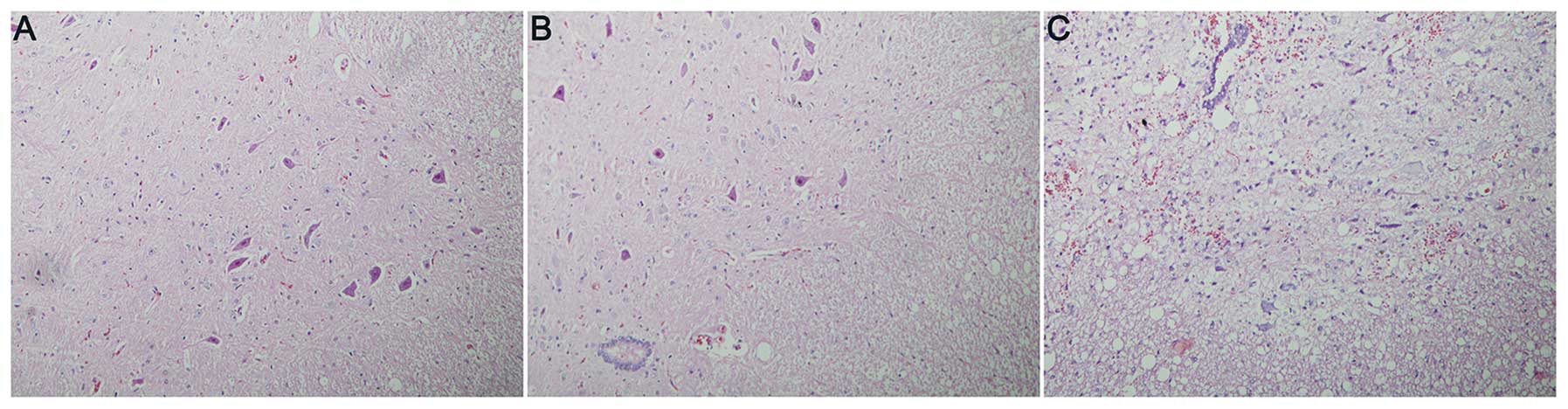
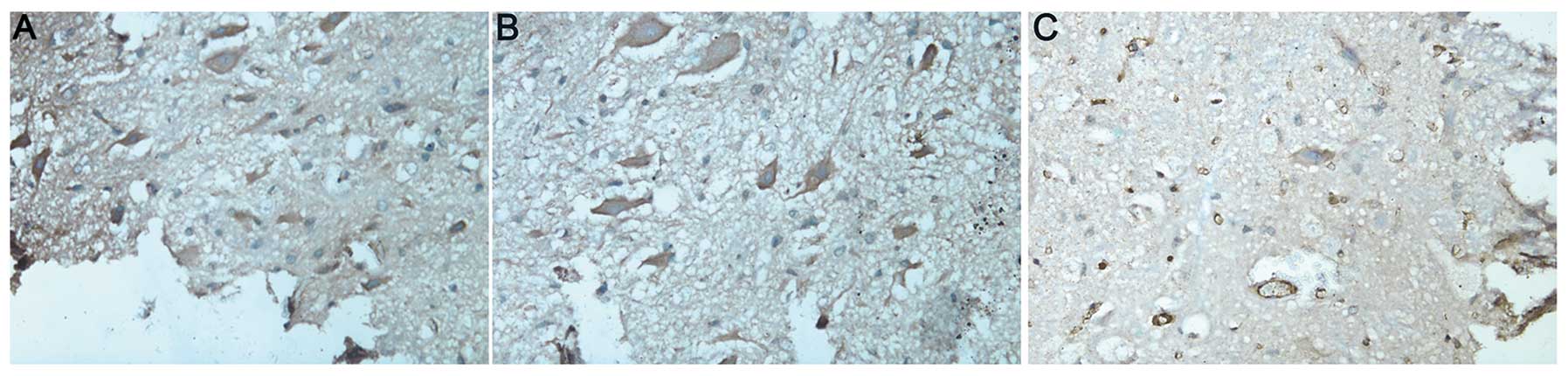
|
1
|
Wiedemann C: Repair: CSI in SCI. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 10:6212009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Cripps RA, Lee BB, Wing P, et al: A global
map for traumatic spinal cord injury epidemiology: towards a living
data repository for injury prevention. Spinal Cord. 49:493–501.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ito Y, Sugimoto Y, Tomioka M, Kai N and
Tanaka M: Does high dose methylprednisolone sodium succinate really
improve neurological status in patient with acute cervical cord
injury?: a prospective study about neurological recovery and early
complications. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 34:2121–2124. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Bracken M: Steroids for acute spinal cord
injury. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 3:CD0010462002.
