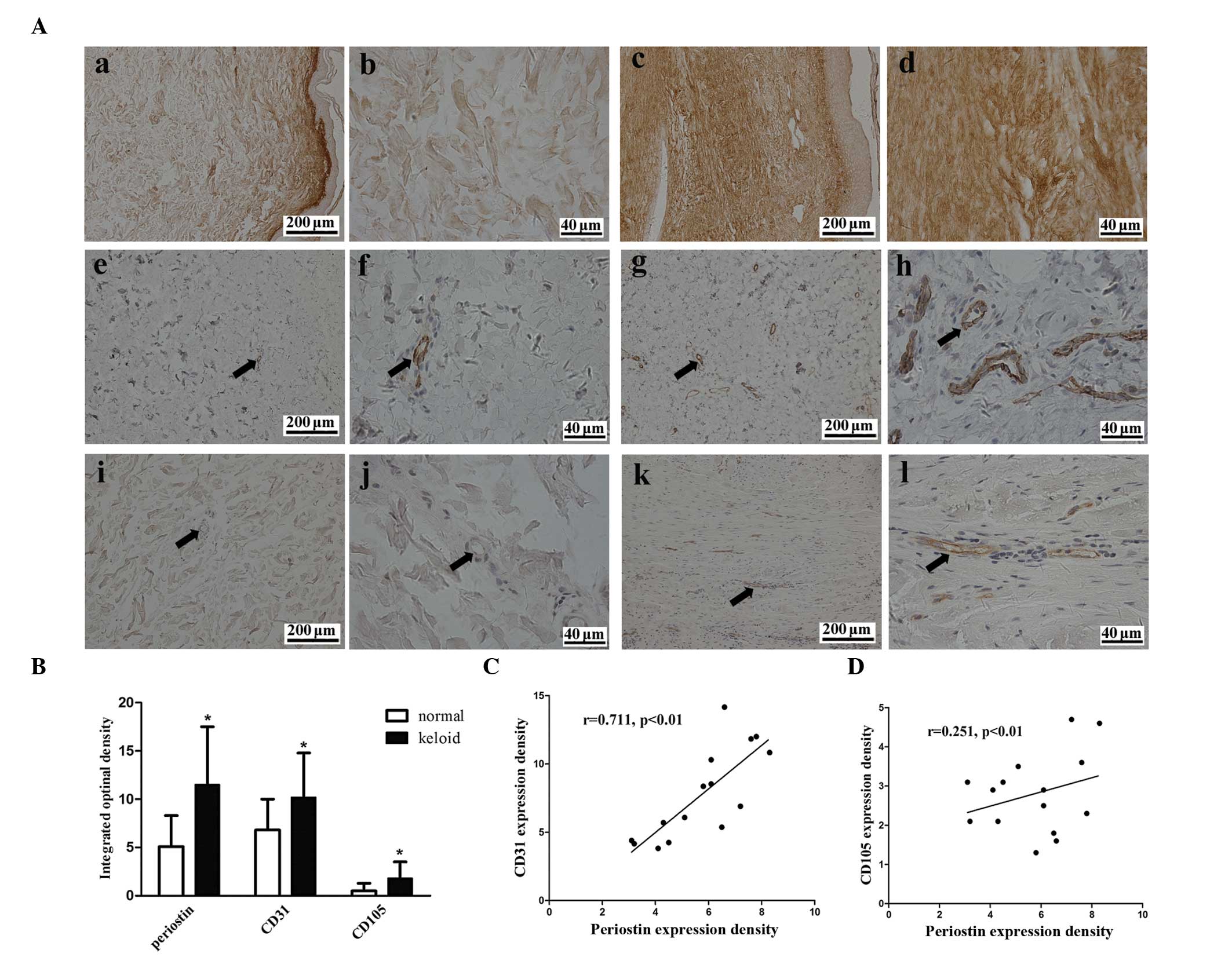
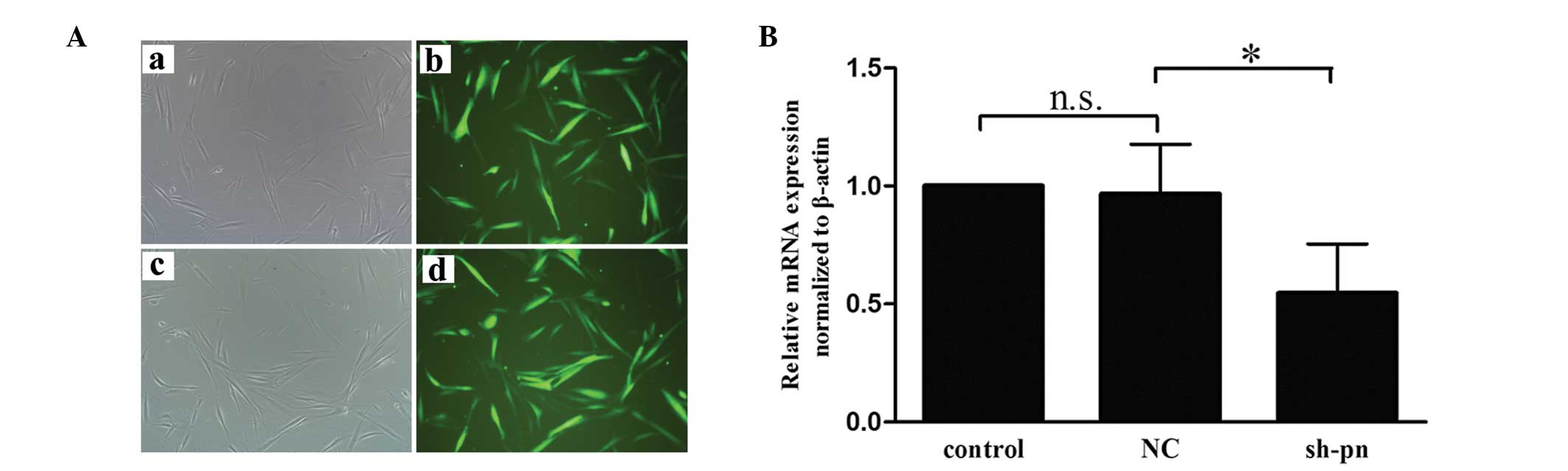
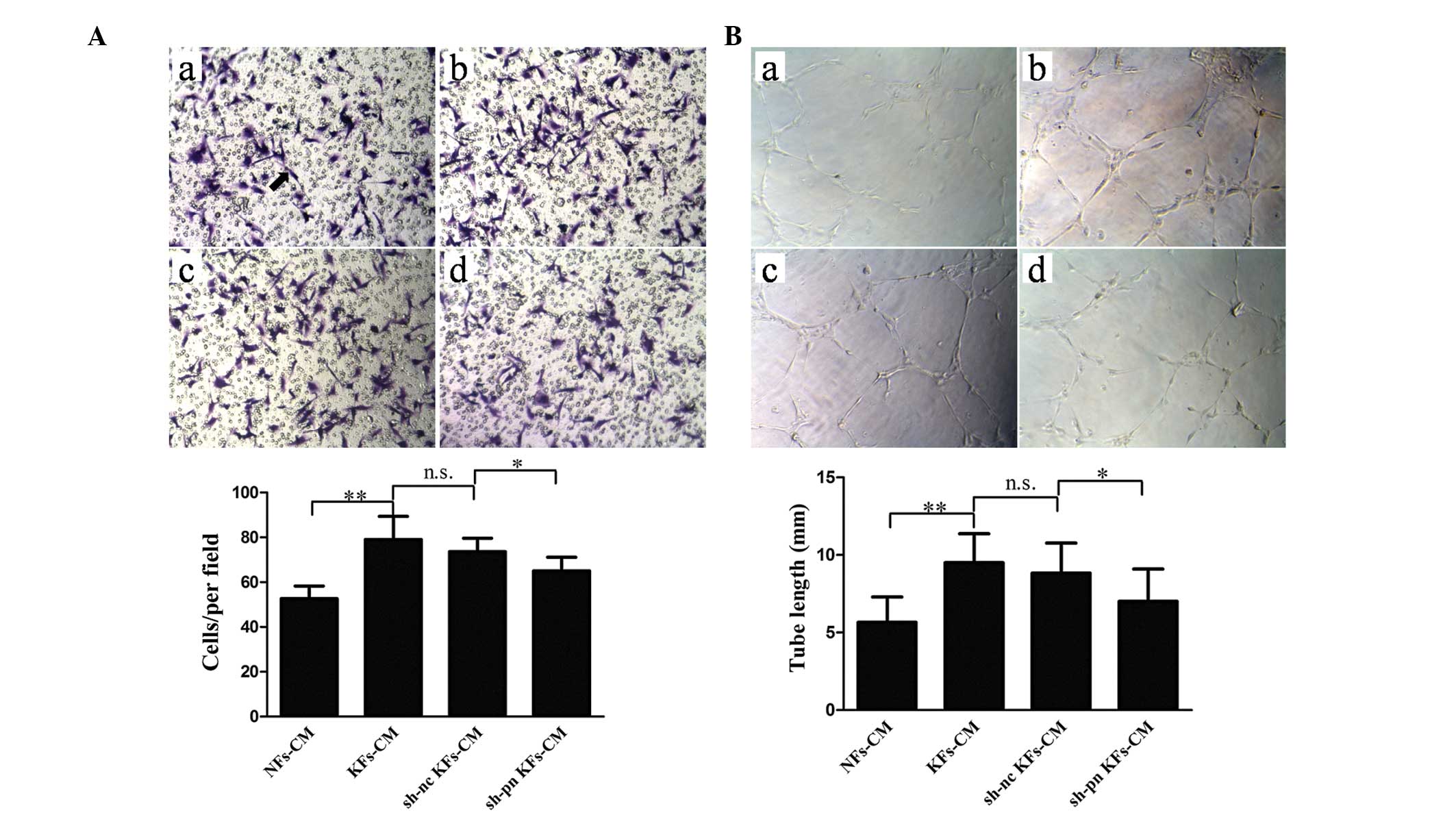
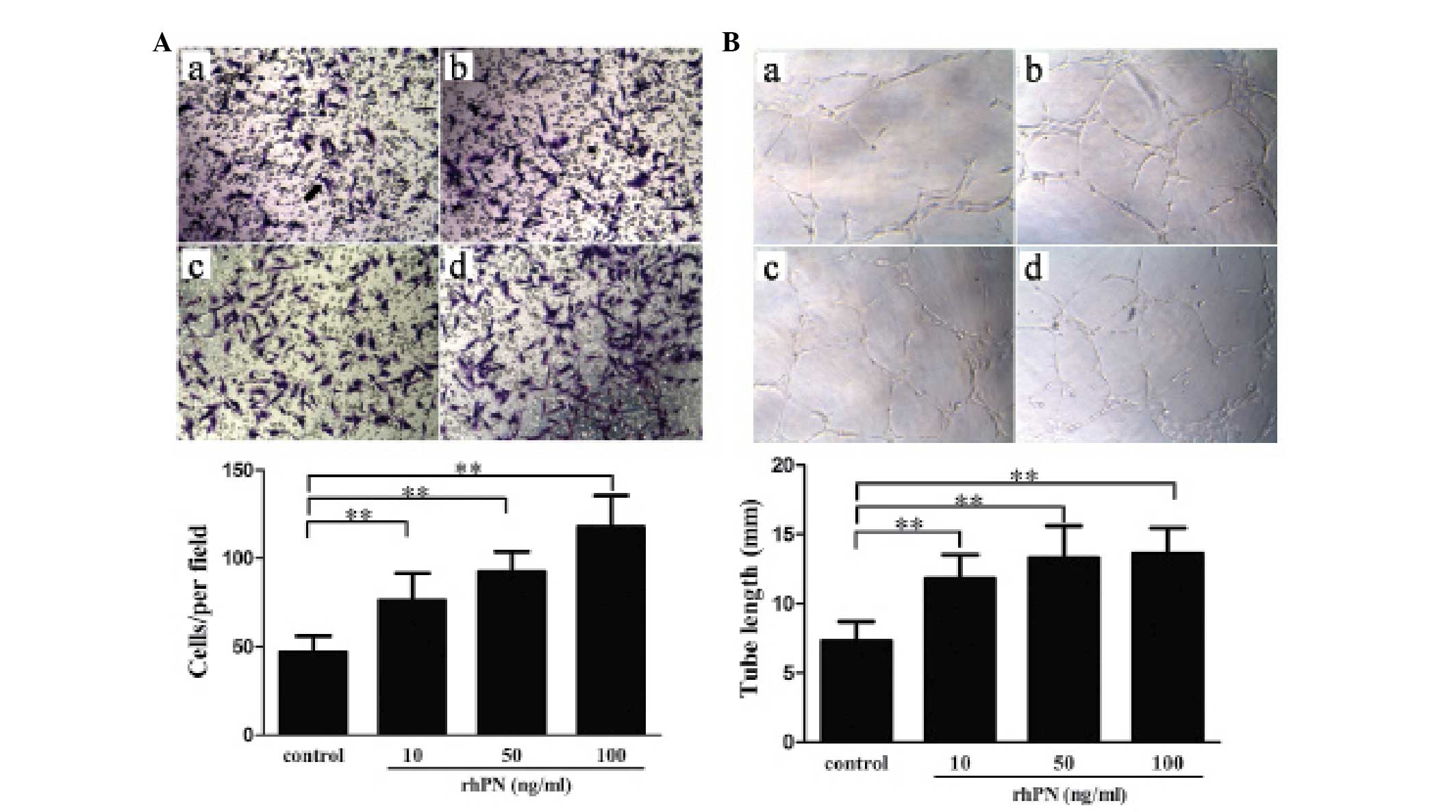
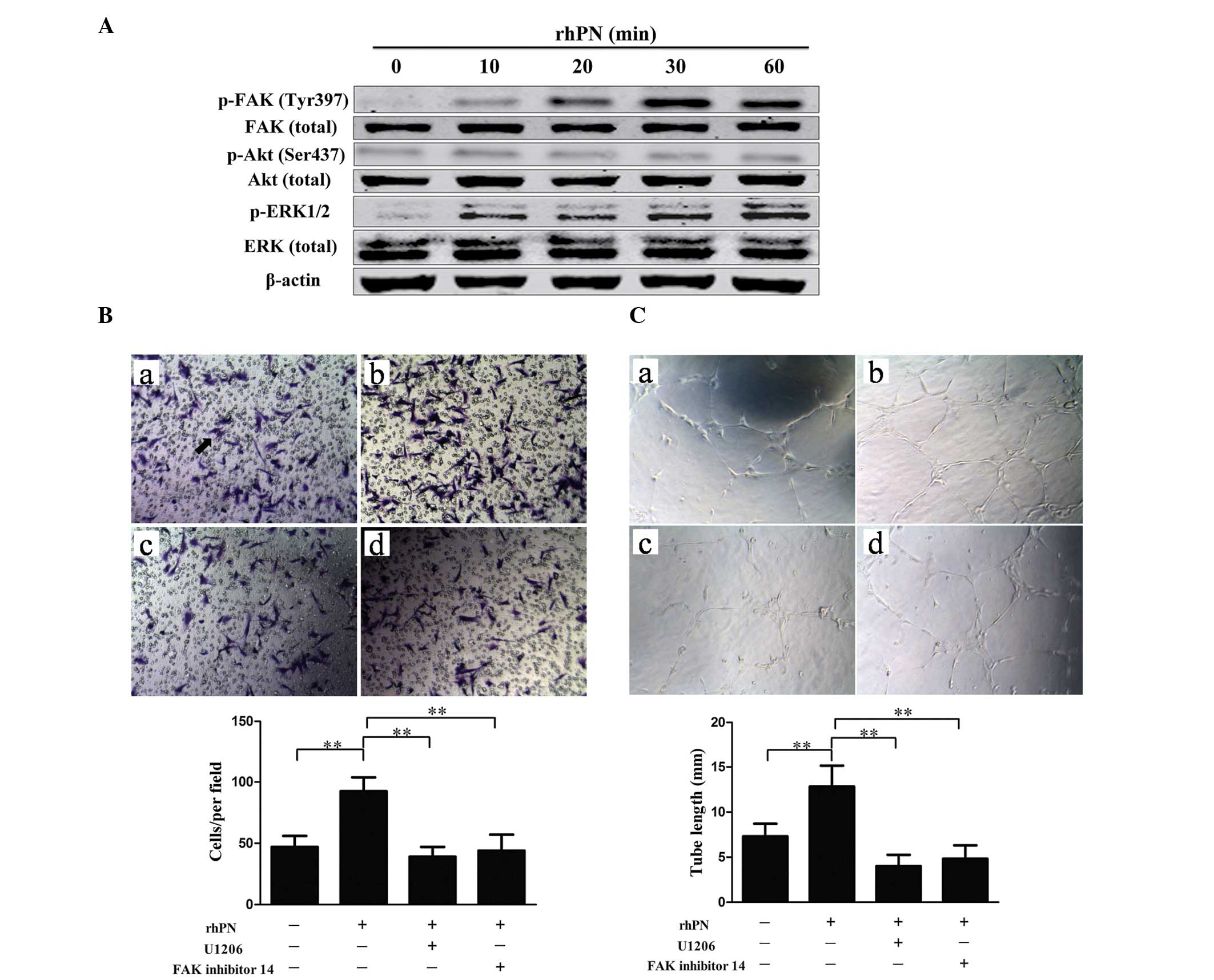
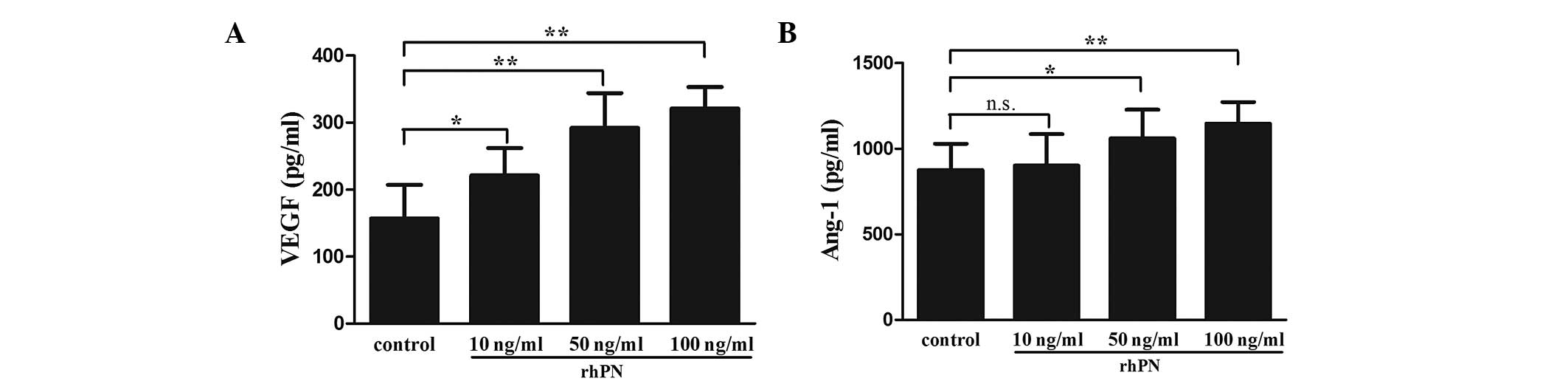
|
1
|
Bran GM, Goessler UR, Hormann K, Riedel F
and Sadick H: Keloids: Current concepts of pathogenesis (Review).
Int J Mol Med. 24:283–293. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Alster TS and Tanzi EL: Hypertrophic scars
and keloids: etiology and management. Am J Clin Dermatol.
4:235–243. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Love PB and Kundu RV: Keloids: an update
