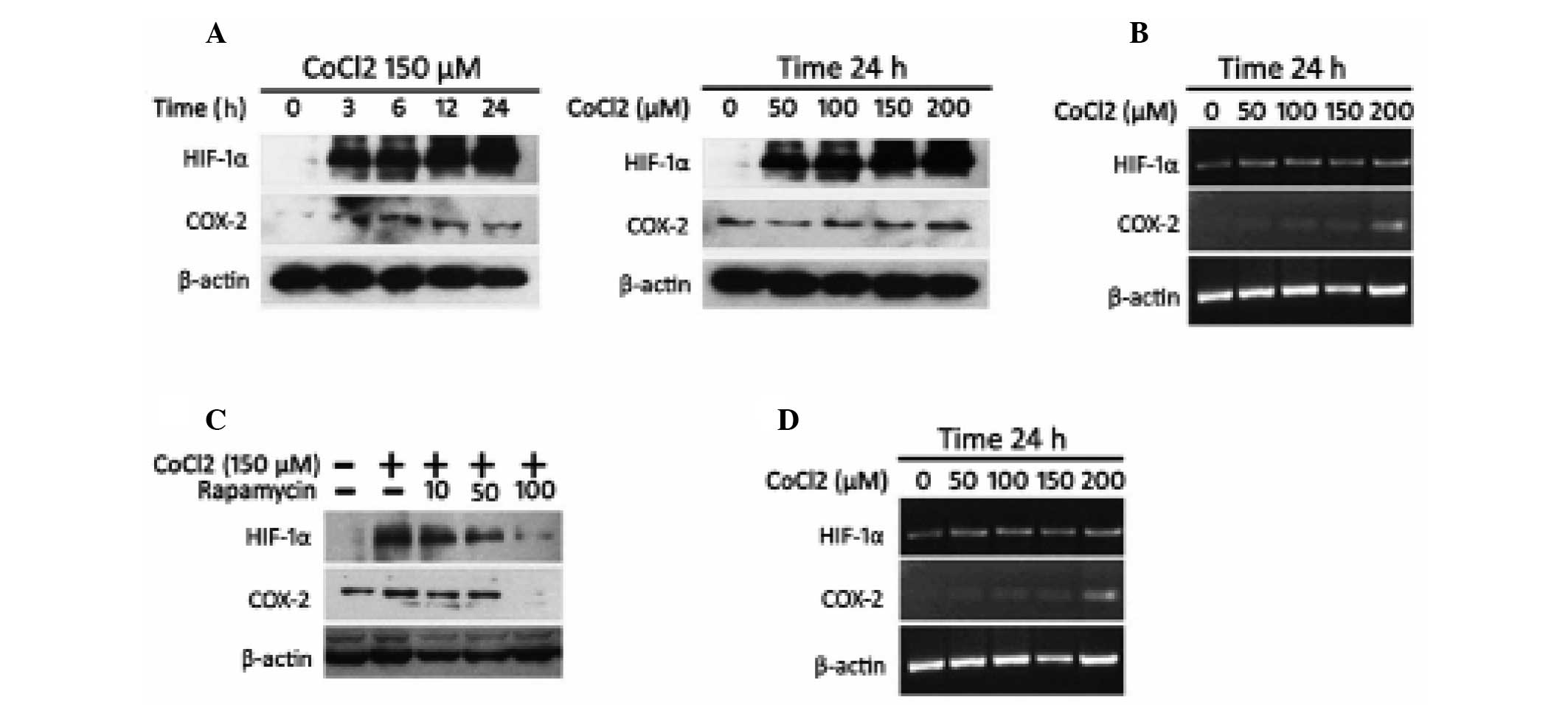
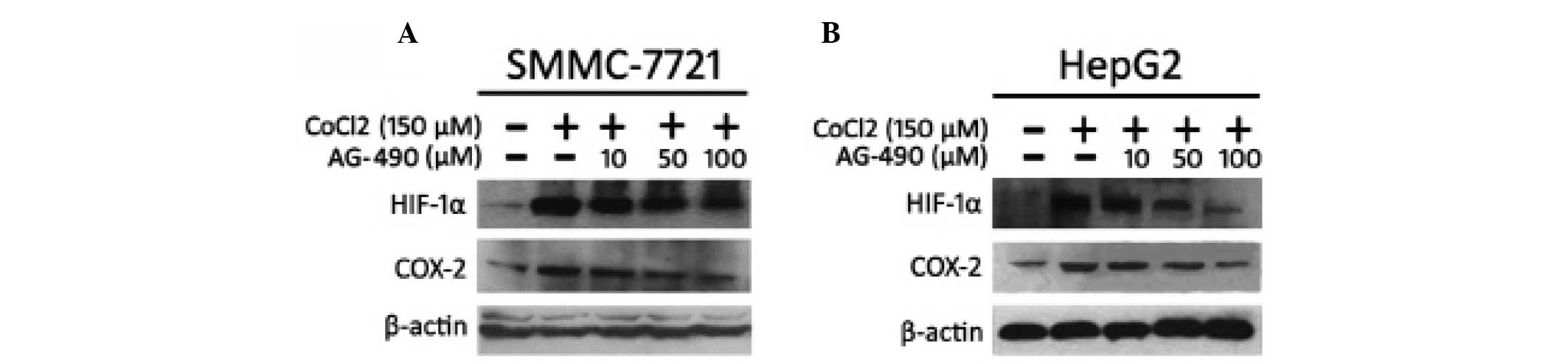
|
1
|
Montalto G, Cervello M, Giannitrapani L,
Dantona F, Terranova A and Castagnetta LA: Epidemiology, risk
factors, and natural history of hepatocellular carcinoma. Ann NY
Acad Sci. 963:3–20. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
El-Serag HB, Marrero JA, Rudolph L and
Reddy KR: Diagnosis and treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 134:1752–1763. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu CN, Yuan ZG, Zhang XL, et al:
Saikosaponin a and its epimer saikosaponin d exhibit
anti-inflammatory activity by suppressing activation of NF-κB
signaling pathway. Int Immunopharmacol. 14:121–126. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Hattori T, Nishimura H, Kase Y and Takeda
S: Saireito and saikosaponin D prevent urinary protein excretion
via glucocorticoid receptor in adrenalectomized WKY rats with
heterologous-phase anti-GBM nephritis. Nephron Physiol. 109:19–27.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Fan J, Li X, Li P, et al: Saikosaponin-d
attenuates the development of liver fibrosis by preventing
hepatocyte injury. Biochem Cell Biol. 85:189–195. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Dang S, Wang B, Cheng Y, Song P, Liu Z and
Li Z: Inhibitory effects of saikosaponin-d on CCl4-induced hepatic
fibrogenesis in rats. World J Gastroenterol. 13:557–563. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kato M, Pu M, Isobe K, et al:
