|
1
|
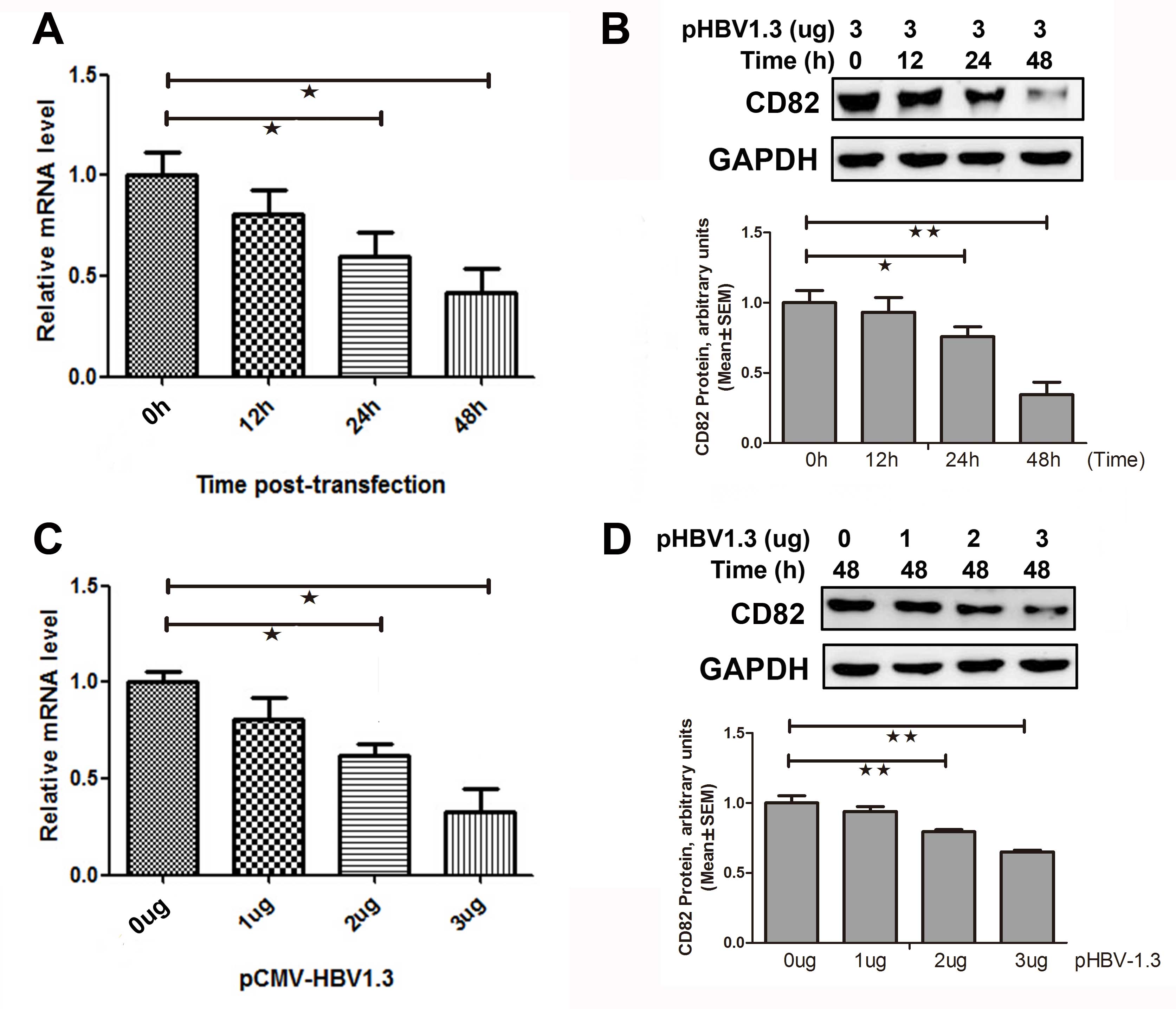
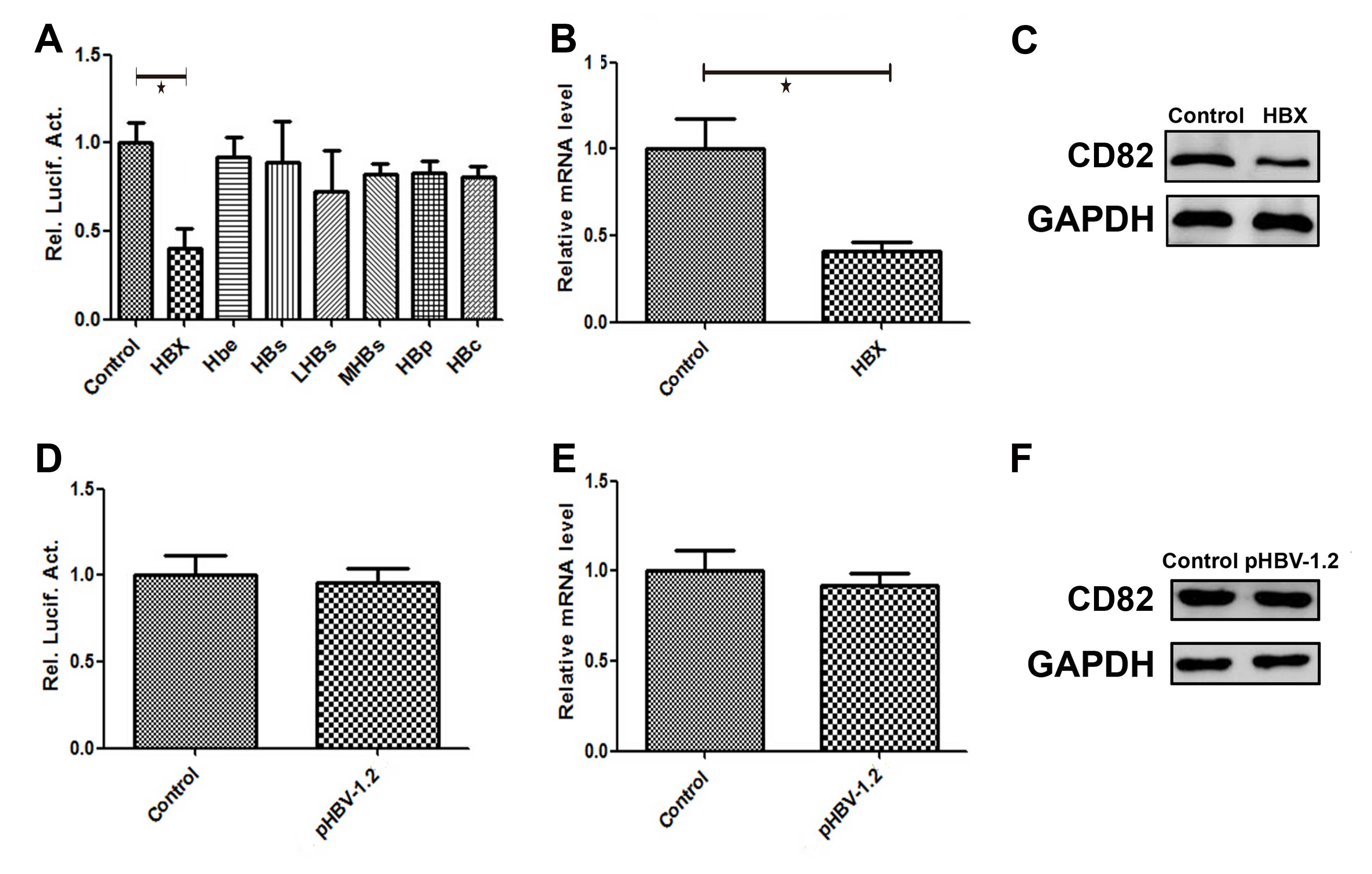
Benhenda S, Cougot D, Buendia MA and
Neuveut C: Hepatitis B virus X protein molecular functions and its
role in virus life cycle and pathogenesis. Adv Cancer Res.
