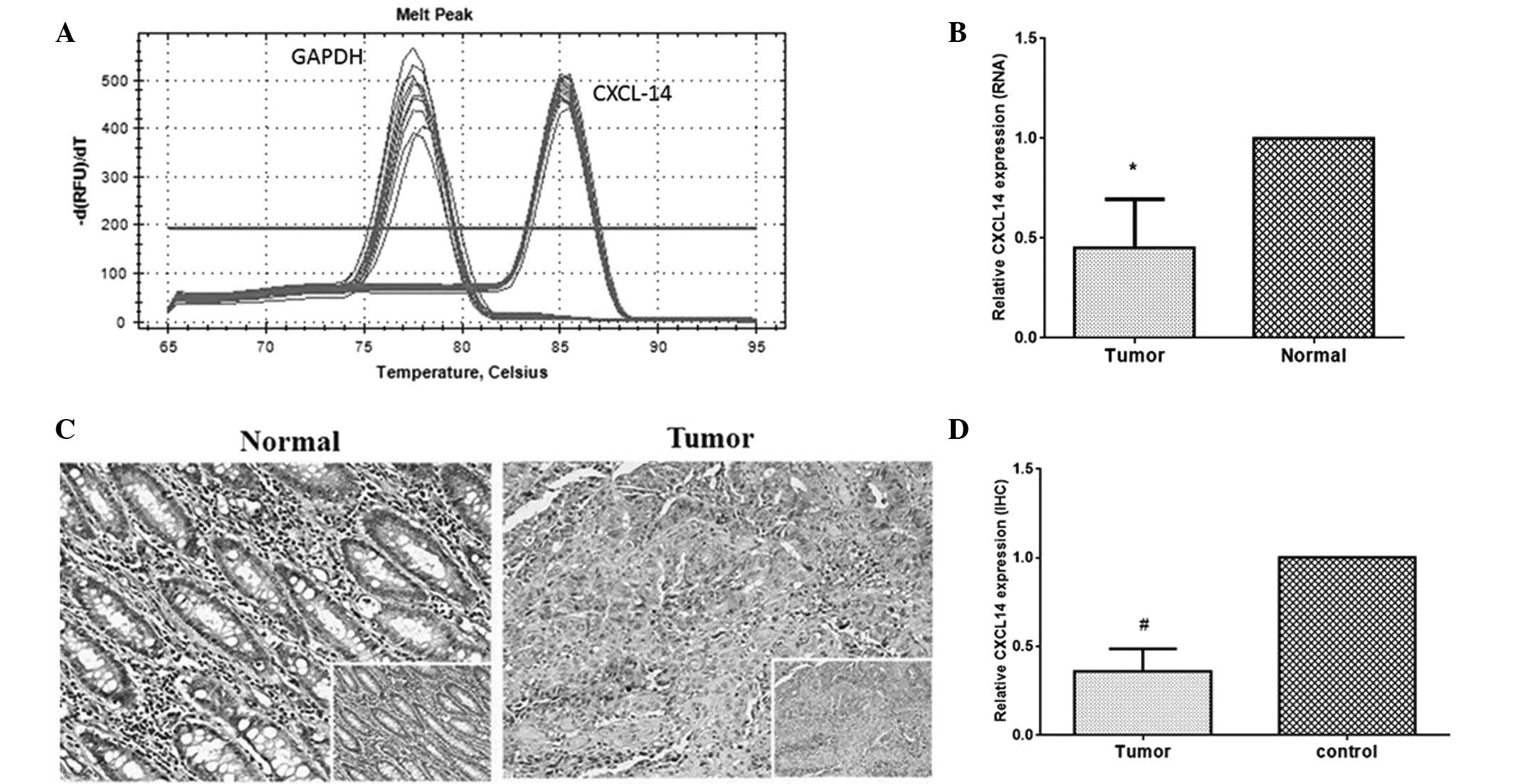
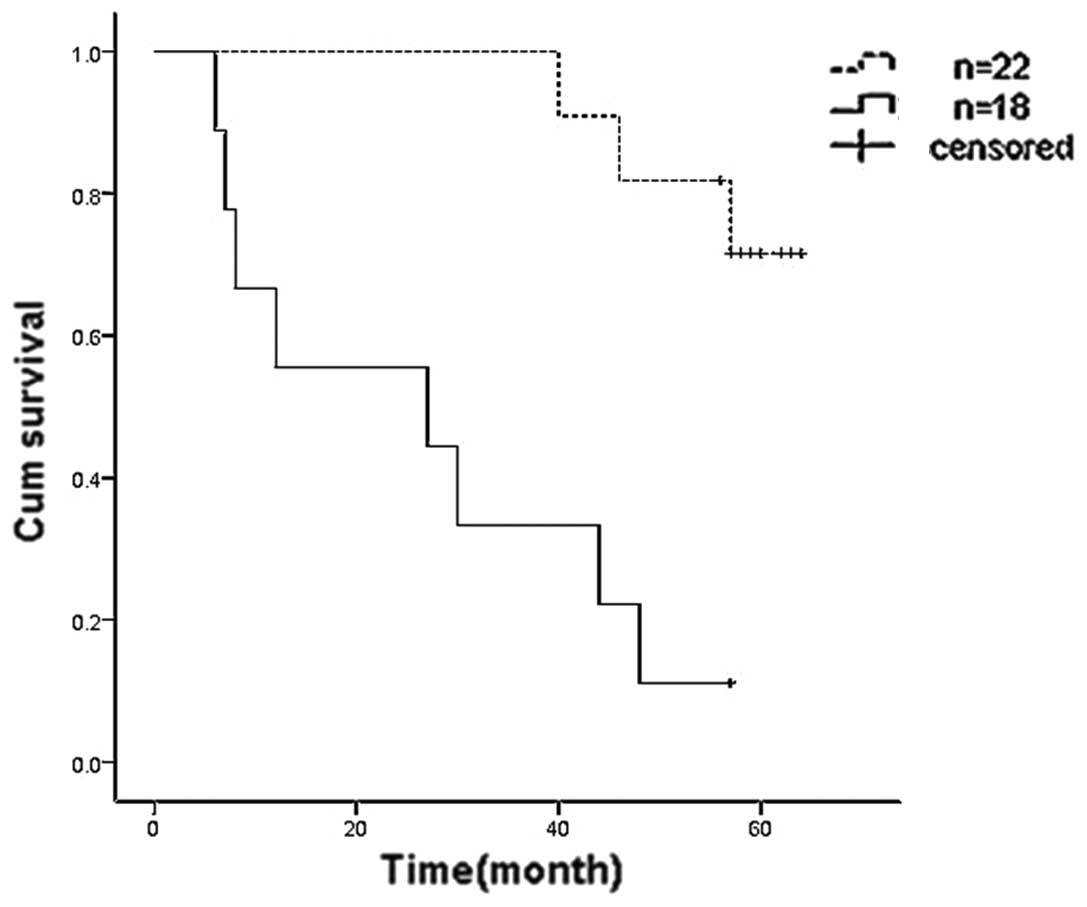
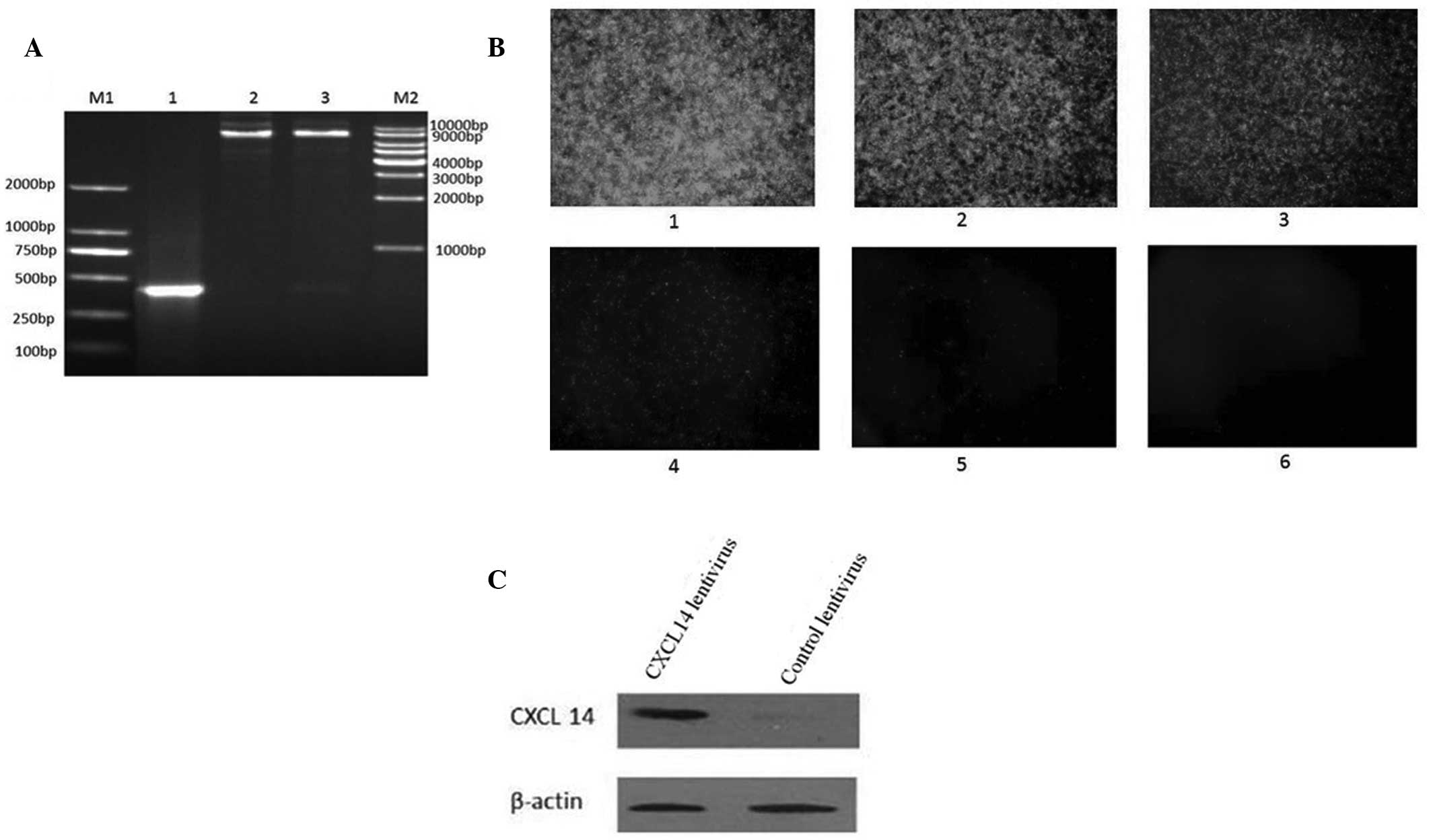
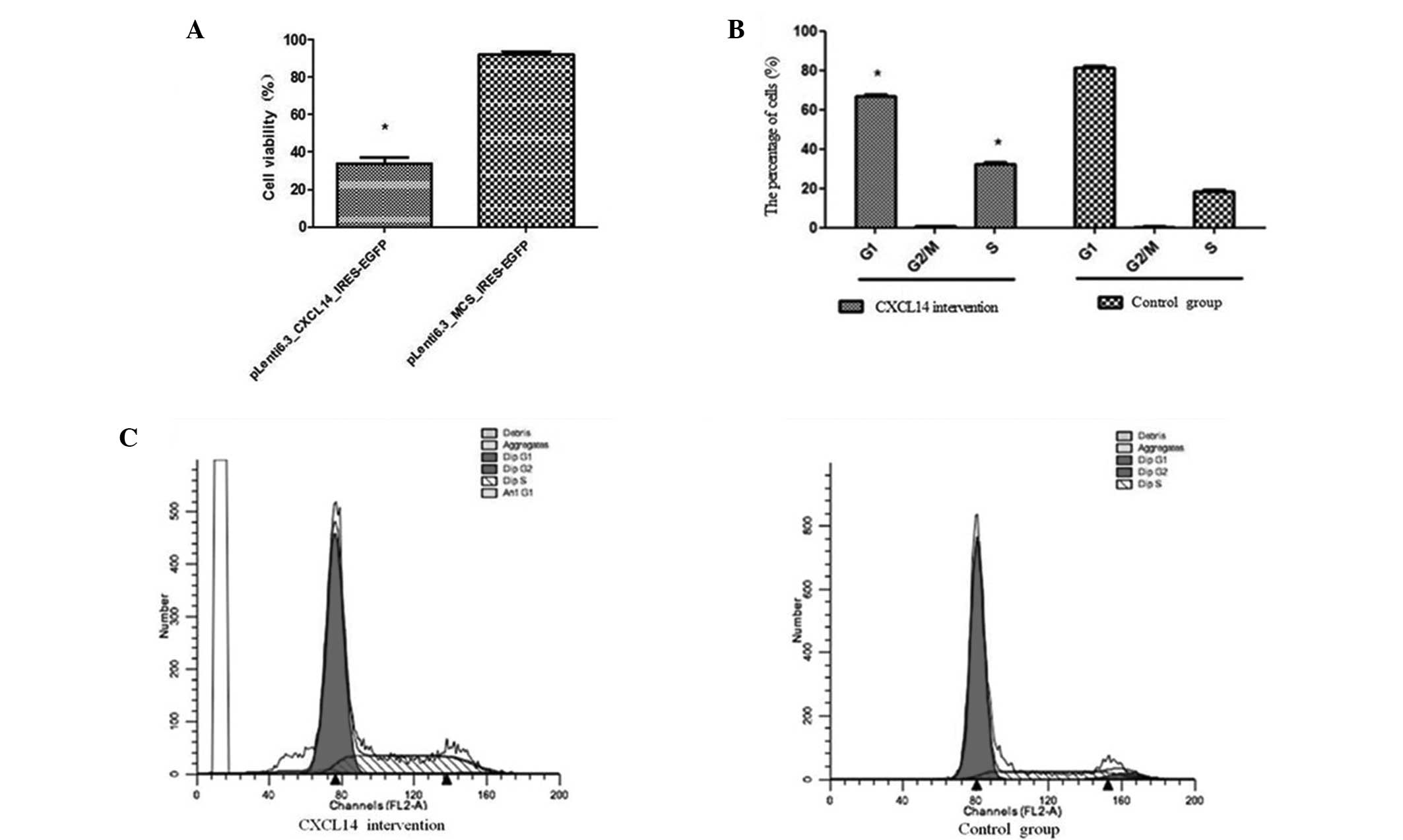
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Devaud C, John LB, Westwood JA, Darcy PK
and Kershaw MH: Immune modulation of the tumor microenvironment for
enhancing cancer immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology. 2:e259612013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Allen SJ, Crown SE and Handel TM:
Chemokine: receptor structure, interactions, and antagonism. Annu
