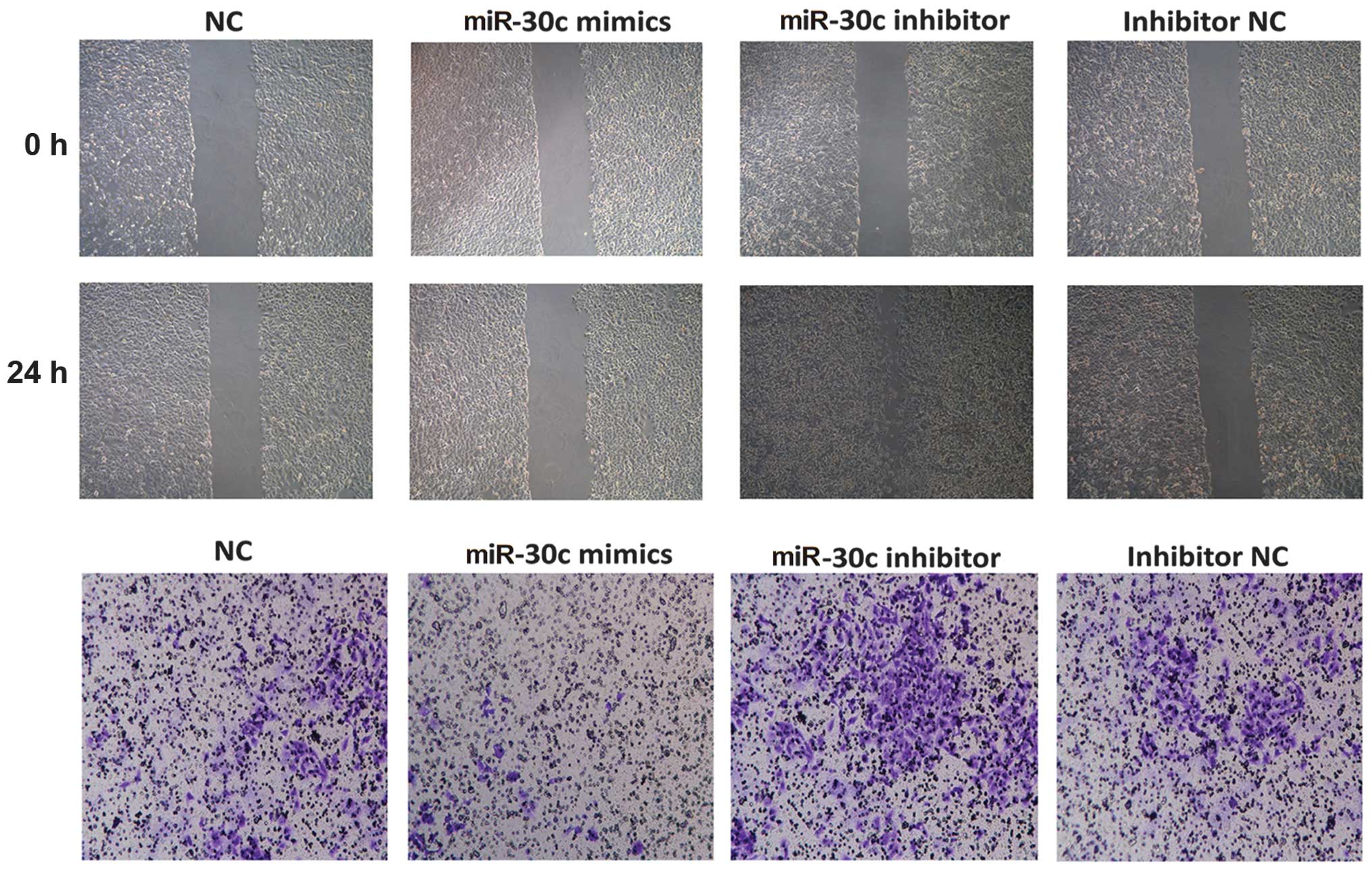
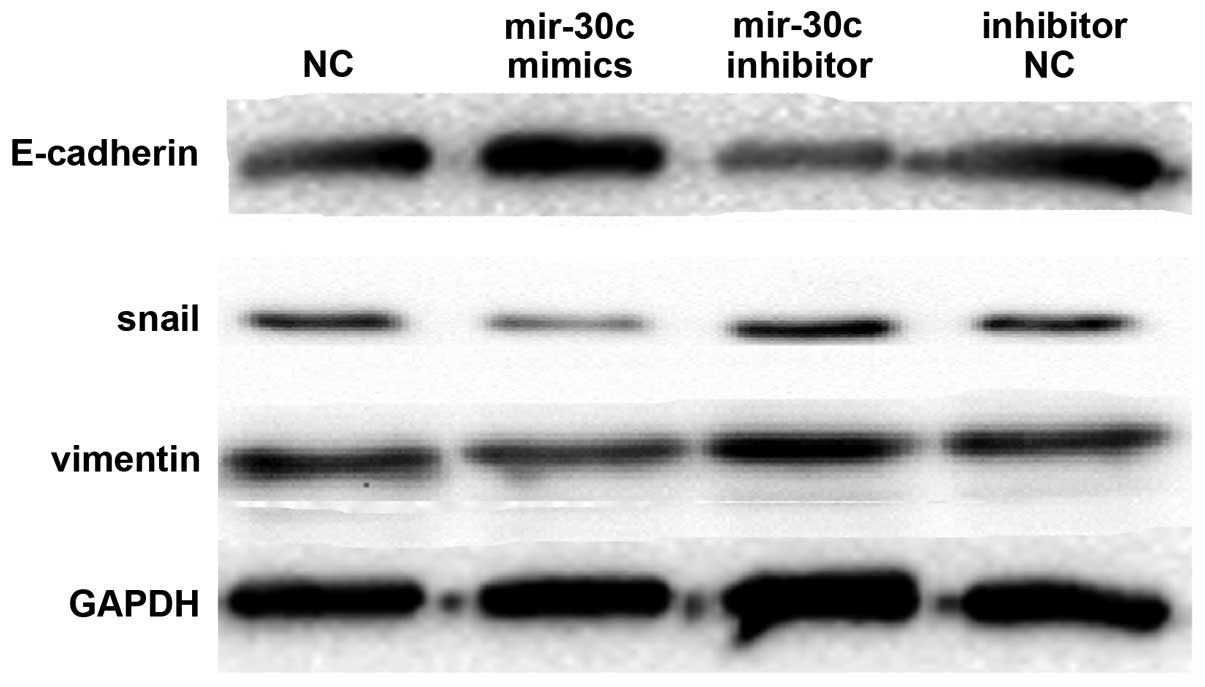
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J and Ward E: Cancer
statistics, 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 60:277–300. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yang L, Parkin DM, Ferlay J, Li L and Chen
Y: Estimates of cancer incidence in China for 2000 and projections
for 2005. Cancer Epidemiol Biomarkers Prev. 14:243–250.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Herbst RS, Heymach JV and Lippman SM: Lung
cancer. New Engl J Med. 359:1367–1380. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brundage MD, Davies D and Mackillop WJ:
Prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer: a decade of
progress. Chest. 122:1037–1057. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zhang J, Kong X, Li J, et al: MiR-96
promotes tumor proliferation and invasion by targeting RECK in
breast cancer. Oncol Rep. 31:1357–1363. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang J, Zhao H, Xin Y and Fan L:
MicroRNA-198 inhibits proliferation and induces apoptosis of lung
cancer cells via targeting FGFR1. J Cell Biochem. 115:987–995.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang F, Xia J, Wang N and Zong H: miR-145
inhibits proliferation and invasion of esophageal squamous cell
carcinoma in part by targeting c-Myc. Onkologie. 36:754–758.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Mita M: Regional differences of the clear
cells in the mouse epididymal duct: a histological study. Hokkaido
Igaku Zasshi. 61:909–920. 1986.(In Japanese).