on medical and surgical treatments. J Drugs Dermatol. 12:403–409.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ishiko T, Naitoh M, Kubota H, et al:
Chondroitinase injection improves keloid pathology by reorganizing
the extracellular matrix with regenerated elastic fibers. J
Dermatol. 40:380–383. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Fujiwara M, Muragaki Y and Ooshima A:
Upregulation of transforming growth factor-beta1 and vascular
endothelial growth factor in cultured keloid fibroblasts: relevance
to angiogenic activity. Arch Dermatol Res. 297:161–169. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bux S and Madaree A: Keloids show regional
distribution of proliferative and degenerate connective tissue
elements. Cells Tissues Organs. 191:213–234. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Gira AK, Brown LF, Washington CV, Cohen C
and Arbiser JL: Keloids demonstrate high-level epidermal expression
of vascular endothelial growth factor. J Am Acad Dermatol.
50:850–853. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Trompezinski S, Pernet I and Mayoux C:
Transforming growth factor-beta1 and ultraviolet A1 radiation
increase production of vascular endothelial growth factor but not
endothelin-1 in human dermal fibroblasts. Br J Dermatol.
143:539–545. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Mogili NS, Krishnaswamy VR, Jayaraman M,
Rajaram R, Venkatraman A and Korrapati PS: Altered angiogenic
balance in keloids: a key to therapeutic intervention. Transl Res.
159:182–189. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Syed F and Bayat A: Notch signaling
pathway in keloid disease: enhanced fibroblast activity in a
Jagged-1 peptide-dependent manner in lesional vs. extralesional
fibroblasts. Wound Repair Regen. 20:688–706. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Song ZH and Qin ZL: Expression of
periostin and the effect of hydrocortisone on it in human
fibroblasts of scar. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 40:301–305. 2008.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Norris RA, Damon B, Mironov V, et al:
Periostin regulates collagen fibrillogenesis and the biomechanical
properties of connective tissues. J Cell Biochem. 101:695–711.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ruan K, Bao S and Ouyang G: The
multifaceted role of periostin in tumorigenesis. Cell Mol Life Sci.