Characterization of the immunoregulatory action of saikosaponin-d.
Cell Immunol. 159:15–25. 1994. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Wong VK, Zhou H, Cheung SS, Li T and Liu
L: Mechanistic study of saikosaponin-d (Ssd) on suppression of
murine T lymphocyte activation. J Cell Biochem. 107:303–315. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Man S, Gao W, Zhang Y, Huang L and Liu C:
Chemical study and medical application of saponins as anti-cancer
agents. Fitoterapia. 81:703–714. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Bachran C, Bachran S, Sutherland M,
Bachran D and Fuchs H: Saponins in tumor therapy. Mini Rev Med
Chem. 8:575–584. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Hsu Y, Kuo P and Lin C: The proliferative
inhibition and apoptotic mechanism of Saikosaponin D in human
non-small cell lung cancer A549 cells. Life Sci. 75:1231–1242.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Hsu Y, Kuo P, Chiang L and Lin C:
Involvement of p53, nuclear factor kappaB and Fas/Fas ligand in
induction of apoptosis and cell cycle arrest by saikosaponin d in
human hepatoma cell lines. Cancer Lett. 213:213–221. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
He SX, Luo JY, Zhao G, et al: Effect of
saikosaponins-d on cyclooxygenase-2 expression of human
hepatocellular carcinoma cell line smmc-7721. Zhonghua Gan Zang
Bing Za Zhi. 14:712–714. 2006.(In Chinese).
