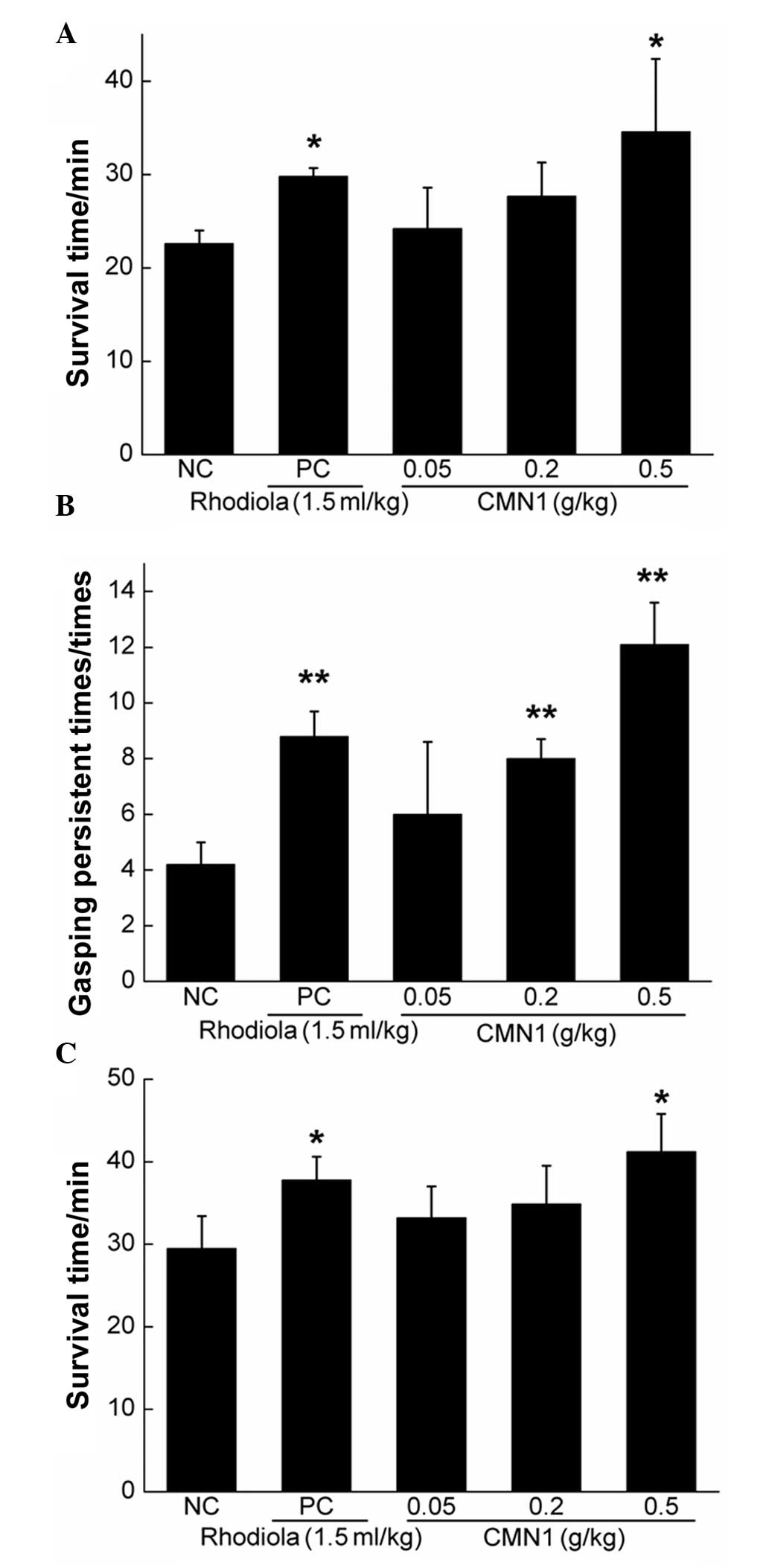
|
1
|
Cueto-Martin B, De La Cruz-Marquez J and
Garcia-Torres L: Effect of altitude in the blood pressure
regulation system (renin-angiotensin-aldosterone) in team sports.
Case study: Female volleyball. Med Sport. 52:261–269. 1999.(In
Italian).
|
|
2
|
Fiore D, Hall S and Shoja P: Altitude
illness: risk factors, prevention, presentation, and treatment. Am
Fam Physician. 82:1103–1110. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang J, Ke T, Zhang X, et al: Effects of
acetazolamide on cognitive performance during high-altitude
exposure. Neurotoxicol Teratol. 35:28–33. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Fagenholz PJ, Gutman JA, Murray AF and
Harris NS: Treatment of high altitude pulmonary edema at 4240 m in
Nepal. High Alt Med Biol. 8:139–146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Li X, Mitchell J, Wood S, Coen C, Lightman
S and O’Byrne K: The effect of oestradiol and progesterone on
hypoglycaemic stress-induced suppression of pulsatile luteinizing
hormone release and on corticotropin-releasing hormone mRNA
expression in the rat. J Neuroendocrinol. 15:468–476. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Kim CS, Lee SY, Cho SH, et al: Cordyceps
militaris induces the IL-18 expression via its promoter activation
for IFN-gamma production. J Ethnopharmacol. 120:366–371. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Rao YK, Fang SH, Wu WS and Tzeng YM:
Constituents isolated from Cordyceps militaris suppress enhanced
inflammatory mediator’s production and human cancer cell
proliferation. J Ethnopharmacol. 131:363–367. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Paterson RR: Cordyceps: a traditional
Chinese medicine and another fungal therapeutic biofactory?
