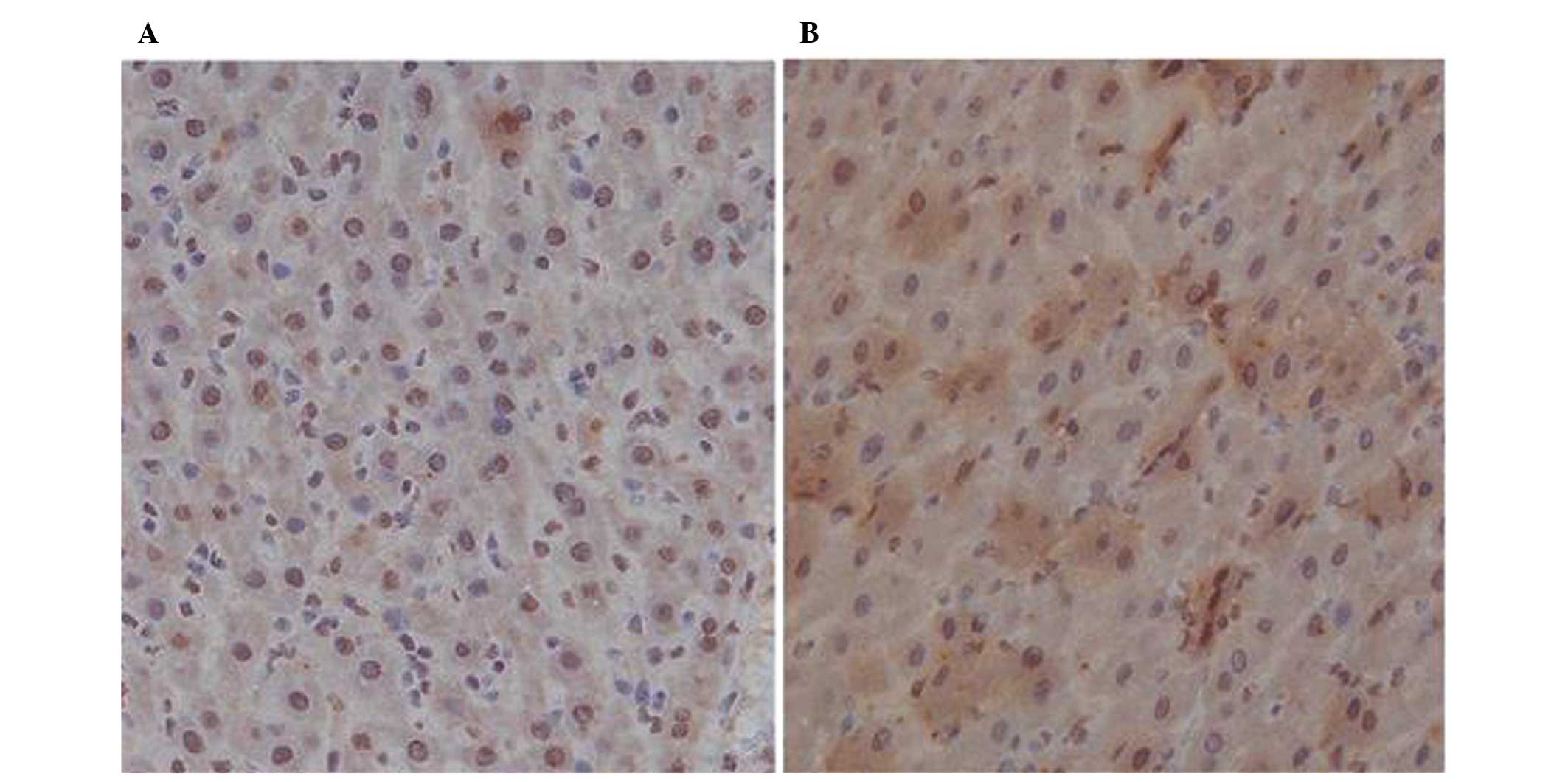
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al: Cancer
statistics, 2008. CA Cancer J Clin. 58:71–96. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cheng AL, Kang YK, Chen Z, et al: Efficacy
and safety of sorafenib in patients in the Asia-Pacific region with
advanced hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised,
double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Oncol. 10:25–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Thorgeirsson SS and Grisham JW: Molecular
pathogenesis of human hepatocellular carcinoma. Nat Genet.
31:339–346. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yao FY, Ferrell L, Bass NM, et al: Liver
transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: expansion of the
tumor size limits does not adversely impact survival. Hepatology.
33:1394–1403. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Escartin A, Sapisochin G, Bilbao I, et al:
Recurrence of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver transplantation.
Transplant Proc. 39:2308–2310. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Vivarelli M, Cucchetti A, Piscaglia F, et
al: Analysis of risk factors for tumor recurrence after liver
transplantation for hepatocellular carcinoma: key role of
immunosuppression. Liver Transpl. 11:497–503. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Leung JY, Zhu AX, Gordon FD, et al: Liver
transplantation outcomes for early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma:
results of a multicenter study. Liver Transpl. 10:1343–1354. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Vivarelli M, Bellusci R, Cucchetti A, et
al: Low recurrence rate of hepatocellular carcinoma after liver
transplantation: better patient selection or lower
immunosuppression? Transplantation. 74:1746–1751. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Haufroid V, Mourad M, Van Kerckhove V, et
al: The effect of CYP3A5 and MDR1 (ABCB1) polymorphisms on
cyclosporine and tacrolimus dose requirements and trough blood
levels in stable renal transplant patients. Pharmacogenetics.
