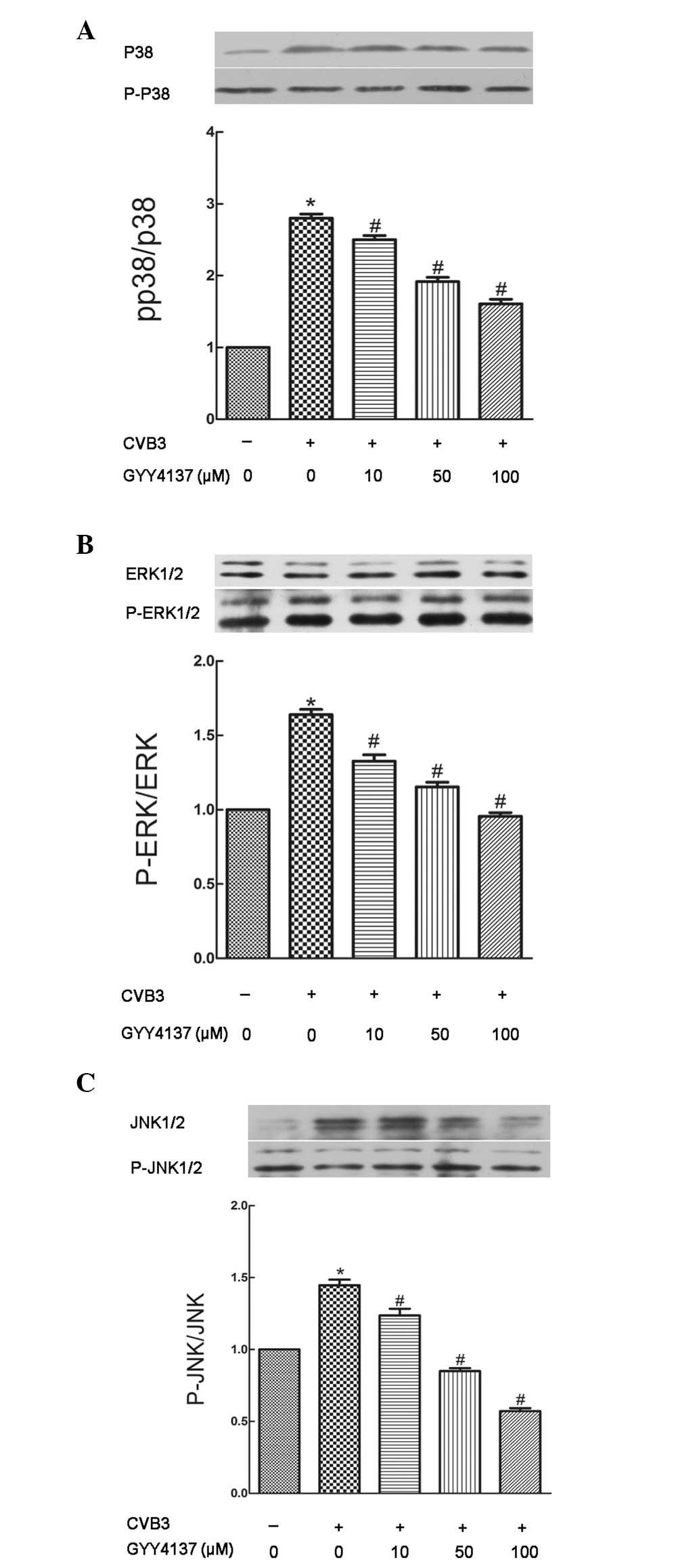
|
1
|
Esfandiarei M and McManus BM: Molecular
biology and pathogenesis of viral myocarditis. Annu Rev Pathol.
3:127–155. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Yajima T and Knowlton KU: Viral
myocarditis: from the perspective of the virus. Circulation.
119:2615–2624. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Sobotta K, Wilsky S, Althof N, Wiesener N,
Wutzler P and Henke A: Inhibition of nuclear factor kappa B
activation reduces Coxsackievirus B3 replication in lymphoid cells.
Virus Res. 163:495–502. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
4
|
Li K, Xu W, Guo Q, et al: Differential
macrophage polarization in male and female BALB/c mice infected
with coxsackievirus B3 defines susceptibility to viral myocarditis.
Circ Res. 105:353–364. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Gui J, Yue Y, Chen R, Xu W and Xiong S:
A20 (TNFAIP3) alleviates CVB3-induced myocarditis via inhibiting
NF-kappaB signaling. PLoS One. 7:e465152012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Predmore BL, Lefer DJ and Gojon G:
Hydrogen sulfide in biochemistry and medicine. Antioxid Redox
Signal. 17:119–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lowicka E and Beltowski J: Hydrogen
sulfide (H2S) - the third gas of interest for
pharmacologists. Pharmacol Rep. 59:4–24. 2007.
|
|
8
|
Bian JS, Yong QC, Pan TT, et al: Role of
hydrogen sulfide in the cardioprotection caused by ischemic
preconditioning in the rat heart and cardiac myocytes. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 316:670–678. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Li L, Bhatia M and Moore PK: Hydrogen
sulphide - a novel mediator of inflammation? Curr Opin Pharmacol.
