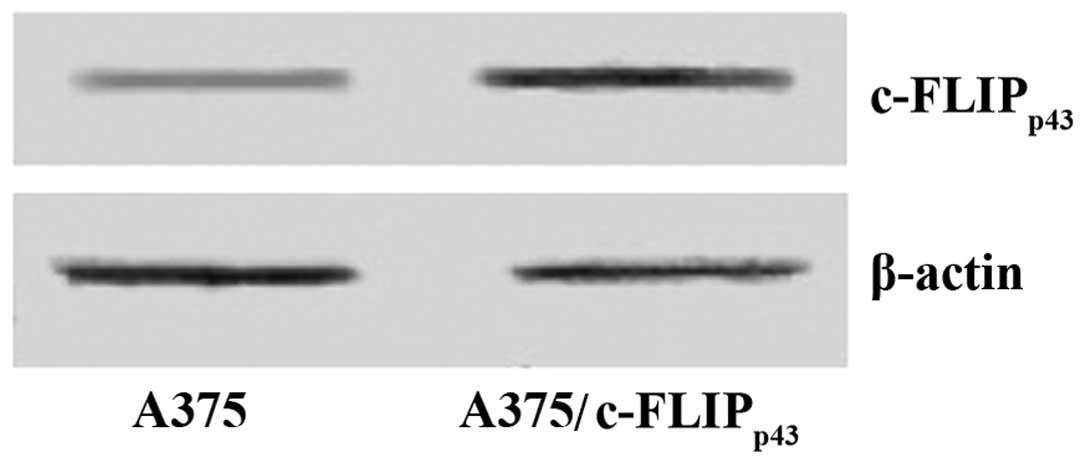
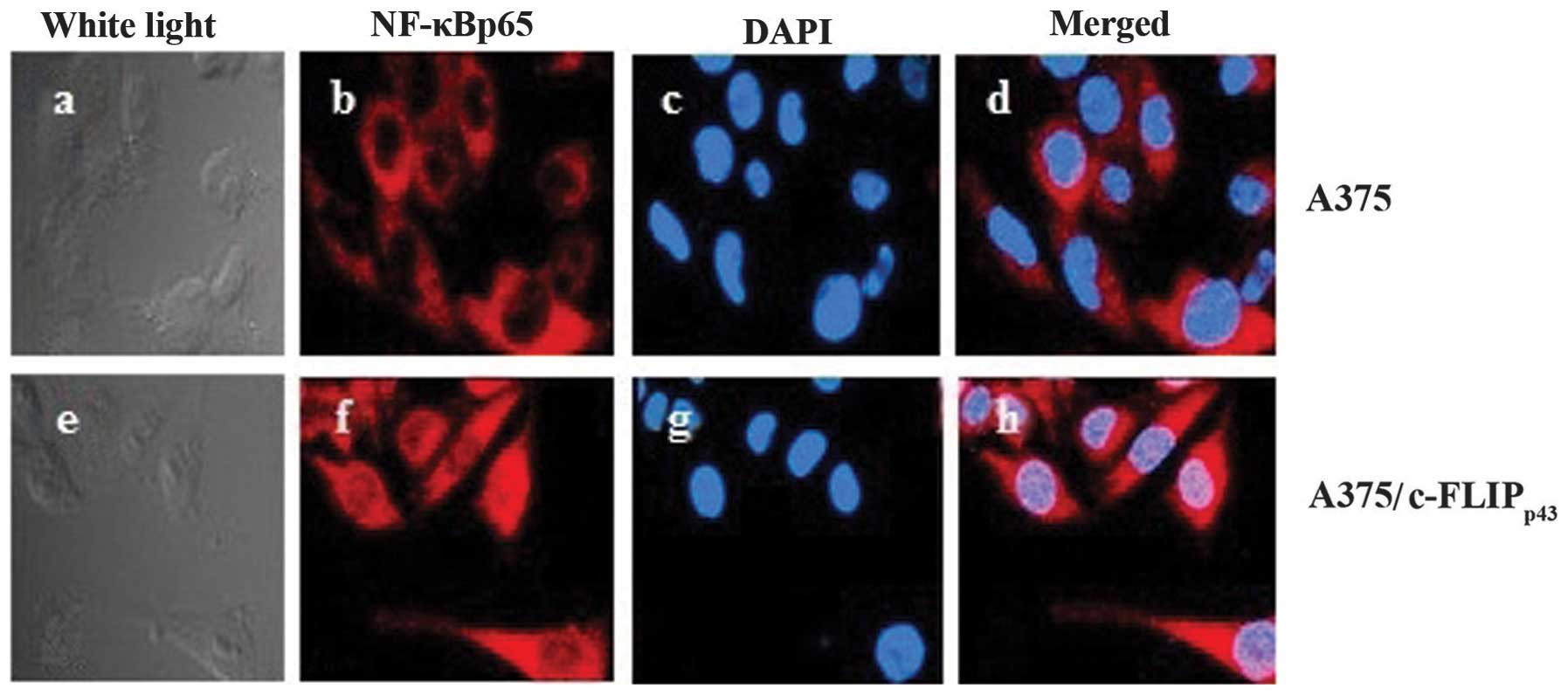
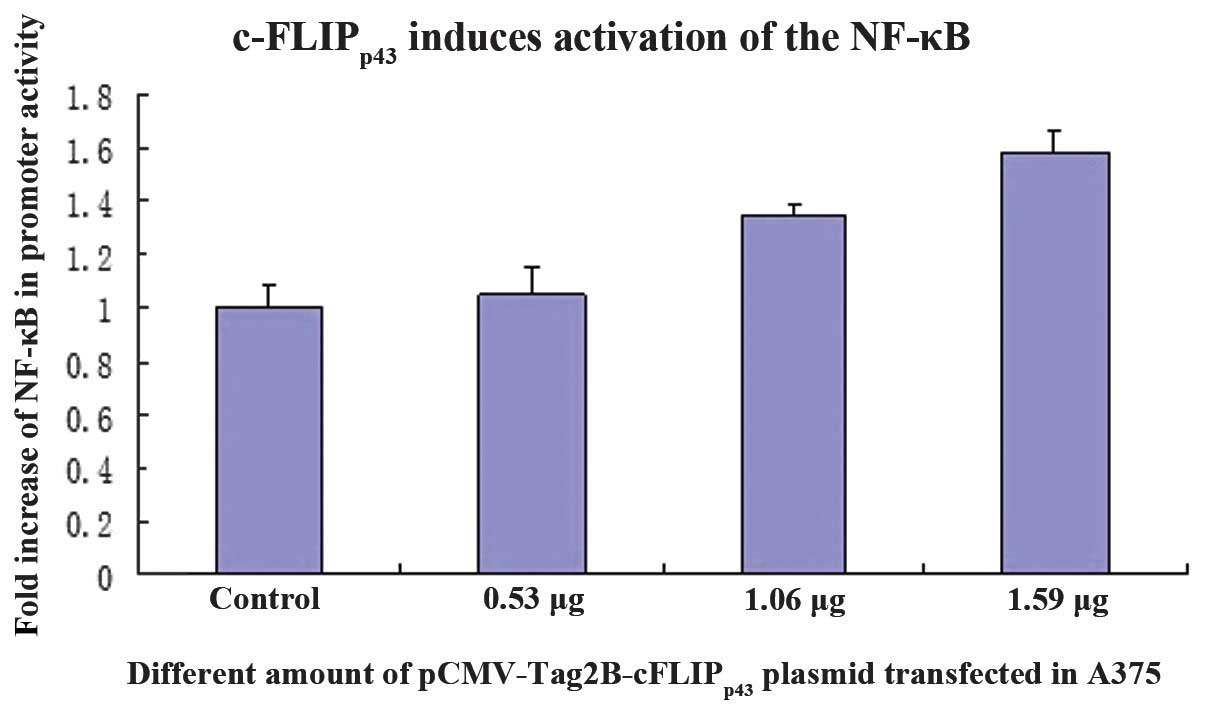
|
1
|
Markovic SN, Erickson LA, Rao RD, et al:
Malignant melanoma in the 21st century, part 1: epidemiology, risk
factors, screening, prevention, and diagnosis. Mayo Clinic Proc.
