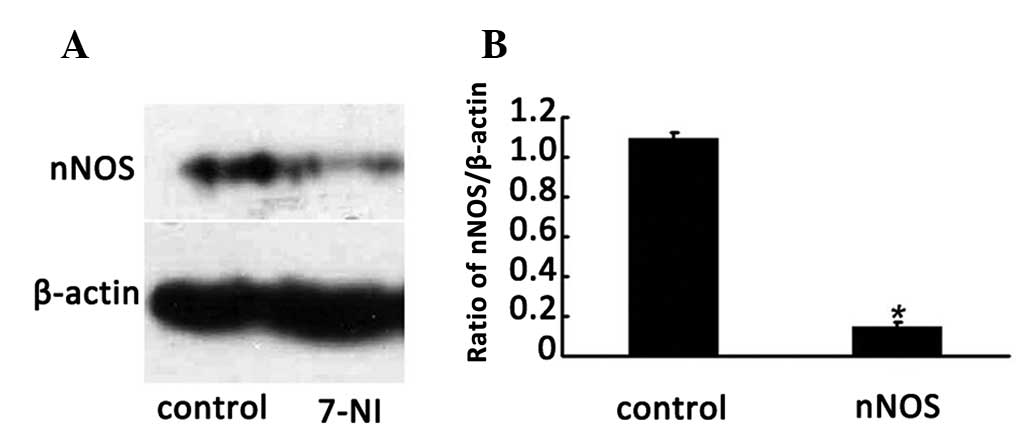
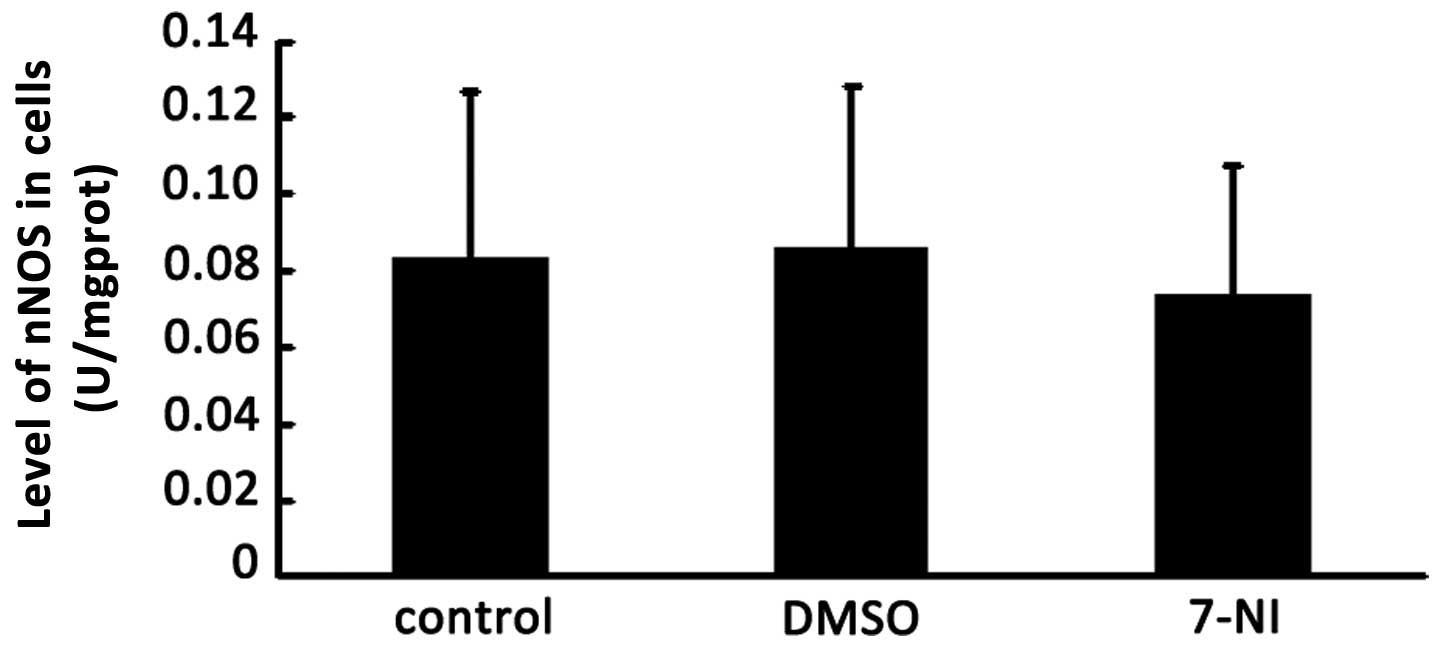
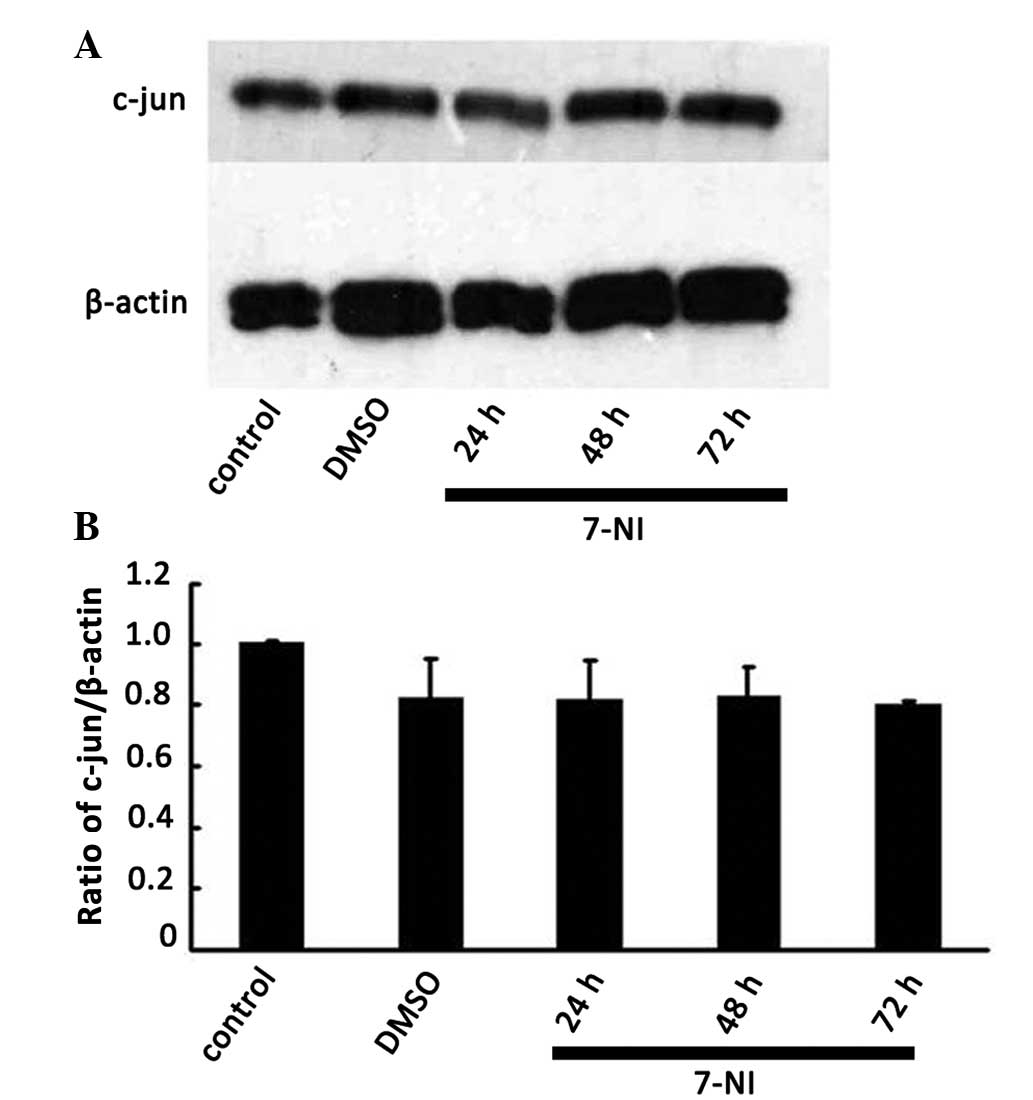
|
1
|
Wu W, Li L, Yick LW, et al: GDNF and BDNF
alter the expression of neuronal NOS, c-Jun, and p75 and prevent
motoneuron death following spinal root avulsion in adult rats. J
Neurotrauma. 20:603–612. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ozdemir M, Attar A and Kuzu L:
Regenerative treatment in spinal cord injury. Curr Stem Cell Res
Ther. 7:364–369. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Förstermann U and Sessa WC: Nitric oxide
synthases: regulation and function. Eur Heart J. 33:829–837.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brown GC: Nitric oxide and neuronal death.
