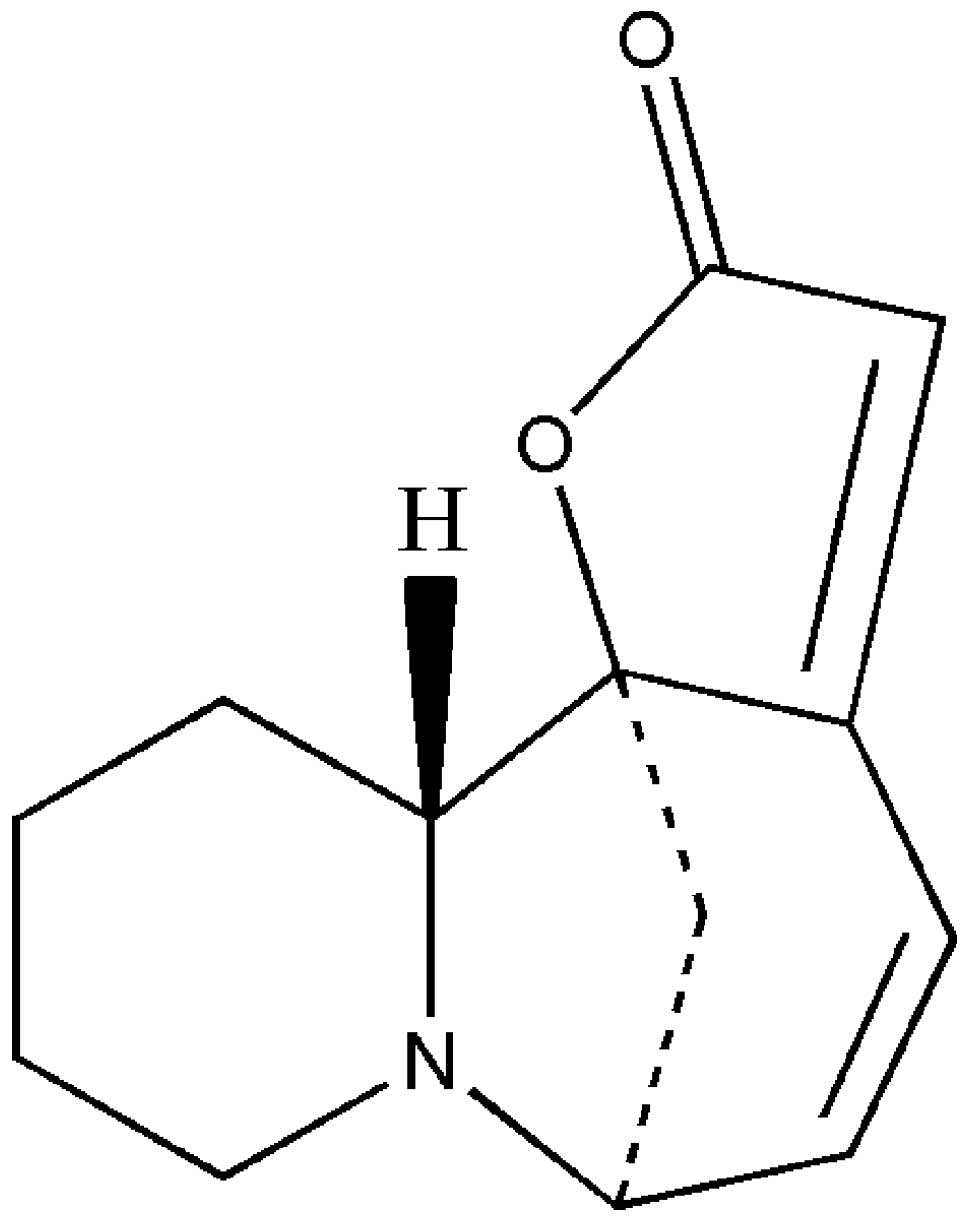
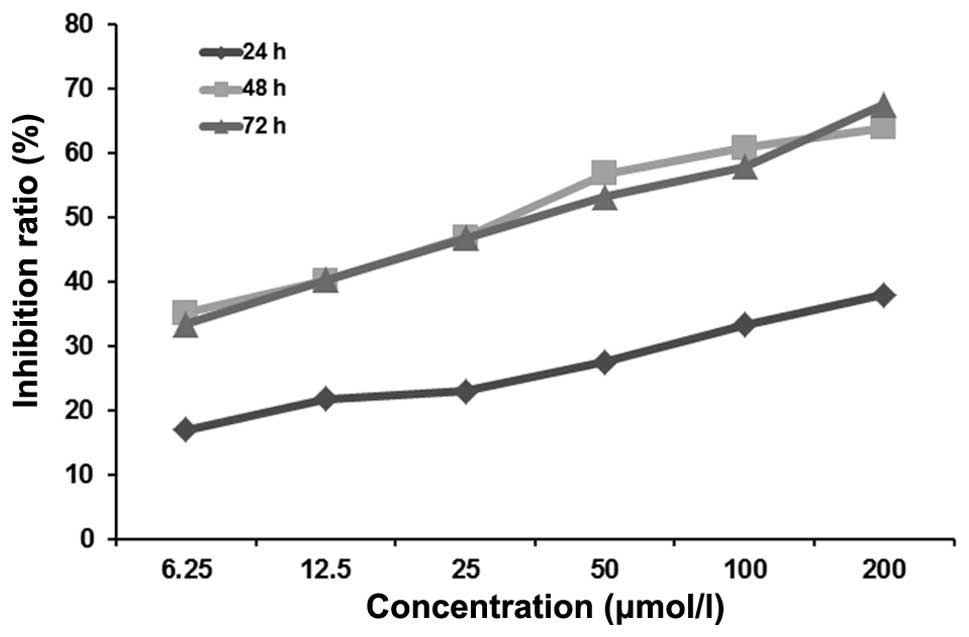
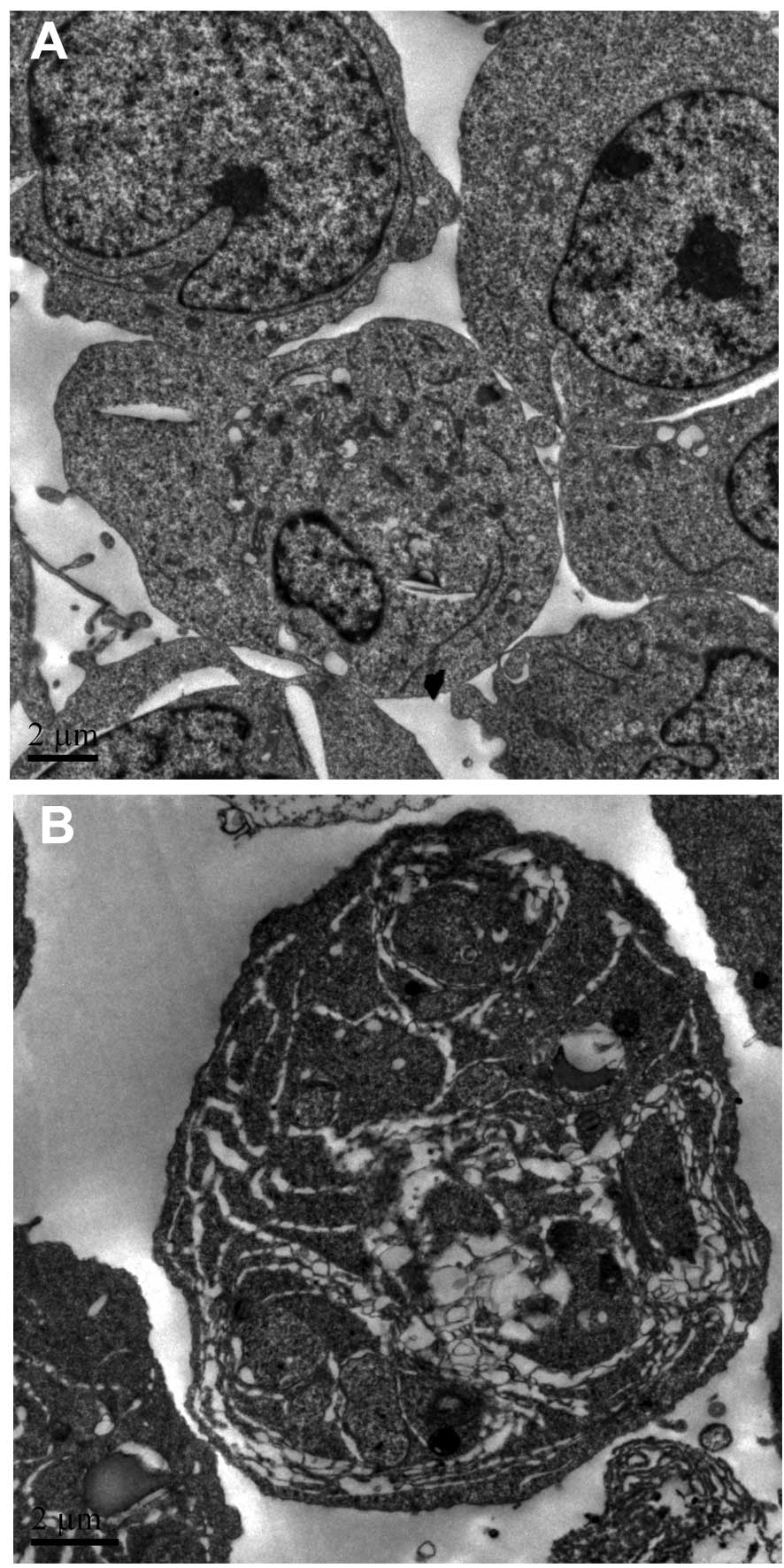
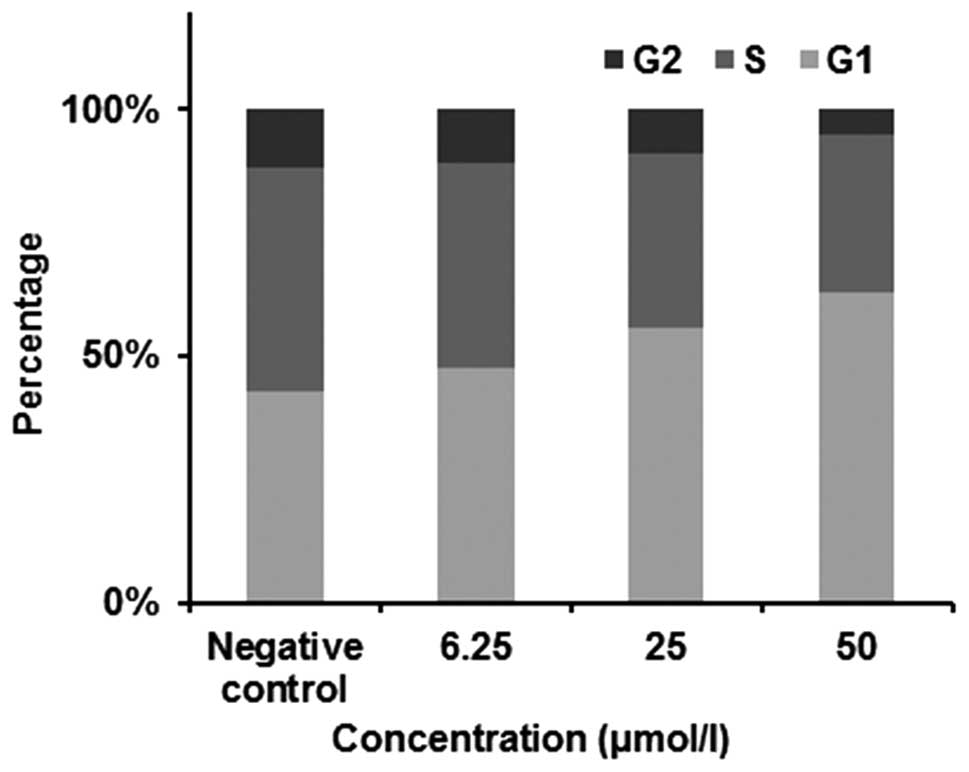
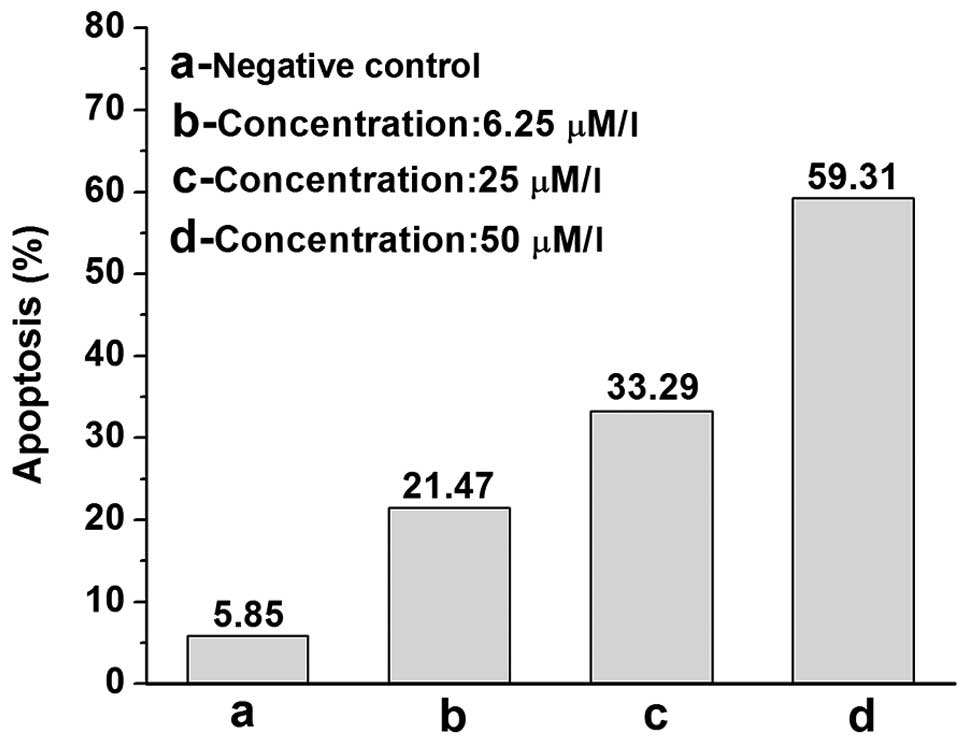
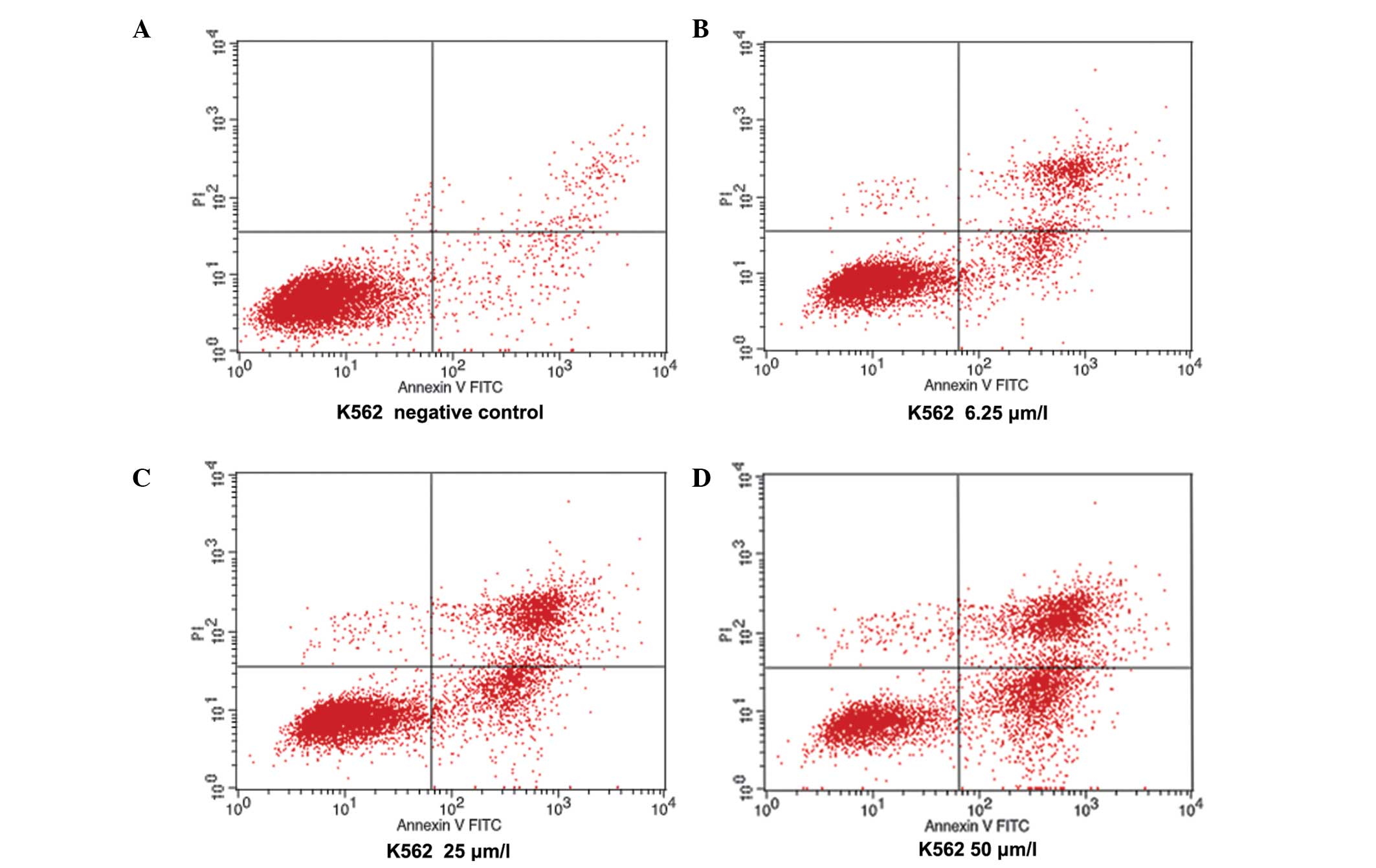
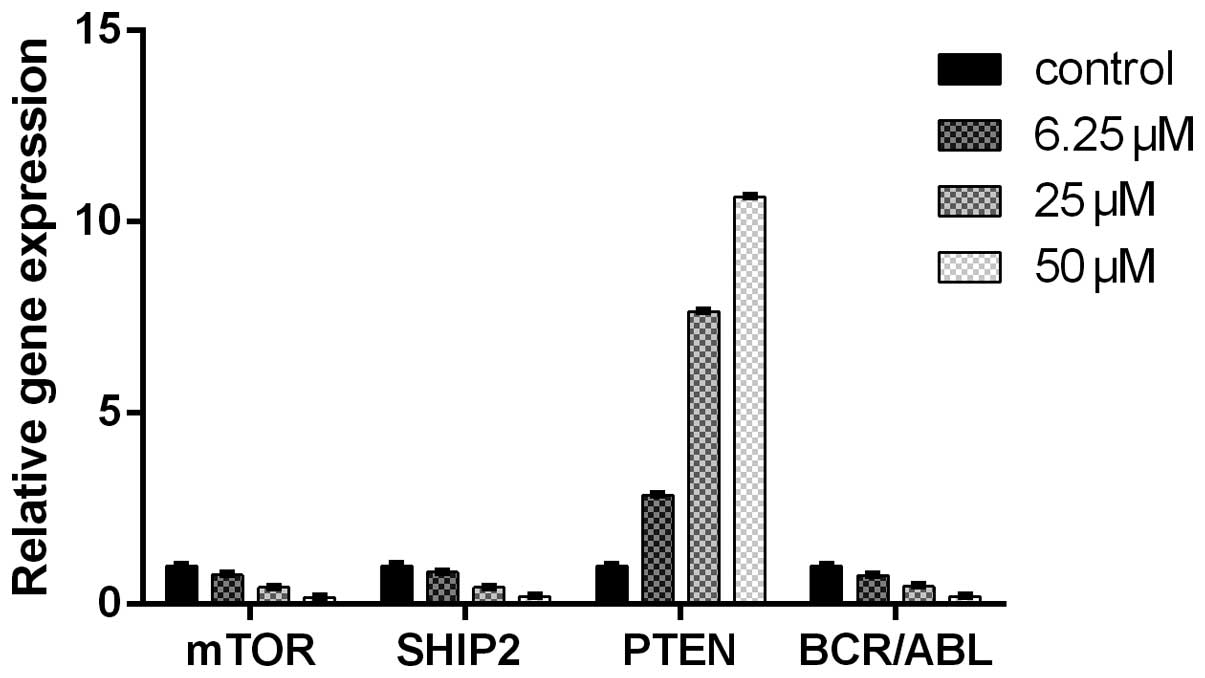
|
1
|
Deininger MW, Goldman JM and Melo JV: The
molecular biology of chronic myeloid leukemia. Blood. 96:3343–3356.
