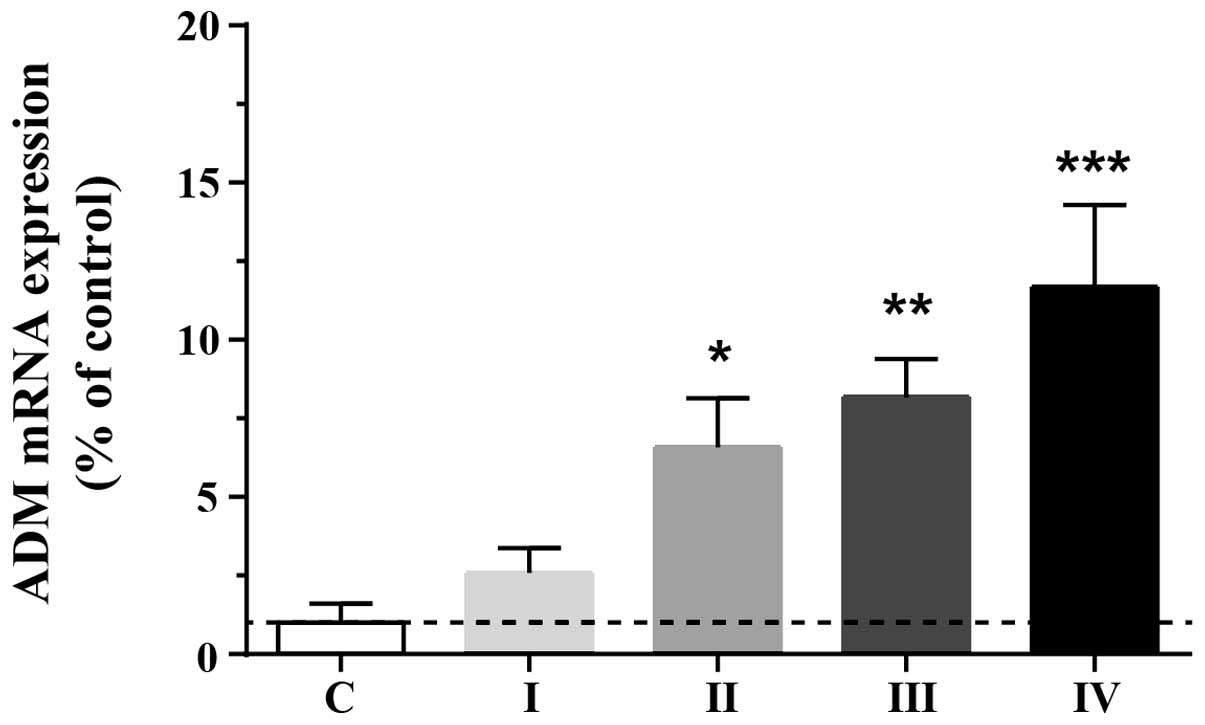
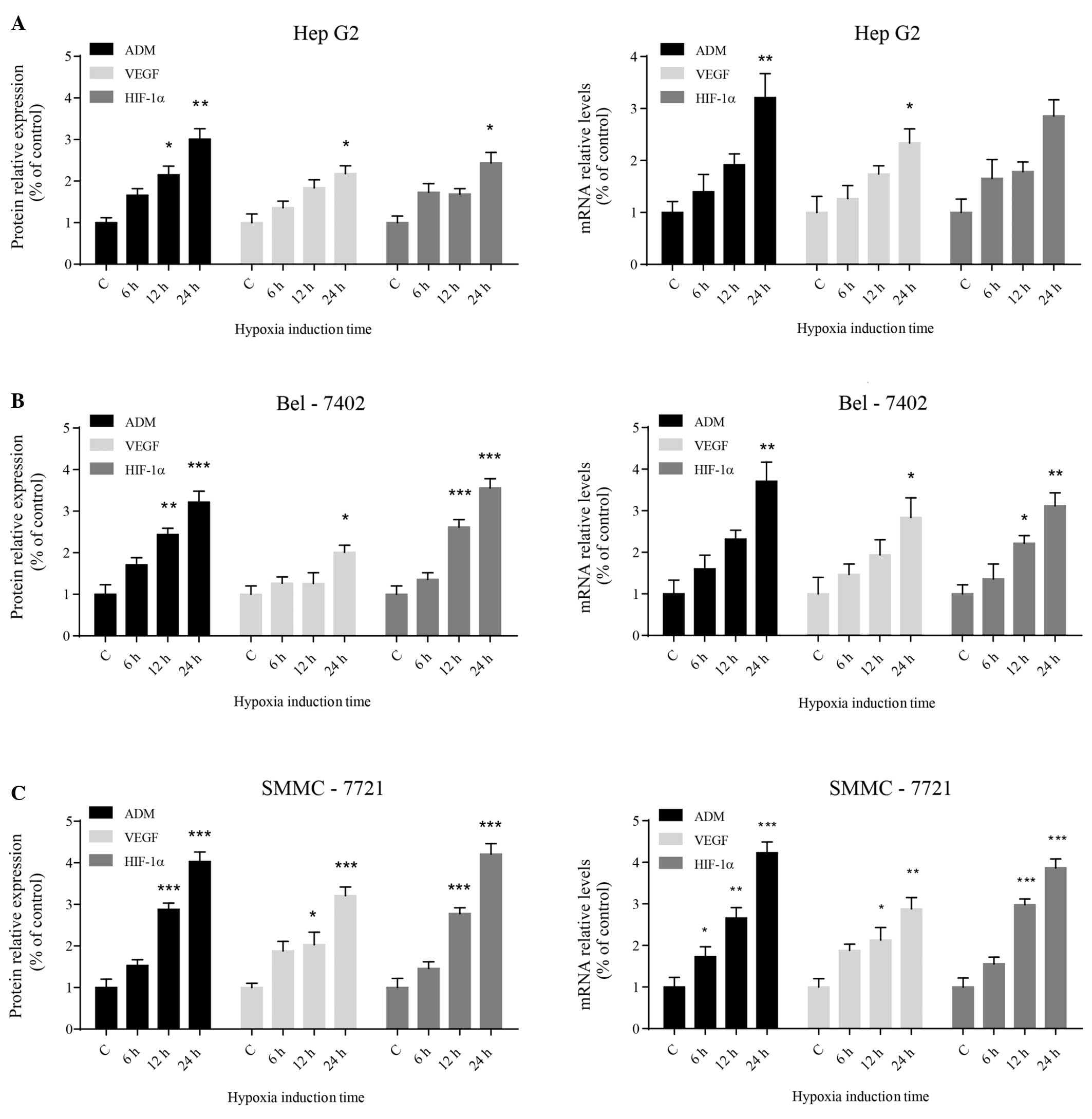
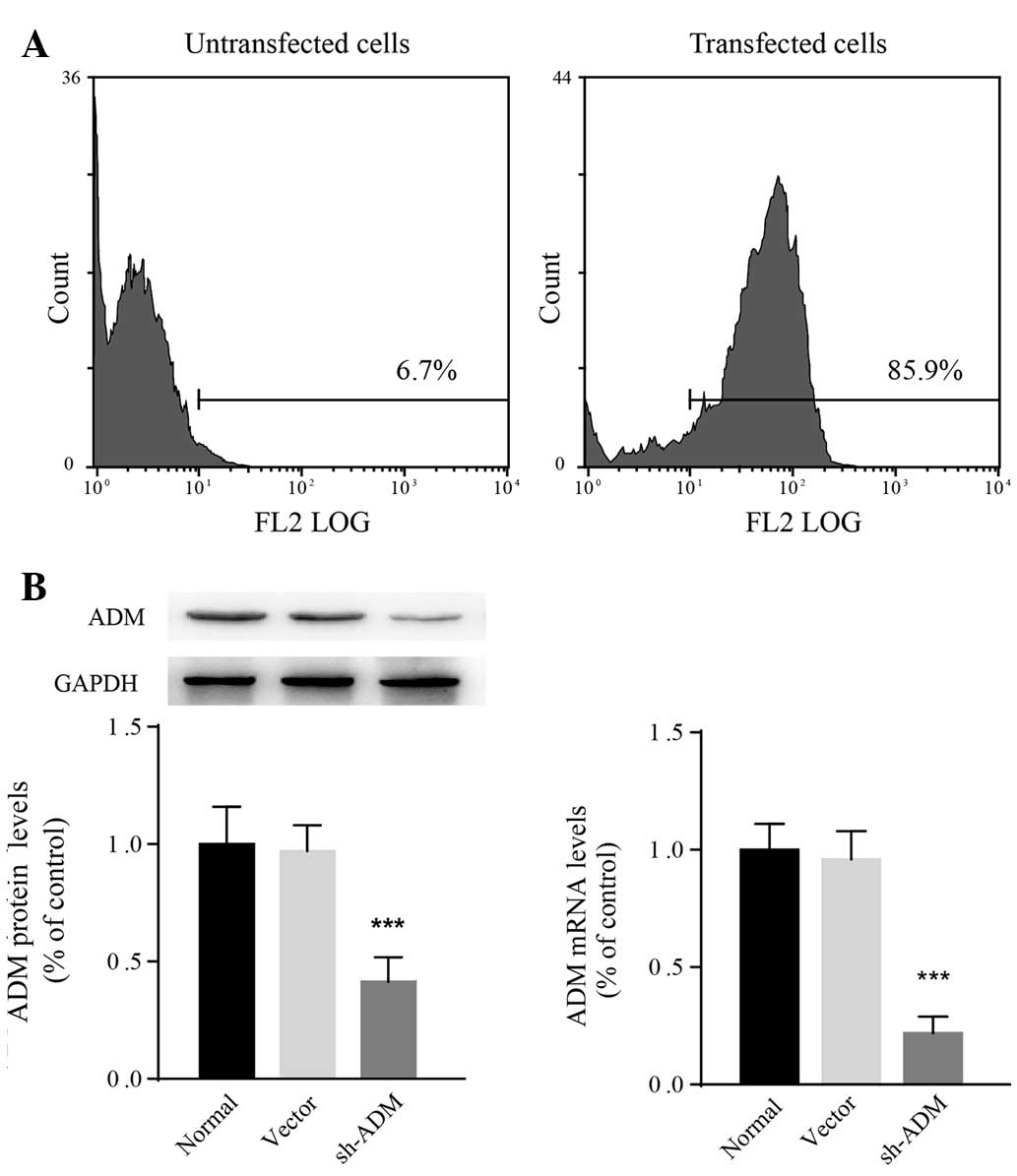
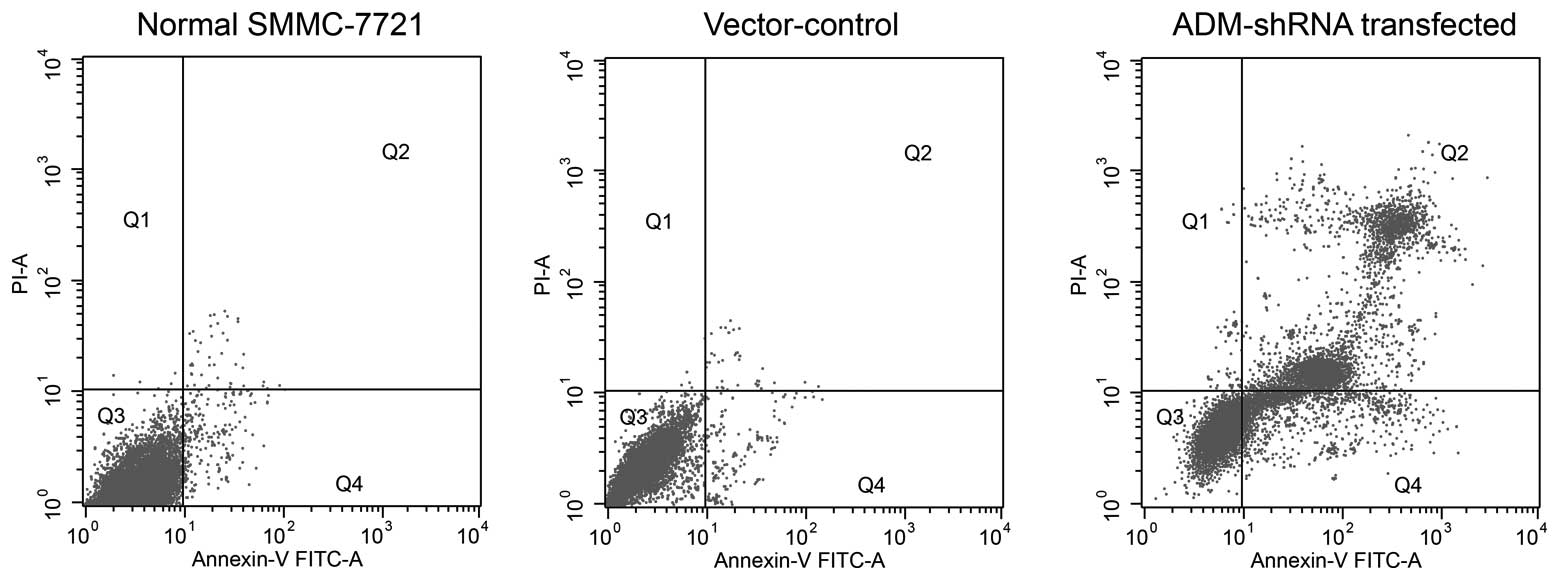
|
1
|
Moradpour D and Blum HE: Pathogenesis of
hepatocellular carcinoma. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 17:477–483.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Tanaka S and Arii S: Current status and
perspective of antiangiogenic therapy for cancer: hepatocellular
carcinoma. Int J Clin Oncol. 11:82–89. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Gwak GY, Yoon JH, Kim KM, Lee HS, Chung JW
