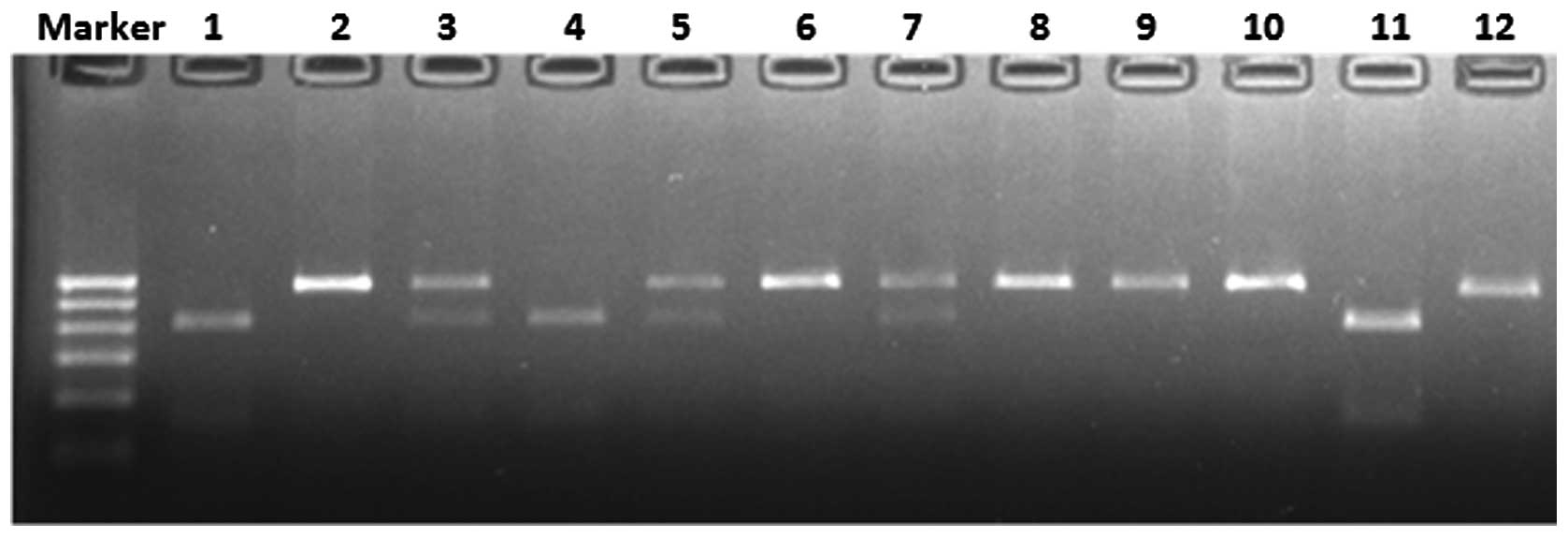
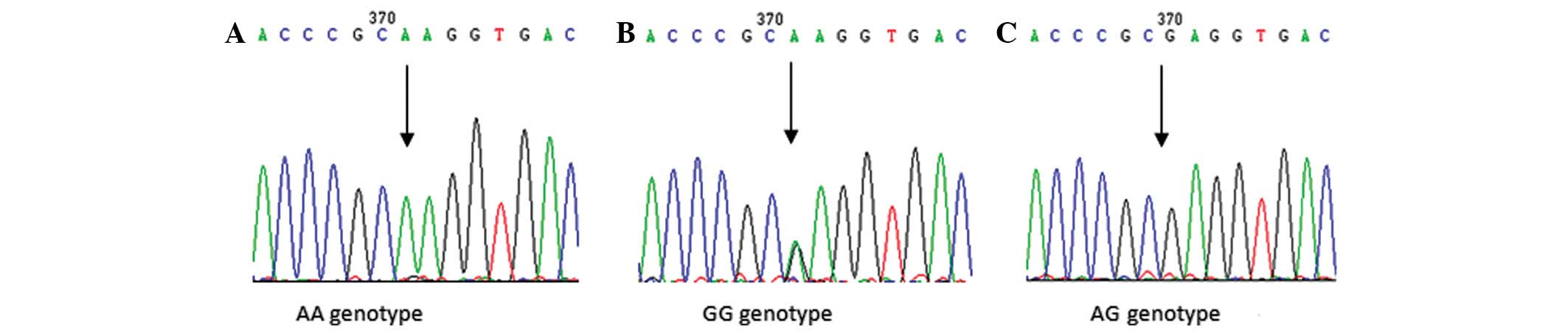
|
1
|
Hwang SJ, Ballantyne CM, Sharrett AR,
Smith LC, Davis CE, et al: Circulating adhesion molecules VCAM-1,
ICAM-1, and E-selectin in carotid atherosclerosis and incident
coronary heart disease cases: the Atherosclerosis Risk In
Communities (ARIC) study. Circulation. 96:4219–4225. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Mizia-Stec K, Zahorska-Markiewicz B and
Goliszek L: Adhesion molecules: atherosclerosis and coronary artery
disease. Przegl Lek. 60:147–150. 2003.(In Polish).
|
|
3
|
Greve JM, Davis G, Meyer AM, Forte CP,
Yost SC, et al: The major human rhinovirus receptor is ICAM-1.