82:364–380. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Igney FH and Krammer PH: Death and
anti-death: tumour resistance to apoptosis. Nature Rev Cancer.
2:277–288. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kataoka T, Schröter M, Hahne M, et al:
FLIP prevents apoptosis induced by death receptors but not by
perforin/granzyme B, chemotherapeutic drugs, and gamma irradiation.
J Immunol. 161:3936–3942. 1998.
|
|
4
|
Irmler M, Thome M, Hahne M, et al:
Inhibition of death receptor signals by cellular FLIP. Nature.
388:190–195. 1997. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Bullani RR, Huard B, Viard-Leveugle I, et
al: Selective expression of FLIP in malignant melanocytic skin
lesions. J Invest Dermatol. 117:360–364. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Tian F, Lu JJ, Wang L, et al: Expression
of c-FLIP in malignant melanoma, and its relationship with the
clinicopathological features of the disease. Clin Exp Dermatol.
37:259–265. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kataoka T and Tschopp J: N-terminal
fragment of c-FLIP(L) processed by caspase 8 specifically interacts
with TRAF2 and induces activation of the NF-kappaB signaling
pathway. Mol Cell Biol. 24:2627–2636. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dohrman A, Kataoka T, Cuenin S, et al:
Cellular FLIP (long form) regulates CD8+ T cell
activation through caspase-8-dependent NF-kappa B activation. J
Immunol. 174:5270–5278. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aggarwal BB: Nuclear factor-kappa B: the
enemy within. Cancer Cell. 6:203–208. 2004.
|
|
10
|
McNulty SE, del Rosario R, Cen D, Meyskens
FL Jr and Yang S: Comparative expression of NFkappaB proteins in
melanocytes of normal skin vs. benign intradermal naevus and human
metastatic melanoma biopsies. Pigment Cell Res. 17:173–180. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Thu YM, Su Y, Yang J, et al: NF-kappaB
inducing kinase (NIK) modulates melanoma tumorigenesis by
regulating expression of pro-survival factors through the β-catenin
pathway. Oncogene. 31:2580–2592. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Griffith TS, Chin WA, Jackson GC, Lynch DH
and Kubin MZ: Intracellular regulation of TRAIL-induced apoptosis
in human melanoma cells. J Immunol. 161:2833–2840. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee SH, Kim HS, Kim SY, et al: Increased
expression of FLIP, an inhibitor of Fas-mediated apoptosis, in
stomach cancer. APMIS. 111:309–314. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nam SY, Jung GA, Hur GC, et al:
Upregulation of FLIP(S) by Akt, a possible inhibition mechanism of
TRAIL-induced apoptosis in human gastric cancers. Cancer Science.
94:1066–1073. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Zhou XD, Yu JP, Liu J, et al:
Overexpression of cellular FLICE-inhibitory protein (FLIP) in
gastric adenocarcinoma. Clin Sci (Lond). 106:397–405. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Wilson NS, Dixit V and Ashkenazi A: Death
receptor signal transducers: nodes of coordination in immune
signaling networks. Nat Immunol. 10:348–355. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Okano H, Shiraki K, Inoue H, et al:
Cellular FLICE/caspase-8-inhibitory protein as a principal
regulator of cell death and survival in human hepatocellular
carcinoma. Lab Invest. 83:1033–1043. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Elnemr A, Ohta T, Yachie A, et al: Human
pancreatic cancer cells disable function of Fas receptors at
several levels in Fas signal transduction pathway. Int J Oncol.
18:311–316. 2001.
|
|
19
|
Xiao CW, Yan X, Li Y, Reddy SA and Tsang
BK: Resistance of human ovarian cancer cells to tumor necrosis
factor alpha is a consequence of nuclear factor kappaB-mediated
induction of Fas-associated death domain-like
interleukin-1beta-converting enzyme-like inhibitory protein.
Endocrinology. 144:623–630. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Zhang X, Jin TG, Yang H, et al: Persistent
c-FLIP(L) expression is necessary and sufficient to maintain
resistance to tumor necrosis factor-related apoptosis-inducing
ligand-mediated apoptosis in prostate cancer. Cancer Res.
