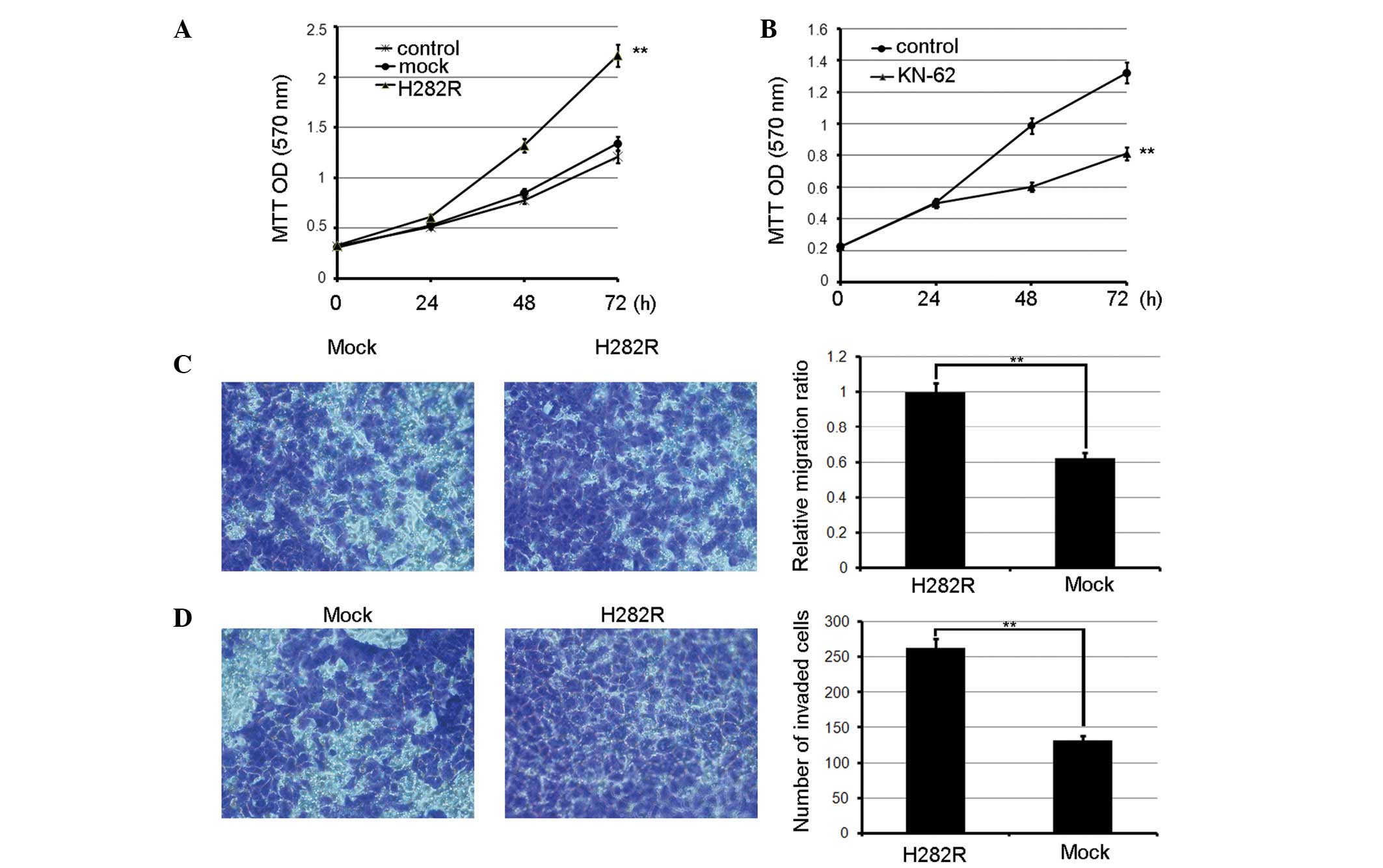
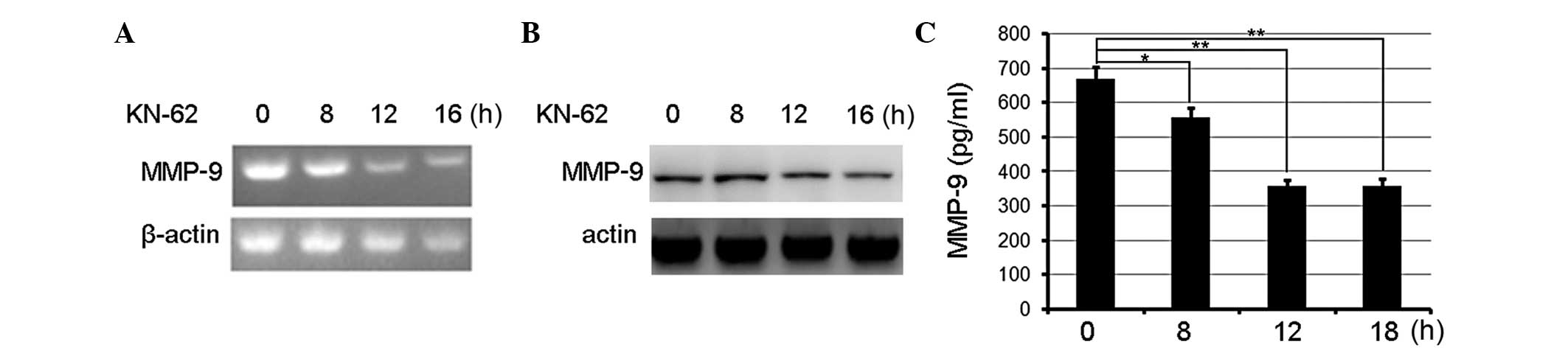
|
1
|
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, Hao Y, Xu J,
Murray T and Thun MJ: Cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
58:71–96. 2008.
|
|
2
|
Ahmad SA, Berman RS and Ellis LM: Biology
of colorectal liver metastases. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 12:135–150.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Cairns RA, Khokha R and Hill RP: Molecular
mechanisms of tumor invasion and metastasis: an integrated view.
Curr Mol Med. 3:659–671. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hudmon A and Schulman H: Neuronal
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II: the role of
structure and autoregulation in cellular function. Annu Rev
Biochem. 71:473–510. 2002.
|
|
5
|
Erickson JR, He BJ, Grumbach IM and
Anderson ME: CaMKII in the cardiovascular system: sensing redox
states. Physiol Rev. 91:889–915. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Braun AP and Schulman H: The
multifunctional calcium/ calmodulin-dependent protein kinase: from
form to function. Annu Rev Physiol. 57:417–445. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Coultrap SJ, Buard I, Kulbe JR, Dell’Acqua
ML and Bayer KU: CaMKII autonomy is substrate-dependent and further
stimulated by Ca2+/calmodulin. J Biol Chem.
285:17930–17937. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ducibella T, Schultz RM and Ozil JP: Role
of calcium signals in early development. Semin Stem Cell Dev Biol.
17:324–332. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zayzafoon M: Calcium/calmodulin signaling
controls osteoblast growth and differentiation. J Cell Biochem.
97:56–70. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang C, Li N, Liu X, Zheng Y and Cao X: A
novel endogenous human CaMKII inhibitory protein suppresses tumor
growth by inducing cell cycle arrest via p27 stabilization. J Biol
