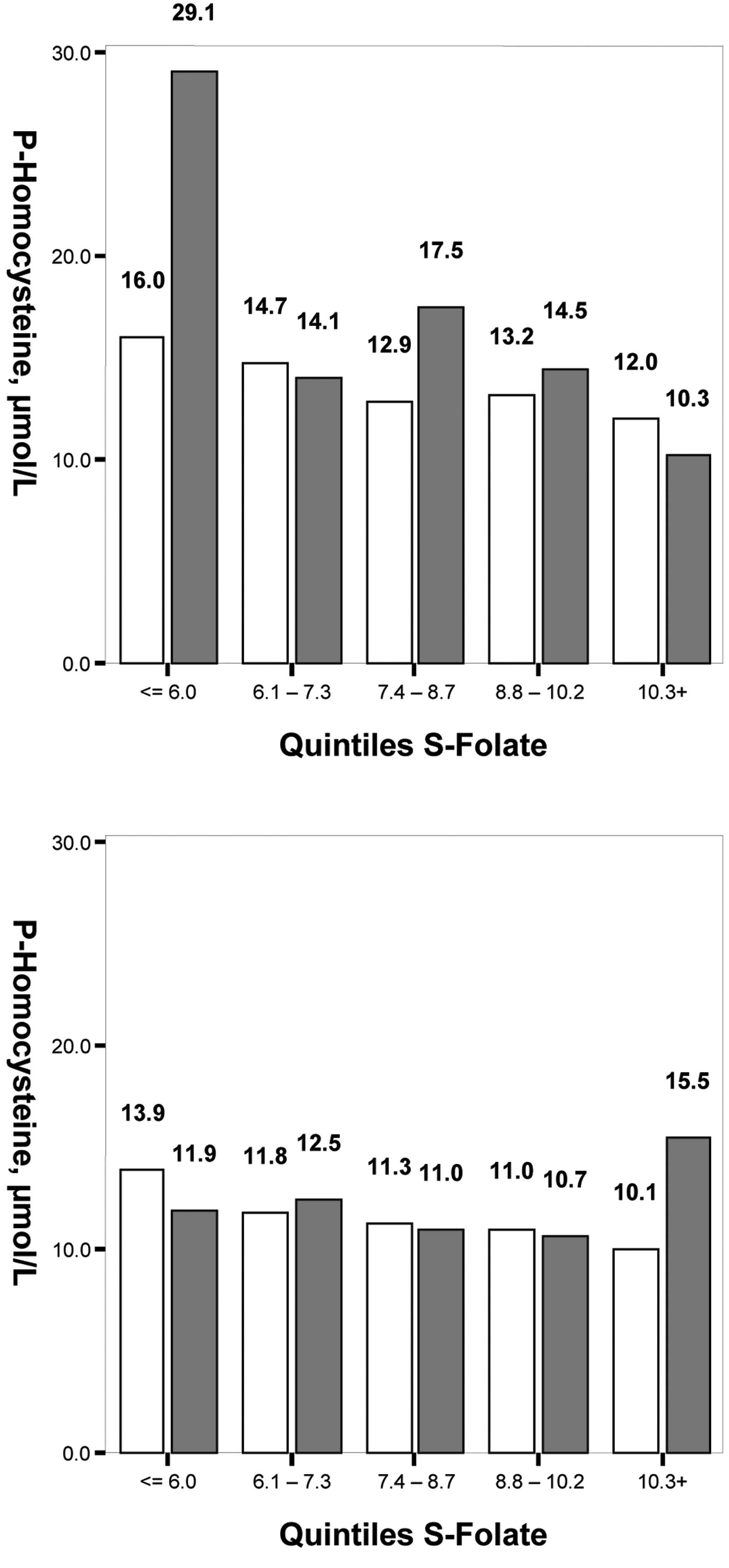
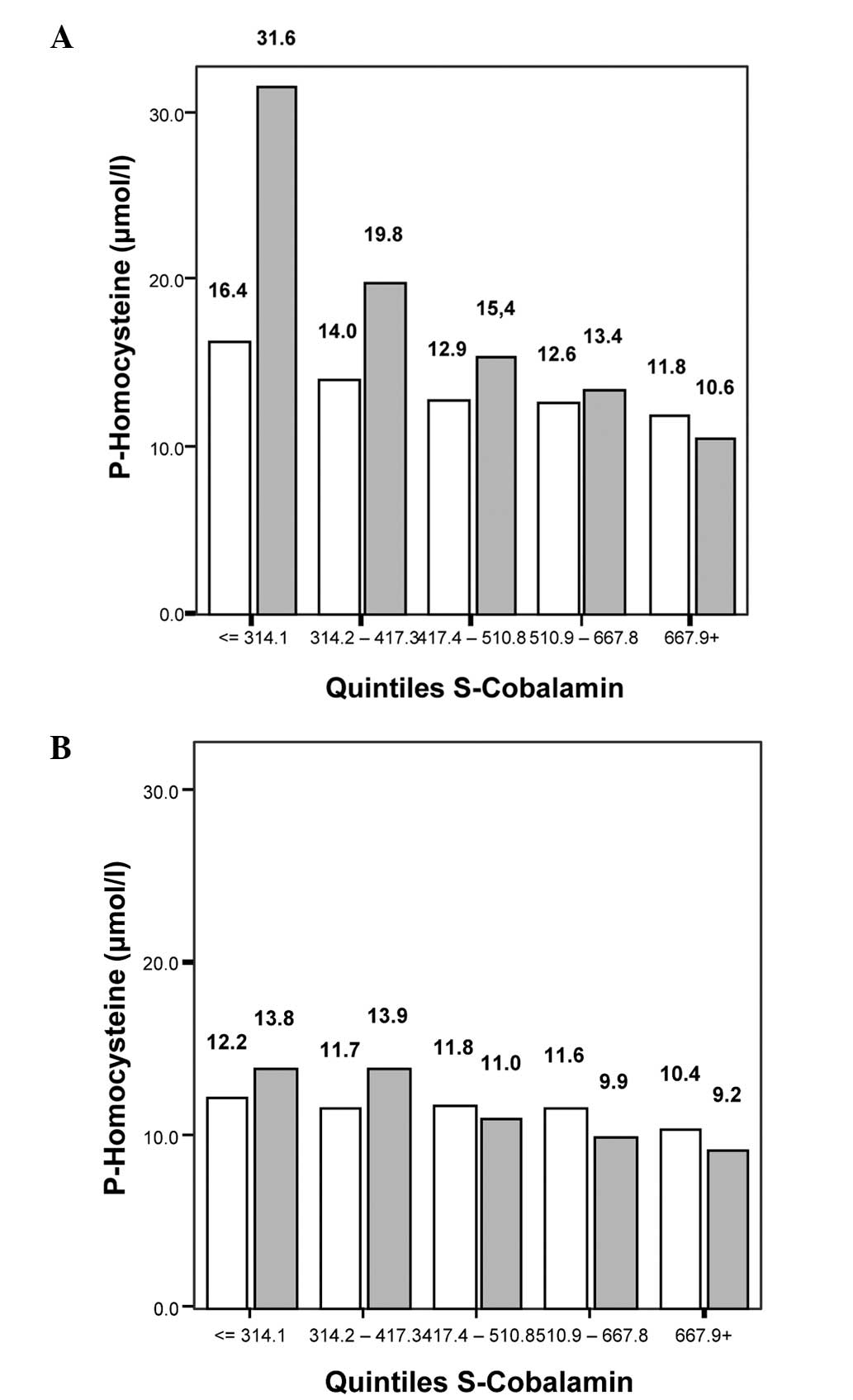
|
1
|
Yamada K, Chen Z, Rozen R and Matthews RG:
Effects of common polymorphisms on the properties of recombinant
human methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
98:14853–14858. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Bolander-Gouaille C and Bottiglieri T:
Homocysteine Related Vitamins and Neuropsychiatric Disorders.
Springer; Paris: 2003
|
|
3
|
Garcia A and Zanibbi K: Homocysteine and
cognitive function in elderly people. CMAJ. 171:897–904. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blom HJ: Determinants of plasma
homocysteine. Am J Clin Nutr. 67:188–189. 1998.
|
|
5
|
Frosst P, Blom HJ, Milos R, Goyette P,
Sheppard CA, Matthews RG, Boers GJ, den Heijer M, Kluijtmans LA,
van den Heuvel LP, et al: A candidate genetic risk factor for
vascular disease: a common mutation in methylenetetrahydrofolate
reductase. Nat Genet. 10:111–113. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lievers KJ, Boers GH, Verhoef P, den
Heijer M, Kluijtmans LA, van der Put NM, Trijbels FJ and Blom HJ: A
second common variant in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
(MTHFR) gene and its relationship to MTHFR enzyme activity,
homocysteine, and cardiovascular disease risk. J Mol Med (Berl).
