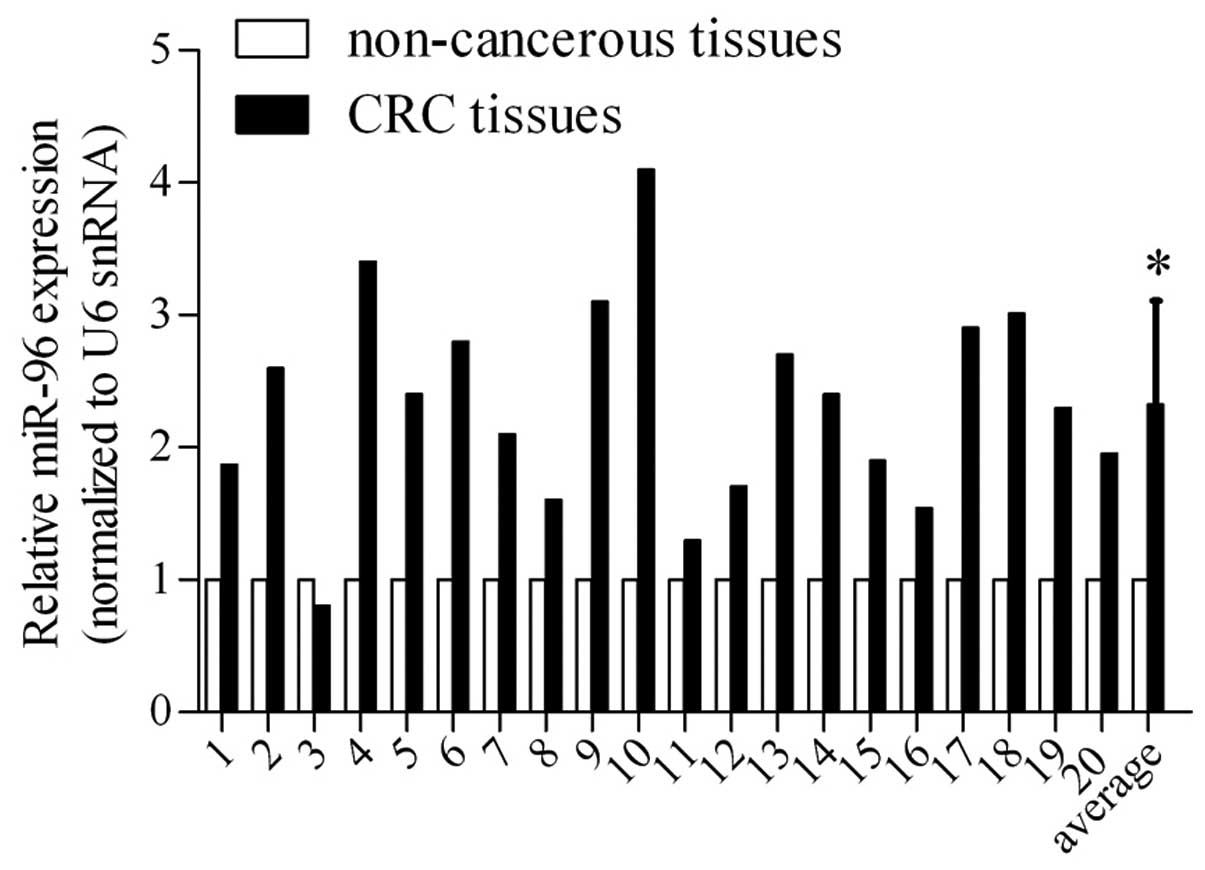
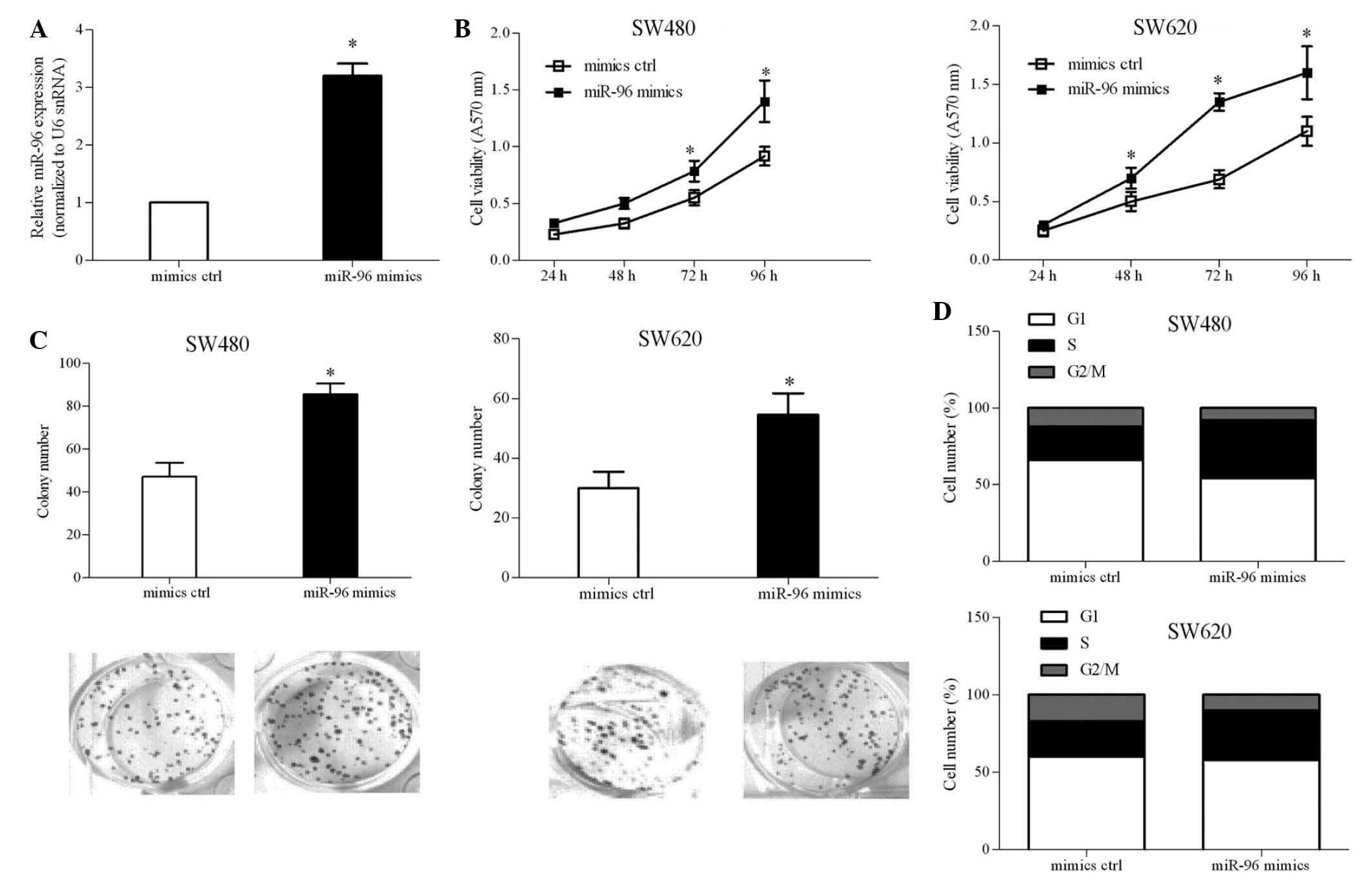
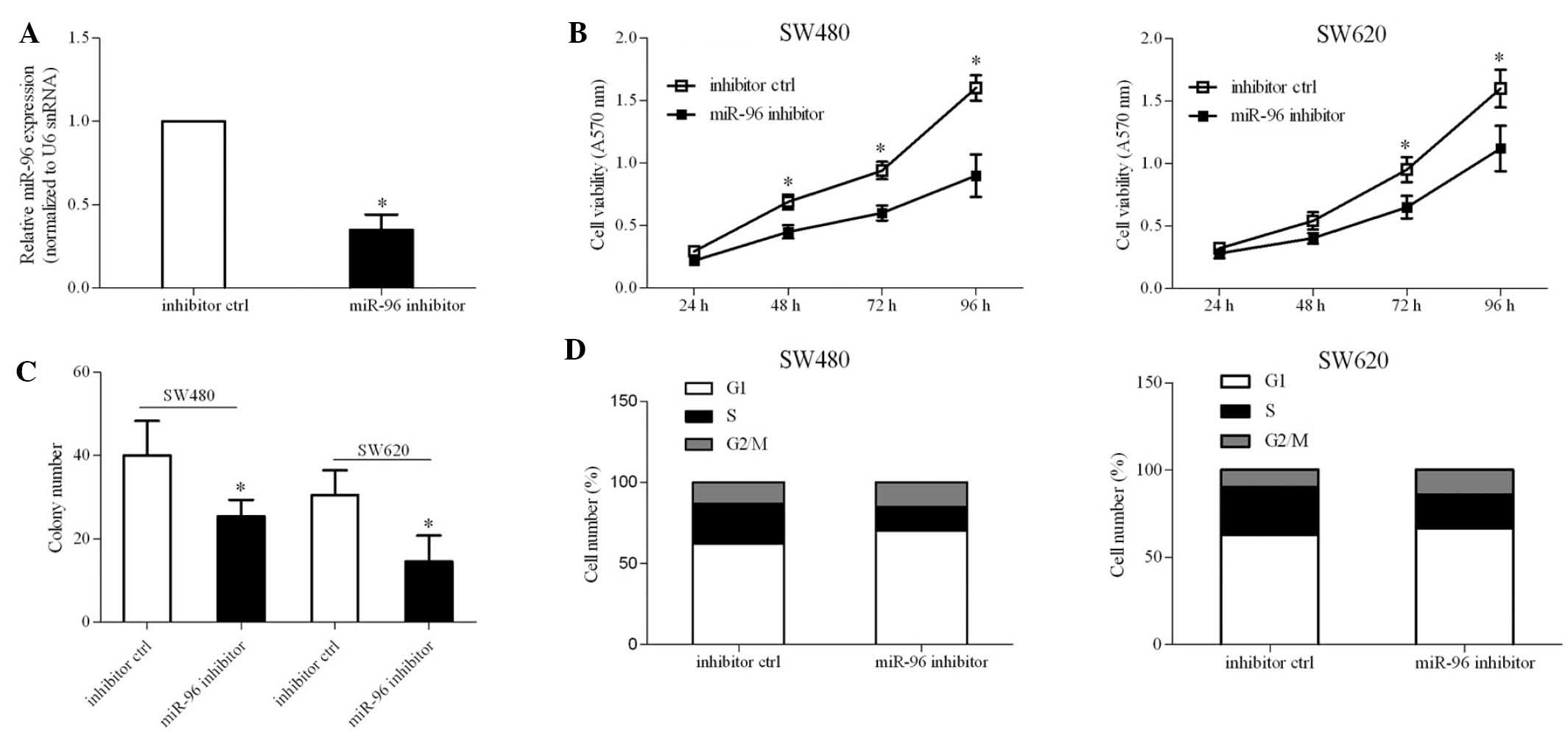
|
1
|
Bartel DP: MicroRNAs: genomics,
biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 116:281–297. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Brennecke J, Stark A, Russell RB and Cohen
SM: Principles of microRNA-target recognition. PLoS Biol.
3:e852005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Ambros V: The functions of animal
microRNAs. Nature. 431:350–355. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Calin GA, Sevignani C, Dumitru CD, et al:
Human microRNA genes are frequently located at fragile sites and
genomic regions involved in cancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
101:2999–3004. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Nassirpour R, Mehta PP and Yin MJ: miR-122
regulates tumorigenesis in hepatocellular carcinoma by targeting
AKT3. PLoS One. 8:e796552013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Gaziel-Sovran A, Segura MF, Di Micco R, et
al: miR-30b/30d regulation of GalNAc transferases enhances invasion
and immunosuppression during metastasis. Cancer Cell. 20:104–118.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Fearon ER: Molecular genetics of
colorectal cancer. Annu Rev Pathol. 6:479–507. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Kanthan R, Senger JL and Kanthan SC:
Molecular events in primary and metastatic colorectal carcinoma: a
review. Patholog Res Int. 2012:5974972012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Kaemmerer E, Klaus C, Jeon MK and Gassler
N: Molecular classification of colorectal carcinomas: The
genotype-to-phenotype relation. World J Gastroenterol.
