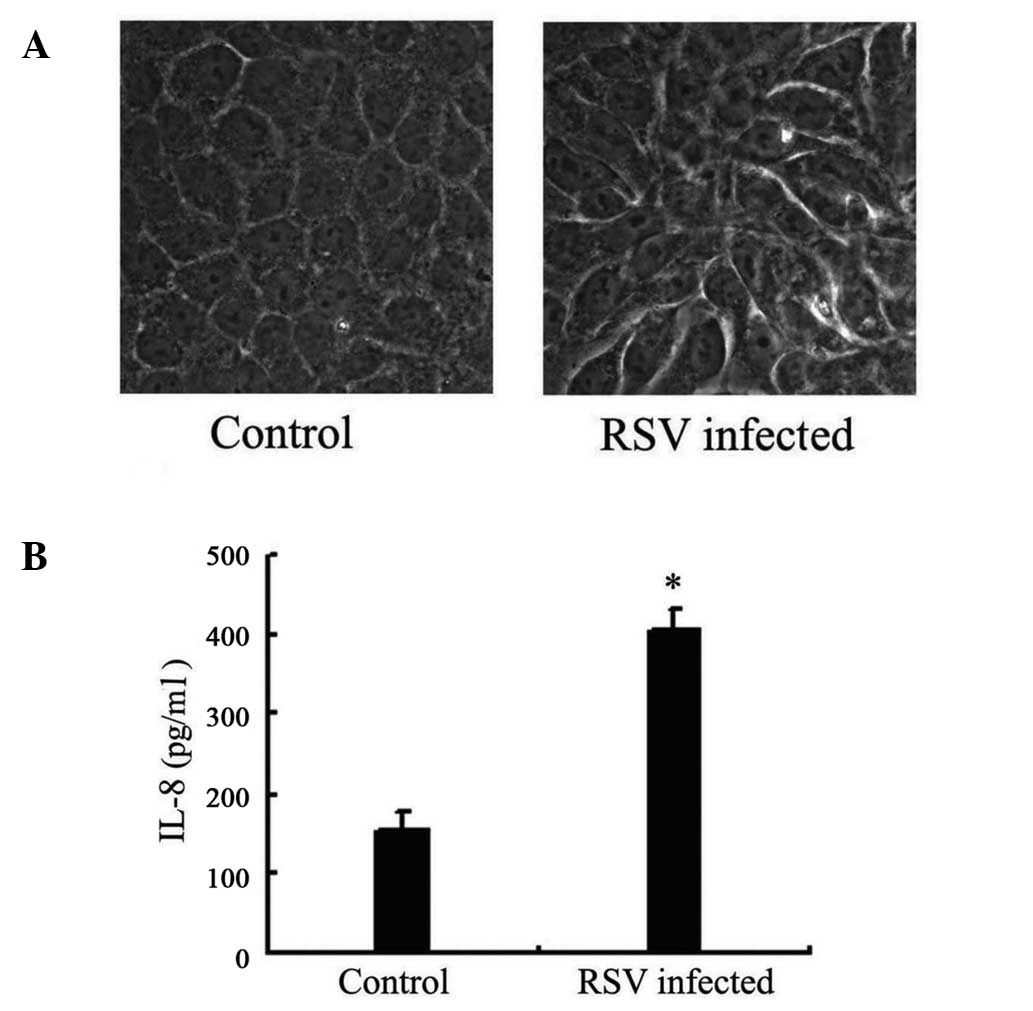
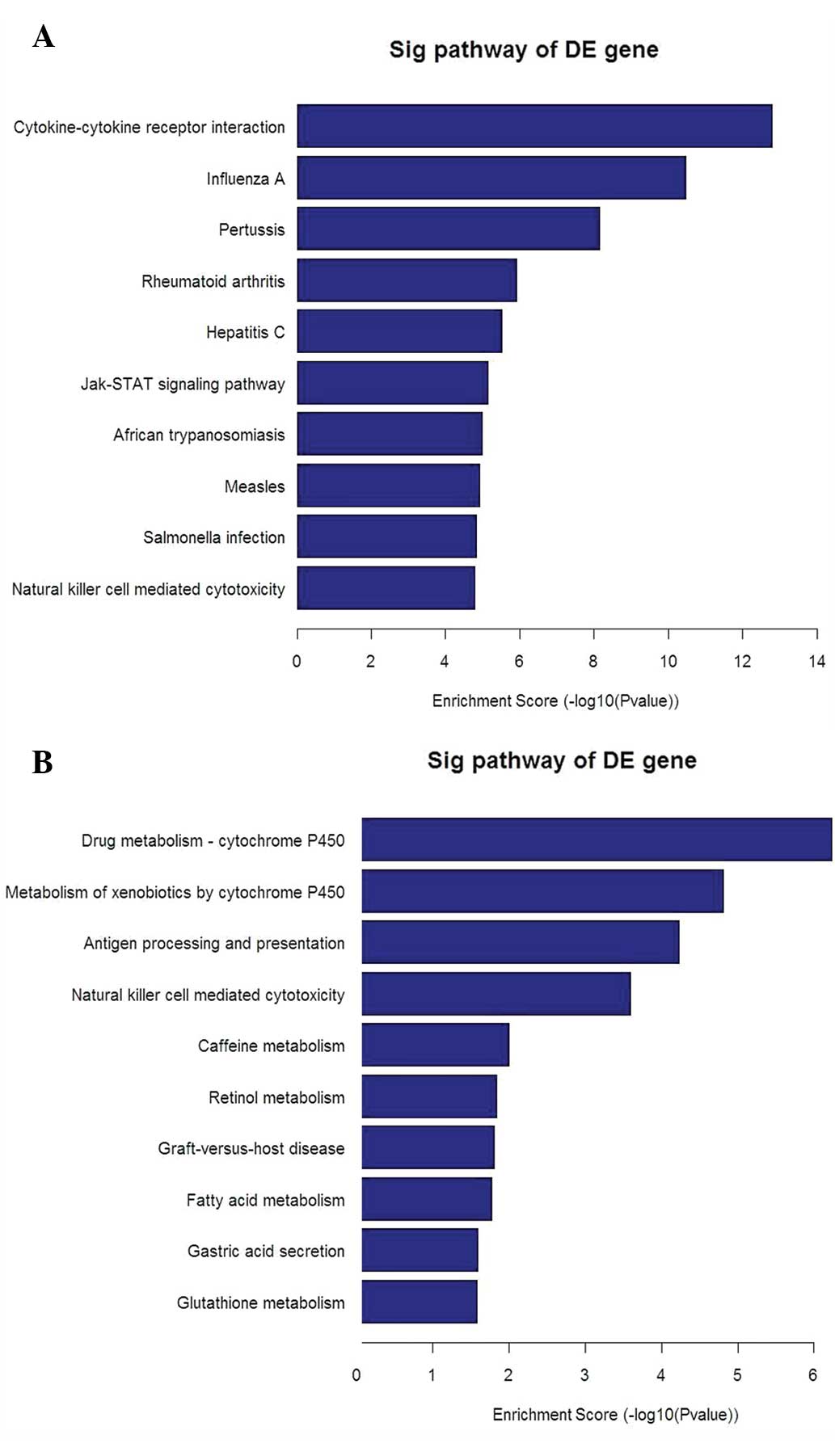
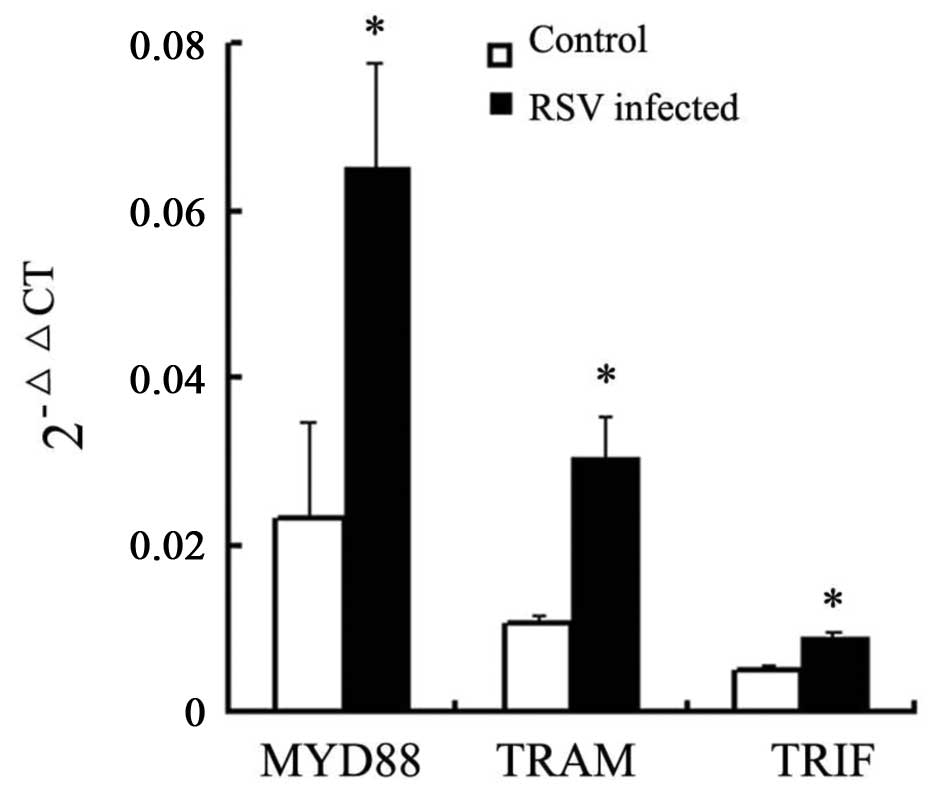
|
1
|
Liu L, Johnson HL, Cousens S, et al; Child
Health Epidemiology Reference Group of WHO and UNICEF. Global,
regional, and national causes of child mortality: an updated
systematic analysis for 2010 with time trends since 2000. Lancet.