66:2219–2230. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wu SQ, Lv YE, Lin BH, et al: Silencing of
periostin inhibits nicotine-mediated tumor cell growth and
epithelial-mesenchymal transition in lung cancer cells. Mol Med
Rep. 7:875–880. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Elliott CG, Wang J, Guo X, et al:
Periostin modulates myofibroblast differentiation during
full-thickness cutaneous wound repair. J Cell Sci. 125:121–132.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Zhu M, Fejzo MS, Anderson L, et al:
Periostin promotes ovarian cancer angiogenesis and metastasis.
Gynecol Oncol. 119:337–344. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Qiu F, Shi CH, Zheng J and Liu YB:
Periostin mediates the increased pro-angiogenic activity of gastric
cancer cells under hypoxic conditions. J Biochem Mol Toxicol.
27:364–369. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Shao R, Bao S, Bai X, et al: Acquired
expression of periostin by human breast cancers promotes tumor
angiogenesis through up-regulation of vascular endothelial growth
factor receptor 2 expression. Mol Cell Biol. 24:3992–4003. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Beer TW, Baldwin HC, Goddard JR, Gallagher
PJ and Wright DH: Angiogenesis in pathological and surgical scars.
Hum Pathol. 29:1273–1278. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Liu C, Song ZH and Qin ZL: Construction of
periostin shRNA vectors and their effects on the expression of
periostin in fibroblasts. Beijing Da Xue Xue Bao. 42:503–508.
2010.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Vincent AS, Phan TT, Mukhopadhyay A, Lim
HY, Halliwell B and Wong KP: Human skin keloid fibroblasts display
bioenergetics of cancer cells. J Invest Dermatol. 128:702–709.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Niessen FB, Spauwen PH, Schalkwijk J and
Kon M: On the nature of hypertrophic scars and keloids: a review.
Plast Reconstr Surg. 104:1435–1458. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Oh CK, Kwon YW, Kim YS, Jang HS and Kwon
KS: Expression of basic fibroblast growth factor, vascular
endothelial growth factor, and thrombospondin-1 related to
microvessel density in nonaggressive and aggressive basal cell
carcinomas. J Dermatol. 30:306–313. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Amadeu T, Braune A, Mandarim-de-Lacerda C,
Porto LC, Desmouliere A and Costa A: Vascularization pattern in
hypertrophic scars and keloids: a stereological analysis. Pathol
Res Pract. 199:469–473. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Appleton I, Brown NJ and Willoughby DA:
Apoptosis, necrosis, and proliferation: possible implications in
the etiology of keloids. Am J Pathol. 149:1441–1447.
1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Takanami I, Abiko T and Koizumi S:
Expression of periostin in patients with non-small cell lung
cancer: correlation with angiogenesis and lymphangiogenesis. Int J
Biol Markers. 23:182–186. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Orecchia P, Conte R, Balza E, et al:
Identification of a novel cell binding site of periostin involved
in tumour growth. Eur J Cancer. 47:2221–2229. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Powazniak Y, Kempfer AC, de la Paz
Dominguez M, et al: Effect of estradiol, progesterone and
testosterone on apoptosis- and proliferation-induced MAPK signaling
in human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Med Rep. 2:441–447.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Esfahanian N, Shakiba Y, Nikbin B, et al:
Effect of metformin on the proliferation, migration, and MMP-2 and
-9 expression of human umbilical vein endothelial cells. Mol Med
Rep. 5:1068–1074. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Baek YY, Cho DH, Choe J, et al:
Extracellular taurine induces angiogenesis by activating ERK-,
Akt-, and FAK-dependent signal pathways. Eur J Pharmacol.
674:188–199. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Eichmann A and Simons M: VEGF signaling
inside vascular endothelial cells and beyond. Curr Opin Cell Biol.
24:188–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Koh GY: Orchestral actions of
angiopoietin-1 in vascular regeneration. Trends Mol Med. 19:31–39.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Lv Y, Wang W, Jia WD, et al: High
preoparative levels of serum periostin are associated with poor
prognosis in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma after
hepatectomy. Eur J Surg Oncol. 39:1129–1135. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Ben QW, Zhao Z, Ge SF, Zhou J, Yuan F and
Yuan YZ: Circulating levels of periostin may help identify patients
with more aggressive colorectal cancer. Int J Oncol. 34:821–828.
2009.PubMed/NCBI
|