Chem. 283:11565–11574. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ma S, Yang Y, Wang C, et al: Endogenous
human CaMKII inhibitory protein suppresses tumor growth by inducing
cell cycle arrest and apoptosis through down-regulation of the
phosphatidylinositide 3-kinase/Akt/HDM2 pathway. J Biol Chem.
284:24773–24782. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gardoni F, Mauceri D, Marcello E, Sala C,
Di Luca M and Jeromin A: SAP97 directs the localization of Kv4.2 to
spines in hippocampal neurons: regulation by CaMKII. J Biol Chem.
282:28691–28699. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Erickson JR, Joiner ML, Guan X, Kutschke
W, Yang J, Oddis CV, Bartlett RK, Lowe JS, O’Donnell SE,
Aykin-Burns N, et al: A dynamic pathway for calcium-independent
activation of CaMKII by methionine oxidation. Cell. 133:462–474.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Rokhlin OW, Taghiyev AF, Bayer KU, Bumcrot
D, Koteliansk VE, Glover RA and Cohen MB:
Calcium/calmodulin-dependent kinase II plays an important role in
prostate cancer cell survival. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:732–742. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Scott JA, Xie L, Li H, Li W, He JB,
Sanders PN, Carter AB, Backs J, Anderson ME and Grumbach IM: The
multifunctional Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent kinase II
regulates vascular smooth muscle migration through matrix
metalloproteinase 9. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
302:H1953–H1964. 2012.
|
|
16
|
Mercure MZ, Ginnan R and Singer HA: CaM
kinase II delta2-dependent regulation of vascular smooth muscle
cell polarization and migration. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
294:C1465–C1475. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang M and Kahn AM: Insulin-inhibited and
stimulated cultured vascular smooth muscle cell migration are
related to divergent effects on protein phosphatase-2A and
autonomous calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II.