Nitric Oxide. 23:153–165. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Umar S and van der Laarse A: Nitric oxide
and nitric oxide synthase isoforms in the normal, hypertrophic, and
failing heart. Mol Cell Biochem. 333:191–201. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Schonhoff CM and Bulseco DA: The Ras-ERK
pathway is required for the induction of neuronal nitric oxide
synthase in differentiating PC12 cells. J Neurochem. 78:631–639.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Raivich G: Transcribing the path to
neurological recovery - from early signals through transcription
factors to downstream effectors of successful regeneration. Ann
Anat. 193:248–258. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kenney AM and Kocsis JD: Peripheral
axotomy induces long-term c-Jun amino-terminal kinase-1 activation
and activator protein-1 binding activity by c-Jun and junD in adult
rat dorsal root ganglia in vivo. J Neurosci. 18:1318–1328.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mruthyunjaya S, Rumma M, Ravibhushan G, et
al: c-Jun/AP-1 transcription factor regulates laminin-1-induced
neurite outgrowth in human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells: role
of multiple signaling pathways. FEBS Lett. 585:1915–1922. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ferrer I, Barrón S, Rodríquez-Farré E, et
al: Ionizing radiation-induced apoptosis is associated with c-Jun
expression and c-Jun/AP-1 activation in the developing cerebellum
of the rat. Neurosci Lett. 202:105–108. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Fonseca MB, Nunes AF and Rodrigues CM:
c-Jun regulates the stability of anti-apoptotic deltaNp63 in
amyloid-beta-induced apoptosis. J Alzheimers Dis. 28:685–694.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Maritz MF, van der Watt PJ, Holderness N,
et al: Inhibition of AP-1 suppresses cervical cancer cell
proliferation and is associated with p21 expression. Biol Chem.
392:439–448. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Raivich G: c-Jun expression, activation
and function in neural cell death, inflammation and repair. J
Neurochem. 107:898–906. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Dragunow M, Xu R, Walton M, et al: c-Jun
promotes neurite outgrowth and survival in PC12 cells. Brain Res
Mol Brain Res. 83:20–33. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wang LL, Zhao XC, Yan LF, et al: C-jun
phosphorylation contributes to down regulation of neuronal nitric
oxide synthase protein and motoneurons death in injured spinal
cords following root-avulsion of the brachial plexus. Neuroscience.
189:397–407. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Zhou LH, Han S, Xie YY, et al: Differences
in c-jun and nNOS expression levels in motoneurons following
different kinds of axonal injury in adult rats. Brain Cell Biol.
36:213–227. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhou L and Wu W: Antisense oligos to
neuronal nitric oxide synthase aggravate motoneuron death induced
by spinal root avulsion in adult rat. Exp Neurol. 197:84–92. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Cheng X, Liu S, Wang YQ, et al:
Suppression of c-jun influences nNOS expression in differentiated
PC12 cells. Mol Med Rep. 6:750–754. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cheng X, Fu R, Gao M, et al: Intrathecal
application of short interfering RNA knocks down c-jun expression
and augments spinal motoneuron death after root avulsion in adult
rats. Neuroscience. 241:268–279. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Li M, Wang L, Peng Y, et al: Knockdown of
the neuronal nitric oxide synthase gene retard the development of
the cerebellar granule neurons in vitro. Dev Dyn. 239:474–481.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Cheng X, Liu FL, Zhang J, et al: EGb761
protects motoneurons against avulsion-induced oxidative stress in
rats. J Brachial Plex Peripher Nerve Inj. 5:122010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li R, Wang WQ, Zhang H, et al: Adiponectin
improves endothelial function in hyperlipidemic rats by reducing
oxidative/nitrative stress and differential regulation of eNOS/iNOS
activity. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 293:1703–1708. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Palmada M, Kanwal S, Rutkoski NJ, et al:
c-jun is essential for sympathetic neuronal death induced by NGF
withdrawal but not by p75 activation. J Cell Biol. 158:453–461.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ham J, Babij C, Whitfeld J, et al: A c-Jun
dominant negative mutant protects sympathetic neurons against
programmed cell death. Neuron. 14:927–939. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Watson A, Eilers A, Lallemand D, et al:
Phosphorylation of c-Jun is necessary for apoptosis induced by
survival signal withdrawal in cerebellar granule neurons. J
Neurosci. 18:751–762. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang X, Tay SS and Ng YK: C-fos and c-jun
expressions in nitric oxide synthase immunoreactive neurons in the
lateral geniculate nucleus of experimental glaucomatous rats. Exp
Brain Res. 144:365–372. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Zeng XW, Li MW, Pan J, et al: Activation
of c-Jun N-terminal kinase 1/2 regulated by nitric oxide is
associated with neuronal survival in hippocampal neurons in a rat
model of ischemia. Chin Med J (Engl). 124:3367–3372. 2011.
|
|
28
|
Lam PY and Cadenas E: Compromised
proteasome degradation elevates neuronal nitric oxide synthase
levels and induced apoptotic cell death. Arch Biochem Biophys.
478:181–186. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|