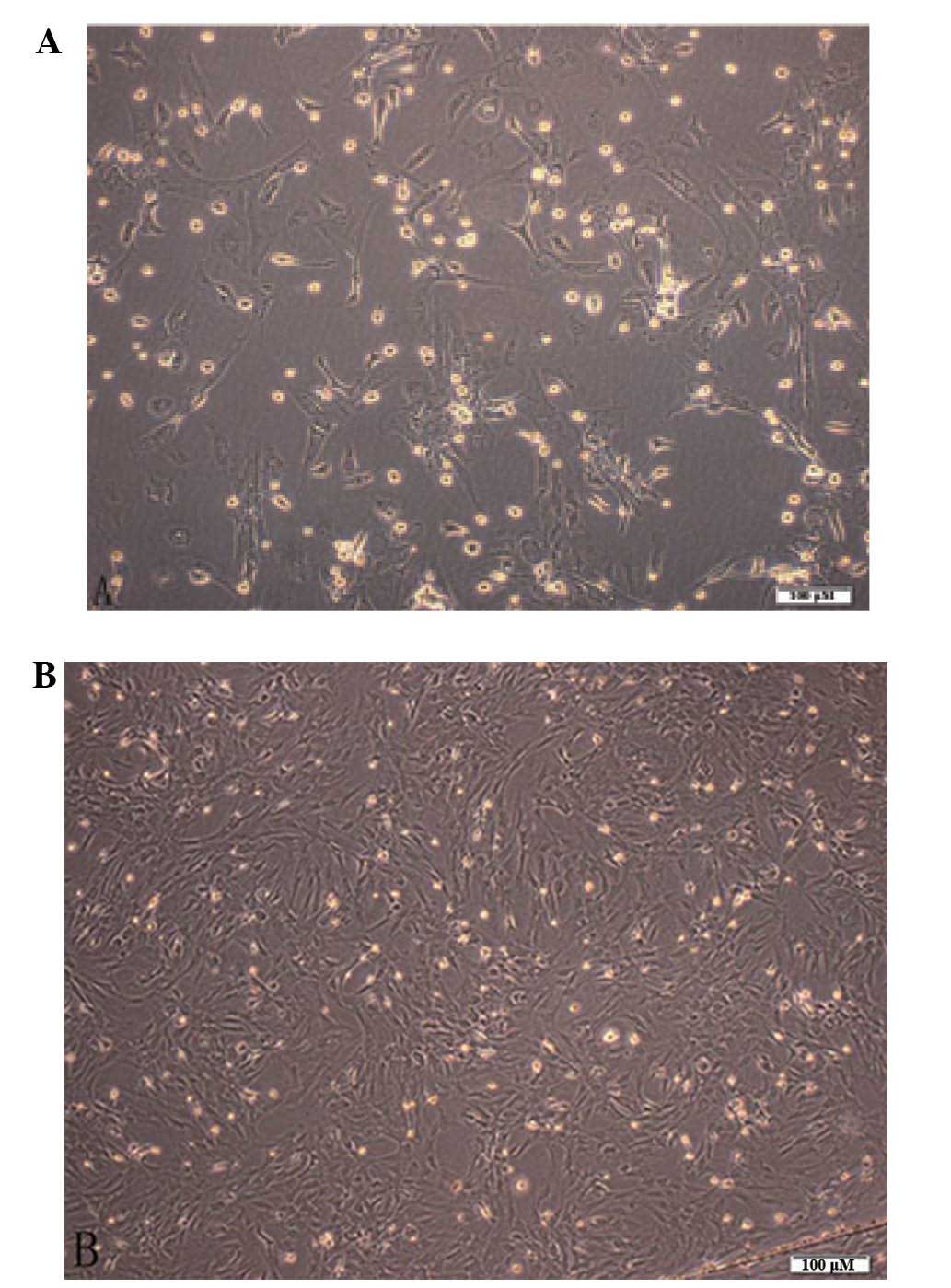
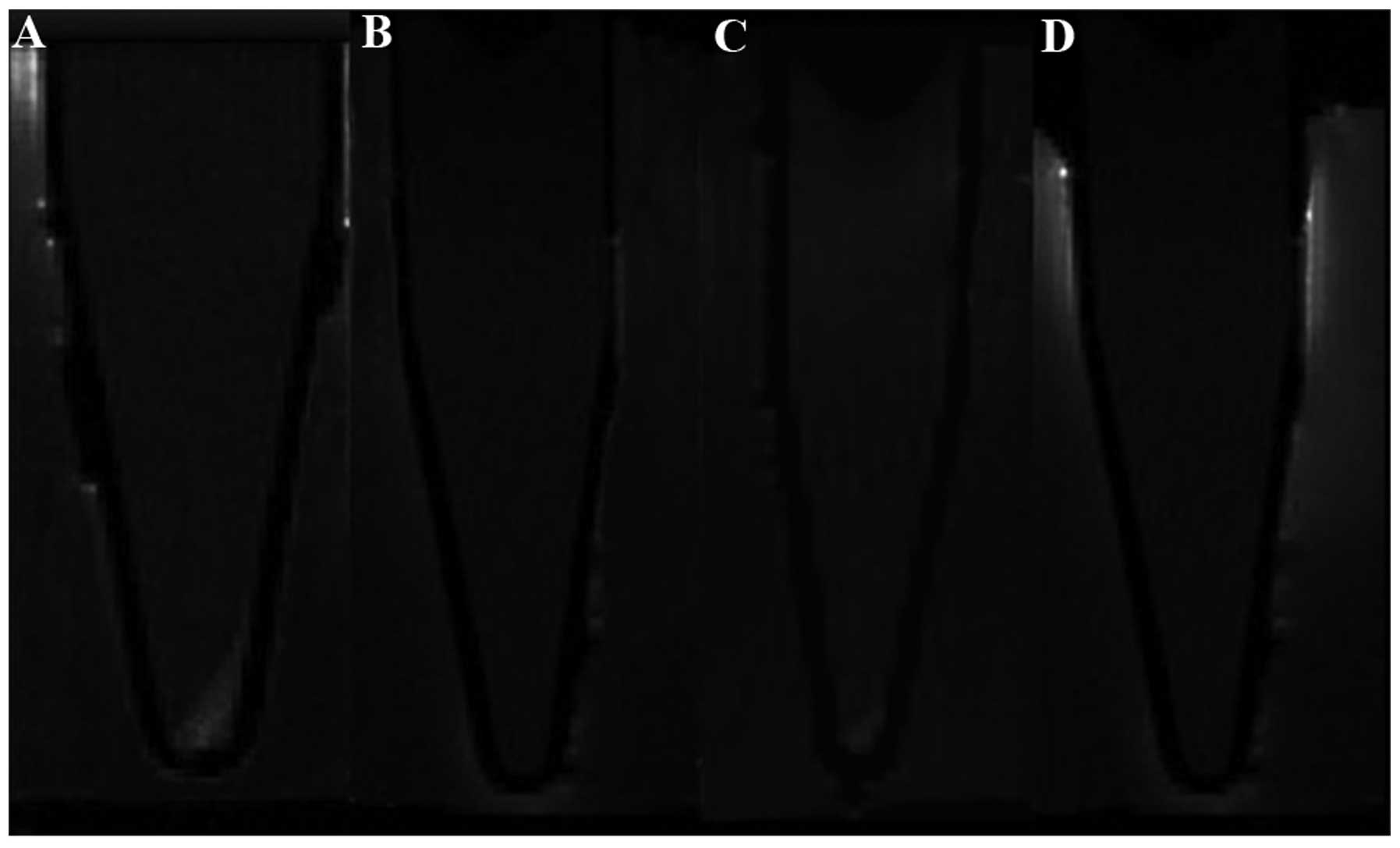
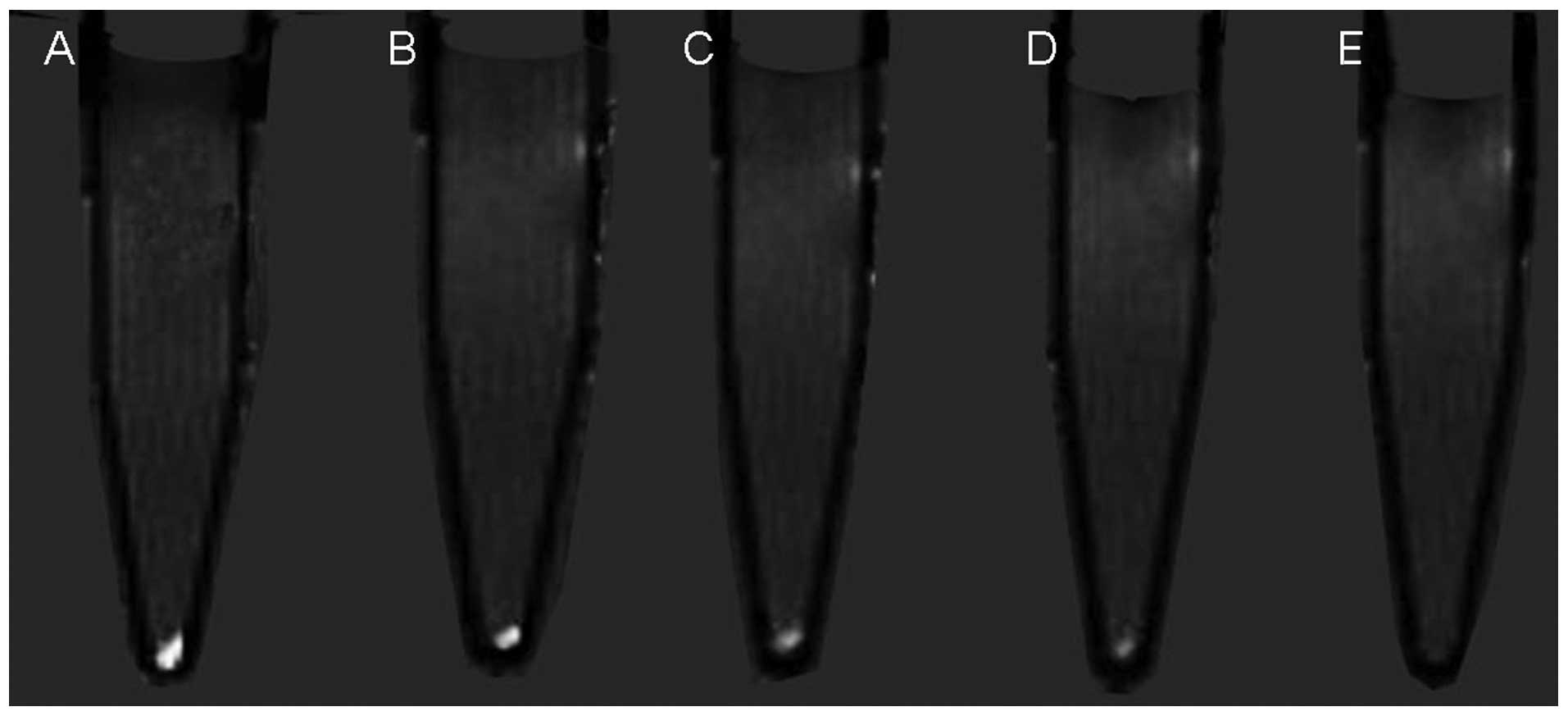
|
1
|
Eftekharpour E, Karimi-Abdolrezaee S and
Fehlings MG: Current status of experimental cell replacement
approaches to spinal cord injury. Neurosurg Focus. 24:E192008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhang ZG, Jiang Q, Zhang R, et al:
Magnetic resonance imaging and neurosphere therapy of stroke in
rat. Ann Neurol. 53:259–263. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Walczak P and Bulte JW: The role of
noninvasive cellular imaging in developing cell-based therapies for
neurodegenerative disorders. Neurodegener Dis. 4:306–313. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Kurozumi K, Nakamura K, Tamiya T, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells that produce neurotrophic factors reduce
ischemic damage in the rat middle cerebral artery occlusion model.
Mol Ther. 11:96–104. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Satake K, Lou J and Lenke LG: Migration of
mesenchymal stem cells through cerebrospinal fluid into injured
spinal cord tissue. Spine (Phila Pa). 1976. 29:1971–1979. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Liu Y, He ZJ, Xu B, et al: Evaluation of
cell tracking effects for transplanted mesenchymal stem cells with
jetPEI/Gd-DTPA complexes in animal models of hemorrhagic spinal
cord injury. Brain Res. 1391:24–35. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Frank J, Anderson S, Kalsih H, et al:
Methods for magnetically labeling stem and other cells for
detection by in vivo magnetic resonance imaging. Cytotherapy.
