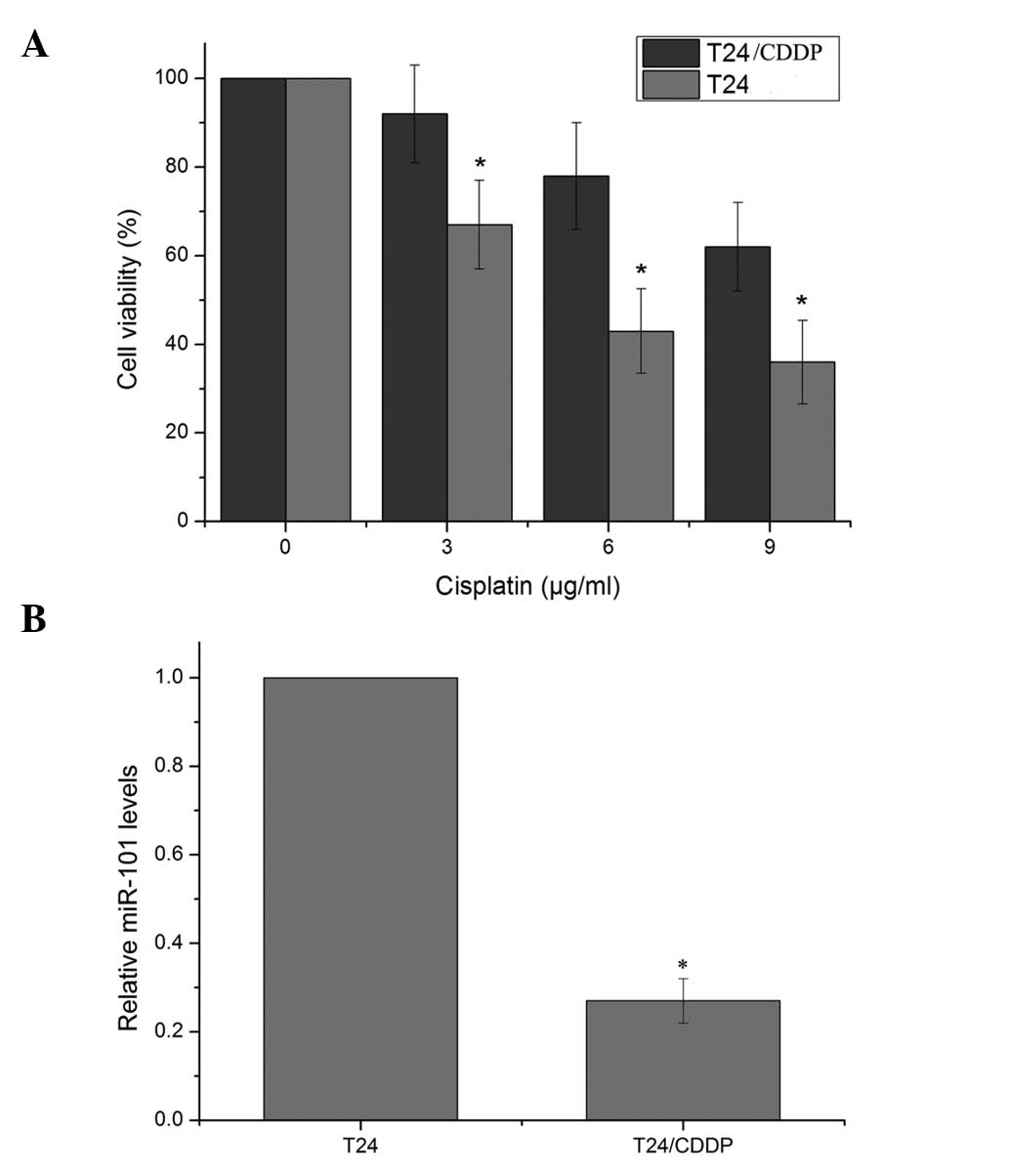
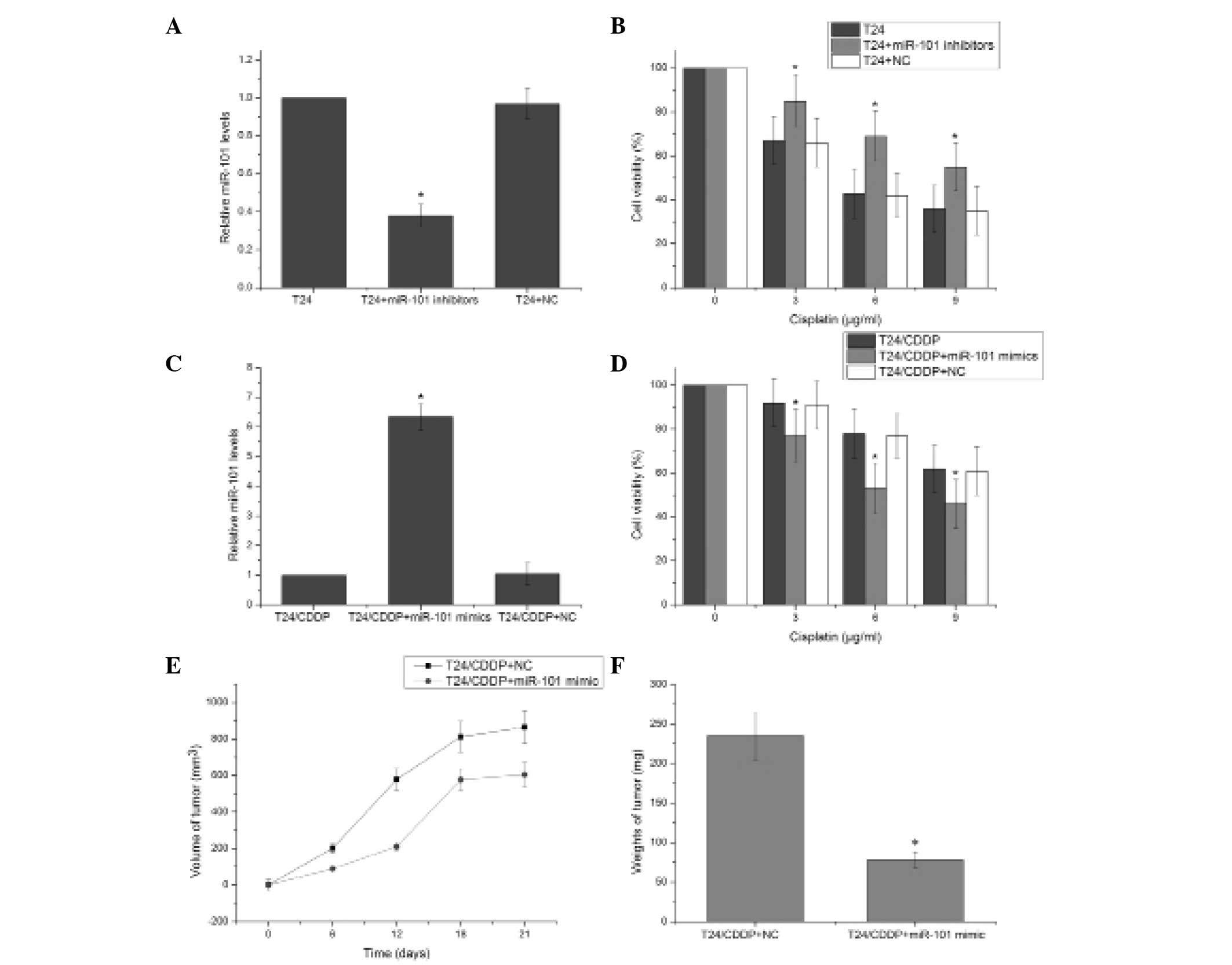
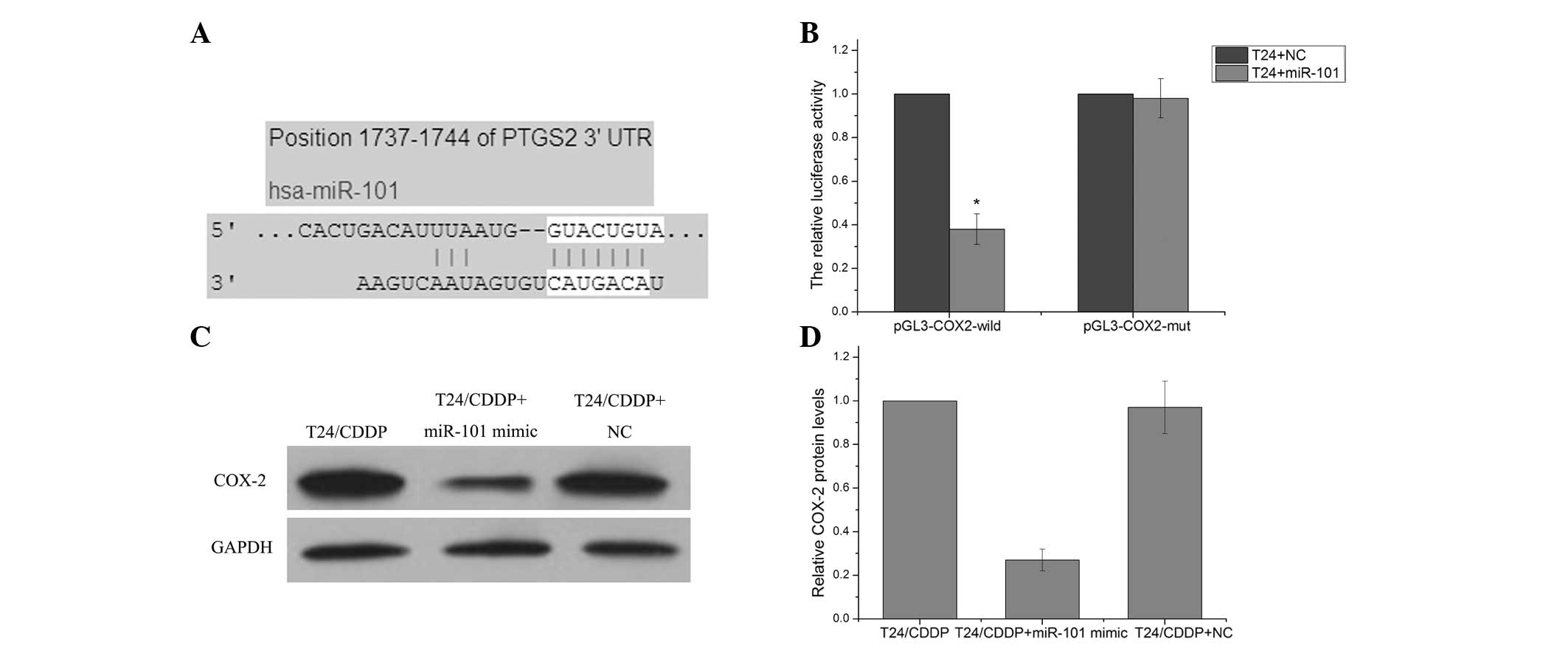
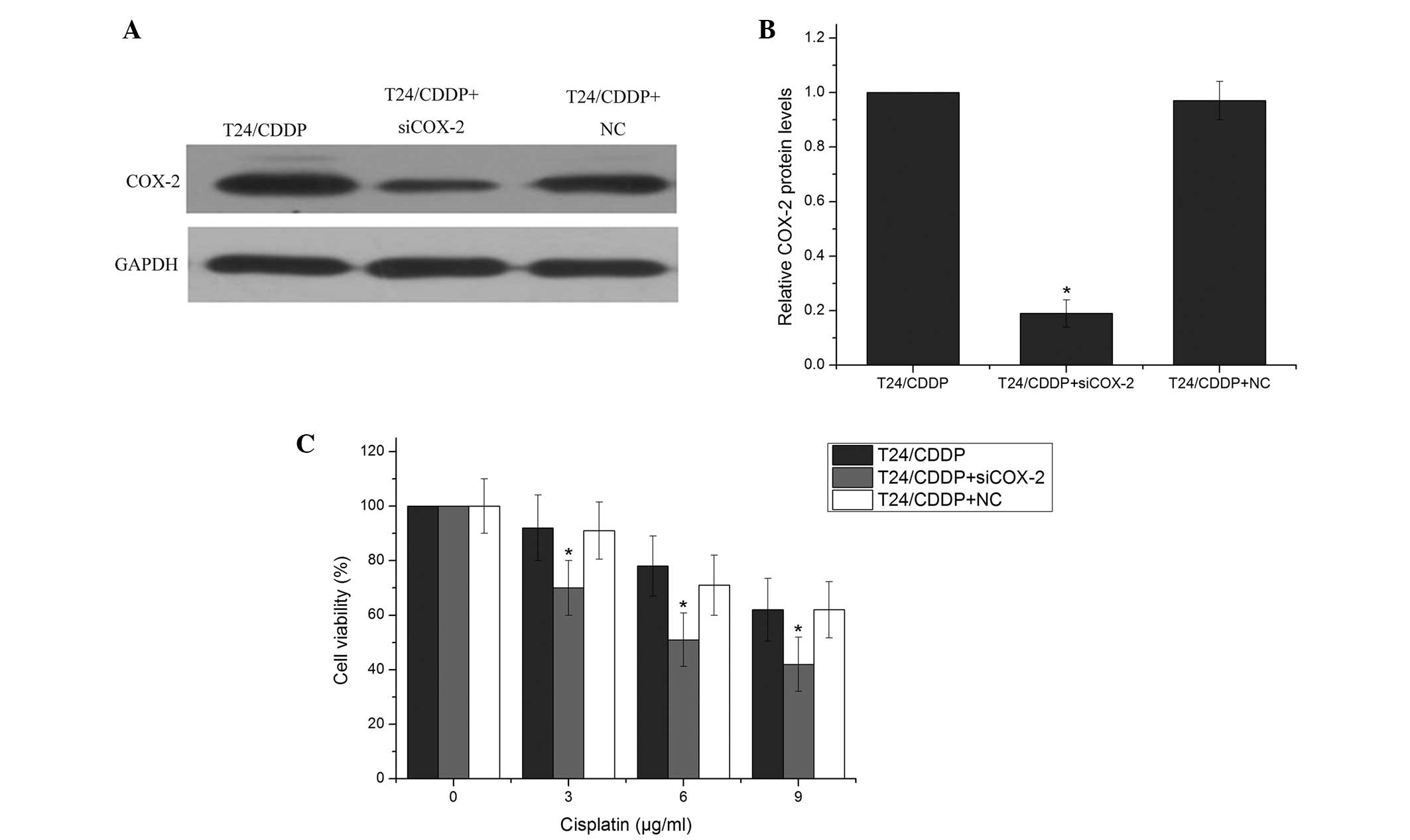
|
1
|
Bo J, Yang G, Huo K, et al: microRNA-203
suppresses bladder cancer development by repressing bcl-w
expression. FEBS J. 278:786–792. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Donat SM: Integrating perioperative
chemotherapy into the treatment of muscle-invasive bladder cancer:
strategy versus reality. J Natl Compr Canc Netw. 7:40–47. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Kakizoe T, Mucci LA, Albertsen PC and