79:522–528. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Mudd SH, Uhlendorf BW, Freeman JM,
Finkelstein JD and Shih VE: Homocystinuria associated with
decreased methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase activity. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 46:905–912. 1972. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Selhub J: Homocysteine metabolism. Annu
Rev Nutr. 19:217–246. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
van der Put NM, Gabreëls F, Stevens EM,
Smeitink JA, Trijbels FJ, Eskes TK, van den Heuvel LP and Blom HJ:
A second common mutation in the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
gene: an additional risk factor for neural-tube defects? Am J Hum
Genet. 62:1044–1051. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Weisberg I, Tran P, Christensen B, Sibani
S and Rozen R: A second genetic polymorphism in
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) associated with
decreased enzyme activity. Mol Genet Metab. 64:169–172. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Viel A, Dall’Agnese L, Simone F,
Canzonieri V, Capozzi E, Visentin MC, Valle R and Boiocchi M: Loss
of heterozygosity at the 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
locus in human ovarian carcinomas. Br J Cancer. 75:1105–1110. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
de Bree A, Verschuren WM, Bjørke-Monsen
AL, van der Put NM, Heil SG, Trijbels FJ and Blom HJ: Effect of the
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase 677C-->T mutation on the
relations among folate intake and plasma folate and homocysteine
concentrations in a general population sample. Am J Clin Nutr.
77:687–693. 2003.
|
|
13
|
Cortese C and Motti C: MTHFR gene
polymorphism, homocysteine and cardiovascular disease. Public
Health Nutr. 4:493–497. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Huemer M, Vonblon K, Födinger M, Krumpholz
R, Hubmann M, Ulmer H and Simma B: Total homocysteine, folate, and
cobalamin, and their relation to genetic polymorphisms, lifestyle
and body mass index in healthy children and adolescents. Pediatr
Res. 60:764–769. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Rady PL, Szucs S, Grady J, Hudnall SD,
Kellner LH, Nitowsky H, Tyring SK and Matalon RK: Genetic
polymorphisms of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase (MTHFR) and
methionine synthase reductase (MTRR) in ethnic populations in
Texas; a report of a novel MTHFR polymorphic site, G1793A. Am J Med
Genet. 107:162–168. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wakutani Y, Kowa H, Kusumi M, Nakaso K,
Yasui K, Isoe-Wada K, Yano H, Urakami K, Takeshima T and Nakashima
K: A haplotype of the methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene is
protective against late-onset Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol Aging.
25:291–294. 2004.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Guenther BD, Sheppard CA, Tran P, Rozen R,
Matthews RG and Ludwig ML: The structure and properties of
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase from Escherichia coli
suggest how folate ameliorates human hyperhomocysteinemia. Nat
Struct Biol. 6:359–365. 1999. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Isotalo PA, Wells GA and Donnelly JG:
Neonatal and fetal methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genetic
polymorphisms: an examination of C677T and A1298C mutations. Am J
Hum Genet. 67:986–990. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Weisberg IS, Jacques PF, Selhub J, Bostom
AG, Chen Z, Curtis Ellison R, Eckfeldt JH and Rozen R: The
1298A-->C polymorphism in methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
(MTHFR): in vitro expression and association with homocysteine.
Atherosclerosis. 156:409–415. 2001.
|
|
20
|
Böttiger AK, Hurtig-Wennlöf A, Sjöström M,
Yngve A and Nilsson TK: Association of total plasma homocysteine
with methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase genotypes 677C>T,
1298A>C, and 1793G>A and the corresponding haplotypes in
Swedish children and adolescents. Int J Mol Med. 19:659–665.
2007.
|
|
21
|
Henríquez P, Doreste J, Deulofeu R, Fiuza
MD and Serra-Majem L: Nutritional determinants of plasma total
homocysteine distribution in the Canary Islands. Eur J Clin Nutr.
61:111–118. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Serra Majem L, Ribas Barba L, Armas
Navarro A, Alvarez León E and Sierra A: Equipo de investigación de
ENCA: Energy and nutrient intake and risk of inadequate intakes in
Canary Islands (1997–98). Arch Latinoam Nutr. 50(Suppl 1): 7–22.
2000.(In Spanish).
|
|
23
|
Börjel AK, Yngve A, Sjöström M and Nilsson
TK: Novel mutations in the 5′-UTR of the FOLR1 gene. Clin Chem Lab
Med. 44:161–167. 2006.
|
|
24
|
Zittan E, Preis M, Asmir I, Cassel A,
Lindenfeld N, Alroy S, Halon DA, Lewis BS, Shiran A, Schliamser JE
and Flugelman MY: High frequency of vitamin B12 deficiency in
asymptomatic individuals homozygous to MTHFR C677T mutation is
associated with endothelial dysfunction and homocysteinemia. Am J
Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 293:H860–H865. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Martínez-Frías ML, Bermejo E,
Rodríguez-Pinilla E, Scala I, Andria G and Botto L: Frequency of
the mutation 677C-T of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene on
a sample of 652 Spanish liveborn infants. Med Clin (Barc).
