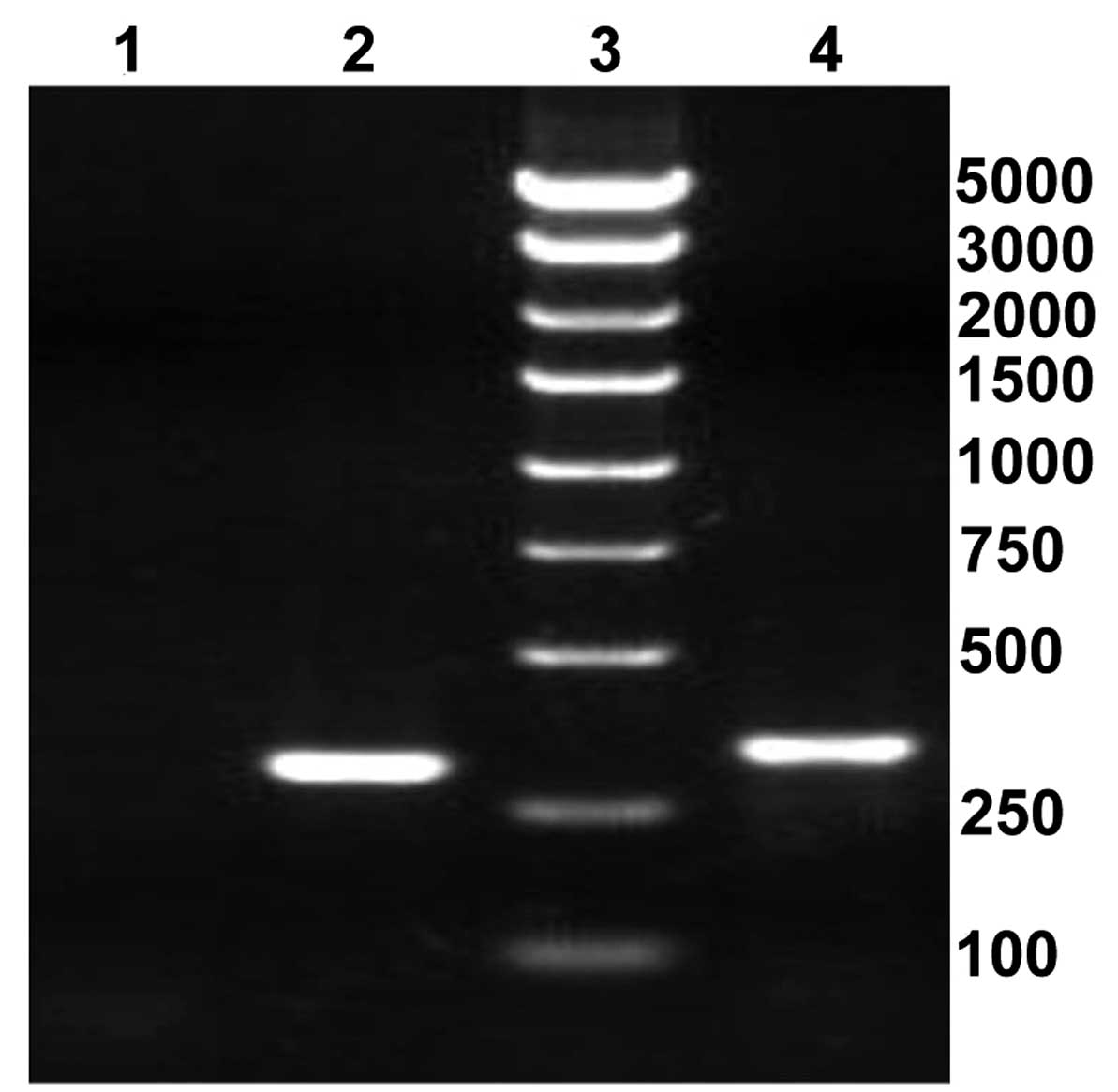
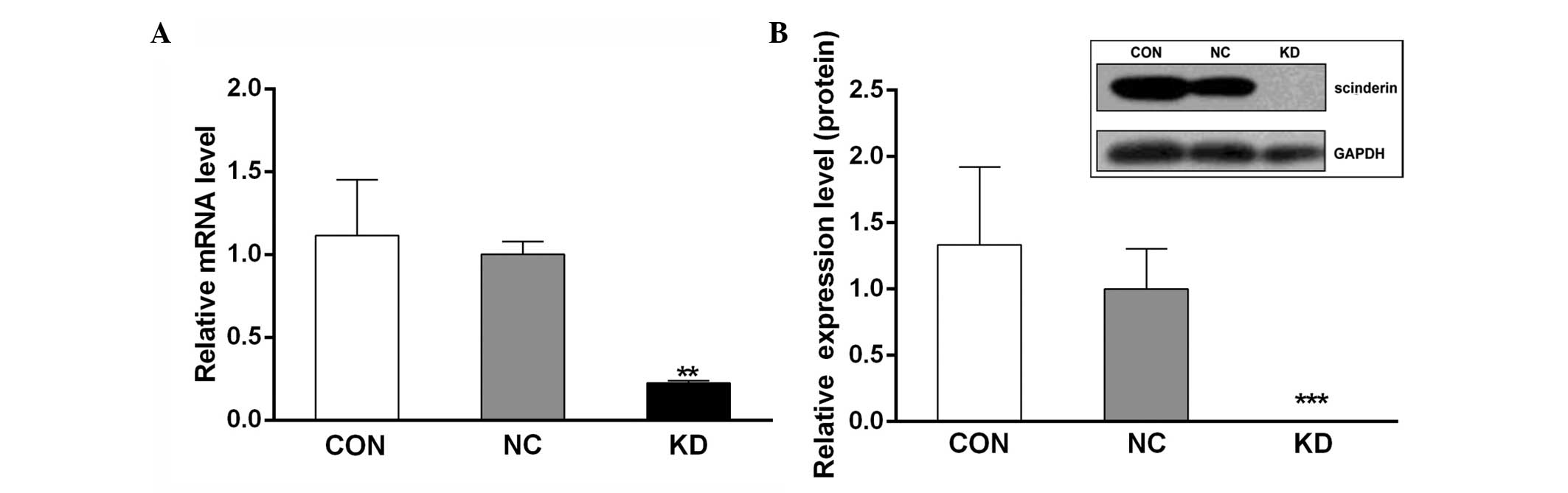
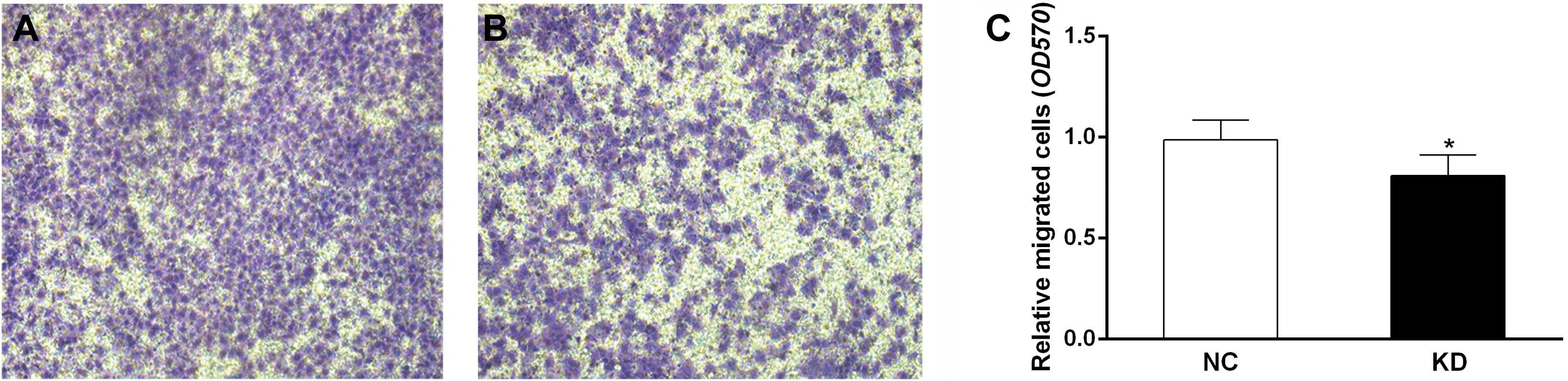
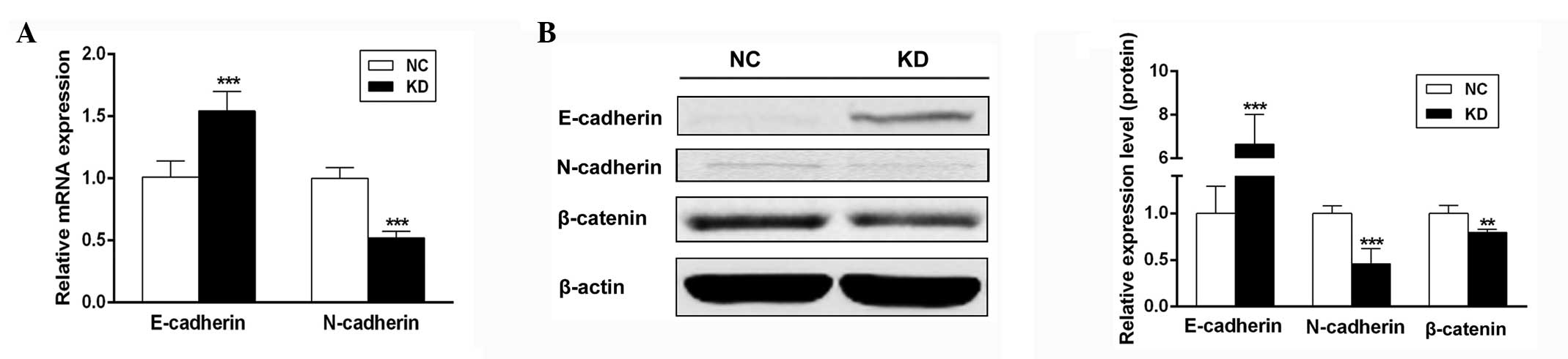
|
1
|
Marcu MG, Zhang L, Elzagallaai A and
Trifaró JM: Localization by segmental deletion analysis and
functional characterization of a third actin-binding site in domain
5 of scinderin. J Biol Chem. 273:3661–3668. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lejen T, Pene TD, Rosé SD and Trifaró JM:
The role of different Scinderin domains in the control of F-actin
cytoskeleton during exocytosis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 971:248–250. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Dumitrescu Pene T, Rosé SD, Lejen T, Marcu
MG and Trifaró JM: Expression of various scinderin domains in
chromaffin cells indicates that this protein acts as a molecular
switch in the control of actin filament dynamics and exocytosis. J
