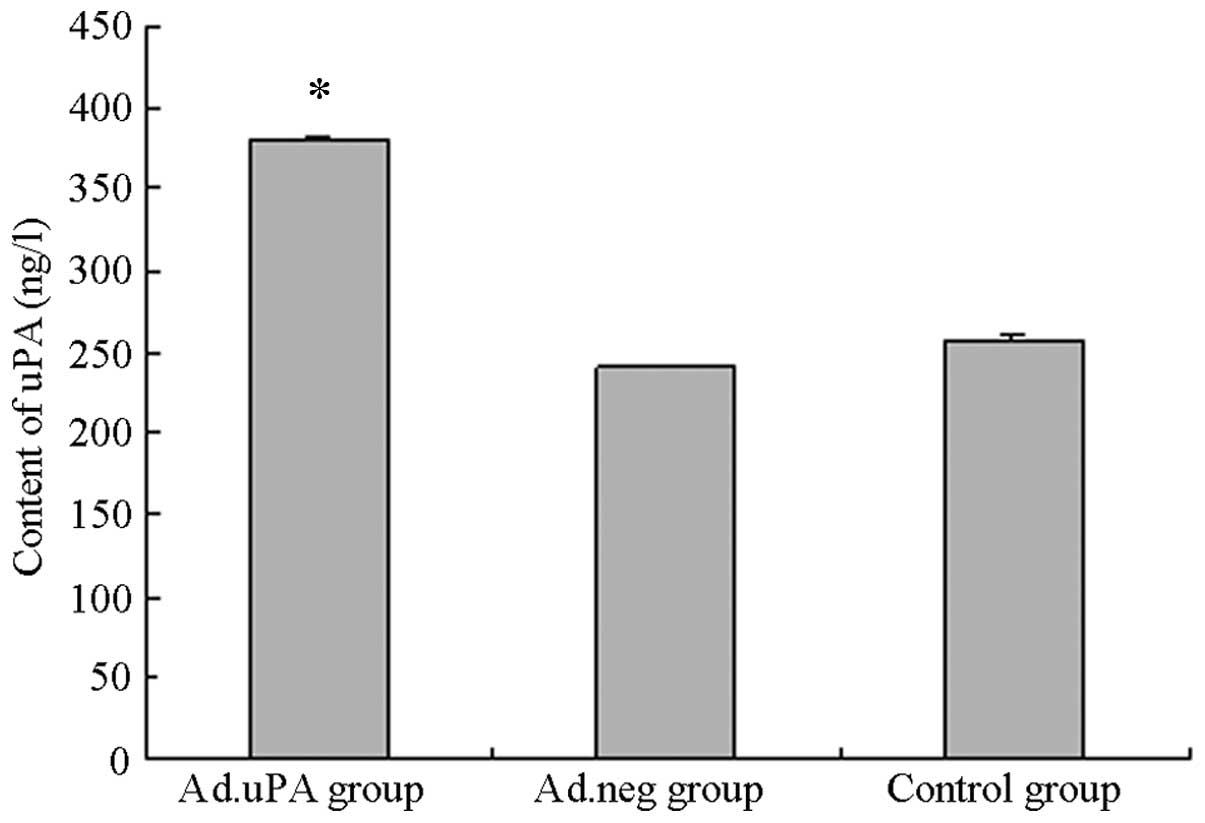
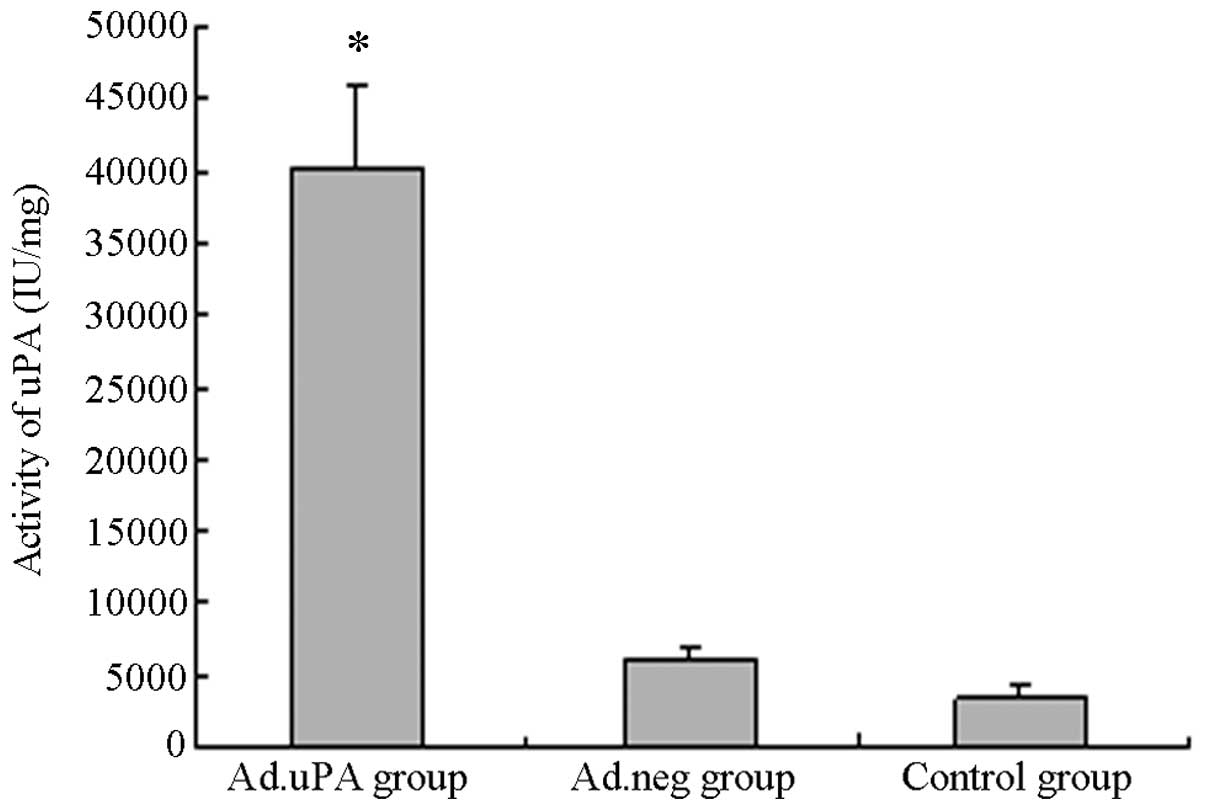
|
1
|
Goldhaber SZ: Pulmonary embolism. Lancet.
363:1295–1305. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Spencer FA, Emery C, Lessard D, et al: The
Worcester Venous Thromboembolism Study: A population based study of
the clinical epidemiology of venous thromboembolism. J Gen Intern
Med. 21:722–727. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Chapman NH, Brighton T, Harris MF, Caplan
GA, Braithwaite J and Chong BH: Venous thromboembolism - management
in general practice. Aust Fam Physician. 38:36–40. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Pengo V, Lensing AW, Prins MH, et al:
Thromboembolic Pulmonary Hypertension Study Group: Incidence of
chronic thromboembolic pulmonary hypertension after pulmonary
embolism. N Engl J Med. 350:2257–2264. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Vincenza Carriero M, Franco P, Vocca I, et
al: Structure, function and antagonists of urokinase-type
plasminogen activator. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 14:3782–3794.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Radha KS, Madhyastha HK, Nakajima Y, Omura
S and Maruyama M: Emodin upregulates urokinase plasminogen
activator, plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 and promotes wound
healing in human fibroblasts. Vascul Pharmacol. 48:184–190. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Nassar T, Yarovoi S, Fanne RA, et al:
Urokinase plasminogen activator regulates pulmonary arterial
contractility and vascular permeability in mice. Am J Respir Cell
Mol Biol. 45:1015–1021. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Baldwin JF, Sood V, Elfline MA, et al: The
role of urokinase plasminogen activator and plasmin activator
inhibitor-1 on vein wall remodeling in experimental deep vein
thrombosis. J Vasc Surg. 56:1089–1097. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Rao Gogineni V, Kumar Nalla A, Gupta R, et
al: Radiation-inducible silencing of uPA and uPAR in vitro and in
vivo in meningioma. Int J Oncol. 36:809–816. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ylä-Herttuala S: Cardiovascular gene
therapy with vascular endothelial growth factors. Gene.