Rev Immunol. 25:787–820. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mellado M, Rodríguez-Frade JM, Mañes S and
Martínez AC: Chemokine signaling and functional responses: the role
of receptor dimerization and TK pathway activation. Annu Rev
Immunol. 19:397–421. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Sallusto F, Mackay CR and Lanzavecchia A:
The role of chemokine receptors in primary, effector, and memory
immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol. 18:593–620. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Ruffini PA, Morandi P, Cabioglu N,
Altundag K and Cristofanilli M: Manipulating the
chemokine-chemokine receptor network to treat cancer. Cancer.
109:2392–2404. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mantovani A, Savino B, Locati M, Zammataro
L, Allavena P and Bonecchi R: The chemokine system in cancer
biology and therapy. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 21:27–39. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Uchida H, Iwashita Y, Sasaki A, Shibata K,
Matsumoto T, Ohta M and Kitano S: Chemokine receptor CCR6 as a
prognostic factor after hepatic resection for hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 21:161–168. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ghadjar P, Coupland SE, Na IK, Noutsias M,
Letsch A, Stroux A, Bauer S, Buhr HJ, Thiel E, Scheibenbogen C and
Keilholz U: Chemokine receptor CCR6 expression level and liver
metastases in colorectal cancer. J Clin Oncol. 24:1910–1916. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hojo S, Koizumi K, Tsuneyama K, Arita Y,
Cui Z, Shinohara K, Minami T, et al: High-level expression of
chemokine CXCL16 by tumor cells correlates with a good prognosis
and increased tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in colorectal cancer.