379:2151–2161. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nair H, Nokes DJ, Gessner BD, Dherani M,
Madhi SA, Singleton RJ, O’Brien KL, Roca A, Wright PF, Bruce N, et
al: Global burden of acute lower respiratory infections due to
respiratory syncytial virus in young children: a systematic review
and meta-analysis. Lancet. 375:1545–1555. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sigurs N, Aljassim F, Kjellman B, Robinson
PD, Sigurbergsson F, Bjarnason R and Gustafsson PM: Asthma and
allergy patterns over 18 years after severe RSV bronchiolitis in
the first year of life. Thorax. 65:1045–1052. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Walsh EE: Respiratory syncytial virus
infection in adults. Semin Respir Crit Care Med. 32:423–432. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zdrenghea MT, Telcian AG, Laza-Stanca V,
Bellettato CM, Edwards MR, Nikonova A, Khaitov MR, Azimi N, Groh V,
Mallia P, et al: RSV infection modulates IL-15 production and MICA
levels in respiratory epithelial cells. Eur Respir J. 39:712–720.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Masaki T, Kojima T, Okabayashi T, et al: A
nuclear factor-κB signaling pathway via protein kinase C δ
regulates replication of respiratory syncytial virus in polarized
normal human nasal epithelial cells. Mol Biol Cell. 22:2144–2156.
2011.
|
|
7
|
Xie XH, Law HK, Wang LJ, Li X, Yang XQ and
Liu EM: Lipopolysaccharide induces IL-6 production in respiratory
syncytial virus-infected airway epithelial cells through the
toll-like receptor 4 signaling pathway. Pediatr Res. 65:156–162.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Abu-Harb M, Bell F, Finn A, Rao WH, Nixon
L, Shale D and Everard ML: IL-8 and neutrophil elastase levels in
the respiratory tract of infants with RSV bronchiolitis. Eur Respir
J. 14:139–143. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gern JE, Martin MS, Anklam KA, Shen K,
Roberg KA, Carlson-Dakes KT, Adler K, Gilbertson-White S, Hamilton
R, Shult PA, et al: Relationships among specific viral pathogens,
virus-induced interleukin-8, and respiratory symptoms in infancy.
Pediatr Allergy Immunol. 13:386–393. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hornsleth A, Loland L and Larsen LB:
Cytokines and chemokines in respiratory secretion and severity of
disease in infants with respiratory syncytial virus (RSV)
infection. J Clin Virol. 21:163–170. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Assefa D, Amin N, Dozor AJ and Parton LA:
Attenuated interleukin-8/leukocyte immunoresponse in preterm
infants compared with term infants hospitalized with respiratory
syncytial virus bronchiolitis: a pilot study. Hum Immunol.
72:708–711. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Puthothu B, Krueger M, Heinze J, Forster J
and Heinzmann A: Impact of IL8 and IL8-receptor alpha polymorphisms
on the genetics of bronchial asthma and severe RSV infections. Clin
Mol Allergy. 4:22006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Govindaraju V, Michoud MC, Ferraro P,
Arkinson J, Safka K, Valderrama-Carvajal H and Martin JG: The
effects of interleukin-8 on airway smooth muscle contraction in
cystic fibrosis. Respir Res. 9:762008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Toshchakov V, Jones BW, Perera PY, Thomas
K, Cody MJ, Zhang S, Williams BR, Major J, Hamilton TA, Fenton MJ
and Vogel SN: TLR4, but not TLR2, mediates IFN-beta-induced
STAT1alpha/beta-dependent gene expression in macrophages. Nat
Immunol. 3:392–398. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kagan JC, Su T, Horng T, Chow A, Akira S
and Medzhitov R: TRAM couples endocytosis of Toll-like receptor 4
to the induction of interferon-beta. Nat Immunol. 9:361–368. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Palsson-McDermott EM, Doyle SL, McGettrick
AF, Hardy M, Husebye H, Banahan K, Gong M, Golenbock D, Espevik T
and O’Neill LA: TAG, a splice variant of the adaptor TRAM,
negatively regulates the adaptor MyD88-independent TLR4 pathway.
Nat Immunol. 10:579–586. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Blasius AL and Beutler B: Intracellular
toll-like receptors. Immunity. 32:305–315. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Eferl R and Wagner EF: AP-1: a
double-edged sword in tumorigenesis. Nat Rev Cancer. 3:859–868.
2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Curran T and Franza BR Jr: Fos and Jun:
the AP-1 connection. Cell. 55:395–397. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kawai T, Sato S, Ishii KJ, Coban C, Hemmi
H, Yamamoto M, Terai K, Matsuda M, Inoue J, Uematsu S, et al:
Interferon-alpha induction through Toll-like receptors involves a
direct interaction of IRF7 with MyD88 and TRAF6. Nat Immunol.
5:1061–1068. 2004. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|