|
|
5
|
Baptiste DC and Fehlings MG: Emerging
drugs for spinal cord injury. Expert Opin Emerg Drugs. 13:63–80.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kwon BK, Hillyer J and Tetzlaff W:
Translational research in spinal cord injury: a survey of opinion
from the SCI community. J Neurotrauma. 27:21–33. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Abe N and Cavalli V: Nerve injury
signaling. Curr Opin Neurobiol. 18:276–283. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Udina E, Ladak A, Furey M, et al:
Rolipram-induced elevation of cAMP or chondroitinase ABC breakdown
of inhibitory proteoglycans in the extracellular matrix promotes
peripheral nerve regeneration. Exp Neurol. 223:143–152. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Hannila SS and Filbin MT: The role of
cyclic AMP signaling in promoting axonal regeneration after spinal
cord injury. Exp Neurol. 209:321–332. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Mekhail M, Almazan G and Tabrizian M:
Oligodendrocyte-protection and remyelination post-spinal cord
injuries: a review. Prog Neurobiol. 96:322–339. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Gancedo JM: Biological roles of cAMP:
variations on a theme in the different kingdoms of life. Biol Rev
Camb Philos Soc. 88:645–668. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Seifert R, Lushington GH, Mou TC, Gille A
and Sprang SR: Inhibitors of membranous adenylyl cyclases. Trends
Pharmacol Sci. 33:64–78. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Michalski JM, Golden G, Ikari J and
Rennard SI: PDE4: a novel target in the treatment of chronic
obstructive pulmonary disease. Clin Pharmacol Ther. 91:134–142.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Whitaker CM, Beaumont E, Wells MJ, et al:
Rolipram attenuates acute oligodendrocyte death in the adult rat
ventrolateral funiculus following contusive cervical spinal cord
injury. Neurosci Lett. 438:200–204. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pavan B, Paganetto G and Dalpiaz A:
Dopamine-sensitive adenylyl cyclases in neuronal development:
physiopathological and pharmacological implications. Drug Discov
Today. 16:520–529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Col JA, Matsuo T, Storm DR and Rodriguez
I: Adenylyl cyclase-dependent axonal targeting in the olfactory
system. Development. 134:2481–2489. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Koozekanani SH, Vise WM, Hashemi RM and
McGhee RB: Possible mechanisms for observed pathophysiological
variability in experimental spinal cord injury by the method of
Allen. J Neurosurg. 44:429–434. 1976. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Rivlin AS and Tator CH: Objective clinical
assessment of motor function after experimental spinal cord injury
in the rat. J Neurosurg. 47:577–581. 1977. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Gale K, Kerasidis H and Wrathall JR:
Spinal cord contusion in the rat: behavioral analysis of functional
neurologic impairment. Exp Neurol. 88:123–134. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Gilman AG: Silver spoons and other
personal reflections. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 52:1–19. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Song XJ, Wang ZB, Gan Q and Walters ET:
cAMP and cGMP contribute to sensory neuron hyperexcitability and
hyperalgesia in rats with dorsal root ganglia compression. J
Neurophysiol. 95:479–492. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Bhatt DH, Otto SJ, Depoister B and Fetcho
JR: Cyclic AMP-induced repair of zebrafish spinal circuits.
Science. 305:254–258. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Nikulina E, Tidwell JL, Dai HN, Bregman BS
and Filbin MT: The phosphodiesterase inhibitor rolipram delivered
after a spinal cord lesion promotes axonal regeneration and
functional recovery. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 101:8786–8790. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pearse DD, Pereira FC, Marcillo AE, et al:
cAMP and Schwann cells promote axonal growth and functional
recovery after spinal cord injury. Nat Med. 10:610–616. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Page CP and Spina D: Selective PDE
inhibitors as novel treatments for respiratory diseases. Curr Opin
Pharmacol. 12:275–286. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhu J, Yang Q, Dai D and Huang Q: X-ray
crystal structure of phosphodiesterase 2 in complex with a highly
selective, nanomolar inhibitor reveals a binding-induced pocket
important for selectivity. J Am Chem Soc. 135:11708–11711. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Liu S, Li Y, Kim S, et al:
Phosphodiesterases coordinate cAMP propagation induced by two
stimulatory G protein-coupled receptors in hearts. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 109:6578–6583. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Perez-Torres S, Miro X, Palacios JM, et
al: Phosphodiesterase type 4 isozymes expression in human brain
examined by in situ hybridization histochemistry and[3H]rolipram
binding autoradiography. Comparison with monkey and rat brain. J
Chem Neuroanat. 20:349–374. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Lamontagne S, Meadows E, Luk P, et al:
Localization of phosphodiesterase-4 isoforms in the medulla and
nodose ganglion of the squirrel monkey. Brain Res. 920:84–96. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Abaffy T, Trubey KR and Chaudhari N:
Adenylyl cyclase expression and modulation of cAMP in rat taste
cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 284:C1420–C1428. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gavaldà A and Roberts RS:
Phosphodiesterase-4 inhibitors: a review of current developments
(2010–2012). Expert Opin Ther Pat. 23:997–1016. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Wu D, Zhao Y, Yang Y, Wang W and Xu R: [A
multicenter clinical study on clinical effects of meglumine cyclic
adenylate in treating patients with chronic pulmonary heart
disease]. Zhonghua nei ke za zhi. 40:467–470. 2001.(In
Chinese).
|
|
33
|
Xing SH, Gu SL and Meng QC: Meglumine
cyclic adenylate pediatric dosage calculations. XuZhou Acta
Academiae Medicinae. 19:370–372. 1999.
|