Cancer Res. 67:4725–4731. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hromas R, Broxmeyer HE, Kim C, Nakshatri
H, Christopherson K II, Azam M and Hou YH: Cloning of BRAK, a novel
divergent CXC chemokine preferentially expressed in normal versus
malignant cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 255:703–706. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Frederick MJ, Henderson Y, Xu X, Deavers
MT, Sahin AA, Wu H, Lewis DE, El-Naggar AK and Clayman GL: In vivo
expression of the novel CXC chemokine BRAK in normal and cancerous
human tissue. Am J Pathol. 156:1937–1950. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Meuter S and Moser B: Constitutive
expression of CXCL14 in healthy human and murine epithelial
tissues. Cytokine. 44:248–255. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Starnes T, Rasila KK, Robertson MJ, Brahmi
Z, Dahl R, Christopherson K and Hromas R: The chemokine CXCL14
(BRAK) stimulates activated NK cell migration: implications for the
downregulation of CXCL14 in malignancy. Exp Hematol. 34:1101–1105.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Juremalm M and Nilsson G: Chemokine
receptor expression by mast cells. Chem Immunol Allergy.
87:130–144. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Shellenberger TD, Wang M, Gujrati M,
Jayakumar A, Strieter RM, Burdick MD, Ioannides CG, Efferson CL,
El-Naggar AK, Roberts D, et al: BRAK/CXCL14 is a potent inhibitor
of angiogenesis and a chemotactic factor for immature dendritic
cells. Cancer Res. 64:8262–8270. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Sleeman MA, Fraser JK, Murison JG, Kelly
SL, Prestidge RL, Palmer DJ, Watson JD and Kumble KD: B cell- and
monocyte-activating chemokine (BMAC), a novel non-ELR
alpha-chemokine. Int Immunol. 12:677–689. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kurth I, Willimann K, Schaerli P, Hunziker
T, Clark-Lewis I and Moser B: Monocyte selectivity and tissue
localization suggests a role for breast and kidney-expressed
chemokine (BRAK) in macrophage development. J Exp Med. 194:855–861.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Hara T and Nakayama Y: CXCL14 and insulin
action. Vitam Horm. 80:107–123. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Tanegashima K, Okamoto S, Nakayama Y, Taya
C, Shitara H, Ishii R, Yonekawa H, Minokoshi Y and Hara T: CXCL14
deficiency in mice attenuates obesity and inhibits feeding behavior
in a novel environment. PLoS One. 5:e103212010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Maerki C, Meuter S, Liebi M, Muhlemann K,
Frederick MJ, Yawalkar N, Moser B and Wolf M: Potent and
broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity of CXCL14 suggests an
immediate role in skin infections. J Immunol. 182:507–514. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lindberg J, af Klint E, Catrina AI,
Nilsson P, Klareskog L, Ulfgren AK and Lundeberg J: Effect of
infliximab on mRNA expression profiles in synovial tissue of
rheumatoid arthritis patients. Arthritis Res Ther. 8:R1792006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hara T and Tanegashima K: Pleiotropic
functions of the CXC-type chemokine CXCL14 in mammals. J Biochem.
151:469–476. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Tessema M, Klinge DM, Yingling CM, Do K,
Van Neste L and Belinsky SA: Re-expression of CXCL14, a common
target for epigenetic silencing in lung cancer, induces tumor
necrosis. Oncogene. 29:5159–5170. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gu XL, Ou ZL, Lin FJ, Yang XL, Luo JM,
Shen ZZ and Shao ZM: Expression of CXCL14 and its anticancer role
in breast cancer. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 135:725–735. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Ozawa S, Kato Y, Ito S, Komori R, Shiiki
N, Tsukinoki K, Ozono S, Maehata Y, et al: Restoration of
BRAK/CXCL14 gene expression by gefitinib is associated with
antitumor efficacy of the drug in head and neck squamous cell
carcinoma. Cancer Sci. 100:2202–2209. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hu C, Lin F, Zhu G, Xue X, Ding Y, Zhao Z,
Zhang L and Shen X: Abnormal hypermethylation of promoter region
downregulates chemokine CXC ligand 14 expression in gastric cancer.
