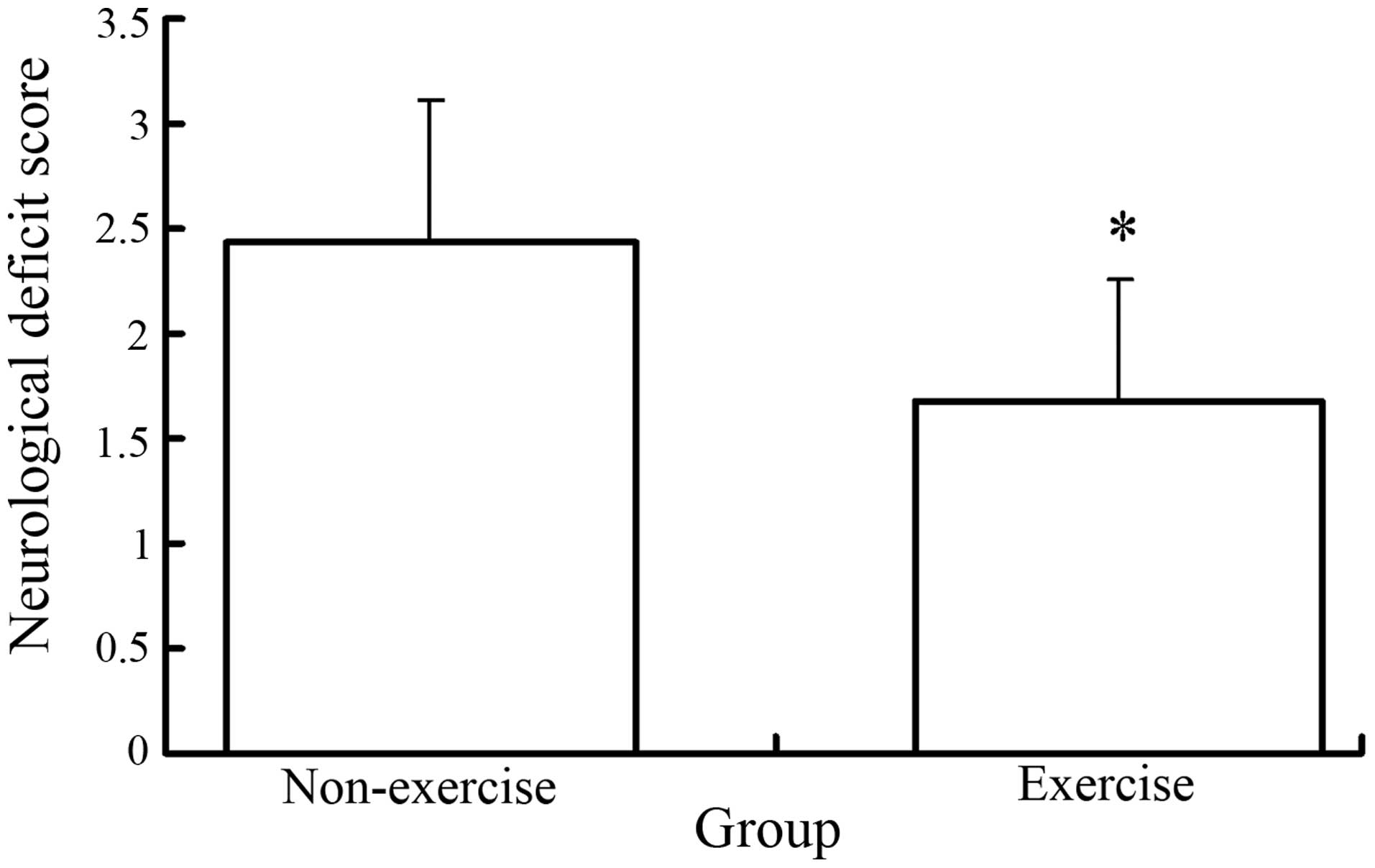
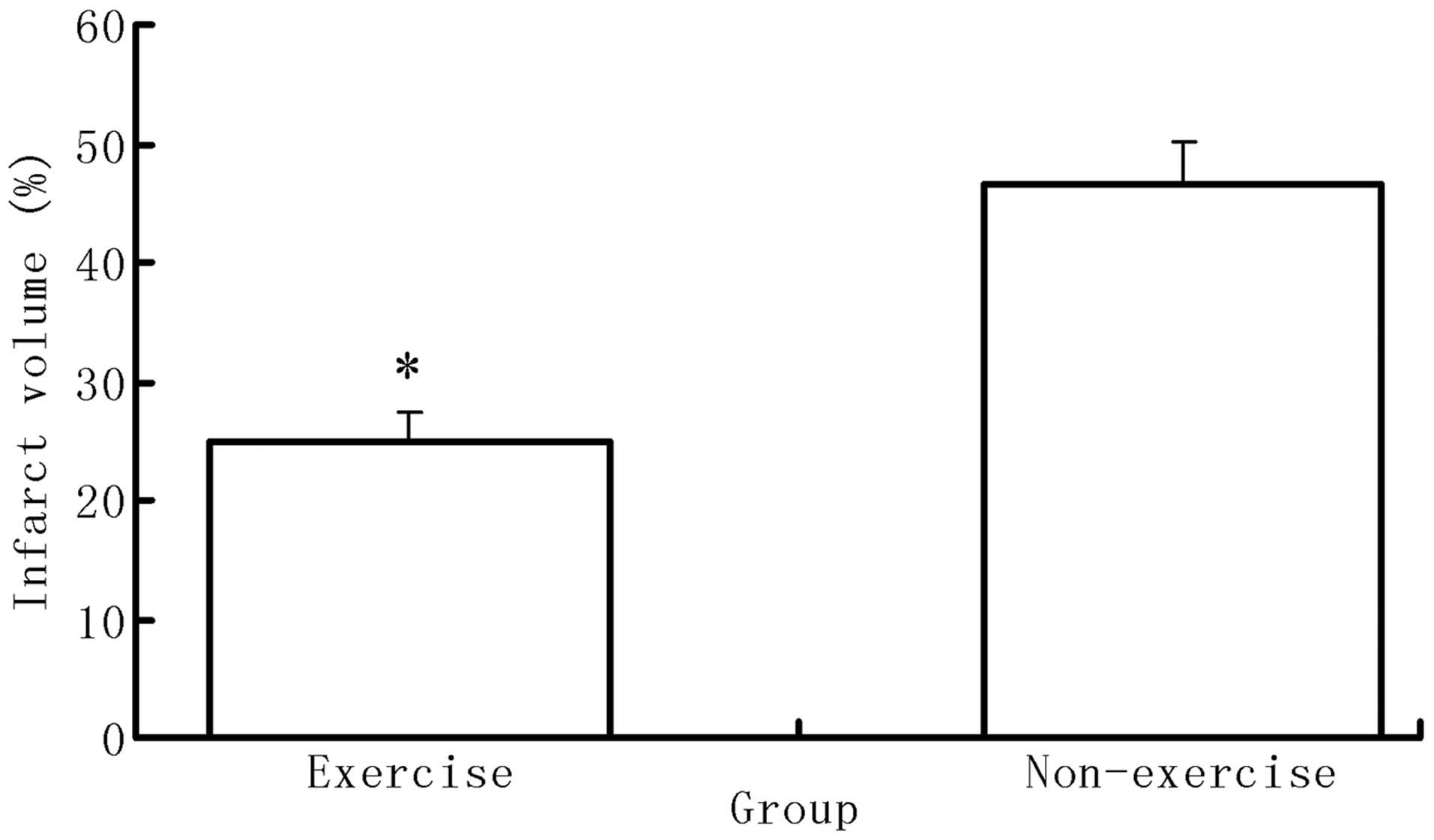
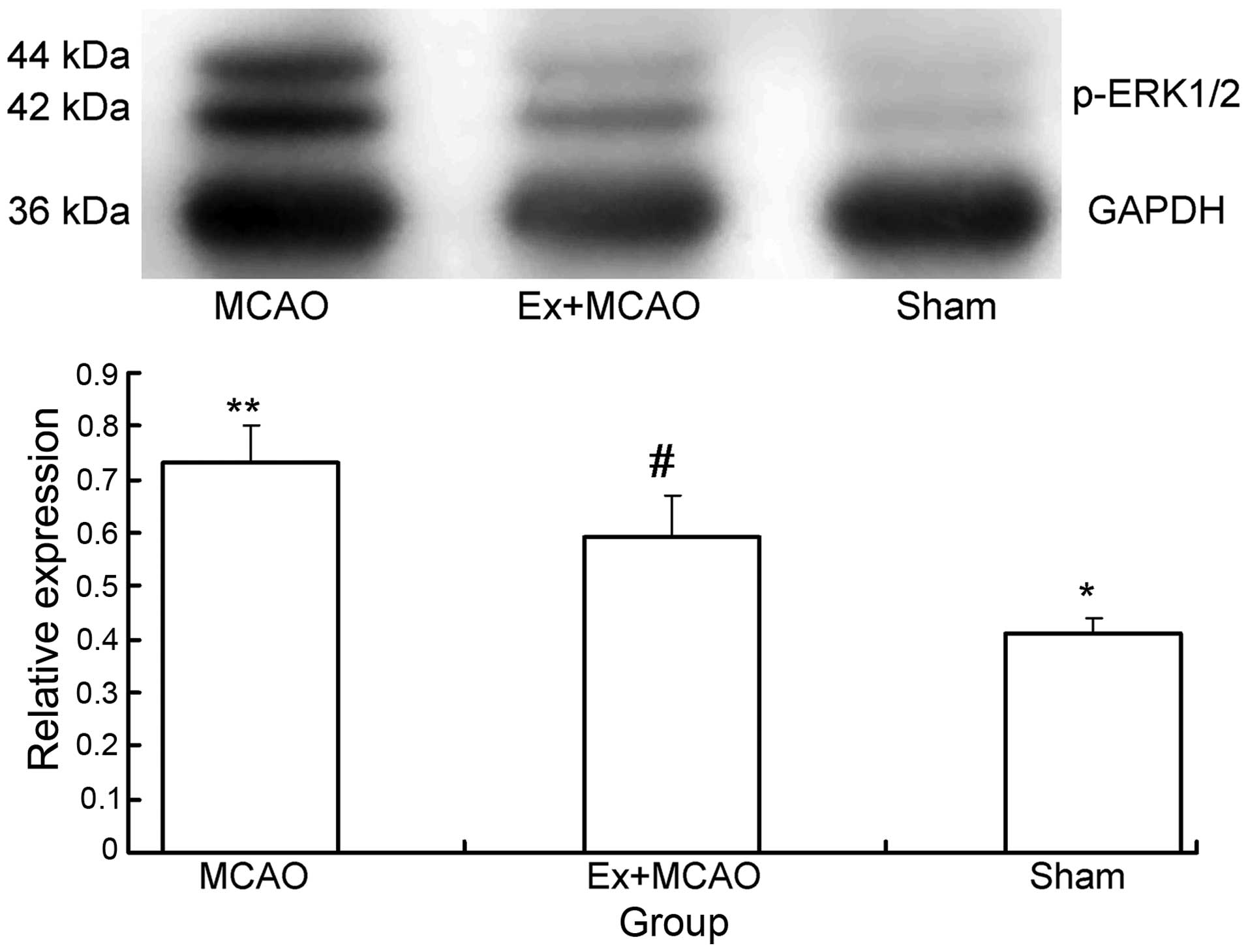