103:75–109. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
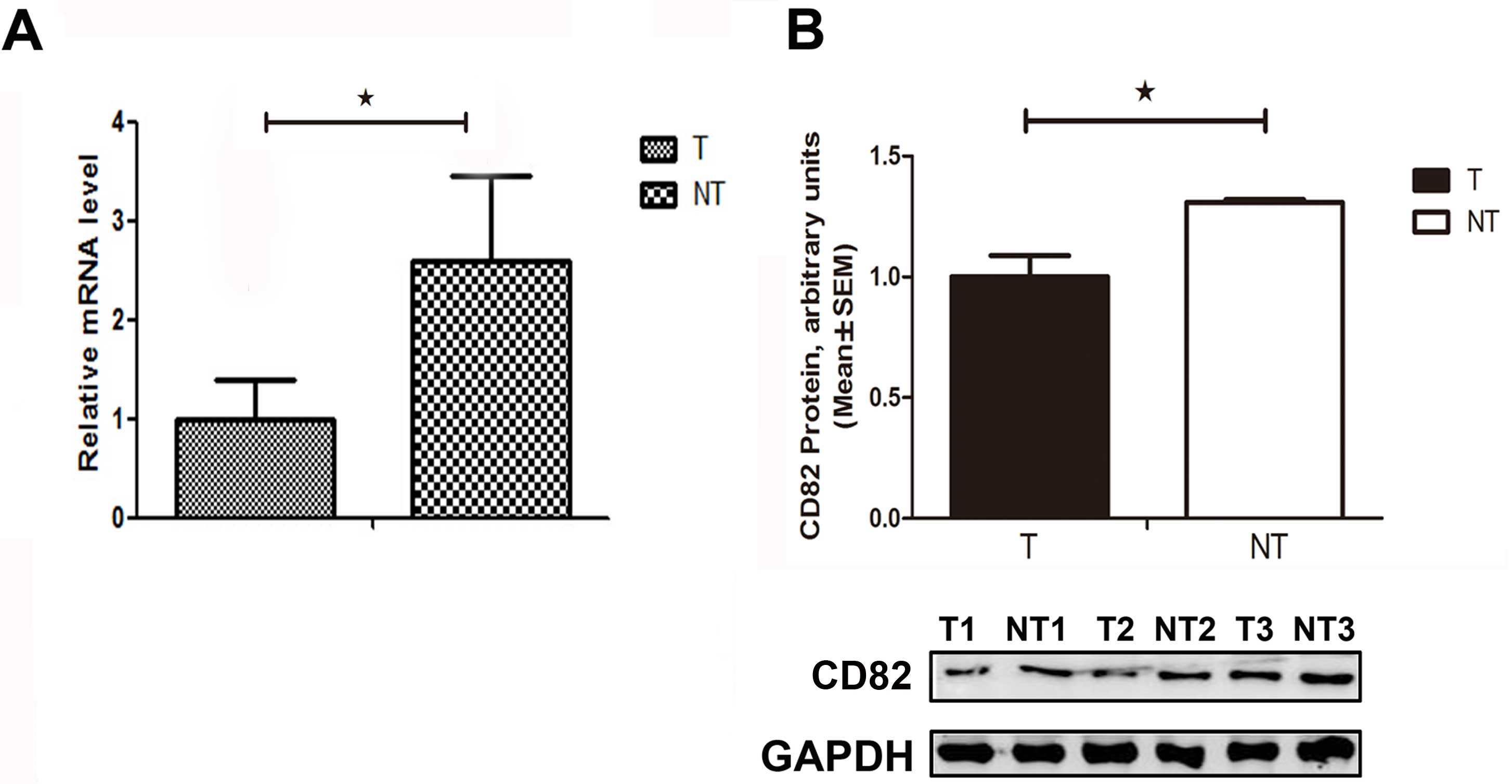
Feitelson MA and Lee J: Hepatitis B virus
integration, fragile sites, and hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett.
