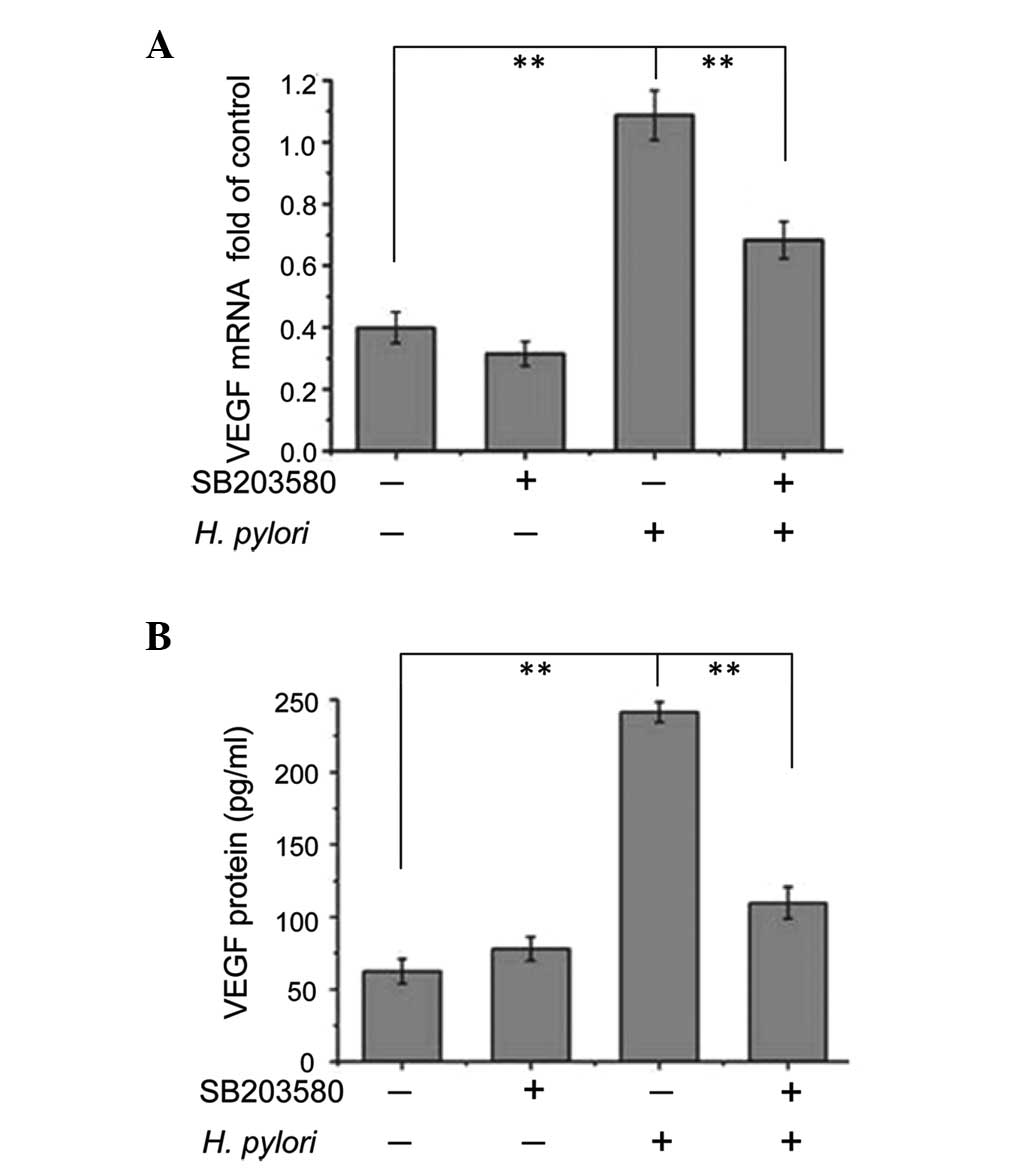
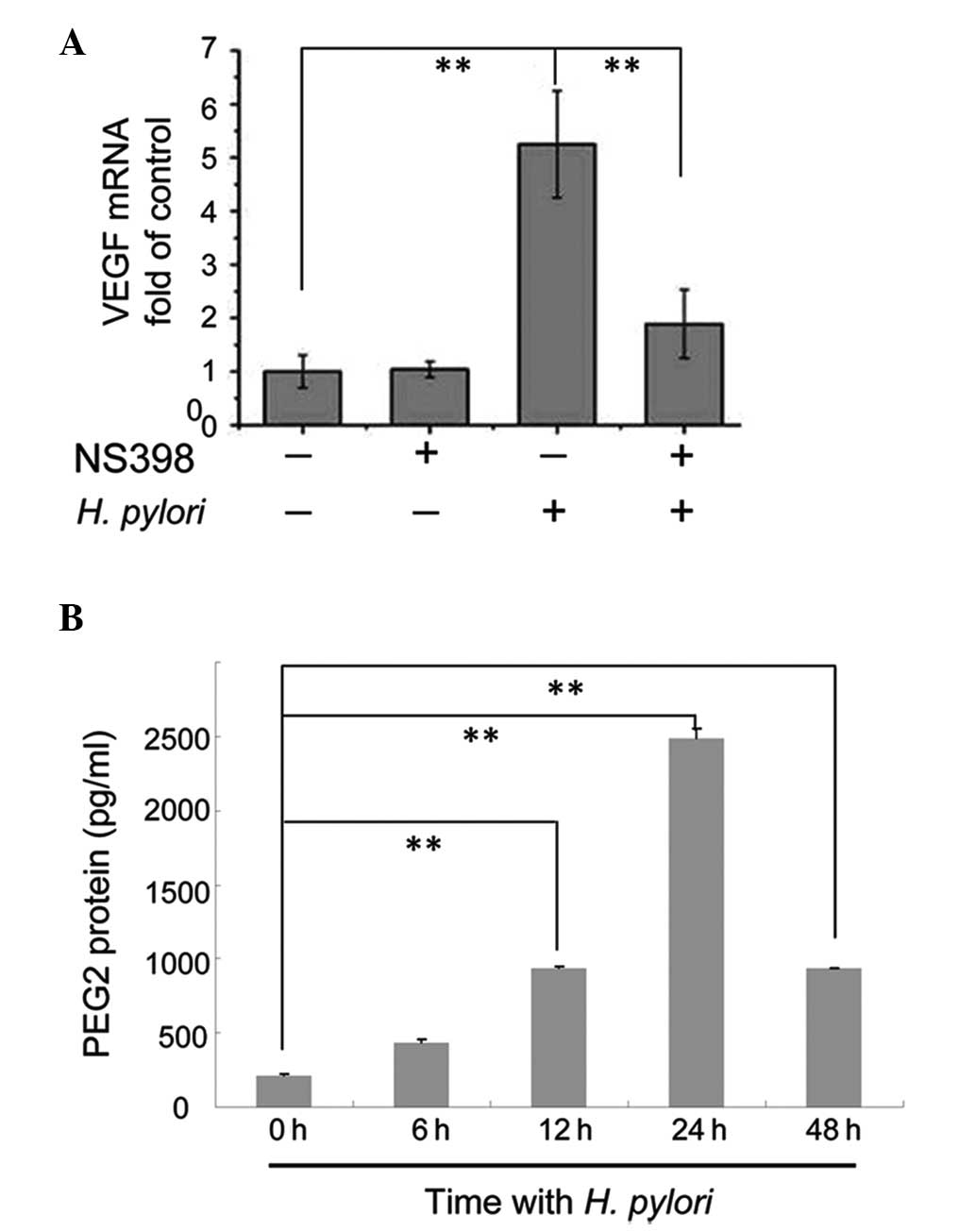
|
1
|
Peek RM Jr and Crabtree JE: Helicobacter
infection and gastric neoplasia. J Pathol. 208:233–248. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Ernst PB, Peura DA and Crowe SE: The
translation of Helicobacter pylori basic research to patient
care. Gastroenterology. 130:188–206; quiz 212–213. 2006.
|
|
3
|
No authors listed. IARC working group on
the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans: some industrial
chemicals; Lyon. 15–22 February 1994; IARC Monogr Eval Carcinog
Risks Hum. 60. pp. 1–560. 1994
|
|
4
|
Wroblewski LE, Peek RM Jr and Wilson KT:
Helicobacter pylori and gastric cancer: factors that
modulate disease risk. Clin Microbiol Rev. 23:713–739. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Conteduca V, Sansonno D, Lauletta G, Russi
S, Ingravallo G and Dammacco F: H. pylori infection and
gastric cancer: state of the art (review). Int J Oncol. 42:5–18.
2013.
|
|
6
|
de Vries EF: Imaging of cyclooxygenase-2
(COX-2) expression: potential use in diagnosis and drug evaluation.
Curr Pharm Des. 12:3847–3856. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Greenhough A, Smartt HJ, Moore AE, et al:
The COX-2/PGE2 pathway: key roles in the hallmarks of cancer and
adaptation to the tumour microenvironment. Carcinogenesis.
30:377–386. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zidar N, Dolenc-Strazar Z, Jeruc J, et al:
Expression of cyclooxygenase-1 and cyclooxygenase-2 in the normal
human heart and in myocardial infarction. Cardiovasc Pathol.
16:300–304. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zidar N, Odar K, Glavac D, Jerse M, Zupanc
T and Stajer D: Cyclooxygenase in normal human tissues - is COX-1
really a constitutive isoform, and COX-2 an inducible isoform? J
Cell Mol Med. 13:3753–3763. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Buskens CJ, Van Rees BP, Sivula A, et al:
Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase 2 expression in
patients with adenocarcinoma of the esophagus. Gastroenterology.