|
|
9
|
Li H, Xu H, Shen H and Li H: microRNA-106a
modulates cisplatin sensitivity by targeting PDCD4 in human ovarian
cancer cells. Oncol Lett. 7:183–188. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ouzounova M, Vuong T, Ancey PB, et al:
MicroRNA miR-30 family regulates non-attachment growth of breast
cancer cells. BMC Genomics. 14:1392013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Haque R, Chun E, Howell JC, et al:
MicroRNA-30b-mediated regulation of catalase expression in human
ARPE-19 cells. PloS One. 7:e425422012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Quintavalle C, Donnarumma E, Iaboni M, et
al: Effect of miR-21 and miR-30b/c on TRAIL-induced apoptosis in
glioma cells. Oncogene. 32:4001–4008. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wu T, Zhou H, Hong Y, et al: miR-30 family
members negatively regulate osteoblast differentiation. J Biol
Chem. 287:7503–7511. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang Y, Wen M, Kwon Y, et al: CUL4A
induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition and promotes cancer
metastasis by regulating ZEB1 expression. Cancer Res. 74:520–531.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Liu J, Ruan B, You N, et al:
Downregulation of miR-200a induces EMT phenotypes and CSC-like
signatures through targeting the β-catenin pathway in hepatic oval
cells. PloS One. 8:e794092013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Dong H, Xie L, Tang C, et al: Snail1
correlates with patient outcomes in E-cadherin-preserved
gastroesophageal junction adenocarcinoma. Clin Transl Oncol. Dec
20–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
17
|
Liu Y, Li H, Feng J, et al: Lin28 induces
epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition and stemness via
downregulation of let-7a in breast cancer cells. PloS One.
8:e830832013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Bao YX, Cao Q, Yang Y, et al: Expression
and prognostic significance of golgiglycoprotein73 (GP73) with
epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) related molecules in
hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). Diagn Pathol. 8:1972013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Kitamura K, Seike M, Okano T, et al:
MiR-134/487b/655 cluster regulates TGF-β-induced
epithelial-mesenchymal transition and drug resistance to gefitinib
by targeting MAGI2 in lung adenocarcinoma cells. Mol Cancer Ther.
13:444–453. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Guo S, Xu X, Tang Y, et al: miR-15a
inhibits cell proliferation and epithelial to mesenchymal
transition in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma by down-regulating
Bmi-1 expression. Cancer Lett. 344:40–46. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamada S, Fuchs BC, Fujii T, et al:
Epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition predicts prognosis of
pancreatic cancer. Surgery. 154:946–954. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Paterson EL, Kazenwadel J, Bert AG, et al:
Down-regulation of the miRNA-200 family at the invasive front of
colorectal cancers with degraded basement membrane indicates EMT is
involved in cancer progression. Neoplasia. 15:180–191. 2013.
|
|
23
|
Bai JX, Yan B, Zhao ZN, et al: Tamoxifen
represses miR-200 microRNAs and promotes epithelial-to-mesenchymal
transition by up-regulating c-Myc in endometrial carcinoma cell
lines. Endocrinology. 154:635–645. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ouyang H, Gore J, Deitz S and Korc M:
MicroRNA-10b enhances pancreatic cancer cell invasion by
suppressing TIP30 expression and promoting EGF and TGF-β actions.
Oncogene. Oct 7–2013.(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
25
|
Brønnum H, Andersen DC, Schneider M, et
al: miR-21 promotes fibrogenic epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition
of epicardial mesothelial cells involving Programmed Cell Death 4
and Sprouty-1. PloS One. 8:e562802013.
|
|
26
|
Han M, Wang Y, Liu M, et al: MiR-21
regulates epithelial-mesenchymal transition phenotype and
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha expression in third-sphere forming
breast cancer stem cell-like cells. Cancer Sci. 103:1058–1064.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Vitalone MJ, Naesens M, Sigdel T, et al:
The dual role of epithelial-to-mesenchymal transition in chronic
allograft injury in pediatric renal transplantation.
Transplantation. 92:787–795. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
López-Novoa JM and Nieto MA: Inflammation
and EMT: an alliance towards organ fibrosis and cancer progression.
EMBO Mol Med. 1:303–314. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mucsi I and Rosivall L:
Epithelial-mesenchymal transition in renal tubular cells in the
pathogenesis of progressive tubulo-interstitial fibrosis. Acta
Physiol Hung. 94:117–131. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|