Phytochemistry. 69:1469–1495. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zhang G, Huang Y, Bian Y, Wong JH, Ng TB
and Wang H: Hypoglycemic activity of the fungi Cordyceps militaris,
Cordyceps sinensis, Tricholoma mongolicum, and Omphalia lapidescens
in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol.
72:1152–1156. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Cheng YW, Chen YI, Tzeng CY, et al:
Extracts of Cordyceps militaris lower blood glucose via the
stimulation of cholinergic activation and insulin secretion in
normal rats. Phytother Res. 26:1173–1177. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Dong Y, Jing T, Meng Q, Liu C, Hu S, Ma Y,
Liu Y, Lu J, Cheng Y, Wang D and Teng LR: Studies on the
anti-diabetic activities of Cordyceps militaris extract in
diet-streptozotocin-induced diabetic Sprague-Dawley rats. Biomed
Res Int. 2014.160980:2104(Epub ahead of print).
|
|
12
|
Methacanon P, Madla S, Kirtikara K and
Prasitsil M: Structural elucidation of bioactive fungi-derived
polymers. Carbohydr Polym. 60:199–203. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wu F, Yan H, Ma X, et al: Comparison of
the structural characterization and biological activity of acidic
polysaccharides from Cordyceps militaris cultured with different
media. World J Microbiol Biotechnol. 28:2029–2038. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Yu RM, Yang W, Song LY, Yan CY, Zhang Z
and Zhao Y: Structural characterization and antioxidant activity of
a polysaccharide from the fruiting bodies of cultured Cordyceps
militaris. Carbohydr Polym. 70:430–436. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Lee JS, Kwon JS, Won DP, et al: Study of
macrophage activation and structural characteristics of purified
polysaccharide from the fruiting body of Cordyceps militaris. J
Microbiol Biotechnol. 20:1053–1060. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Castilho LR, Mirchel DA and Freire DM:
Production of polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHAs) from waste materials and
by-products by submerged and solid-state fermentation. Bioresour
Technol. 100:5996–6009. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shih IL, Tsai KL and Hsieh C: Effects of
culture conditions on the mycelial growth and bioactive metabolite
production in submerged culture of Cordyceps militaris. Biochem Eng
J. 33:193–201. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Du L, Song J, Wang H, et al: Optimization
of the fermentation medium for Paecilomyces tenuipes N45 using
statistical approach. Afr J Microbiol Res. 6:6130–6141. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Dhanabal S, Kokate C, Ramanathan M, Kumar
E and Suresh B: Hypoglycaemic activity of Pterocarpus marsupium
Roxb. Phytother Res. 20:4–8. 2006. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yan H, Zhu D, Xu D, Wu J and Bian X: A
study on Cordyceps militaris polysaccharide purification,
composition and activity analysis. Afr J Biotechnol. 7:4004–4009.
2008.
|
|
21
|
Zhang Al, Lu JH, Zhang N, Zheng D, Zhang
GR and Teng LR: Extraction, purification and anti-tumor activity of
polysaccharide from mycelium of mutant Cordyceps militaris. Chem
Res Chin Univ. 26:798–802. 2010.(In Chinese).
|
|
22
|
Zhang N, Liu Y, Lu J, et al: Isolation,
purification and bioactivities of polysaccharides from Irpex
lacteus. Chem Res Chin Univ. 28:249–254. 2012.(In Chinese).
|
|
23
|
Cui H, Chen Y, Wang S, Kai G and Fang Y:
Isolation, partial characterisation and immunomodulatory activities
of polysaccharide from Morchella esculenta. J Sci Food Agric.
91:2180–2185. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Chambers RE and Clamp JR: An assessment of
methanolysis and other factors used in the analysis of
carbohydrate-containing materials. Biochem J. 125:1009–1018.
1971.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Xie J, Xie M, Nie S, Shen M, Wang Y and Li
C: Isolation, chemical composition and antioxidant activities of a
water-soluble polysaccharide from Cyclocarya paliurus (Batal.)
Iljinskaja. Food Chem. 119:1626–1632. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Linker A, Evans L and Impallomeni G: The
structure of a polysaccharide from infectious strains of
Burkholderia cepacia. Carbohydr Res. 335:45–54. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang CX and Dai ZR: Anti-hypoxia activity
of a polysaccharide extracted from the Sipunculus nudus L. Int J
Biol Macromol. 49:523–526. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Xie Y, Jiang SP, Su DH, Pi NN, Ma C and
Gao P: Composition analysis and anti-hypoxia activity of
polysaccharide from Brassica rapa L. Int J Biol Macromol.
47:528–533. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu D, Chen F, Guan C, Yang F and Qu Y:
Anti-hypoxia effect of adenovirus-mediated expression of heat shock
protein 70 (HSP70) on primary cultured neurons. J Neurosci Res.
91:1174–1182. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Cai Y, Lu Y, Chen R, Wei Q and Lu X:
Anti-hypoxia activity and related components of Rhodobryum
giganteum Par. Phytomedicine. 18:224–229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Fang X, Jiang B and Wang X: Purification
and partial characterization of an acidic polysaccharide with
complement fixing ability from the stems of Avicennia marina. J
Biochem Mol Biol. 39:546–555. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Santhiya D, Subramanian S and Natarajan K:
Surface chemical studies on sphalerite and galena using
extracellular polysaccharides isolated from Bacillus polymyxa. J
Colloid Interface Sci. 256:237–248. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Duh PD: Rebuttal on comparison of
protective effects between cultured Cordyceps militaris and natural
Cordyceps sinensis against oxidative damage. J Agric Food Chem.
55:7215–7216. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|