6:621–625. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Modo M, Hoehn M and Bulte J: Cellular MR
imaging. Mol Imaging. 4:143–164. 2004.
|
|
9
|
Bulte J, Zhang SC, Van Gelderen P, et al:
Neurotransplantation of magnetically labeled oligodendrocyte
progenitors: magnetic resonance tracking of cell migration and
myelination. Proceedings of the Natl Acad Sci USA. 96:15256–15261.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Josephson L, Tung C-H, Moore A and
Weissleder R: High-efficiency intracellular magnetic labeling with
novel superparamagnetic-Tat peptide conjugates. Bioconj Chem.
10:186–191. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Meincke M, Schlorf T, Kossel E, Jansen O,
Glueer CC and Mentlein R: Iron oxide-loaded liposomes for MR
imaging. Front Biosci. 13:40022008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Ris F, Lepetit-Coiffe M, Meda P, et al:
Assessment of human islet labeling with clinical grade iron
nanoparticles prior to transplantation for graft monitoring by MRI.
Cell Transplant. 19:1573–1585. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Arbab AS, Liu W and Frank JA: Cellular
magnetic resonance imaging: current status and future prospects.
Expert Rev Med Devices. 3:427–439. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu YL, Ye Q, Foley LM, et al: In situ
labeling of immune cells with iron oxide particles: an approach to
detect organ rejection by cellular MRI. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
103:1852–1857. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Schafer R, Ayturan M, Bantleon R, et al:
The use of clinically approved small particles of iron oxide (SPIO)
for labeling of mesenchymal stem cells aggravates clinical symptoms
in experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis and influences their
in vivo distribution. Cell Transplant. 17:923–941. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
So PW, Kalber T, Hunt D, et al: Efficient
and rapid labeling of transplanted cell populations with
superparamagnetic iron oxide nanoparticles using cell surface
chemical biotinylation for in vivo monitoring by MRI. Cell
Transplant. 19:419–429. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Suzuki Y, Zhang S, Kundu P, Yeung AC,
Robbins RC and Yang PC: In vitro comparison of the biological
effects of three transfection methods for magnetically labeling
mouse embryonic stem cells with ferumoxides. Magn Reson Med.
57:1173–1179. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
van Tiel ST, Wielopolski PA, Houston GC,
Krestin GP and Bernsen MR: Variations in labeling protocol
influence incorporation, distribution and retention of iron oxide
nanoparticles into human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Contrast
Media Mol Imaging. 5:247–257. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Jara H, Yu B, Caruthers S, Melhem E and
Yucel E: Voxel sensitivity function description of flow-induced
signal loss in MR imaging: Implications for black-blood MR
angiography with turbo spin-echo sequences. Magnetic Reson Med.
41:575–590. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Reichenbach JR, Venkatesan R, Yablonskiy
DA, Thompson MR, Lai S and Haacke EM: Theory and application of
static field inhomogeneity effects in gradient-echo imaging.
Journal of Magn Reson Imaging. 7:266–279. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Van Den Bos EJ, Baks T, Moelker AD, et al:
Magnetic resonance imaging of haemorrhage within reperfused
myocardial infarcts: possible interference with iron oxide-labelled
cell tracking? Eur Heart J. 27:1620–1626. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Kraitchman DL, Gilson WD and Lorenz CH:
Stem cell therapy: MRI guidance and monitoring. J Magn Reson
Imaging. 27:299–310. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rudelius M, Daldrup-Link HE, Heinzmann U,
et al: Highly efficient paramagnetic labelling of embryonic and
neuronal stem cells. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging. 30:1038–1044.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Modo M, Cash D, Mellodew K, et al:
Tracking transplanted stem cell migration using bifunctional,
contrast agent-enhanced, magnetic resonance imaging. Neuroimage.
17:803–811. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Klasson A, Ahrén M, Hellqvist E, et al:
Positive MRI contrast enhancement in THP-1 cells with
Gd2O3 nanoparticles. Contrast Media Mol
Imaging. 3:106–111. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Sitharaman B, Tran LA, Pham QP, et al:
Gadofullerenes as nanoscale magnetic labels for cellular MRI.
