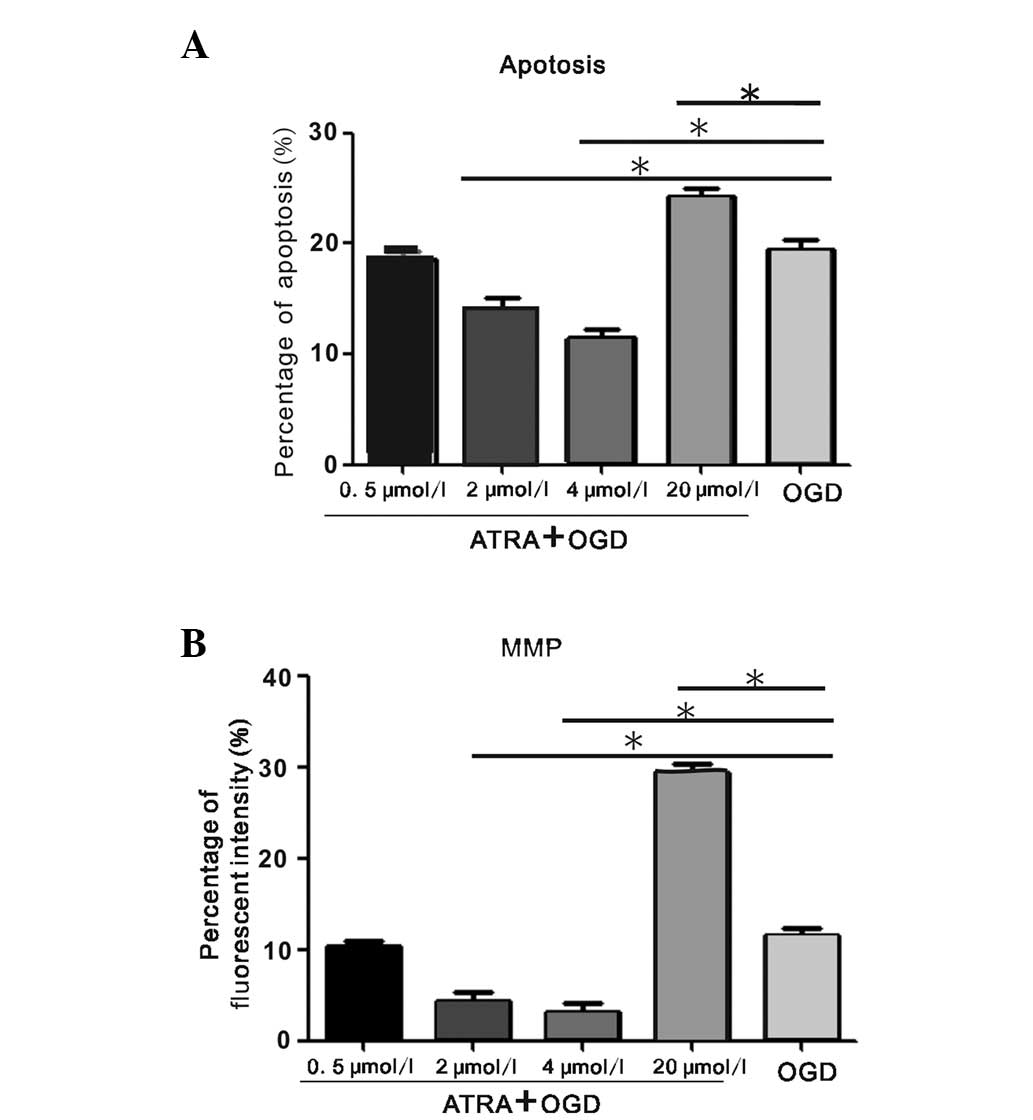
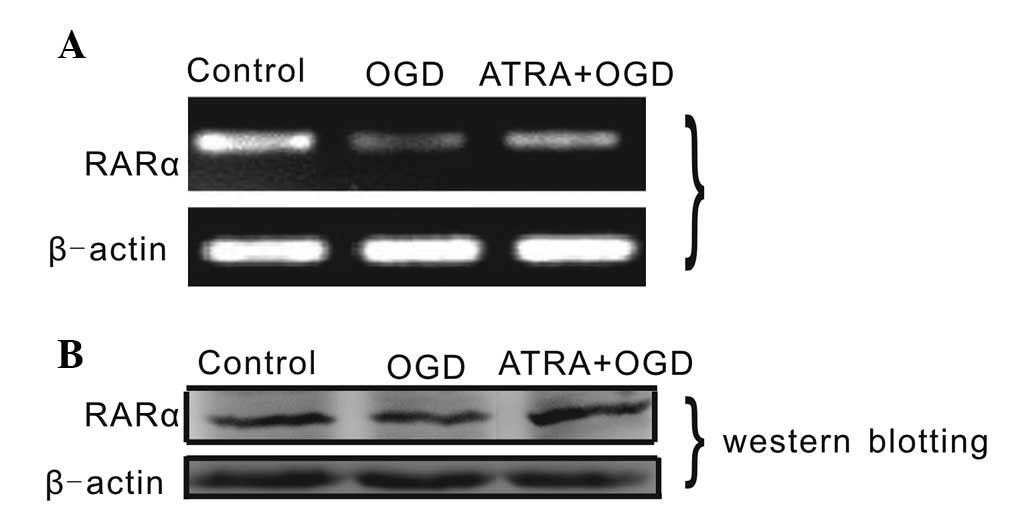
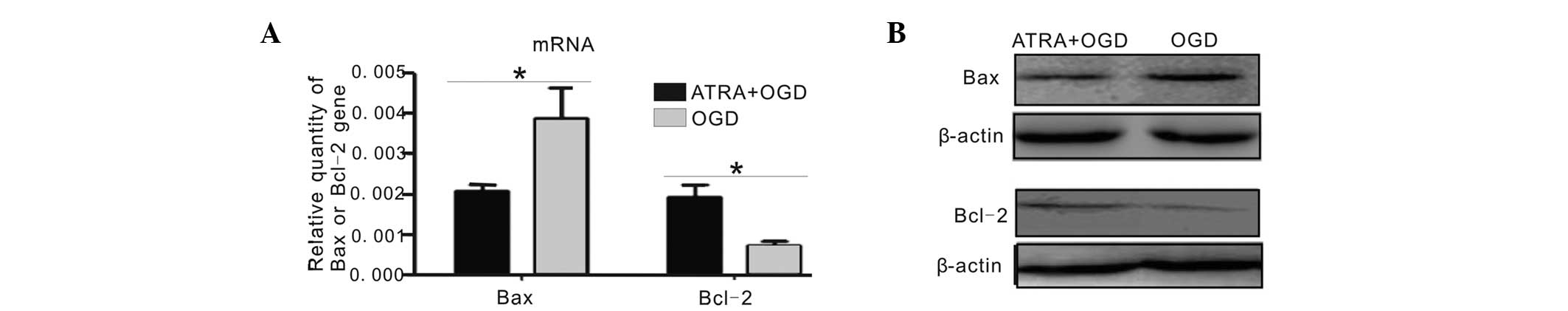
|
1
|
Janesick A, Shiotsugu J, Taketani M and
Blumberg B: RIPPLY3 is a retinoic acid-inducible repressor required
for setting the borders of the pre-placodal ectoderm. Development.
139:1213–1224. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Hale LA, Tallafuss A, Yan YL, Dudley L,
Eisen JS and Postlethwait JH: Characterization of the retinoic acid
receptor genes raraa, rarab and rarg during zebrafish development.
Gene Expr Patterns. 6:546–555. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Grandel H, Lun K, Rauch GJ, et al:
Retinoic acid signalling in the zebrafish embryo is necessary
during pre-segmentation stages to pattern the anterior-posterior
axis of the CNS and to induce a pectoral fin bud. Development.
129:2851–2865. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang X, Chen K, Chen J, Liu YX, Qu P and
Li TY: Effect of marginal vitamin A deficiency during pregnancy on
retinoic acid receptors and N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor
expression in the offspring of rats. J Nutr Biochem. 22:1112–1120.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Jiang W, Yu Q, Gong M, et al: Vitamin A
deficiency impairs postnatal cognitive function via inhibition of
neuronal calcium excitability in hippocampus. J Neurochem.