Droller MJ: Screening for bladder cancer: theoretical and practical
issues in considering the treated and untreated natural history of
the various forms of the disease. Scand J Urol Nephrol Suppl.
191–212. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Noguchi S, Mori T, Hoshino Y, et al:
MicroRNA-143 functions as a tumor suppressor in human bladder
cancer T24 cells. Cancer Lett. 307:211–220. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Andrews PA and Howell SB: Cellular
pharmacology of cisplatin: perspectives on mechanisms of acquired
resistance. Cancer Cells. 2:35–43. 1990.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Cho HJ, Kim JK, Kim KD, et al:
Upregulation of Bcl-2 is associated with cisplatin-resistance via
inhibition of Bax translocation in human bladder cancer cells.
Cancer Lett. 237:56–66. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kim VN and Nam JW: Genomics of microRNA.
Trends Genet. 22:165–173. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Shyu AB, Wilkinson MF and van Hoof A:
Messenger RNA regulation: to translate or to degrade. EMBO J.
27:471–481. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Iorio MV, Ferracin M, Liu CG, et al:
MicroRNA gene expression deregulation in human breast cancer.
Cancer Res. 65:7065–7070. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Lu J, Getz G, Miska EA, et al: MicroRNA
expression profiles classify human cancers. Nature. 435:834–838.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Volinia S, Calin GA, Liu CG, et al: A
microRNA expression signature of human solid tumors defines cancer
gene targets. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:2257–2261. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kovalchuk O, Filkowski J, Meservy J, et
al: Involvement of microRNA-451 in resistance of the MCF-7 breast
cancer cells to chemotherapeutic drug doxorubicin. Mol Cancer Ther.
