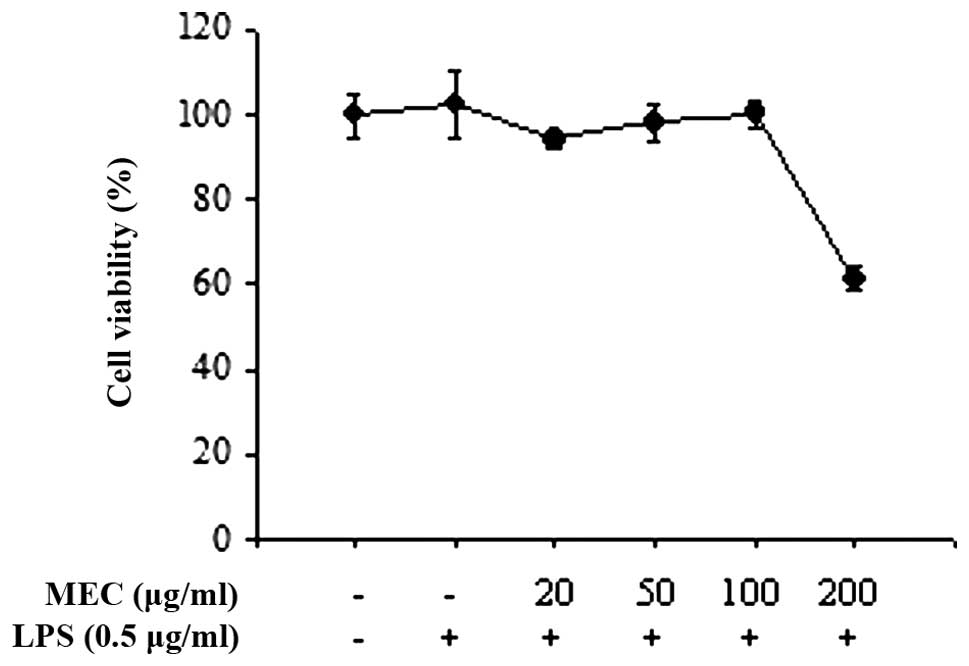
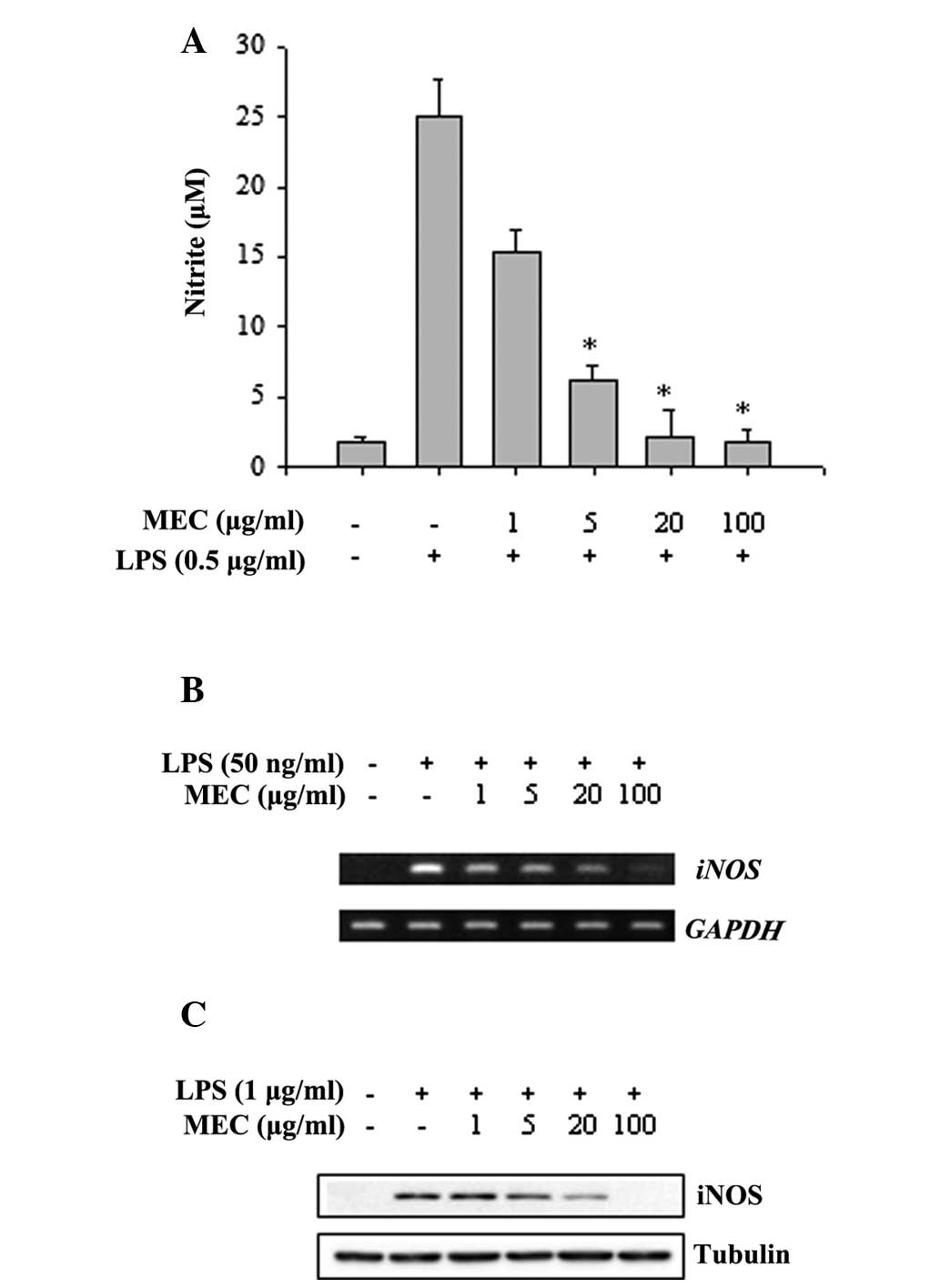
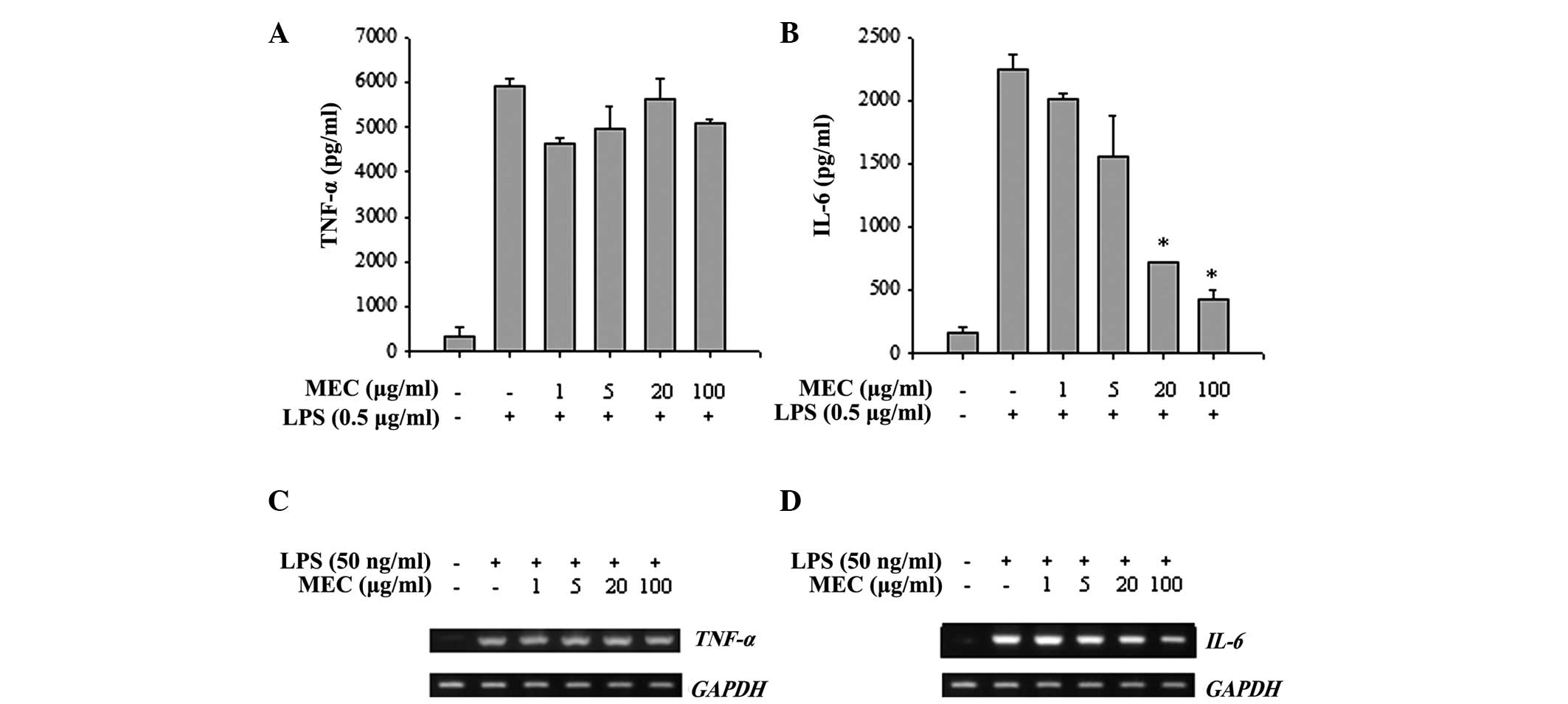
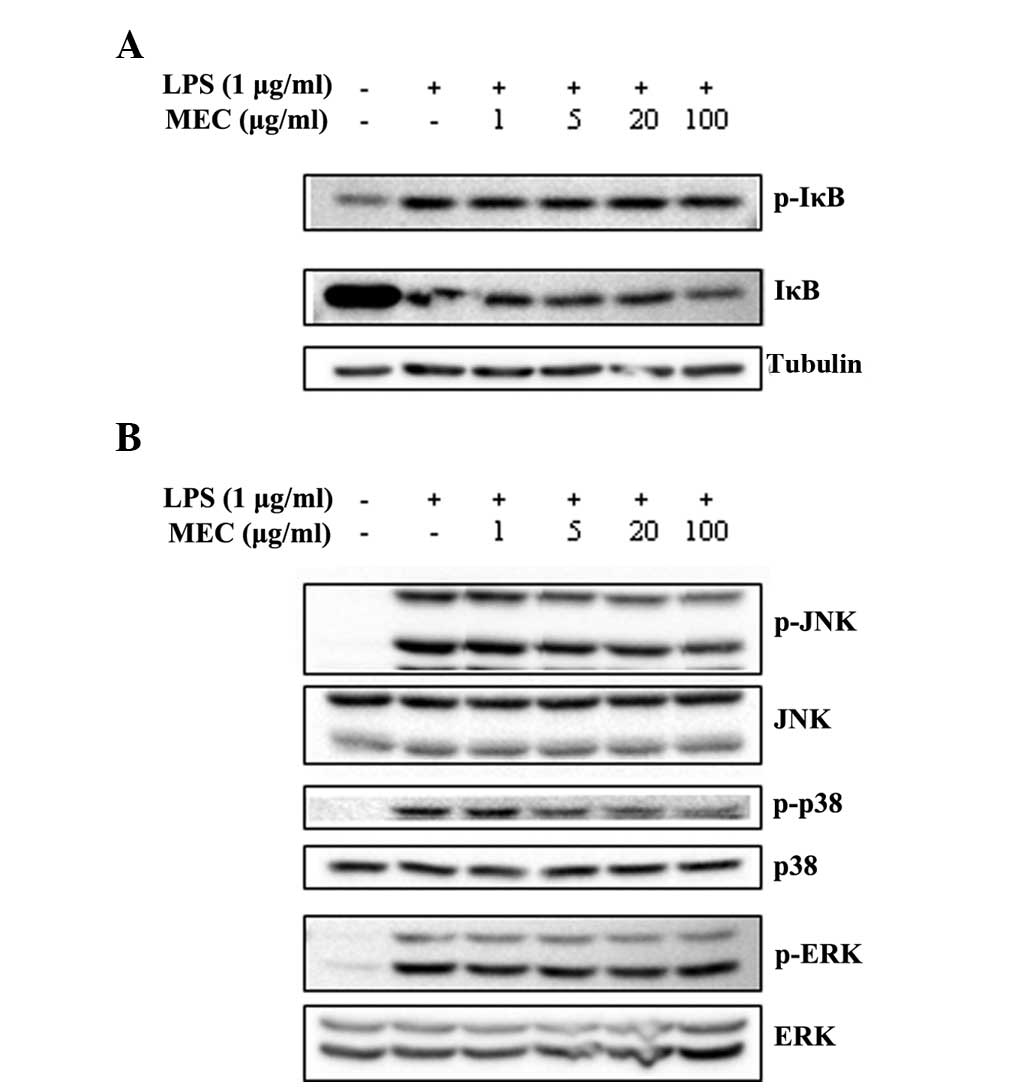
|
1
|
Fujiwara N and Kobayashi K: Macrophages in
inflammation. Curr Drug Targets Inflamm Allergy. 4:281–286. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Schroder K, Sweet MJ and Hume DA: Signal
integration between IFNgamma and TLR signalling pathways in
macrophages. Immunobiology. 211:511–524. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Aderem A and Underhill DM: Mechanisms of
phagocytosis in macrophages. Annu Rev Immunol. 17:593–623. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Aderem A and Ulevitch RJ: Toll-like
receptors in the induction of the innate immune response. Nature.
