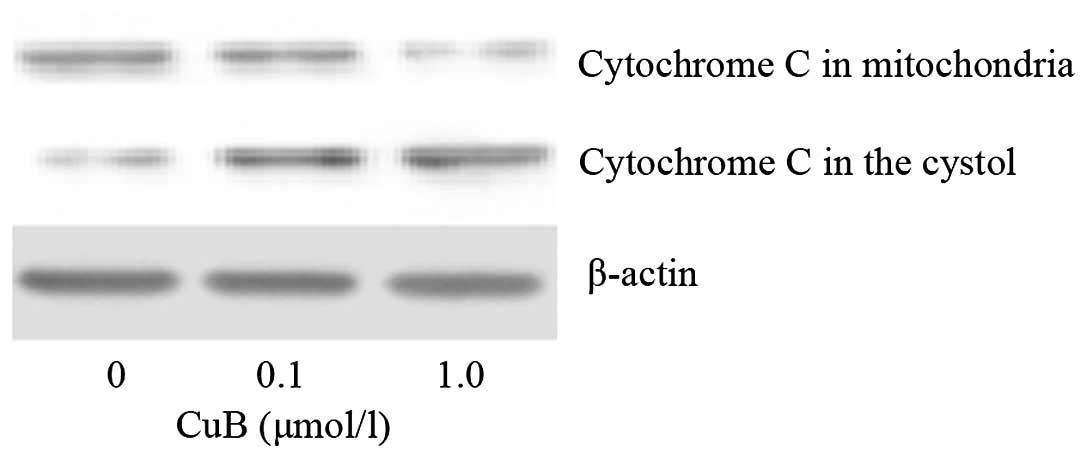
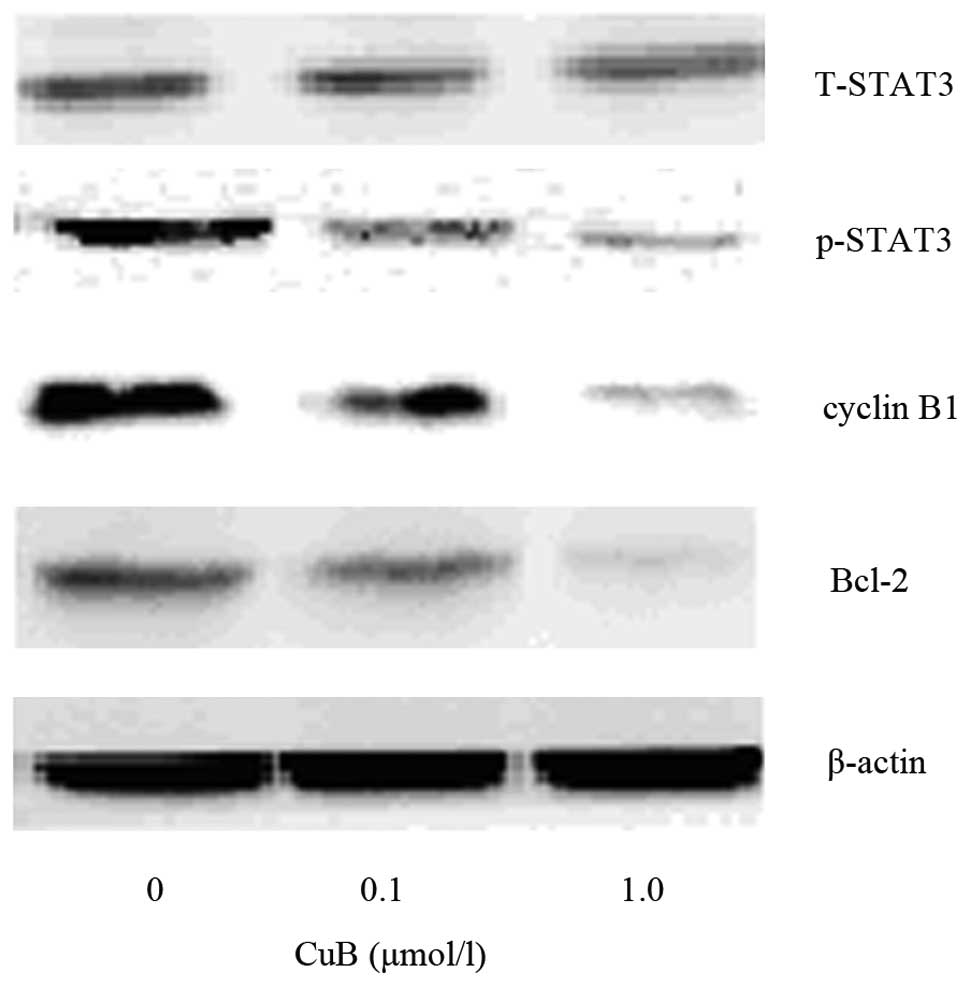
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, et al: Global
cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin. 61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Schiller JH, Harrington D, Belani CP, et
al: Comparison of four chemotherapy regimens for advanced
non-small-cell lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 346:92–98. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Zhang Y, Zhang GB, Xu XM, et al:
Suppression of growth of A549 lung cancer cells by waltonitone and
its mechanisms of action. Oncol Rep. 28:1029–1035. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Reyes-Zurita FJ, Rufino-Palomares EE,
Lupiañez JA and Cascante M: Maslinic acid, a natural triterpene
from Olea europaea L., induces apoptosis in HT29 human
colon-cancer cells via the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway. Cancer
Lett. 273:44–54. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Liu T, Zhang M, Zhang H, et al: Combined
antitumor activity of cucurbitacin B and docetaxel in laryngeal
cancer. Eur J Pharmacol. 587:78–84. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Jayaprakasam B, Seeram NP and Nair MG:
Anticancer and antiinflammatory activities of cucurbitacins from
Cucurbita andreana. Cancer Lett. 189:11–16. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kongtun S, Jiratchariyakul W, Kummalue T,
et al: Cytotoxic properties of root extract and fruit juice of
Trichosanthes cucumerina. Planta Med. 75:839–842. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang M, Zhang H, Sun C, et al: Targeted
constitutive activation of signal transducer and activator of
transcription 3 in human hepatocellular carcinoma cells by
cucurbitacin B. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 63:635–642. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Hsu HF, Houng JY, Kuo CF, Tsao N and Wu
YC: Glossogin, a novel phenylpropanoid from Glossogyne
tenuifolia, induced apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells. Food
Chem Toxicol. 46:3785–3791. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Magesh V, Lee JC, Ahn KS, et al: Ocimum
sanctum induces apoptosis in A549 lung cancer cells and
suppresses the in vivo growth of Lewis lung carcinoma cells.