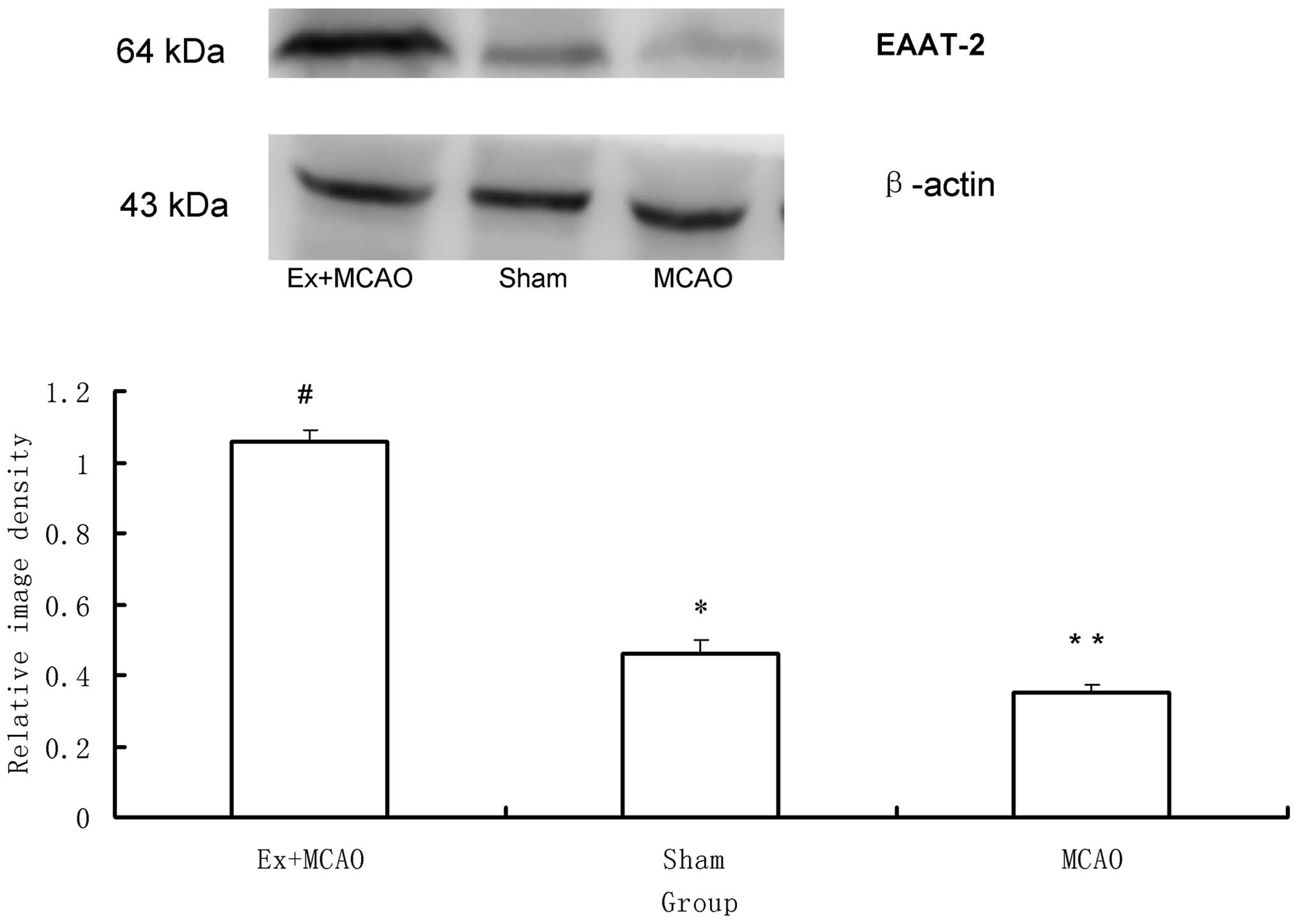
|
1
|
Stummer W, Baethmann A, Murr R, et al:
Cerebral protection against ischemia by locomotor-activity in
gerbils. Underlying mechanisms. Stroke. 26:1423–1429. 1995.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Ang ET, Wong PTH, Moochhala S and Ng YK:
Neuroprotection associated with running: is it a result of
increased endogenous neurotrophic factors? Neuroscience.