Atherosclerosis. 196:227–233. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Chen JH, Huang SM, Chen CC, Tsai CF, Yeh
WL, Chou SJ, Hsieh WT and Lu DY: Ghrelin induces cell migration
through GHS-R, CaMKII, AMPK, and NF-κB signaling pathway in glioma
cells. J Cell Biochem. 112:2931–2941. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Cuddapah VA and Sontheimer H: Molecular
interaction and functional regulation of ClC-3 by
Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase II (CaMKII) in
human malignant glioma. J Biol Chem. 285:11188–11196. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Asahi M, Asahi K, Jung JC, del Zoppo GJ,
Fini ME and Lo EH: Role for matrix metalloproteinase 9 after focal
cerebral ischemia: effects of gene knockout and enzyme inhibition
with BB-94. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 20:1681–1689. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Galis ZS, Sukhova GK, Kranzhöfer R, Clark
S and Libby P: Macrophage foam cells from experimental atheroma
constitutively produce matrix-degrading proteinase. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 92:402–406. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Klein G, Vellenga E, Fraaije MW, Kamps WA
and de Bont ES: The possible role of matrixmetalloproteinase
(MMP)-2 and MMP-9 in cancer, e.g acute leukemia. Crit Rev Oncol
Hematol. 50:87–100. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ishiguro K, Green T, Rapley J, Wachtel H,
Giallourakis C, Landry A, Cao Z, Lu N, Takafumi A, Goto H, Daly MJ
and Xavier RJ: Ca2+/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase
II is a modulator of CARMA1-mediated NF-kappaB activation. Mol Cell
Biol. 26:5497–5508. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chou YC, Sheu JR, Chung CL, Chen CY, Lin
FL, Hsu MJ, Kuo YH and Hsiao G: Nuclear-targeted inhibition of
NF-kappaB on MMP-9 production by N-2-(4-bromophenyl) ethyl
caffeamide in human monocytic cells. Chem Biol Interact.
184:403–412. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Deryugina EI and Quigley JP: Matrix
metalloproteinases and tumor metastasis. Cancer Metastasis Rev.
25:9–34. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Egeblad M and Werb Z: New functions for
the matrix metalloproteinases in cancer progression. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:161–174. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
He BJ, Joiner ML, Singh MV, et al:
Oxidation of CaMKII determines the cardiotoxic effects of
aldosterone. Nat Med. 17:1610–1618. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Cheng CY, Hsieh HL, Hsiao LD and Yang CM:
PI3-K/Akt/JNK/NF-κB is essential for MMP-9 expression and outgrowth
in human limbal epithelial cells on intact amniotic membrane. Stem
Cell Res. 9:9–23. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Liang KC, Lee CW, Lin WN, Lin CC, Wu CB,
Luo SF and Yang CM: Interleukin-1beta induces MMP-9 expression via
p42/p44 MAPK, p38 MAPK, JNK, and nuclear factor-kappaB signaling
pathways in human tracheal smooth muscle cells. J Cell Physiol.
211:759–770. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bond M, Chase AJ, Baker AH and Newby AC:
Inhibition of transcription factor NF-kappaB reduces matrix
metalloproteinase-1, -3 and -9 production by vascular smooth muscle
cells. Cardiovasc Res. 50:556–565. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Bond M, Fabunmi RP, Baker AH and Newby AC:
Synergistic upregulation of metalloproteinase-9 by growth factors
and inflammatory cytokines: an absolute requirement for
transcription factor NF-kappa B. FEBS Lett. 435:29–34. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Rhee JW, Lee KW, Kim D, Lee Y, Jeon OH,
Kwon HJ and Kim DS: NF-kappaB-dependent regulation of matrix
metalloproteinase-9 gene expression by lipopolysaccharide in a
macrophage cell line RAW 264.7. J Biochem Mol Biol. 40:88–94. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|