Neurochem. 92:780–789. 2005.
|
|
4
|
Chumnarnsilpa S, Lee ML, Nag S, et al: The
crystal structure of the C-terminus of adseverin reveals the
actin-binding interface. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:13719–13724.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lueck A, Brown D and Kwiatkowski DJ: The
actin-binding proteins adseverin and gelsolin are both highly
expressed but differentially localized in kidney and intestine. J
Cell Sci. 111:3633–3643. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Trifaró JM, Vitale ML and Rodríguez Del
Castillo A: Scinderin and chromaffin cell actin network dynamics
during neurotransmitter release. J Physiol Paris. 87:89–106.
1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Trifaró JM, Rosé SD and Marcu MG:
Scinderin, a Ca2+-dependent actin filament severing
protein that controls cortical actin network dynamics during
secretion. Neurochem Res. 25:133–144. 2000.
|
|
8
|
Trifaró JM, Gasman S and Gutiérrez LM:
Cytoskeletal control of vesicle transport and exocytosis in
chromaffin cells. Acta Physiol (Oxf). 192:165–172. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Ehre C, Rossi AH, Abdullah LH, et al:
Barrier role of actin filaments in regulated mucin secretion from
airway goblet cells. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol. 288:C46–C56.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zunino R, Li Q, Rosé SD, et al: Expression
of scinderin in megakaryoblastic leukemia cells induces
differentiation, maturation, and apoptosis with release of
plateletlike particles and inhibits proliferation and
tumorigenesis. Blood. 98:2210–2219. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Bush WS, McCauley JL, DeJager PL, et al: A
knowledge-driven interaction analysis reveals potential
neurodegenerative mechanism of multiple sclerosis susceptibility.