121:932–943. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jiang T, Gao L, Shi J, Lu J, Wang Y and
Zhang Y: Angiotensin-(1–7) modulates renin-angiotensin system
associated with reducing oxidative stress and attenuating neuronal
apoptosis in the brain of hypertensive rats. Pharmacol Res.
67:84–93. 2013.
|
|
7
|
Raveendran AT and Skaria PC: Learning and
cognitive deficits in hypoxic neonatal rats intensified by BAX
mediated apoptosis: protective role of glucose, oxygen, and
epinephrine. Int J Neurosci. 123:80–88. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Cheng O, Li Z, Han Y, Jiang Q, Yan Y and
Cheng K: Baicalin improved the spatial learning ability of global
ischemia/reperfusion rats by reducing hippocampal apoptosis. Brain
Res. 1470:111–118. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wang YQ, Wang L, Zhang MY, et al:
Necrostatin-1 suppresses autophagy and apoptosis in mice traumatic
brain injury model. Neurochem Res. 37:1849–1858. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Hill JW, Poddar R, Thompson JF, Rosenberg
GA and Yang Y: Intranuclear matrix metalloproteinases promote DNA
damage and apoptosis induced by oxygen-glucose deprivation in
neurons. Neuroscience. 220:277–290. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Piao CS, Loane DJ, Stoica BA, et al:
Combined inhibition of cell death induced by apoptosis inducing
factor and caspases provides additive neuroprotection in
experimental traumatic brain injury. Neurobiol Dis. 46:745–758.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Chaung WW, Wu R, Ji Y, et al: Peripheral
administration of human adrenomedullin and its binding protein
attenuates stroke-induced apoptosis and brain injury in rats. Mol
Med. 17:1075–1083. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Tang LH, Xia ZY, Zhao B, Wei XD, Luo T and
Meng QT: Phosphocreatine preconditioning attenuates apoptosis in
ischemia-reperfusion injury of rat brain. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:1070912011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Jin W, Ni H, Dai Y, et al: Effects of
tert-butylhydroquinone on intestinal inflammatory response and
apoptosis following traumatic brain injury in mice. Mediators
Inflamm. 2010:5025642010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jacobs S, Lie DC, DeCicco KL, et al:
Retinoic acid is required early during adult neurogenesis in the
dentate gyrus. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 103:3902–3907. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Maden M: Retinoic acid in the development,
regeneration and maintenance of the nervous system. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 8:755–765. 2007. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shinozaki Y, Sato Y, Koizumi S, Ohno Y,
Nagao T and Inoue K: Retinoic acids acting through retinoid
receptors protect hippocampal neurons from oxygen-glucose
deprivation-mediated cell death by inhibition of c-jun-N-terminal
kinase and p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase. Neuroscience.
147:153–163. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Karmakar S, Banik NL and Ray SK:
Combination of all-trans retinoic acid and paclitaxel-induced
differentiation and apoptosis in human glioblastoma U87MG
xenografts in nude mice. Cancer. 112:596–607. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Keedwell RG, Zhao Y, Hammond LA, et al: A
retinoid-related molecule that does not bind to classical retinoid
receptors potently induces apoptosis in human prostate cancer cells
through rapid caspase activation. Cancer Res. 64:3302–3312. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Thin TH, Li L, Chung TK, Sun H and Taneja
R: Stra13 is induced by genotoxic stress and regulates
ionizing-radiation-induced apoptosis. EMBO Rep. 8:401–407. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li J, Orr B, White K, et al: Chmp 1A is a
mediator of the anti-proliferative effects of all-trans retinoic
acid in human pancreatic cancer cells. Mol Cancer. 8:72009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Jiang W, Wen EY, Gong M, et al: The
pattern of retinoic acid receptor expression and subcellular,
anatomic and functional area translocation during the postnatal
development of the rat cerebral cortex and white matter. Brain Res.
1382:77–87. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Katsuki H, Kurimoto E, Takemori S, et al:
Retinoic acid receptor stimulation protects midbrain dopaminergic
neurons from inflammatory degeneration via BDNF-mediated signaling.
J Neurochem. 110:707–718. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|