Phytother Res. 23:1385–1391. 2009. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Thoennissen NH, Iwanski GB, Doan NB, et
al: Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis by inhibition of the JAK/STAT
pathway and potentiates antiproliferative effects of gemcitabine on
pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res. 69:5876–5884. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Liu T, Zhang M, Zhang H, Sun C and Deng Y:
Inhibitory effects of cucurbitacin B on laryngeal squamous cell
carcinoma. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 265:1225–1232. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Chan KT, Meng FY, Li Q, et al:
Cucurbitacin B induces apoptosis and S phase cell cycle arrest in
BEL-7402 human hepatocellular carcinoma cells and is effective via
oral administration. Cancer Lett. 294:118–124. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Xu X, Zhang Y, Qu D, Jiang T and Li S:
Osthole induces G2/M arrest and apoptosis in lung cancer A549 cells
by modulating PI3K/Akt pathway. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 30:332011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Jackman M, Lindon C, Nigg EA and Pines J:
Active cyclin B1-Cdk1 first appears on centrosomes in prophase. Nat
Cell Biol. 5:143–148. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yasuda S, Yogosawa S, Izutani Y, et al:
Cucurbitacin B induces G2 arrest and apoptosis via a reactive
oxygen species-dependent mechanism in human colon adenocarcinoma
SW480 cells. Mol Nutr Food Res. 54:559–565. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yang L, Wu S, Zhang Q, Liu F and Wu P:
23,24-Dihydrocucurbitacin B induces G2/M cell-cycle arrest and
mitochondria-dependent apoptosis in human breast cancer cells
(Bcap37). Cancer Lett. 256:267–278. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Braun F, de Carne Trecesson S,
Bertin-Ciftci J and Juin P: Protect and serve: Bcl-2 proteins as
guardians and rulers of cancer cell survival. Cell Cycle.
12:2937–2947. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yang J, Liu X, Bhalla K, et al: Prevention
of apoptosis by Bcl-2: release of cytochrome C from mitochondria
blocked. Science. 275:1129–1132. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hu Y, Benedict MA, Ding L and Nuñez G:
Role of cytochrome C and dATP/ATP hydrolysis in Apaf-1-mediated
caspase-9 activation and apoptosis. EMBO J. 18:3586–3595. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Malladi S, Challa-Malladi M, Fearnhead HO
and Bratton SB: The Apaf-1*procaspase-9 apoptosome
complex functions as a proteolytic-based molecular timer. EMBO J.
28:1916–1925. 2009.
|
|
22
|
Inoue S, Browne G, Melino G and Cohen GM:
Ordering of caspases in cells undergoing apoptosis by the intrinsic
pathway. Cell Death Differ. 16:1053–1061. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Niu G, Wright KL, Huang M, et al:
Constitutive Stat3 activity up-regulates VEGF expression and tumor
angiogenesis. Oncogene. 21:2000–2008. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Diaz N, Minton S, Cox C, et al: Activation
of stat3 in primary tumors from high-risk breast cancer patients is
associated with elevated levels of activated SRC and survivin
expression. Clin Cancer Res. 12:20–28. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Yeh HH, Chang WT, Lu KC, et al:
Upregulation of tissue factor by activated Stat3 contributes to
malignant pleural effusion generation via enhancing tumor
metastasis and vascular permeability in lung adenocarcinoma. PLoS
One. 8:e752872013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Chan KS, Sano S, Kiguchi K, et al:
Disruption of Stat3 reveals a critical role in both the initiation
and the promotion stages of epithelial carcinogenesis. J Clin
Invest. 114:720–728. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Yu H and Jove R: The STATs of cancer - new
molecular targets come of age. Nat Rev Cancer. 4:97–105. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|