Int J Oncol. 43:1487–1494. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang W, Huang P, Zhang L, Wei J, Xie Q,
Sun Q, Zhou X, Xie H, Zhou L and Zheng S: Antitumor efficacy of
C-X-C motif chemokine ligand 14 in hepatocellular carcinoma in
vitro and in vivo. Cancer Sci. 104:1523–1531. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song EY, Shurin MR, Tourkova IL, Gutkin DW
and Shurin GV: Epigenetic mechanisms of promigratory chemokine
CXCL14 regulation in human prostate cancer cells. Cancer Res.
70:4394–4401. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Augsten M, Hagglof C, Olsson E, Stolz C,
Tsagozis P, Levchenko T, Frederick MJ, Borg A, Micke P, Egevad L
and Ostman A: CXCL14 is an autocrine growth factor for fibroblasts
and acts as a multi-modal stimulator of prostate tumor growth. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:3414–3419. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wente MN, Mayer C, Gaida MM, Michalski CW,
Giese T, Bergmann F, Giese NA, Büchler MW and Friess H: CXCL14
expression and potential function in pancreatic cancer. Cancer
Lett. 259:209–217. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zeng J, Yang X, Cheng L, Liu R, Lei Y,
Dong D, Li F, Lau QC, et al: Chemokine CXCL14 is associated with
prognosis in patients with colorectal carcinoma after curative
resection. J Transl Med. 11:62013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Cao B, Yang Y, Pan Y, Jia Y, Brock MV,
Herman JG and Guo M: Epigenetic silencing of CXCL14 induced
colorectal cancer migration and invasion. Discov Med. 16:137–147.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Winawer SJ, Krabshuis J, Lambert R,
O’Brien M and Fried M; World Gastroenterology Organization
Guidelines Committee. Cascade colorectal cancer screening
guidelines: a global conceptual model. J Chin Gastroenterol.
45:297–300. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Benson AB 3rd, Bekaii-Saab T, Chan E, Chen
YJ, Choti MA, Cooper HS, et al: Localized colon cancer, version
3.2013: featured updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J Natl Compr Canc
Netw. 11:519–528. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Zlotnik A and Yoshie O: Chemokines: a new
classification system and their role in immunity. Immunity.
12:121–127. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Campanelli AP, Brodskyn CI, Boaventura V,
Silva C, Roselino AM, Costa J, Saldanha AC, de Freitas LA, et al:
Chemokines and chemokine receptors coordinate the inflammatory
immune response in human cutaneous leishmaniasis. Hum Immunol.
71:1220–1227. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Wong MM and Fish EN: Chemokines:
attractive mediators of the immune response. Semin Immunol.
15:5–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Moser B, Wolf M, Walz A and Loetscher P:
Chemokines: multiple levels of leukocyte migration control. Trends
Immunol. 25:75–84. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Krieg C and Boyman O: The role of
chemokines in cancer immune surveillance by the adaptive immune
system. Semin Cancer Biol. 19:76–83. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Balkwill FR: The chemokine system and
cancer. J Pathol. 226:148–157. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Zlotnik A, Burkhardt AM and Homey B:
Homeostatic chemokine receptors and organ-specific metastasis. Nat
Rev Immunol. 11:597–606. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Shurin GV, Ferris RL, Tourkova IL, Perez
L, Lokshin A, Balkir L, Collins B, Chatta GS and Shurin MR: Loss of
new chemokine CXCL14 in tumor tissue is associated with low
infiltration by dendritic cells (DC), while restoration of human
CXCL14 expression in tumor cells causes attraction of DC both in
vitro and in vivo. J Immunol. 174:5490–5498. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Izukuri K, Suzuki K, Yajima N, Ozawa S,
Ito S, Kubota E and Hata R: Chemokine CXCL14/BRAK transgenic mice
suppress growth of carcinoma cell transplants [corrected].
Transgenic Res. 19:1109–1117. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Allinen M, Beroukhim R, Cai L, Brennan C,
Lahti-Domenici J, Huang H, et al: Molecular characterization of the
tumor microenvironment in breast cancer. Cancer Cell. 6:17–32.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|