and Gores GJ: Hypoxia stimulates proliferation of human hepatoma
cells through the induction of hexokinase II expression. J Hepatol.
42:358–364. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Liotta LA, Steeg PS and Stetler-Stevenson
WG: Cancer metastasis and angiogenesis: an imbalance of positive
and negative regulation. Cell. 64:327–336. 1991. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hanahan D and Folkman J: Patterns and
emerging mechanisms of the angiogenic switch during tumorigenesis.
Cell. 86:353–364. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dvorak HF: Vascular permeability
factor/vascular endothelial growth factor: a critical cytokine in
tumor angiogenesis and a potential target for diagnosis and
therapy. J Clin Oncol. 20:4368–4380. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kitamura K, Kangawa K, Kawamoto M, et al:
Adrenomedullin: a novel hypotensive peptide isolated from human
pheochromocytoma. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 192:553–560. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Nikitenko LL, Fox SB, Kehoe S, Rees MC and
Bicknell R: Adrenomedullin and tumour angiogenesis. Br J Cancer.
94:1–7. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Jiménez N, Abasolo I, Jongsma J, et al:
Androgen-independent expression of adrenomedullin and
peptidylglycine alpha-amidating monooxygenase in human prostatic
carcinoma. Mol Carcinog. 38:14–24. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Li Z, Takeuchi S, Otani T and Maruo T:
Implications of adrenomedullin expression in the invasion of
squamous cell carcinoma of the uterine cervix. Int J Clin Oncol.