Genes Immun. 12:335–340. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Abouzahr S, Bismuth G, Gaudin C, et al:
Identification of target actin content and polymerization status as
a mechanism of tumor resistance after cytolytic T lymphocyte
pressure. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:1428–1433. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Miura N, Takemori N, Kikugawa T, et al:
Adseverin: a novel cisplatin-resistant marker in the human bladder
cancer cell line HT1376 identified by quantitative proteomic
analysis. Mol Oncol. 6:311–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zavadil J, Haley J, Kalluri R, Muthuswamy
SK and Thompson E: Epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Cancer Res.
68:9574–9577. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Kalluri R and Weinberg RA: The basics of
epithelial-mesenchymal transition. J Clin Invest. 119:1420–1428.
2009. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Scanlon CS, Van Tubergen EA, Inglehart RC
and D’Silva NJ: Biomarkers of epithelial-mesenchymal transition in
squamous cell carcinoma. J Dent Res. 92:114–121. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Turley EA, Veiseh M, Radisky DC and
Bissell MJ: Mechanisms of disease: epithelial-mesenchymal
transition-does cellular plasticity fuel neoplastic progression.
Nat Clin Pract Oncol. 5:280–290. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
De Craene B and Berx G: Regulatory
networks defining EMT during cancer initiation and progression. Nat
Rev Cancer. 13:97–110. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Zheng H and Kang Y: Multilayer control of
the EMT master regulators. Oncogene. 33:1755–1763. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Iorio MV and Croce CM: MicroRNA
dysregulation in cancer: diagnostics, monitoring and therapeutics.
A comprehensive review. EMBO Mol Med. 4:143–159. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Beltran M, Puig l, Peña C, et al: A
natural antisense transcript regulates Zeb2/Sip1 gene expression
during Snail1-induced epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Genes Dev.
22:756–769. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Luo M, Li Z, Wang W, et al: Long
non-coding RNA H19 increases bladder cancer metastasis by
associating with EZH2 and inhibiting E-cadherin expression. Cancer
Lett. 333:213–221. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Haifu Wu: Correlated function study of
scinderin gene in liver metastasis of colorectal cancer
(unpublished PhD thesis). Fudan University; 2010
|
|
24
|
Khurana S and George SP: Regulation of
cell structure and function by actin-binding proteins: villin’s
perspective. FEBS Lett. 582:2128–2139. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Tomar A, Wang Y, Kumar N, et al:
Regulation of cell motility by tyrosine phosphorylated villin. Mol
Biol Cell. 15:4807–4817. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Li GH, Arora PD, Chen Y, McCulloch CA and
Liu P: Multifunctional roles of gelsolin in health and diseases.
Med Res Rev. 32:999–1025. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Valenta T, Hausmann G and Basler K: The
many faces and functions of β-catenin. EMBO J. 31:2714–2736.
2012.
|
|
28
|
Tanaka H, Shirkoohi R, Nakagawa K, et al:
siRNA gelsolin knockdown induces epithelial-mesenchymal transition
with a cadherin switch in human mammary epithelial cells. Int J
Cancer. 118:1680–1691. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Conacci-Sorrell M, Simcha I, Ben-Yedidia
T, et al: Autoregulation of E-cadherin expression by
cadherin-cadherin interactions: the roles of beta-catenin
signaling, Slug, and MAPK. J Cell Biol. 163:847–857. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Onder TT, Gupta PB, Mani SA, et al: Loss
of E-cadherin promotes metastasis via multiple downstream
transcriptional pathways. Cancer Res. 68:3645–3654. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Gradl D, Kühl M and Wedlich D: The Wnt/Wg
signal transducer beta-catenin controls fibronectin expression. Mol
Cell Biol. 19:5576–5587. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Anastas JN and Moon RT: WNT signalling
pathways as therapeutic targets in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer.
13:11–26. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Wang D, Sun SQ, Yu YH, et al: Suppression
of SCIN inhibits human prostate cancer cell proliferation and
induces G0/G1 phase arrest. Int J Oncol. 44:161–166.
2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Valastyan S and Weinberg RA: Tumor
metastasis: molecular insights and evolving paradigms. Cell.
147:275–292. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|