19:8163–8167. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Siegel R, Naishadham D and Jemal A: Cancer
statistics, 2013. CA Cancer J Clin. 63:11–30. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Sarver AL, French AJ, Borralho PM, et al:
Human colon cancer profiles show differential microRNA expression
depending on mismatch repair status and are characteristic of
undifferentiated proliferative states. BMC Cancer. 9:4012009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Bandres E, Cubedo E, Agirre X, et al:
Identification by real-time PCR of 13 mature microRNAs
differentially expressed in colorectal cancer and non-tumoral
tissues. Mol Cancer. 5:292006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sarver AL, Li L and Subramanian S:
MicroRNA miR-183 functions as an oncogene by targeting the
transcription factor EGR1 and promoting tumor cell migration.
Cancer Res. 70:9570–9580. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Khatri R and Subramanian S: MicroRNA-135b
and its circuitry networks as potential therapeutic targets in
colon cancer. Front Oncol. 3:2682013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Cekaite L, Rantala JK, Bruun J, et al:
MiR-9, -31, and -182 deregulation promote proliferation and tumor
cell survival in colon cancer. Neoplasia. 14:868–879.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Chen C, Ridzon DA, Broomer AJ, et al:
Real-time quantification of microRNAs by stem-loop RT-PCR. Nucleic
Acids Res. 33:e1792005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Haflidadottir BS, Larne O, Martin M, et
al: Upregulation of miR-96 enhances cellular proliferation of
prostate cancer cells through FOXO1. PLoS One. 8:e724002013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin H, Dai T, Xiong H, et al: Unregulated
miR-96 induces cell proliferation in human breast cancer by
downregulating transcriptional factor FOXO3a. PLoS One.
5:e157972010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Guttilla IK and White BA: Coordinate
regulation of FOXO1 by miR-27a, miR-96, and miR-182 in breast
cancer cells. J Biol Chem. 284:23204–23216. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Xu D, He X, Chang Y, et al: Inhibition of
miR-96 expression reduces cell proliferation and clonogenicity of
HepG2 hepatoma cells. Oncol Rep. 29:653–661. 2013.
|
|
21
|
Fendler A, Jung M, Stephan C, et al: The
antiapoptotic function of miR-96 in prostate cancer by inhibition
of FOXO1. PLoS One. 8:e808072013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu S, Lu Z, Liu C, et al: miRNA-96
suppresses KRAS and functions as a tumor suppressor gene in
pancreatic cancer. Cancer Res. 70:6015–6025. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Xu N, Zhang L, Meisgen F, et al:
MicroRNA-125b down-regulates matrix metallopeptidase 13 and
inhibits cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma cell proliferation,
migration, and invasion. J Biol Chem. 287:29899–29908. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Jiang F, Liu T, He Y, et al: MiR-125b
promotes proliferation and migration of type II endometrial
carcinoma cells through targeting TP53INP1 tumor suppressor in
vitro and in vivo. BMC Cancer. 11:4252011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zhang CM, Zhao J and Deng HY: MiR-155
promotes proliferation of human breast cancer MCF-7 cells through
targeting tumor protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1. J Biomed Sci.
20:792013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Jiang PH, Motoo Y, Garcia S, et al:
Down-expression of tumor protein p53-induced nuclear protein 1 in
human gastric cancer. World J Gastroenterol. 12:691–696.
2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shahbazi J, Lock R and Liu T: Tumor
protein 53-induced nuclear protein 1 enhances p53 function and
represses tumorigenesis. Front Genet. 4:802013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ito Y, Motoo Y, Yoshida H, et al:
Decreased expression of tumor protein p53-induced nuclear protein 1
(TP53INP1) in breast carcinoma. Anticancer Res. 26:4391–4395.
2006.
|
|
29
|
Maiese K, Chong ZZ, Shang YC and Hou J:
Clever cancer strategies with FoxO transcription factors. Cell
Cycle. 7:3829–3839. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Guo JP, Tian W, Shu S, et al: IKBKE
phosphorylation and inhibition of FOXO3a: a mechanism of IKBKE
oncogenic function. PLoS One. 8:e636362013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|