118:335–345. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Endres M, Gertz K, Lindauer U, et al:
Mechanisms of stroke protection by physical activity. Ann Neurol.
54:582–590. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Li J, Luan XD, Clark JC, et al:
Neuroprotection against transient cerebral ischemia by exercise
pre-conditioning in rats. Neurol Res. 26:404–408. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ding YH, Ding Y, Li J, et al: Exercise
pre-conditioning strengthens brain microvascular integrity in a rat
stroke model. Neurol Res. 28:184–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Guyot LL, Diaz FG, O’Regan MH, McLeod S,
Park H and Phillis JW: Real-time measurement of glutamate release
from the ischemic penumbra of the rat cerebral cortex using a focal
middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Neurosci Lett. 299:37–40.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhang F, Jia J, Wu Y, Hu Y and Wang Y: The
effect of treadmill training pre-exercise on glutamate receptor
expression in rats after cerebral ischemia. Int J Mol Sci.
11:2658–2669. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zhang F, Wu Y, Jia J and Hu YS:
Pre-ischemic treadmill training induces tolerance to brain
ischemia: involvement of glutamate and ERK1/2. Molecules.
15:5246–5257. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Beart PM and O’Shea RD: Transporters for
L-glutamate: an update on their molecular pharmacology and
pathological involvement. Br J Pharmacol. 150:5–17. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Suchak SK, Baloyianni NV, Perkinton MS,
Williams RJ, Meldrum BS and Rattray M: The ‘glial’ glutamate
transporter, EAAT2 (Glt-1) accounts for high affinity glutamate
uptake into adult rodent nerve endings. J Neurochem. 84:522–532.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liebelt B, Papapetrou P, Ali A, et al:
Exercise preconditioning reduces neuronal apoptosis in stroke by
up-regulating heat shock protein-70 (heat shock protein-72) and
extracellular signal-regulated-kinase 1/2. Neuroscience.
166:1091–1100. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Lu ZM and Xu SC: ERK1/2 MAP kinases in
cell survival and apoptosis. IUBMB Life. 58:621–631. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Alessandrini A, Namura S, Moskowitz MA and
Bonventre JV: MEK1 protein kinase inhibition protects against
damage resulting from focal cerebral ischemia. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 96:12866–12869. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Namura S, Iihara K, Takami S, et al:
Intravenous administration of MEK inhibitor U0126 affords brain
protection against forebrain ischemia and focal cerebral ischemia.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 98:11569–11574. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ding YH, Ding Y, Li J, Bessert DA and
Rafols JA: Exercise pre-conditioning strengthens brain
microvascular integrity in a rat stroke model. Neurol Res.
28:184–189. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
National Center for Health Statistics.
Health, United States, 2010: With Special Feature on Death and
Dying. Hyattsville (MD, USA): 2011
|
|
18
|
Krarup LH, Truelsen T, Gluud C, et al:
ExStroke Pilot Trial Group: Prestroke physical activity is
associated with severity and long-term outcome from first-ever
stroke. Neurology. 71:1313–1318. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Hinzman JM, Thomas TC, Quintero JE,
Gerhardt GA and Lifshit J: Disruptions in the regulation of
extracellular glutamate by neurons and glia in the rat striatum two
days after diffuse brain injury. J Neurotrauma. 29:1197–1208. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Kanai Y and Hediger MA: The
glutamate/neutral amino acid transporter family SLC1: molecular,
physiological and pharmacological aspects. Pflugers Arch.
447:469–479. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
21
|
Verma R, Mishra V, Sasmal D and Raghubir
R: Pharmacological evaluation of glutamate transporter 1 (GLT-1)
mediated neuroprotection following cerebral ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Eur J Pharmacol. 638:65–71. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Tanaka K, Watase K, Manabe T, et al:
Epilepsy and exacerbation of brain injury in mice lacking the
glutamate transporter GLT-1. Science. 276:1699–1702. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|