2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Cancer statistics, 2009. CA Cancer J Clin.
59:225–249. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Lin H and Chen ZL: Progress of researching
in anti-tumor drugs. Chin J Hosp Pharm. 8:226–228. 1998.(In
Chinese).
|
|
4
|
Saito S, Kotera K, Shigematsu N, Ide A,
Sugimoto N, Horii Z, et al: Structure of securinine. Tetrahedron.
19:2085–2099. 1963. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Beutler JA, Karbon EW, Brubaker AN, Malik
R, Curtis DR and Enna SJ: Securinine alkaloids: a new class of GABA
receptor antagonist. Brain Res. 330:135–140. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Weenen H, Nkunya MH, Bray DH, Mwasumbi LB,
Kinabo LS, Kilimali VA, et al: Antimalarial compounds containing an
alpha, beta-unsaturated carbonyl moiety from Tanzanian medicinal
plants. Planta Med. 56:371–373. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Mensah JL, Lagarde I, Ceschin C, Michel G,
Gleye J and Fouraste I: Antibacterial activity of the leaves of
Phyllanthus discoideus. J Ethnopharmacol. 28:129–133. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Dong NZ and Gu ZL: Study on the antitumor
effect of securinine and its mechanism. Chin Tradit Pat Med.
21:193–195. 1999.(In Chinese).
|
|
9
|
Jiang XY: The effect of securinine and
aminophylline on hemopoietic stem cells and granulopoietic
progenitors in mice. Tianjin Med J. 10:99–100. 1982.(In
Chinese).
|
|
10
|
Liu WJ, Gu ZL and Zhou WX: Securinine
induced apoptosis in K562 cells. Chin Pharmacol Bull. 115:135–158.
1999.
|
|
11
|
Pérez JM, Quiroga AG, Montero EI, Alonso C
and Navarro-Ranninger C: A cycloplatinated compound of
p-isopropylbenzaldehyde thiosemicarbazone and its chloro-bridged
derivative induce apoptosis in cis-DDP resistant cells which
overexpress the H-ras oncogene. J Inorg Biochem. 73:235–243.