6:263–270. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Park SC, Yoon JH, Lee JH, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible adrenomedullin accelerates hepatocellular
carcinoma cell growth. Cancer Lett. 271:314–322. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Edmondson HA and Steiner PE: Primary
carcinoma of the liver: a study of 100 cases among 48,900
necropsies. Cancer. 7:462–503. 1954. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Deville JL, Salas S, Figarella-Branger D,
et al: Adrenomedullin as a therapeutic target in angiogenesis.
Expert Opin Ther Targets. 14:1059–1072. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wu SD, Ma YS, Fang Y, Liu LL, Fu D and
Shen XZ: Role of the microenvironment in hepatocellular carcinoma
development and progression. Cancer Treat Rev. 38:218–225. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zudaire E, Martínez A and Cuttitta F:
Adrenomedullin and cancer. Regul Pept. 112:175–183. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Oehler MK, Norbury C, Hague S, Rees MC and
Bicknell R: Adrenomedullin inhibits hypoxic cell death by
upregulation of Bcl-2 in endometrial cancer cells: a possible
promotion mechanism for tumour growth. Oncogene. 20:2937–2945.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Oladipupo S, Hu S, Kovalski J, et al: VEGF
is essential for hypoxia-inducible factor-mediated
neovascularization but dispensable for endothelial sprouting. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:13264–13269. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Frede S, Freitag P, Otto T, Heilmaier C
and Fandrey J: The proinflammatory cytokine interleukin 1beta and
hypoxia cooperatively induce the expression of adrenomedullin in
ovarian carcinoma cells through hypoxia inducible factor 1
activation. Cancer Res. 65:4690–4697. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Ribatti D, Nico B, Spinazzi R, Vacca A and
Nussdorfer GG: The role of adrenomedullin in angiogenesis.
Peptides. 26:1670–1675. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Jung KH, Zheng HM, Jeong Y, et al:
Suppression of tumor proliferation and angiogenesis of
hepatocellular carcinoma by HS-104, a novel phosphoinositide
3-kinase inhibitor. Cancer Lett. 328:176–187. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Harris AL: Hypoxia - a key regulatory
factor in tumour growth. Nat Rev Cancer. 2:38–47. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kim Y, Lin Q, Glazer PM and Yun Z: Hypoxic
tumor microenvironment and cancer cell differentiation. Curr Mol
Med. 9:425–434. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tang N, Wang L, Esko J, et al: Loss of
HIF-1alpha in endothelial cells disrupts a hypoxia-driven VEGF
autocrine loop necessary for tumorigenesis. Cancer Cell. 6:485–495.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Carmeliet P, Dor Y, Herbert JM, et al:
Role of HIF-1alpha in hypoxia-mediated apoptosis, cell
proliferation and tumour angiogenesis. Nature. 394:485–490. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Iwase T, Nagaya N, Fujii T, et al:
Adrenomedullin enhances angiogenic potency of bone marrow
transplantation in a rat model of hindlimb ischemia. Circulation.
111:356–362. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hazan RB, Phillips GR, Qiao RF, Norton L
and Aaronson SA: Exogenous expression of N-cadherin in breast
cancer cells induces cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. J
Cell Biol. 148:779–790. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Gwak GY, Yoon JH, Yu SJ, et al:
Anti-apoptotic N-cadherin signaling and its prognostic implication
in human hepatocellular carcinomas. Oncol Rep. 15:1117–1123.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Shichiri M and Hirata Y: Regulation of
cell growth and apoptosis by adrenomedullin. Hypertens Res.
26(Suppl): S9–S14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Pang X, Shang H, Deng B, Wen F and Zhang
Y: The interaction of adrenomedullin and macrophages induces
ovarian cancer cell migration via activation of RhoA signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Sci. 14:2774–2787. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|