252:157–170. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
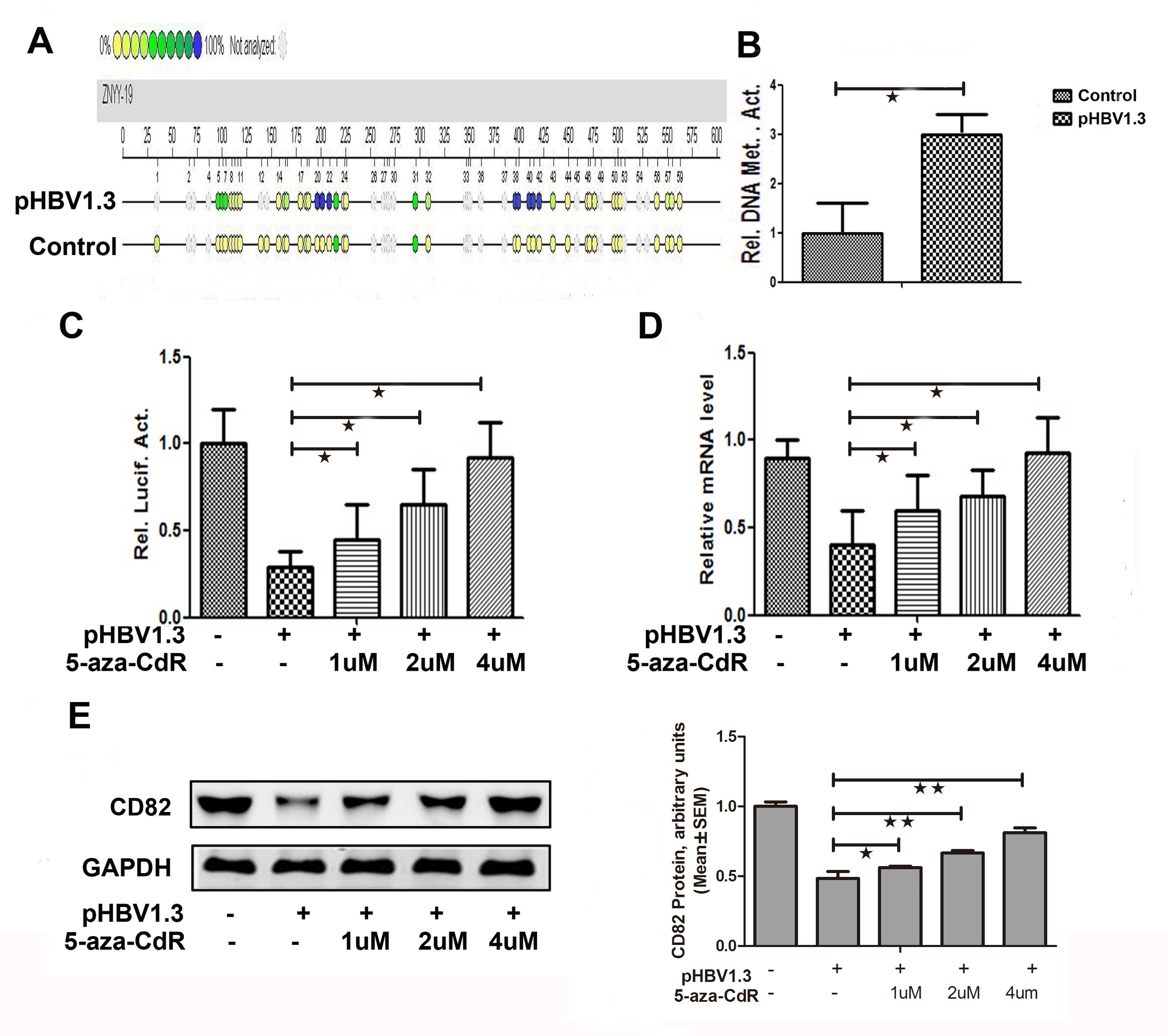
|
Chan DW and Ng IO: Knock-down of hepatitis
B virus X protein reduces the tumorigenicity of hepatocellular
carcinoma cells. J Pathol. 208:372–380. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Cheng AS, Wong N, Tse AM, Chan KY, Chan
KK, Sung JJ and Chan HL: RNA interference targeting HBx suppresses
tumor growth and enhances cisplatin chemosensitivity in human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 253:43–52. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang X, Zhang H and Ye L: Effects of
hepatitis B virus X protein on the development of liver cancer. J
Lab Clin Med. 147:58–66. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Moon EJ, Jeong CH, Jeong JW, Kim KR, Yu
DY, Murakami S, Kim CW and Kim KW: Hepatitis B virus X protein
induces angiogenesis by stabilizing hypoxia-inducible
factor-1alpha. FASEB J. 18:382–384. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Robinson WS: Molecular events in the
pathogenesis of hepadnavirus-associated hepatocellular carcinoma.
