|
1
|
Braun T and Schett G: Pathways for bone
loss in inflammatory disease. Curr Osteoporos Rep. 10:101–108.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Gümüş P, Nizam N, Lappin DF and Buduneli
N: Saliva and serum levels of B-cell activating factors and tumor
necrosis factor-α in patients with periodontitis. J Periodontol.
85:270–280. 2014.
|
|
3
|
Jiang ZL, Cui YQ, Gao R, Li Y, Fu ZC,
Zhang B and Guan CC: Study of TNF-α, IL-1β and LPS levels in the
gingival crevicular fluid of a rat model of diabetes mellitus and
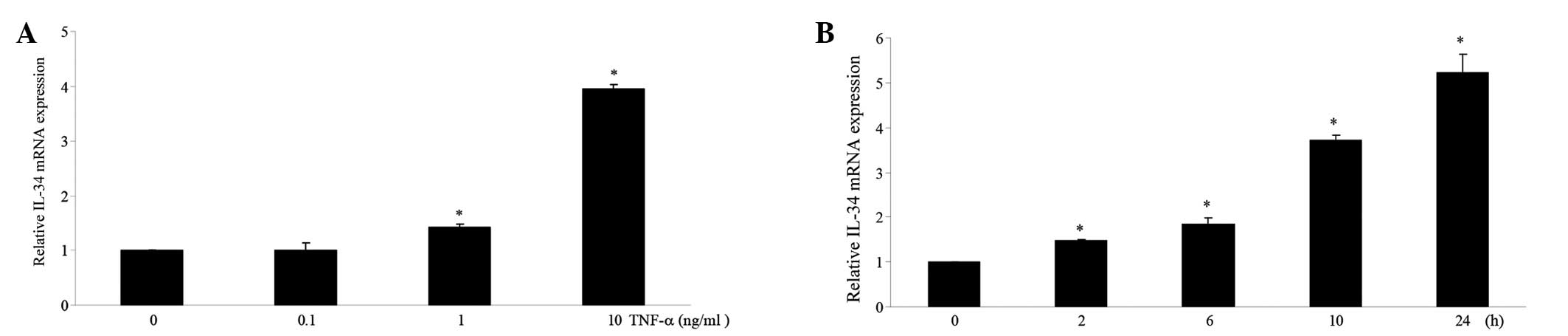
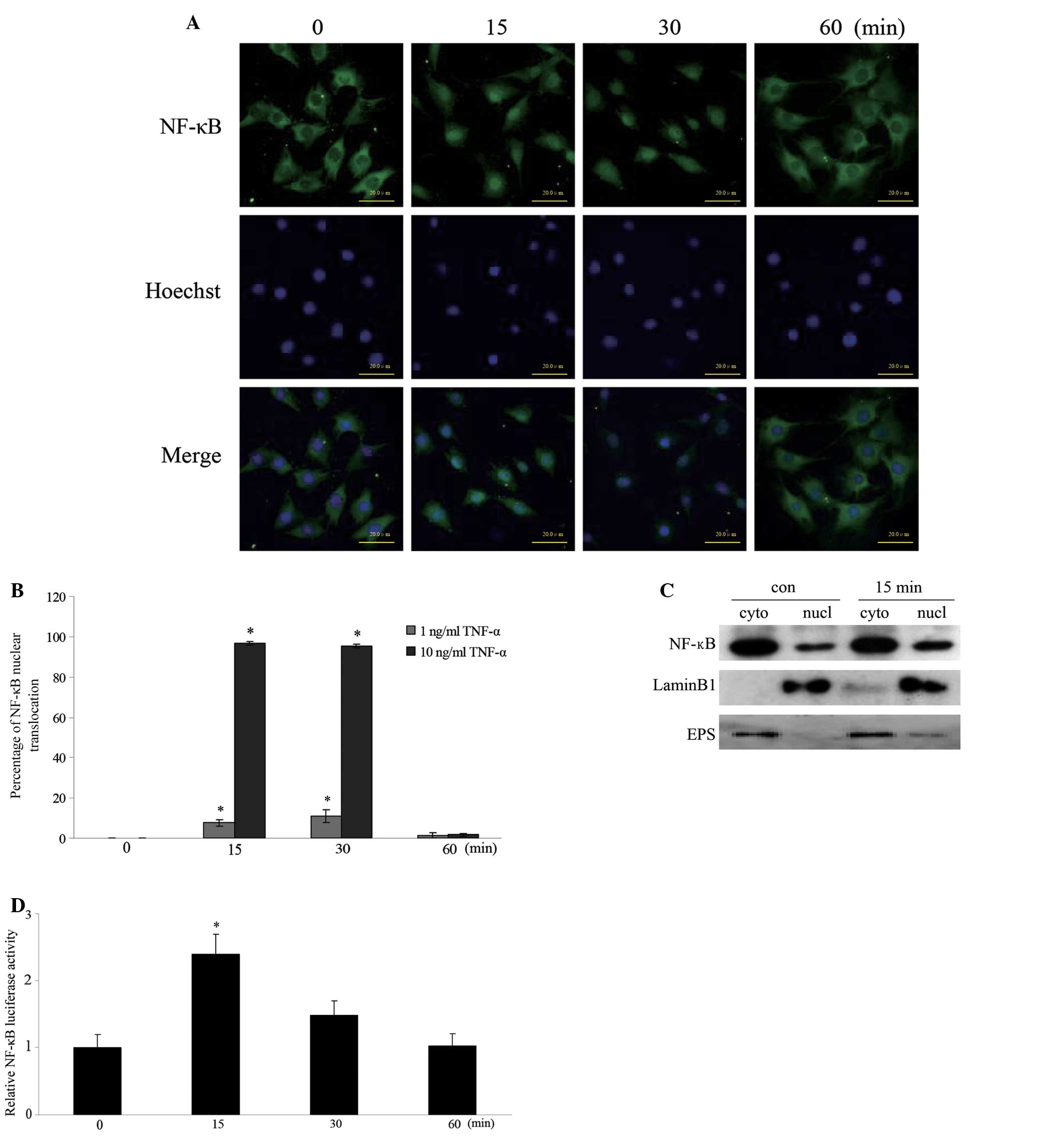
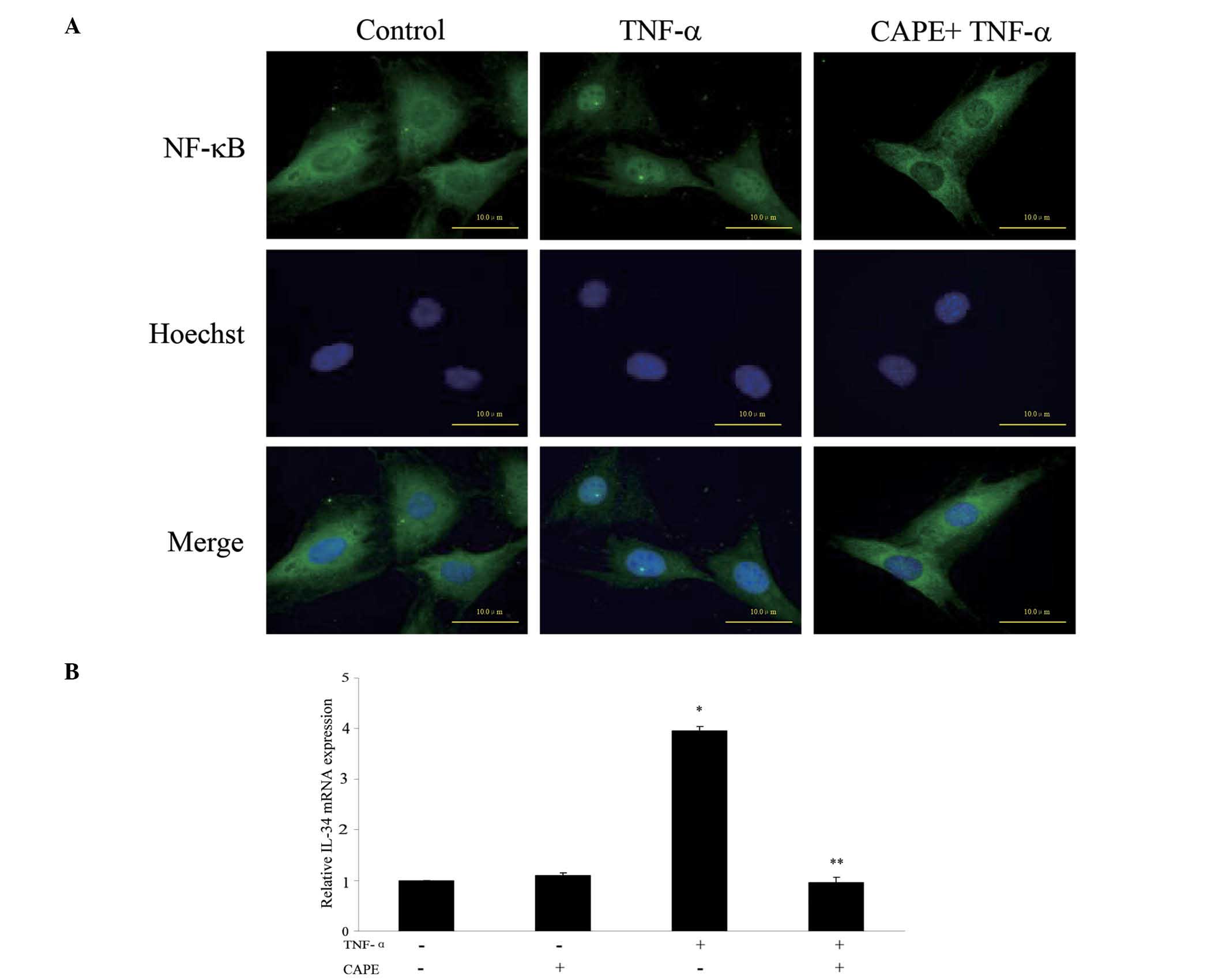
periodontitis. Dis Markers. 34:295–304. 2013.
|
|
4
|
Yue Y, Liu Q, Xu C, et al: Comparative
evaluation of cytokines in gingival crevicular fluid and saliva of
patients with aggressive periodontitis. Int J Biol Markers.