122:361–364. 2004.(In Spanish).
|
|
26
|
Martín I, Obrador A, Gibert MJ, Hernanz A,
Fuster A, Pintos C, Garcia A and Tur J: Folate status and a new
repletion cut-off value in a group of healthy Majorcan females.
Clin Nutr. 22:53–58. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Brattström L, Zhang Y, Hurtig M, Refsum H,
Ostensson S, Fransson L, Jonés K, Landgren F, Brudin L and Ueland
PM: A common methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase gene mutation and
longevity. Atherosclerosis. 141:315–319. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Brown KS, Kluijtmans LA, Young IS, Murray
L, McMaster D, Woodside JV, Yarnell JW, Boreham CA, McNulty H,
Strain JJ, et al: The 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
C677T polymorphism interacts with smoking to increase homocysteine.
Atherosclerosis. 174:315–322. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Chango A, Potier De Courcy G, Boisson F,
Guilland JC, Barbé F, Perrin MO, Christidès JP, Rabhi K, Pfister M,
Galan P, et al: 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase common
mutations, folate status and plasma homocysteine in healthy French
adults of the Supplemalestation en Vitamines et Mineraux
Antioxydants (SU.VIMAX) cohort. Br J Nutr. 84:891–896. 2000.
|
|
30
|
Kluijtmans LA, Young IS, Boreham CA,
Murray L, McMaster D, McNulty H, Strain JJ, McPartlin J, Scott JM
and Whitehead AS: Genetic and nutritional factors contributing to
hyperhomocysteinemia in young adults. Blood. 101:2483–2488. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Dimitrova KR, DeGroot K, Myers AK and Kim
YD: Estrogen and homocysteine. Cardiovasc Res. 53:577–588. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Fischer LM, da Costa KA, Galanko J, Sha W,
Stephenson B, Vick J and Zeisel SH: Choline intake and genetic
polymorphisms influence choline metabolite concentrations in human
breast milk and plasma. Am J Clin Nutr. 92:336–346. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Stead LM, Brosnan JT, Brosnan ME, Vance DE
and Jacobs RL: Is it time to reevaluate methyl balance in humans?
Am J Clin Nutr. 83:5–10. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yang QH, Botto LD, Gallagher M, Friedman
JM, Sanders CL, Koontz D, Nikolova S, Erickson JD and Steinberg K:
Prevalence and effects of gene-gene and gene-nutrient interactions
on serum folate and serum total homocysteine concentrations in the
United States: findings from the third National Health and
Nutrition Examination Survey DNA Bank. Am J Clin Nutr. 88:232–246.
2008.
|
|
35
|
Guéant-Rodriguez RM, Guéant JL, Debard R,
Thirion S, Hong LX, Bronowicki JP, Namour F, Chabi NW, Sanni A,
Anello G, et al: Prevalence of methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase
677T and 1298C alleles and folate status: a comparative study in
Mexican, West African, and European populations. Am J Clin Nutr.
83:701–707. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
D’Angelo A, Coppola A, Madonna P, Fermo I,
Pagano A, Mazzola G, Galli L and Cerbone AM: The role of vitamin
B12 in fasting hyperhomocysteinemia and its interaction with the
homozygous C677T mutation of the methylenetetrahydrofolate
reductase (MTHFR) gene. A case-control study of patients with
early-onset thrombotic events. Thromb Haemost. 83:563–570.
2000.
|
|
37
|
Hustad S, Midttun Ø, Schneede J, Vollset
SE, Grotmol T and Ueland PM: The methylenetetrahydrofolate
reductase 677C-->T polymorphism as a modulator of a B vitamin
network with major effects on homocysteine metabolism. Am J Hum
Genet. 80:846–855. 2007.
|
|
38
|
Sensoy N, Şoysal Y, Kahraman A, Doǧan N
and Imirzalioǧlu N: Modulator effects of the
methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase C677T polymorphism on response
to vitamin B12 therapy and homocysteine metabolism. DNA Cell Biol.
31:820–825. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Arjona Mateos CR, Criado Velasco J and
Sánches Solís L: Enfermedades crónicas y consumo de fármacos en
mayores de 65 años. Medicina General. 47:684–695. 2002.(In
Spanish).
|
|
40
|
Gonzalez-Gross M, Sola R, Albers U,
Barrios L, Alder M, Castillo MJ and Pietrzik K: B-vitamins and
homocysteine in Spanish institutionalized elderly. Int J Vitam Nutr
Res. 77:22–33. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|