122:1800–1807. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Erkinheimo TL, Lassus H, Sivula A, et al:
Cytoplasmic HuR expression correlates with poor outcome and with
cyclooxygenase 2 expression in serous ovarian carcinoma. Cancer
Res. 63:7591–7594. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Juuti A, Louhimo J, Nordling S, Ristimäki
A and Haglund C: Cyclooxygenase-2 expression correlates with poor
prognosis in pancreatic cancer. J Clin Pathol. 59:382–386. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Menter DG, Schilsky RL and DuBois RN:
Cyclooxygenase-2 and cancer treatment: understanding the risk
should be worth the reward. Clin Cancer Res. 16:1384–1390. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ristimäki A, Sivula A, Lundin J, et al:
Prognostic significance of elevated cyclooxygenase-2 expression in
breast cancer. Cancer Res. 62:632–635. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thiel A, Mrena J and Ristimäki A:
Cyclooxygenase-2 and gastric cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
30:387–395. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li Q, Liu N, Shen B, et al:
Helicobacter pylori enhances cyclooxygenase 2 expression via
p38MAPK/ATF-2 signaling pathway in MKN45 cells. Cancer Lett.
278:97–103. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Fujino H, Xu W and Regan JW: Prostaglandin
E2 induced functional expression of early growth response factor-1
by EP4, but not EP2, prostanoid receptors via the
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase and extracellular signal-regulated
kinases. J Biol Chem. 278:12151–12156. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Golijanin D, Tan JY, Kazior A, et al:
Cyclooxygenase-2 and microsomal prostaglandin E synthase-1 are
overexpressed in squamous cell carcinoma of the penis. Clin Cancer
Res. 10:1024–1031. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Sheng H, Shao J, Washington MK and DuBois
RN: Prostaglandin E2 increases growth and motility of colorectal
carcinoma cells. J Biol Chem. 276:18075–18081. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Ding YB, Shi RH, Tong JD, et al: PGE2
up-regulates vascular endothelial growth factor expression in MKN28
gastric cancer cells via epidermal growth factor receptor signaling
system. Exp Oncol. 27:108–113. 2005.
|
|
21
|
Pai R, Szabo IL, Soreghan BA, Atay S,
Kawanaka H and Tarnawski AS: PGE(2) stimulates VEGF expression in
endothelial cells via ERK2/JNK1 signaling pathways. Biochem Biophys
Res Commun. 286:923–928. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Araki H, Ukawa H, Sugawa Y, Yagi K, Suzuki
K and Takeuchi K: The roles of prostaglandin E receptor subtypes in
the cytoprotective action of prostaglandin E2 in rat stomach.
Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 14(Suppl 1): 116–124. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Breyer RM, Emeson RB, Tarng JL, et al:
Alternative splicing generates multiple isoforms of a rabbit
prostaglandin E2 receptor. J Biol Chem. 269:6163–6169.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Pang L and Knox AJ: Bradykinin stimulates
IL-8 production in cultured human airway smooth muscle cells: role
of cyclooxygenase products. J Immunol. 161:2509–2515.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Takeuchi K, Araki H, Umeda M, Komoike Y
and Suzuki K: Adaptive gastric cytoprotection is mediated by
prostaglandin EP1 receptors: a study using rats and knockout mice.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 297:1160–1165. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jain S, Chakraborty G, Raja R, Kale S and
Kundu GC: Prostaglandin E2 regulates tumor angiogenesis in prostate
cancer. Cancer Res. 68:7750–7759. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Cuenda A and Rousseau S: p38 MAP-kinases
pathway regulation, function and role in human diseases. Biochim
Biophys Acta. 1773:1358–1375. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Choi IJ, Kim JS, Kim JM, Jung HC and Song
IS: Effect of inhibition of extracellular signal-regulated kinase 1
and 2 pathway on apoptosis and bcl-2 expression in Helicobacter
pylori-infected AGS cells. Infection Immun. 71:830–837. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Kim H, Seo JH and Kim KH: The effect of
p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase on mucin gene expression and
apoptosis in Helicobacter pylori-infected gastric epithelial
cells. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1010:90–94. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Seo JH, Lim JW, Kim H and Kim KH:
Helicobacter pylori in a Korean isolate activates
mitogen-activated protein kinases, AP-1, and NF-kappaB and induces
chemokine expression in gastric epithelial AGS cells. Lab Invest.
84:49–62. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Kim JH, Studer RK, Vo NV, Sowa GA and Kang
JD: p38 MAPK inhibition selectively mitigates inflammatory
mediators and VEGF production in AF cells co-cultured with
activated macrophage-like THP-1 cells. Osteoarthritis Cartilage.
17:1662–1669. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Goel HL and Mercurio AM: VEGF targets the
tumour cell. Nat Rev Cancer. 13:871–882. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wu CY, Wang CJ, Tseng CC, et al:
Helicobacter pylori promote gastric cancer cells invasion
through a NF-kappaB and COX-2-mediated pathway. World J
Gastroenterol. 11:3197–3203. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Liu NN, Wang Y and Wu Q: Jianpi jiedu
recipe inhibited Helicobacter pylori-induced the expression
of cyclooxygenase-2 via p38MAPK/ATF-2 signal transduction pathway
in human gastric cancer cells. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za Zhi.
31:926–931. 2011.(In Chinese).
|