14:147–154. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
McAlister VC, Gao Z, Peltekian K,
Domingues J, Mahalati K and MacDonald AS: Sirolimus-tacrolimus
combination immunosuppression. Lancet. 355:376–377. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Dumont FJ: FK506, an immunosuppressant
targeting calcineurin function. Curr Med Chem. 7:731–748. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Paloyan EB, Swinnen LJ, Montoya A,
Lonchyna V, Sullivan HJ and Garrity E: Lung transplantation for
advanced bronchioloalveolar carcinoma confined to the lungs.
Transplantation. 69:2446–2448. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou ZJ, Dai Z, Zhou SL, et al:
Overexpression of HnRNP A1 promotes tumor invasion through
regulating CD44v6 and indicates poor prognosis for hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Cancer. 132:1080–1089. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Ogawa T, Tashiro H, Miyata Y, et al:
Rho-associated kinase inhibitor reduces tumor recurrence after
liver transplantation in a rat hepatoma model. Am J Transplant.
7:347–355. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hatse S, Princen K, Bridger G, De Clercq E
and Schols D: Chemokine receptor inhibition by AMD3100 is strictly
confined to CXCR4. FEBS Lett. 527:255–262. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Schimanski CC, Bahre R, Gockel I, et al:
Dissemination of hepatocellular carcinoma is mediated via chemokine
receptor CXCR4. Br J Cancer. 95:210–217. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sehgal A, Ricks S, Boynton AL, Warrick J
and Murphy GP: Molecular characterization of CXCR-4: a potential
brain tumor-associated gene. J Surg Oncol. 69:239–248. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Muller A, Homey B, Soto H, et al:
Involvement of chemokine receptors in breast cancer metastasis.
Nature. 410:50–56. 2001. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Kucia M, Jankowski K, Reca R, et al:
CXCR4-SDF-1 signalling, locomotion, chemotaxis and adhesion. J Mol
Histol. 35:233–245. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Libura J, Drukala J, Majka M, et al:
CXCR4-SDF-1 signaling is active in rhabdomyosarcoma cells and
regulates locomotion, chemotaxis, and adhesion. Blood.
100:2597–2606. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Gao Q, Wang XY, Qiu SJ, et al:
Overexpression of PD-L1 significantly associates with tumor
aggressiveness and postoperative recurrence in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Clin Cancer Res. 15:971–979. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Gao Q, Qiu SJ, Fan J, et al: Intratumoral
balance of regulatory and cytotoxic T cells is associated with
prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma after resection. J Clin
Oncol. 25:2586–2593. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Semela D, Piguet AC, Kolev M, et al:
Vascular remodeling and antitumoral effects of mTOR inhibition in a
rat model of hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 46:840–848. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Yang R, Rescorla FJ, Reilly CR, et al: A
reproducible rat liver cancer model for experimental therapy:
introducing a technique of intrahepatic tumor implantation. J Surg
Res. 52:193–198. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang GQ, Han F, Fang XZ and Ma XM: CD4+,
IL17 and Foxp3 expression in different pTNM stages of operable
non-small cell lung cancer and effects on disease prognosis. Asian
Pac J Cancer Prev. 13:3955–3960. 2012.
|
|
28
|
Maluccio M, Sharma V, Lagman M, et al:
Tacrolimus enhances transforming growth factor-beta1 expression and
promotes tumor progression. Transplantation. 76:597–602. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Gutierrez-Dalmau A and Campistol JM:
Immunosuppressive therapy and malignancy in organ transplant
recipients: a systematic review. Drugs. 67:1167–1198. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang JP, Lu WG, Ye F, Chen HZ, Zhou CY
and Xie X: Study on CXCR4/SDF-1alpha axis in lymph node metastasis
of cervical squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Gynecol Cancer.
17:478–483. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Mitra P, De A, Ethier MF, et al: Loss of
chemokine SDF-1alpha-mediated CXCR4 signalling and receptor
internalization in human hepatoma cell line HepG2. Cell Signal.
13:311–319. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kim SW, Kim HY, Song IC, et al:
Cytoplasmic trapping of CXCR4 in hepatocellular carcinoma cell
lines. Cancer Res Treat. 40:53–61. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sutton A, Friand V, Brule-Donneger S, et
al: Stromal cell-derived factor-1/chemokine (C-X-C motif) ligand 12
stimulates human hepatoma cell growth, migration, and invasion. Mol
Cancer Res. 5:21–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Arakaki R, Tamamura H, Premanathan M, et
al: T134, a small-molecule CXCR4 inhibitor, has no cross-drug
resistance with AMD3100, a CXCR4 antagonist with a different
structure. J Virol. 73:1719–1723. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|