7:2152–2159. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nordentoft I, Birkenkamp-Demtroder K,
Agerbæk M, et al: miRNAs associated with chemo-sensitivity in cell
lines and in advanced bladder cancer. BMC Med Genomics. 5:402012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, et al:
The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and
adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis.
30:377–386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Hasegawa K, Ishikawa K, Kawai S, et al:
Overcoming paclitaxel resistance in uterine endometrial cancer
using a COX-2 inhibitor. Oncol Rep. 30:2937–2944. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wu XL, Cheng B, Li PY, et al: MicroRNA-143
suppresses gastric cancer cell growth and induces apoptosis by
targeting COX-2. World J Gastroenterol. 19:7758–7765. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
He XP, Shao Y, Li XL, et al:
Downregulation of miR-101 in gastric cancer correlates with
cyclooxygenase-2 overexpression and tumor growth. FEBS J.
279:4201–4212. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Xia L, Zhang D, Du R, et al: miR-15b and
miR-16 modulate multidrug resistance by targeting BCL2 in human
gastric cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 123:372–379. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Srivastava SK, Tetsuka T, Daphna-Iken D
and Morrison AR: IL-1 beta stabilizes COX II mRNA in renal
mesangial cells: role of 3′-untranslated region. Am J Physiol.
267:F504–F508. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Xiang KM and Li XR: MiR-133b acts as a
tumor suppressor and negatively regulates TBPL1 in colorectal
cancer cells. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev. 15:3767–3772. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu T, Zhou Q, Zhou J, et al: Carboxyl
terminus of Hsp70-interacting protein (CHIP) contributes to human
glioma oncogenesis. Cancer Sci. 102:959–966. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kang JH, Song KH, Jeong KC, et al:
Involvement of Cox-2 in the metastatic potential of
chemotherapy-resistant breast cancer cells. BMC Cancer. 11:3342011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Akutsu Y, Hanari N, Yusup G, et al: COX2
expression predicts resistance to chemoradiotherapy in esophageal
squamous cell carcinoma. Ann Surg Oncol. 18:2946–2951. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hong JH, Lee E, Hong J, Shin YJ and Ahn H:
Antisense Bcl2 oligonucleotide in cisplatin-resistant bladder
cancer cell lines. BJU Int. 90:113–117. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Friedman JM, Liang G, Liu CC, et al: The
putative tumor suppressor microRNA-101 modulates the cancer
epigenome by repressing the polycomb group protein EZH2. Cancer
Res. 69:2623–2629. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Strillacci A, Griffoni C, Sansone P, et
al: MiR-101 downregulation is involved in cyclooxygenase-2
overexpression in human colon cancer cells. Exp Cell Res.
315:1439–1447. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Varambally S, Cao Q, Mani RS, et al:
Genomic loss of microRNA-101 leads to overexpression of histone
methyltransferase EZH2 in cancer. Science. 322:1695–1699. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Zhang JG, Guo JF, Liu DL, Liu Q and Wang
JJ: MicroRNA-101 exerts tumor-suppressive functions in non-small
cell lung cancer through directly targeting enhancer of zeste
homolog 2. J Thorac Oncol. 6:671–678. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Wang HJ, Ruan HJ, He XJ, et al:
MicroRNA-101 is down-regulated in gastric cancer and involved in
cell migration and invasion. Eur J Cancer. 46:2295–2303. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Chen S, Wang H, Ng WL, Curran WJ and Wang
Y: Radiosensitizing effects of ectopic miR-101 on non-small-cell
lung cancer cells depend on the endogenous miR-101 level. Int J
Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 81:1524–1529. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Xu Y, An Y, Wang Y, et al: miR-101
inhibits autophagy and enhances cisplatin-induced apoptosis in
hepatocellular carcinoma cells. Oncol Rep. 29:2019–2024.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Hwang MK, Kang NJ, Heo YS, Lee KW and Lee
HJ: Fyn kinase is a direct molecular target of delphinidin for the
inhibition of cyclooxygenase-2 expression induced by tumor necrosis
factor-alpha. Biochem Pharmacol. 77:1213–1222. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Duffy CP, Elliott CJ, O’Connor RA, et al:
Enhancement of chemotherapeutic drug toxicity to human tumour cells
in vitro by a subset of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
(NSAIDs). Eur J Cancer. 34:1250–1259. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|