|
|
15
|
Ristimaki A: Cyclooxygenase 2: from
inflammation to carcinogenesis. Novartis Found Symp. 256:215–269.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Bin W, He W, Feng Z, et al: Prognostic
relevance of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) expression in Chinese
patients with prostate cancer. Acta Histochem. 113:131–136. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Matsubayashi H, Infante JR, Winter JM, et
al: Tumor COX-2 expression and prognosis of patients with
resectable pancreatic cancer. Cancer Biol Ther. 6:1569–1575. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Mascaux C, Martin B, Paesmans M, et al:
Has Cox-2 a prognostic role in non-small-cell lung cancer? A
systematic review of the literature with meta-analysis of the
survival results. Br J Cancer. 95:139–145. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Harris RE: Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2)
blockade in the chemoprevention of cancers of the colon, breast,
prostate, and lung. Inflammopharmacology. 17:55–67. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Harris RE, Beebe-Donk J and Alshafie GA:
Cancer chemoprevention by cyclooxygenase 2 (COX-2) blockade:
results of case control studies. Subcell Biochem. 42:193–212. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Bae SH, Jung ES, Park YM, et al:
Expression of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) in hepatocellular carcinoma
and growth inhibition of hepatoma cell lines by a COX-2 inhibitor,
NS-398. Clin Cancer Res. 7:1410–1418. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Cha YI and DuBois RN: NSAIDs and cancer
prevention: Targets downstream of COX-2. Annu Rev Med. 58:239–252.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yuan Y, Hilliard G, Ferguson T and
Millhorn DE: Cobalt inhibits the interaction between
hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha and von Hippel-Lindau protein by
direct binding to hypoxia-inducible factor-alpha. J Biol Chem.
278:15911–15916. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Xu Q, Briggs J, Park S, et al: Targeting
Stat3 blocks both HIF-1 and VEGF expression induced by multiple
oncogenic growth signaling pathways. Oncogene. 24(36): 5552–5560.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Yu JH, Kim KH and Kim H: Suppression of
IL-1beta expression by the Jak 2 inhibitor AG490 in
cerulein-stimulated pancreatic acinar cells. Biochem Pharmacol.
72:1555–1562. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Bu S, Xu J and Sun J: Effect of
saikosaponin-d on up-regulating GR mRNA expression and inhibiting
cell growth in human leukemia cells. Zhongguo Zhong Xi Yi Jie He Za
Zhi. 20:350–352. 2000.(In Chinese).
|
|
27
|
Tsai YJ, Chen I, Horng LY and Wu RT:
Induction of differentiation in rat C6 glioma cells with
Saikosaponins. Phytother Res. 16:117–121. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Wang B, Dai Z, Wang X, et al:
Saikosaponin-d increases the radiosensitivity of smmc-7721
hepatocellular carcinoma cells by adjusting the g0/g1 and g2/m
checkpoints of the cell cycle. BMC Complement Altern Med.
13:2632013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Whiteside TL: The tumor microenvironment
and its role in promoting tumor growth. Oncogene. 27:5904–5912.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bartkowiak K, Riethdorf S and Pantel K:
The interrelating dynamics of hypoxic tumor microenvironments and
cancer cell phenotypes in cancer metastasis. Cancer Microenviron.
5:59–72. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ke Q and Costa M: Hypoxia-inducible
factor-1 (HIF-1). Mol Pharmacol. 70:1469–1480. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zheng S, Chen X, Yin X and Zhang B:
Prognostic significance of HIF-1α expression in hepatocellular
carcinoma: a meta-analysis. PLoS One. 8:e657532013.
|
|
33
|
Csiki I, Yanagisawa K, Haruki N, et al:
Thioredoxin-1 modulates transcription of cyclooxygenase-2 via
hypoxia-inducible factor-1alpha in non-small cell lung cancer.
Cancer Res. 66:143–150. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Kaidi A, Qualtrough D, Williams AC and
Paraskeva C: Direct transcriptional up-regulation of
cyclooxygenase-2 by hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF)-1 promotes
colorectal tumor cell survival and enhances HIF-1 transcriptional
activity during hypoxia. Cancer Res. 66:6683–6691. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Dai C, Gao Q, Qiu S, et al:
Hypoxia-inducible factor-1 alpha, in association with inflammation,
angiogenesis and MYC, is a critical prognostic factor in patients
with HCC after surgery. BMC Cancer. 9:4182009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Jung JE, Lee HG, Cho IH, et al: STAT3 is a
potential modulator of HIF-1-mediated VEGF expression in human
renal carcinoma cells. FASEB J. 19:1296–1298. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Wang M, Tan J, Coffey A, Fehrenbacher J,
Weil BR and Meldrum DR: Signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3-stimulated hypoxia inducible factor-1 alpha
mediates estrogen receptor-alpha-induced mesenchymal stem cell
vascular endothelial growth factor production. J Thorac Cardiovasc
Surg. 138:163–171. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
38
|
Cascio S, D’Andrea A, Ferla R, et al:
miR-20b modulates VEGF expression by targeting HIF-1 alpha and
STAT3 in MCF-7 breast cancer cells. J Cell Physiol. 224:242–249.
2010.PubMed/NCBI
|