406:782–787. 2000. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cario E, Rosenberg IM, Brandwein SL, Beck
PL, Reinecker HC and Podolsky DK: Lipopolysaccharide activates
distinct signaling pathways in intestinal epithelial cell lines
expressing Toll-like receptors. J Immunol. 164:966–972. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fujihara M, Muroi M, Tanamoto K, Suzuki T,
Azuma H and Ikeda H: Molecular mechanisms of macrophage activation
and deactivation by lipopolysaccharide: roles of the receptor
complex. Pharmacol Ther. 100:171–194. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Hanada T and Yoshimura A: Regulation of
cytokine signaling and inflammation. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev.
13:413–421. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Nathan C and Xie QW: Regulation of
biosynthesis of nitric oxide. J Biol Chem. 269:13725–13728.
1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
MacMicking J, Xie QW and Nathan C: Nitric
oxide and macrophage function. Annu Rev Immunol. 15:323–350. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Clancy RM, Amin AR and Abramson SB: The
role of nitric oxide in inflammation and immunity. Arthritis Rheum.
41:1141–1151. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Moncada S: Nitric oxide: discovery and
impact on clinical medicine. J R Soc Med. 92:164–169.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Dinarello CA: Anti-inflammatory agents:
present and future. Cell. 140:935–950. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Eke T, Al-Husainy S and Raynor MK: The
spectrum of ocular inflammation caused by Euphorbia plant
sap. Arch Ophthalmol. 18:13–16. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Lazarini CA, Uema AH, Brandão GM,
Guimarães AP and Bernardi MM: Croton zehntneri essential oil:
effects on behavioral models related to depression and anxiety.
Phytomedicine. 7:477–481. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Thyagarajan SP, Subramanian S,
Thirunalasundari T, Venkateswaran PS and Blumberg BS: Effect of
Phyllanthus amarus on chronic carriers of hepatitis B virus.
Lancet. 1:764–766. 1988. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Suarez AI, Compagnone RS, Salazar-Bookaman
MM, et al: Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of
Croton malambo bark aqueous extract. J
Ethnopharmacol. 88:11–14. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pereira U, Garcia-Le Gal C, Le Gal G, et
al: Effects of sangre de drago in an in vitro model of cutaneous
neurogenic inflammation. Exp Dermatol. 19:796–799. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Risco E, Ghia F, Vila R, Iglesias J,
Alvarez E and Cañigueral S: Immunomodulatory activity and chemical
characterisation of sangre de drago (dragon’s blood) from Croton
lechleri. Planta Med. 69:785–794. 2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Nathan C and Xie QW: Nitric oxide
synthases: roles, tolls, and controls. Cell. 78:915–918. 1994.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Szabo C and Thiemermann C: Regulation of
the expression of the inducible isoform of nitric oxide synthase.