Cell. 56:839–847. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Dietrich JB: The adhesion molecule ICAM-1
and its regulation in relation with the blood-brain barrier. J
Neuroimmunol. 128:58–68. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
van de Stolpe A and van der Saag PT:
Intercellular adhesion molecule-1. J Mol Med (Berl). 74:13–33.
1996.
|
|
6
|
Watanabe T and Fan J: Atherosclerosis and
inflammation mononuclear cell recruitment and adhesion molecules
with reference to the implication of ICAM-1/LFA-1 pathway in
atherogenesis. Int J Cardiol. 66(Suppl 1): S45–S53; discussion S55.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Cybulsky MI, Iiyama K, Li H, Zhu S, Chen
M, et al: A major role for VCAM-1, but not ICAM-1, in early
atherosclerosis. J Clin Invest. 107:1255–1262. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Xie X, Ma YT, Yang YN, Fu ZY, Li XM, et
al: Polymorphisms in the SAA1/2 gene are associated with carotid
intima media thickness in healthy Han Chinese subjects: the
Cardiovascular Risk Survey. PLoS One. 5:e139972010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Gaetani E, Flex A, Pola R, Papaleo P, De
Martini D, et al: The K469E polymorphism of the ICAM-1 gene is a
risk factor for peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Blood Coagul
Fibrinolysis. 13:483–488. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iwao M, Morisaki H and Morisaki T:
Single-nucleotide polymorphism g. 1548G > A (E469K) in human
ICAM-1 gene affects mRNA splicing pattern and TPA-induced
apoptosis. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 317:729–735. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Kitagawa K, Matsumoto M, Sasaki T,
Hashimoto H, Kuwabara K, et al: Involvement of ICAM-1 in the
progression of atherosclerosis in APOE-knockout mice.
Atherosclerosis. 160:305–310. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Hulthe J, Wikstrand J, Mattsson-Hultén L
and Fagerberg B: Circulating ICAM-1 (intercellular cell-adhesion
molecule 1) is associated with early stages of atherosclerosis
development and with inflammatory cytokines in healthy 58-year-old
men: the Atherosclerosis and Insulin Resistance (AIR) study. Clin
Sci (Lond). 103:123–129. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Puthothu B, Krueger M, Bernhardt M and
Heinzmann A: ICAM1 amino-acid variant K469E is associated with
paediatric bronchial asthma and elevated sICAM1 levels. Genes
Immun. 7:322–326. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Bielinski SJ, Reiner AP, Nickerson D,
Carlson C, Bailey KR, et al: Polymorphisms in the ICAM1 gene
predict circulating soluble intercellular adhesion
molecule-1(sICAM-1). Atherosclerosis. 216:390–394. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou YL, Zhu MA, Ding Y, et al:
Association between intercellular adhension molecule-1 gene
polymorphism and coronary heart disease. J Clin Cardiol. 9:519–522.
2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
16
|
Zhang SR, Xu LX, Gao QQ, Zhang HQ, Xu BS,
et al: The correlation between ICAM-1 gene K469E polymorphism and
coronary heart disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi Chuan Xue Za Zhi.
23:205–207. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
17
|
Lu FH, Shang Q, Wen PE, Su GH, Wu JM, et
al: A study on K469E polymorphism of ICAM1 gene and ICAM1 plasma
level in patients with coronary heart disease. Zhonghua Yi Xue Yi
Chuan Xue Za Zhi. 23:195–197. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
18
|
Mohamed AA, Rashed L, Amin H, Abu-Farha M,
El Fadl SA and Pakhoum S: K469E polymorphism of the intercellular
adhesion molecule-1 gene in Egyptians with coronary heart disease.
Ann Saudi Med. 30:432–436. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McGlinchey PG, Spence MS, Patterson CC,
Allen AR, Murphy G, et al: The intercellular adhesion molecule-1
(ICAM-1) gene K469E polymorphism is not associated with ischaemic
heart disease: an investigation using family-based tests of
association. Eur J Immunogenet. 31:201–206. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Aminian B, Abdi Ardekani AR and Arandi N:
ICAM-1 polymorphisms (G241R, K469E), in coronary artery disease and
myocardial infarction. Iran J Immunol. 4:227–235. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Milutinović A and Petrovic D: The K469E
polymorphism of the intracellular adhesion molecule 1 (ICAM-1) gene
is not associated with myocardial infarction in Caucasians with
type 2 diabetes. Folia Biol (Praha). 52:79–80. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Wang MY, Bai DC, Zhu P, Fu Y, Bu DF and
Zhang Y: Effects of ICAM-1 gene K469E, K56M polymorphisms on plasma
sICAM-1 expression levels in Chinese Yugur, Tibetan and Han
nationalities. Zhongguo Shi Yan Xue Ye Xue Za Zhi. 20:1205–1211.
2012.(In Chinese).
|