28:108–112. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Martinho FC, Chiesa WM, Leite FR, Cirelli
JA and Gomes BP: Correlation between clinical/radiographic features
and inflammatory cytokine networks produced by macrophages
stimulated with endodontic content. J Endod. 38:740–745. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Oliveira LD, Carvalho CA, Carvalho AS, de
Alves JS, Valera MC and Jorge AO: Efficacy of endodontic treatment
for endotoxin reduction in primarily infected root canals and
evaluation of cytotoxic effects. J Endod. 38:1053–1057. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Chitu V and Stanley ER: Colony-stimulating
factor-1 in immunity and inflammation. Curr Opin Immunol. 18:39–48.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Felix R, Fleisch H and Elford PR:
Bone-resorbing cytokines enhance release of macrophage
colony-stimulating activity by the osteoblastic cell MC3T3-E1.
Calcif Tissue Int. 44:356–360. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Tanaka H, Tanabe N, Shoji M, et al:
Nicotine and lipopolysaccharide stimulate the formation of
osteoclast-like cells by increasing macrophage colony-stimulating
factor and prostaglandin E2 production by osteoblasts. Life Sci.
78:1733–1740. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Katono T, Kawato T, Tanabe N, et al:
Nicotine treatment induces expression of matrix metalloproteinases
in human osteoblastic Saos-2 cells. Acta Biochim Biophys Sin
(Shanghai). 38:874–882. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lin H, Lee E, Hestir K, et al: Discovery
of a cytokine and its receptor by functional screening of the
extracellular proteome. Science. 320:807–811. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Z, Buki K, Vääräniemi J, Gu G and
Väänänen HK: The critical role of IL-34 in osteoclastogenesis. PLoS
One. 6:e186892011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Boyce BF, Yao Z and Xing L: Functions of
nuclear factor kappaB in bone. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1192:367–375. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Novack DV: Role of NF-κB in the skeleton.
Cell Res. 21:169–182. 2011.
|
|
15
|
Wang T, Zhang X and Li JJ: The role of
NF-kappaB in the regulation of cell stress responses. Int
Immunopharmacol. 2:1509–1520. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kobayashi K, Kambe F, Kurokouchi K, et al:
TNF-alpha-dependent activation of NF-kappa B in human osteoblastic
HOS-TE85 cells is repressed in vector-averaged gravity using
clinostat rotation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 279:258–264. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Kurokouchi K, Kambe F, Yasukawa K, Izumi
R, Ishiguro N, Iwata H and Seo H: TNF-alpha increases expression of
IL-6 and ICAM-1 genes through activation of NF-kappaB in
osteoblast-like ROS17/2.8 cells. J Bone Miner Res. 13:1290–1299.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Boyce BF, Li P, Yao Z, et al: TNF-alpha
and pathologic bone resorption. Keio J Med. 54:127–131. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sato K, Kasono K, Fujii Y, Kawakami M,
Tsushima T and Shizume K: Tumor necrosis factor type alpha
(cachectin) stimulates mouse osteoblast-like cells (MC3T3-E1) to
produce macrophage colony stimulating activity and prostaglandin
E2. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 145:323–329. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Yao GQ, Sun BH, Insogna KL and Weir EC:
Nuclear factor-kappaB p50 is required for tumor necrosis
factor-alpha-induced colony-stimulating factor-1 gene expression in
osteoblasts. Endocrinology. 141:2914–2922. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Eda H, Shimada H, Beidler DR and Monahan
JB: Proinflammatory cytokines, IL-1β and TNF-α, induce expression
of interleukin-34 mRNA via JNK- and p44/42 MAPK-NF-κB pathway but
not p38 pathway in osteoblasts. Rheumatol Int. 31:1525–1530.
2011.
|
|
22
|
Chemel M, Le Goff B, Brion R, et al:
Interleukin 34 expression is associated with synovitis severity in
rheumatoid arthritis patients. Ann Rheum Dis. 71:150–154. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hwang SJ, Choi B, Kang SS, et al:
Interleukin-34 produced by human fibroblast-like synovial cells in
rheumatoid arthritis supports osteoclastogenesis. Arthritis Res
Ther. 14:R142012. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kurokouchi K, Jacobs CR and Donahue HJ:
Oscillating fluid flow inhibits TNF-alpha-induced NF-kappa B
activation via an Ikappa B kinase pathway in osteoblast-like UMR106
cells. J Biol Chem. 276:13499–13504. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kurokouchi K, Kambe F, Kikumori T, et al:
Effects of glucocorticoids on tumor necrosis factor alpha-dependent
activation of nuclear factor kappaB and expression of the
intercellular adhesion molecule 1 gene in osteoblast-like ROS17/2.8
cells. J Bone Miner Res. 15:1707–1715. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wei S, Nandi S, Chitu V, et al: Functional
overlap but differential expression of CSF-1 and IL-34 in their
CSF-1 receptor-mediated regulation of myeloid cells. J Leukoc Biol.
88:495–505. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|