Adv Pharmacol. 34:113–153. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bosca L, Zeini M, Traves PG and Hortelano
S: Nitric oxide and cell viability in inflammatory cells: a role
for NO in macrophage function and fate. Toxicology. 208:249–258.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kröncke KD, Fehsel K and Kolb-Bachofen V:
Inducible nitric oxide synthase in human diseases. Clin Exp
Immunol. 113:147–156. 1998.
|
|
23
|
Guadagni F, Ferroni P, Palmirotta R,
Portarena I, Formica V and Roselli M: Review. TNF/VEGF cross-talk
in chronic inflammation-related cancer initiation and progression:
an early target in anticancer therapeutic strategy. In Vivo.
21:147–161. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Nishimoto N and Kishimoto T: Interleukin
6: from bench to bedside. Nat Clin Pract Rheumatol. 2:619–626.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Kavanaugh A: Interleukin-6 inhibition and
clinical efficacy in rheumatoid arthritis treatment - data from
randomized clinical trials. Bull NYU Hosp Jt Dis. 65:S16–S20.
2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Straub RH, Harle P, Yamana S, et al:
Anti-interleukin-6 receptor antibody therapy favors adrenal
androgen secretion in patients with rheumatoid arthritis: a
randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled study. Arthritis
Rheum. 54:1778–1785. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Samavati L, Rastogi R, Du W, Huttemann M,
Fite A and Franchi L: STAT3 tyrosine phosphorylation is critical
for interleukin 1 beta and interleukin-6 production in response to
lipopolysaccharide and live bacteria. Mol Immunol. 46:1867–1877.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Zhu ZG, Jin H, Yu PJ, Tian YX, Zhang JJ
and Wu SG: Mollugin inhibits the inflammatory response in
lipopolysaccharide-stimulated RAW264.7 macrophages by blocking the
janus kinase-signal transducers and activators of transcription
signaling pathway. Biol Pharm Bull. 36:399–406. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Lee C, Lim HK, Sakong J, Lee YS, Kim JR
and Baek SH: Janus kinase-signal transducer and activator of
transcription mediates phosphatidic acid-induced interleukin
(IL)-1beta and IL-6 production. Mol Pharmacol. 69:1041–1047.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Stalinska K, Guzdek A, Rokicki M and Koj
A: Transcription factors as targets of the anti-inflammatory
treatment. A cell culture study with extracts from some
Mediterranean diet plants. J Physiol Pharmaco. 56:S157–S169.
2005.
|
|
31
|
Burk DR, Senechal-Willis P, Lopez LC,
Hogue BG and Daskalova SM: Suppression of
lipopolysaccharide-induced inflammatory responses in RAW 264.7
murine macrophages by aqueous extract of Clinopodium vulgare
L. (Lamiaceae). J Ethnopharmacol. 126:397–405. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Liu H, Bargouti M, Zughaier S, et al:
Osteoinductive LIM mineralization protein-1 suppresses activation
of NF-kappaB and selectively regulates MAPK pathways in
pre-osteoclasts. Bone. 46:1328–1335. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shan J, Fu J, Zhao Z, et al: Chlorogenic
acid inhibits lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2
expression in RAW264.7 cells through suppressing NF-kappaB and
JNK/AP-1 activation. Int Immunopharmacol. 9:1042–1048. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Watters JJ, Sommer JA, Pfeiffer ZA, Prabhu
U, Guerra AN and Bertics PJ: A differential role for the
mitogen-activated protein kinases in lipopolysaccharide signaling:
the MEK/ERK pathway is not essential for nitric oxide and
interleukin 1beta production. J Biol Chem. 277:9077–9087. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Karin M and Ben-Neriah Y: Phosphorylation
meets ubiquitination: the control of NF-[kappa]B activity. Annu Rev
Immunol. 18:621–663. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Karin M and Delhase M: The I kappa B
kinase (IKK) and NF-kappa B: key elements of proinflammatory
signalling. Semin Immunol. 12:85–98. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Surh YJ, Chun KS, Cha HH, et al: Molecular
mechanisms underlying chemopreventive activities of
anti-inflammatory phytochemicals: down-regulation of COX-2 and iNOS
through suppression of NF-kappa B activation. Mutat Res.
480–481:243–268. 2001.
|
|
38
|
Verma IM, Stevenson JK, Schwarz EM, Van
Antwerp D and Miyamoto S: Rel/NF-kappa B/I kappa B family: intimate
tales of association and dissociation. Genes Dev. 9:2723–2735.
1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|