Contrast Media Molr Imaging. 2:139–146. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Okamoto T, Aoyama T, Nakayama T, et al:
Clonal heterogeneity in differentiation potential of immortalized
human mesenchymal stem cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun.
295:354–361. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Shen J, Cheng LN, Zhong XM, Duan XH, Guo
RM and Hong GB: Efficient in vitro labeling rabbit neural stem cell
with paramagnetic Gd-DTPA and fluorescent substance. Eur J Radiol.
75:397–405. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
29
|
Denizot F and Lang R: Rapid colorimetric
assay for cell growth and survival: modifications to the
tetrazolium dye procedure giving improved sensitivity and
reliability. J Immunol Methods. 89:271–277. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Ward R, Wilmet S, Legssyer R and Crichton
R: The influence of iron homoeostasis on macrophage function.
Biochem Soc Trans. 30:762–765. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Engström M, Klasson A, Pedersen H,
Vahlberg C, Käll P-O and Uvdal K: High proton relaxivity for
gadolinium oxide nanoparticles. MAGMA. 19:180–186. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Gutiérrez-Fernández M, Rodríguez-Frutos B,
Alvarez-Grech J, et al: Functional recovery after hematic
administration of allogenic mesenchymal stem cells in acute
ischemic stroke in rats. Neuroscience. 175:394–405. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Cho H, Choi YK, Lee DH, et al: Effects of
magnetic nanoparticle-incorporated human bone marrow-derived
mesenchymal stem cells exposed to pulsed electromagnetic fields on
injured rat spinal cord. Biotechnolo Appl Biochem. 60:596–602.
2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Barry F and Murphy M: Mesenchymal stem
cells in joint disease and repair. Nat Rev Rheumatol. 9:584–594.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
van Velthoven CT, Sheldon RA, Kavelaars A,
et al: Mesenchymal stem cell transplantation attenuates brain
injury after neonatal stroke. Stroke. 44:1426–1432. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Guenoun J, Koning GA, Doeswijk G, et al:
Cationic Gd-DTPA liposomes for highly efficient labeling of
mesenchymal stem cells and cell tracking with MRI. Cell Transplant.
21:191–205. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
37
|
Sun R, Dittrich J, Le-Huu M, et al:
Physical and biological characterization of superparamagnetic iron
oxide-and ultrasmall superparamagnetic iron oxide-labeled cells: a
comparison. Invest Radiol. 40:504–513. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Hoehn M, Küstermann E, Blunk J, et al:
Monitoring of implanted stem cell migration in vivo: a highly
resolved in vivo magnetic resonance imaging investigation of
experimental stroke in rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 99:16267–16272.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Drey F, Choi Y, Neef K, et al: Noninvasive
in vivo tracking of mesenchymal stem cells and evaluation of cell
therapeutic effects in a murine model using a clinical 3.0 T MRI.
Cell Transplant. 22:1971–1980. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Crichton RR, Wilmet S, Legssyer R and Ward
RJ: Molecular and cellular mechanisms of iron homeostasis and
toxicity in mammalian cells. J Inorg Biochem. 91:9–18. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Rosenberg JT, Sellgren KL, Sachi-Kocher A,
et al: Magnetic resonance contrast and biological effects of
intracellular superparamagnetic iron oxides on human mesenchymal
stem cells with long-term culture and hypoxic exposure.
Cytotherapy. 15:307–322. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
van den Bos EJ, Wagner A, Mahrholdt H, et
al: Improved efficacy of stem cell labeling for magnetic resonance
imaging studies by the use of cationic liposomes. Cell Transplant.
12:743–756. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Daldrup-Link HE, Rudelius M, Oostendorp
RA, et al: Targeting of Hematopoietic Progenitor Cells with MR
Contrast Agents. Radiology. 228:760–767. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Shyu W-C, Chen C-P, Lin S-Z, Lee Y-J and
Li H: Efficient tracking of non-iron-labeled mesenchymal stem cells
with serial MRI in chronic stroke rats. Stroke. 38:367–374. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
45
|
Kim T, Momin E, Choi J, et al: Mesoporous
silica-coated hollow manganese oxide nanoparticles as positive T 1
contrast agents for labeling and MRI tracking of adipose-derived
mesenchymal stem cells. J Am Chem Soc. 133:2955–2961. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|