525:217–219. 2013.
|
|
11
|
Zhao B, Li X, Dai X and Gong N:
Adenovirus-mediated anti-sense extracellular signal-regulated
kinase 2 gene therapy inhibits activation of vascular smooth muscle
cells and angiogenesis, and ameliorates transplant
arteriosclerosis. Transplant Proc. 45:639–642. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Dragneva G, Korpisalo P and Ylä-Herttuala
S: Promoting blood vessel growth in ischemic diseases: challenges
in translating preclinical potential into clinical success. Dis
Model Mech. 6:312–322. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Kral BG and Kraitchman DL: From mice to
men: gene therapy’s future for treatment of myocardial infarction.
Circ Cardiovasc Imaging. 6:360–362. 2013.
|
|
14
|
Botkjaer KA, Fogh S, Bekes EC, et al:
Targeting the autolysis loop of urokinase-type plasminogen
activator with conformation-specific monoclonal antibodies. Biochem
J. 438:39–51. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Sood V, Luke CE, Deatrick KB, et al:
Urokinase plasminogen activator independent early experimental
thrombus resolution: MMP2 as an alternative mechanism. Thromb
Haemost. 104:1174–1183. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Humphries J, Gossage JA, Modarai B, et al:
Monocyte urokinase-type plasminogen activator up-regulation reduces
thrombus size in a model of venous thrombosis. J Vasc Surg.
50:1127–1134. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Madhyastha R, Madhyastha H, Nakajima Y,
Omura S and Maruyama M: Curcumin facilitates fibrinolysis and
cellular migration during wound healing by modulating urokinase
plasminogen activator expression. Pathophysiol Haemost Thromb.
37:59–66. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Shenkman B, Livnat T, Budnik I, Tamarin I,
Einav Y and Martinowitz U: Plasma tissue-type plasminogen activator
increases fibrinolytic activity of exogenous urokinase-type
plasminogen activator. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 23:729–733. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Lipskaia L, Hadri L, Lopez JJ, Hajjar RJ
and Bobe R: Benefit of SERCA2a gene transfer to vascular
endothelial and smooth muscle cells: a new aspect in therapy of
cardiovascular diseases. Curr Vasc Pharmacol. 11:465–479. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Hennessy EJ and Moore KJ: Using microRNA
as an alternative treatment for hyperlipidemia and cardiovascular
disease: cardio-miRs in the pipeline. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
62:247–254. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Won YW, McGinn AN, Lee M, Nam K, Bull DA
and Kim SW: Post-translational regulation of a hypoxia-responsive
VEGF plasmid for the treatment of myocardial ischemia.
Biomaterials. 34:6229–6238. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yamaguchi Y, Yamada K, Suzuki T, et al:
Induction of uPA release in human peripheral blood lymphocytes by
[deamino-Cysl, D-Arg8]-vasopressin (dDAVP). Am J Physiol Endocrinol
Metab. 287:E970–E976. 2004.
|
|
23
|
De Meyer SF, Deckmyn H and Vanhoorelbeke
K: von Willebrand factor to the rescue. Blood. 113:5049–5057.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chey S, Claus C and Liebert UG: Validation
and application of normalization factors for gene expression
studies in rubella virus-infected cell lines with quantitative
real-time PCR. J Cell Biochem. 110:118–128. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gu Z, Pan J, Bankowski MJ and Hayden RT:
Quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction detection of BK
virus using labeled primers. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 134:444–448.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Livak KJ and Schmittgen TD: Analysis of
relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and
the 2(−Delta Delta C(T)) Method. Methods. 25:402–408. 2001.
|
|
27
|
Oliveira MS, Skinner F, Arshadmansab MF,
et al: Altered expression and function of small-conductance (SK)
Ca(2+)-activated K+ channels in pilocarpine-treated
epileptic rats. Brain Res. 1348:187–199. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Liang F, Arora N, Zhang KL, et al: A new,
multiplex, quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction system
for nucleic Acid detection and quantification. Methods Mol Biol.
1039:51–68. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Wagner EM: Monitoring gene expression:
quantitative real-time rt-PCR. Methods Mol Biol. 1027:19–45. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Gentilini F and Turba ME: Two novel
real-time PCR methods for genotyping the von Willebrand disease
type I mutation in Doberman Pinscher dogs. Vet J. 197:457–460.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|