64:7086–7091. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Olsson A, Diaz T, Aguilar-Santelises M, et
al: Sensitization to TRAIL-induced apoptosis and modulation of
FLICE-inhibitory protein in B chronic lymphocytic leukemia by
actinomycin D. Leukemia. 15:1868–1877. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
MacFarlane M, Harper N, Snowden RT, et al:
Mechanisms of resistance to TRAIL-induced apoptosis in primary B
cell chronic lymphocytic leukaemia. Oncogene. 21:6809–6818. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Korkolopoulou P, Goudopoulou A, Voutsinas
G, et al: c-FLIP expression in bladder urothelial carcinomas: its
role in resistance to Fas-mediated apoptosis and clinicopathologic
correlations. Urology. 63:1198–1204. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Djerbi M, Screpanti V, Catrina AI, et al:
The inhibitor of death receptor signaling, FLICE-inhibitory protein
defines a new class of tumor progression factors. J Exp Med.
190:1025–1032. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ullenhag GJ, Mukherjee A, Watson NF, et
al: Overexpression of FLIPL is an independent marker of poor
prognosis in colorectal cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res.
13:5070–5075. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang W, Wang S, Song X, et al: The
relationship between c-FLIP expression and human papillomavirus E2
gene disruption in cervical carcinogenesis. Gynecol Oncol.
105:571–577. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Valnet-Rabier MB, Challier B, Thiebault S,
et al: c-Flip protein expression in Burkitt’s lymphomas is
associated with a poor clinical outcome. Br J Haematol.
128:767–773. 2005.
|
|
28
|
Valente G, Manfroi F, Peracchio C, et al:
cFLIP expression correlates with tumour progression and patient
outcome in non-Hodgkin lymphomas of low grade of malignancy. Br J
Haematol. 132:560–570. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Zeise E, Weichenthal M, Schwarz T and
Kulms D: Resistance of human melanoma cells against the death
ligand TRAIL is reversed by ultraviolet-B radiation via
downregulation of FLIP. J Invest Dermatol. 123:746–754. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ricci MS, Jin Z, Dews M, et al: Direct
repression of FLIP expression by c-myc is a major determinant of
TRAIL sensitivity. Mol Cell Biol. 24:8541–8555. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Li W, Zhang X and Olumi AF: MG-132
sensitizes TRAIL-resistant prostate cancer cells by activating
c-Fos/c-Jun heterodimers and repressing c-FLIP(L). Cancer Res.
67:2247–2255. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Kreuz S, Siegmund D, Rumpf JJ, et al:
NFkappaB activation by Fas is mediated through FADD, caspase-8, and
RIP and is inhibited by FLIP. J Cell Biol. 166:369–380. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Neumann L, Pforr C, Beaudouin J, et al:
Dynamics within the CD95 death-inducing signaling complex decide
life and death of cells. Mol Syst Biol. 6:3522010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hu WH, Johnson H and Shu HB: Activation of
NF-kappaB by FADD, Casper, and caspase-8. J Biol Chem.
275:10838–10844. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Oztürk S, Schleich K and Lavrik IN:
Cellular FLICE-like inhibitory proteins (c-FLIPs): fine-tuners of
life and death decisions. Exp Cell Res. 318:1324–1331.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Amiri KI and Richmond A: Role of nuclear
factor-kappa B in melanoma. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 24:301–313.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Mayo MW and Baldwin AS: The transcription
factor NF-kappaB: control of oncogenesis and cancer therapy
resistance. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1470:M55–M62. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Huang S, DeGuzman A, Bucana CD and Fidler
IJ: Nuclear factor-kappaB activity correlates with growth,
angiogenesis, and metastasis of human melanoma cells in nude mice.
Clin Cancer Res. 6:2573–2581. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Galligan L, Longley DB, McEwan M, et al:
Chemotherapy and TRAIL-mediated colon cancer cell death: the roles
of p53, TRAIL receptors, and c-FLIP. Mol Cancer Ther. 4:2026–2036.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|