Annu Rev Med. 45:297–323. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nephew KP and Huang TH: Epigenetic gene
silencing in cancer initiation and progression. Cancer Lett.
190:125–133. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Li J, Lin S, Chen Q, Peng L, Zhai J, Liu Y
and Yuan Z: Inhibition of hepatitis B virus replication by MyD88
involves accelerated degradation of pregenomic RNA and nuclear
retention of pre-S/S RNAs. J Virol. 84:6387–6399. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li LC and Dahiya R: MethPrimer: designing
primers for methylation PCRs. Bioinformatics. 18:1427–1431. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dong JT, Lamb PW, Rinker-Schaeffer CW,
Vukanovic J, Ichikawa T, Isaacs JT and Barrett JC: CD82, a
metastasis suppressor gene for prostate cancer on human chromosome
11p11.2. Science. 268:884–886. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Miranti CK: Controlling cell surface
dynamics and signaling: how CD82/CD82 suppresses metastasis. Cell
Signal. 21:196–211. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ai X, Zhang X, Wu Z, Ma X, Ju Z, Wang B
and Shi T: Expression of CD82/CD82 and MRP-1/CD9 in transitional
cell carcinoma of bladder. J Huazhong Univ Sci Technolog Med Sci.
27:79–82. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Nelson WG, Yegnasubramanian S, Agoston AT,
Bastian PJ, Lee BH, Nakayama M and De Marzo AM: Abnormal DNA
methylation, epigenetics, and prostate cancer. Front Biosci.
12:4254–4266. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dalmay T and Edwards DR: MicroRNAs and the
hallmarks of cancer. Oncogene. 25:6170–6175. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Kent OA and Mendell JT: A small piece in
the cancer puzzle: microRNAs as tumor suppressors and oncogenes.
Oncogene. 25:6188–6196. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhu J: DNA methylation and hepatocellular
carcinoma. J Hepatobiliary Pancreat Surg. 13:265–73. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Yang B, Guo M, Herman JG and Clark DP:
Aberrant promoter methylation profiles of tumor suppressor genes in
hepatocellular carcinoma. Am J Pathol. 163:1101–1107. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lee S, Lee HJ, Kim JH, Lee HS, Jang JJ and
Kang GH: Aberrant CpG island hypermethylation along multistep
hepatocarcinogenesis. Am J Pathol. 163:1371–1378. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Pogribny IP and Rusyn I: Role of
epigenetic aberrations in the development and progression of human
hepatocellular carcinoma. Cancer Lett. 342:223–230. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Shiraha H, Yamamoto K and Namba M: Human
hepatocyte carcinogenesis (review). Int J Oncol. 42:1133–1138.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Li LH, He J, Hua D, Guo ZJ and Gao Q:
Lentivirus-mediated inhibition of Med19 suppresses growth of breast
cancer cells in vitro. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 68:207–215.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Perz JF, Armstrong GL, Farrington LA,
Hutin YJ and Bell BP: The contributions of hepatitis B virus and
hepatitis C virus infections to cirrhosis and primary liver cancer
worldwide. J Hepatol. 45:529–538. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|