1999.
|
|
12
|
Kerr JF, Wyllie AH and Currie AR:
Apoptosis: a basic biological phenomenon with wide ranging
implications in tissue kinetics. Br J Cancer. 26:239–257. 1972.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Steller H: Mechanisms and genes of
cellular suicide. Science. 267:1445–1449. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Hector S, Rehm M, Schmid J, Kehoe J,
McCawley N, Dicker P, et al: Clinical application of a systems
model of apoptosis execution for the prediction of colorectal
cancer therapy responses and personalisation of therapy. Gut.
11:725–733. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huber HJ, Dussmann H, Kilbride SM, Rehm M
and Prehn JH: Glucose metabolism determines resistance of cancer
cells to bioenergetic crisis after cytochrome-c release. Mol Syst
Biol. 7:4702011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Lee MJ, Ye AS, Gardino AK, Heijink AM,
Sorger PK, MacBeath G and Yaffe MB: Sequential application of
anticancer drugs enhances cell death by rewiring apoptotic
signaling networks. Cell. 149:780–794. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hay N and Sonenberg N: Upstream and
downstream of mTOR. Genes Dev. 18:1926–1945. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Montiel-Duarte C, Cordeu L, Agirre X,
Román-Gómez J, Jiménez-Velasco A, José-Eneriz ES, et al: Resistance
to Imatinib Mesylate-induced apoptosis in acute lymphoblastic
leukemia is associated with PTEN down-regulation due to promoter
hypermethylation. Leuk Res. 32:709–716. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Wiencke JK, Zheng S, Jelluma N, Tihan T,
Vandenberg S, Tamgüney T, et al: Methylation of the PTEN promoter
defines low-grade gliomas and secondary glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol.
9:271–279. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Mirmohammadsadegh A, Marini A, Nambiar S,
Hassan M, Tannapfel A, Ruzicka T, et al: Epigenetic silencing of
the PTEN gene in melanoma. Cancer Res. 66:6546–6552. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Noro R, Gemma A, Miyanaga A, Kosaihira S,
Minegishi Y, Nara M, et al: PTEN inactivation in lung cancer cells
and the effect of its recovery on treatment with epidermal growth
factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors. Int J Oncol.
31:1157–1163. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Athanassiadou P, Athanassiades P, Grapsa
D, Gonidi M, Athanassiadou AM, Stamati PN and Patsouris E: The
prognostic value of PTEN, p53, and beta-catenin in endometrial
carcinoma: a prospective immunocytochemical study. Int J Gynecol
Cancer. 17:697–704. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Goldman JM and Melo JV: BCR-ABL in chronic
myelogenous leukemia-how does it work? Acta Haematol. 13:212–217.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Kantarjian H, Sawyers C, Hochhaus A,
Guilhot F, Schiffer C, Gambacorti-Passerini C, et al: Hematologic
and cytogenetic responses to imatinib mesylate in chronic
myelogenous leukemia. N Engl J Med. 346:645–652. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Ooms LM, Horan KA, Rahman P, Seaton G,
Gurung R, Kethesparan DS and Mitchell CA: The role of the inositol
polyphosphate 5-phosphatases in cellular function and human
disease. Biochem J. 419:29–49. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Suwa A, Kurama T and Shimokawa T: HIP2 and
its involvement in various diseases. Expert Opin Ther Targets.
14:727–737. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Suwa A, Yamamoto T, Sawada A, Minoura K,
Hosogai N, Tahara A, et al: Discovery and functional
characterization of a novel small molecule inhibitor of the
intracellular phosphatase, SHIP2. J Pharmacol. 158:879–887.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Fuhler GM, Brooks R, Toms B, Iyer S, Gengo
EA, Park MY, et al: Therapeutic potential of SH2 domain-containing
inositol-5′-phosphatase 1 (SHIP1) and SHIP2 inhibition in cancer.
Mol Med. 18:65–75. 2012.
|