6:125–129. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Rinaldi L, Gobbi G, Pambianco M, Micheloni
C, Mirandola P and Vitale M: Hydrogen sulfide prevents apoptosis of
human PMN via inhibition of p38 and caspase 3. Lab Invest.
86:391–397. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu LF, Lu M, Wu ZY, Wong PT and Bian JS:
Hydrogen sulfide inhibits rotenone-induced apoptosis via
preservation of mitochondrial function. Mol Pharmacol. 75:27–34.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Li L, Bhatia M, Zhu YZ, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide is a novel mediator of lipopolysaccharide-induced
inflammation in the mouse. FASEB J. 19:1196–1198. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Li T, Zhao B, Wang C, et al: Regulatory
effects of hydrogen sulfide on IL-6, IL-8 and IL-10 levels in the
plasma and pulmonary tissue of rats with acute lung injury. Exp
Biol Med (Maywood). 233:1081–1087. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Tamizhselvi R, Sun J, Koh YH and Bhatia M:
Effect of hydrogen sulfide on the phosphatidylinositol
3-kinase-protein kinase B pathway and on caerulein-induced cytokine
production in isolated mouse pancreatic acinar cells. J Pharmacol
Exp Ther. 329:1166–1177. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Li L, Salto-Tellez M, Tan CH, Whiteman M
and Moore PK: GYY4137, a novel hydrogen sulfide-releasing molecule,
protects against endotoxic shock in the rat. Free Radic Biol Med.
47:103–113. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Li L, Fox B, Keeble J, et al: The complex
effects of the slow-releasing hydrogen sulfide donor GYY4137 in a
model of acute joint inflammation and in human cartilage cells. J
Cell Mol Med. 17:365–376. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Hommes DW, Peppelenbosch MP and van
Deventer SJ: Mitogen activated protein (MAP) kinase signal
transduction pathways and novel anti-inflammatory targets. Gut.
52:144–151. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Zhang H, Moochhala SM and Bhatia M:
Endogenous hydrogen sulfide regulates inflammatory response by
activating the ERK pathway in polymicrobial sepsis. J Immunol.
181:4320–4331. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Si X, Luo H, Morgan A, et al:
Stress-activated protein kinases are involved in coxsackievirus B3
viral progeny release. J Virol. 79:13875–13881. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Zhang C, Lin G, Wan W, et al: Resveratrol,
a polyphenol phytoalexin, protects cardiomyocytes against
anoxia/reoxygenation injury via the TLR4/NF-kappaB signaling
pathway. Int J Mol Med. 29:557–563. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Li Q and Verma IM: NF-kappaB regulation in
the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol. 2:725–734. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Szabó C: Hydrogen sulphide and its
therapeutic potential. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 6:917–935. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Yang C, Yang Z, Zhang M, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity and
inflammation in HaCaT cells through inhibition of
ROS/NF-kappaB/COX-2 pathway. PLoS One. 6:e219712011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Chen Y, Liu Z and Xie X: Hydrogen sulphide
attenuates renal and cardiac injury after total hepatic ischemia
and reperfusion. J Surg Res. 164:e305–e313. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hayden MS and Ghosh S: Shared principles
in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell. 132:344–362. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Whiteman M, Li L, Rose P, Tan CH,
Parkinson DB and Moore PK: The effect of hydrogen sulfide donors on
lipopolysaccharide-induced formation of inflammatory mediators in
macrophages. Antioxid Redox Signal. 12:1147–1154. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
27
|
Chen TH, Kao YC, Chen BC, Chen CH, Chan P
and Lee HM: Dipyridamole activation of mitogen-activated protein
kinase phosphatase-1 mediates inhibition of
lipopolysaccharide-induced cyclooxygenase-2 expression in RAW 264.7
cells. Eur J Pharmacol. 541:138–146. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Yuen S, Smith J, Caruso L, Balan M and
Opavsky MA: The coxsackie-adenovirus receptor induces an
inflammatory cardiomyopathy independent of viral infection. J Mol
Cell Cardiol. 50:826–840. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Marchant D, Dou Y, Luo H, et al: Bosentan
enhances viral load via endothelin-1 receptor type-A-mediated p38
mitogen-activated protein kinase activation while improving cardiac
function during coxsackievirus-induced myocarditis. Circ Res.
104:813–821. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|