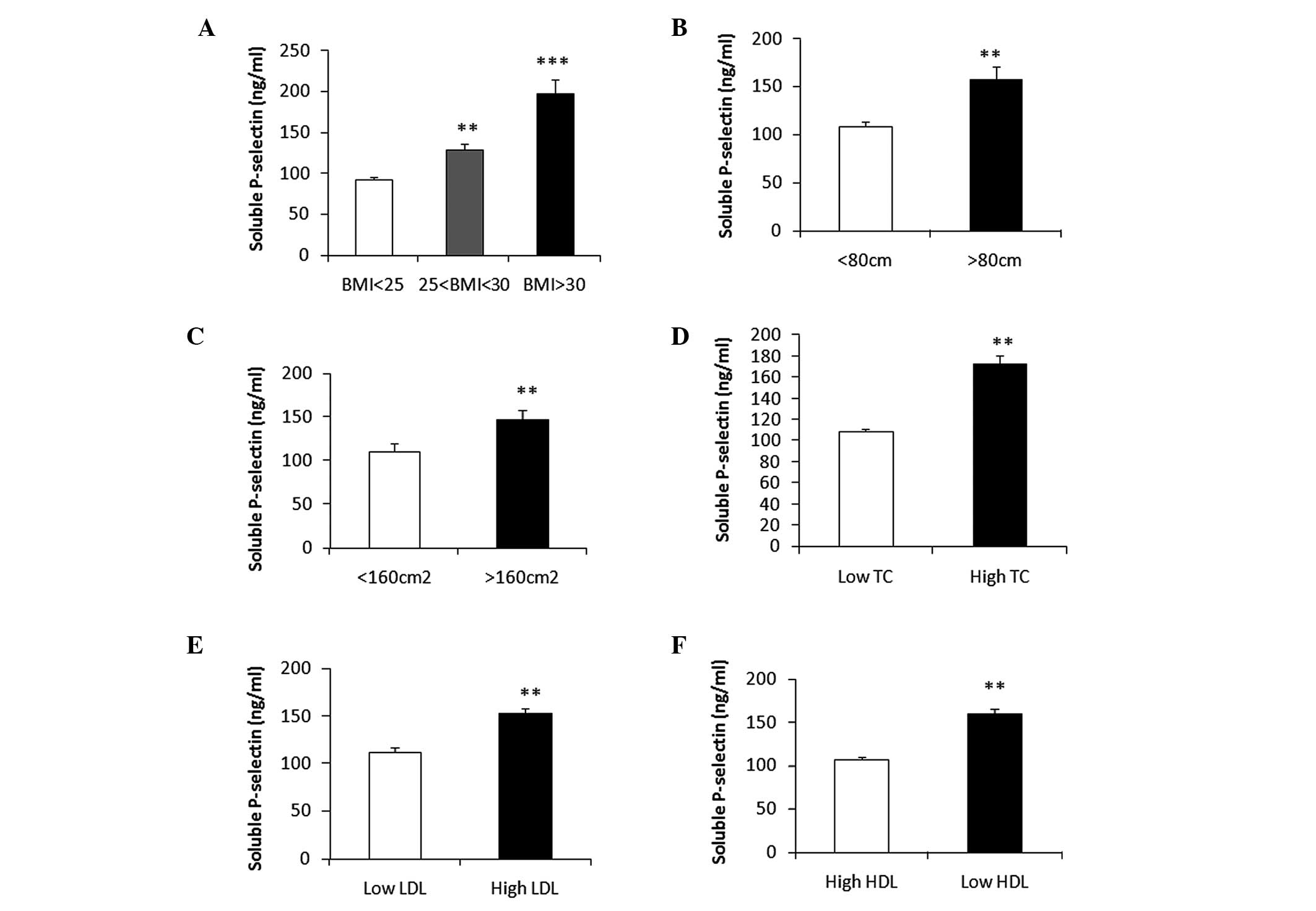
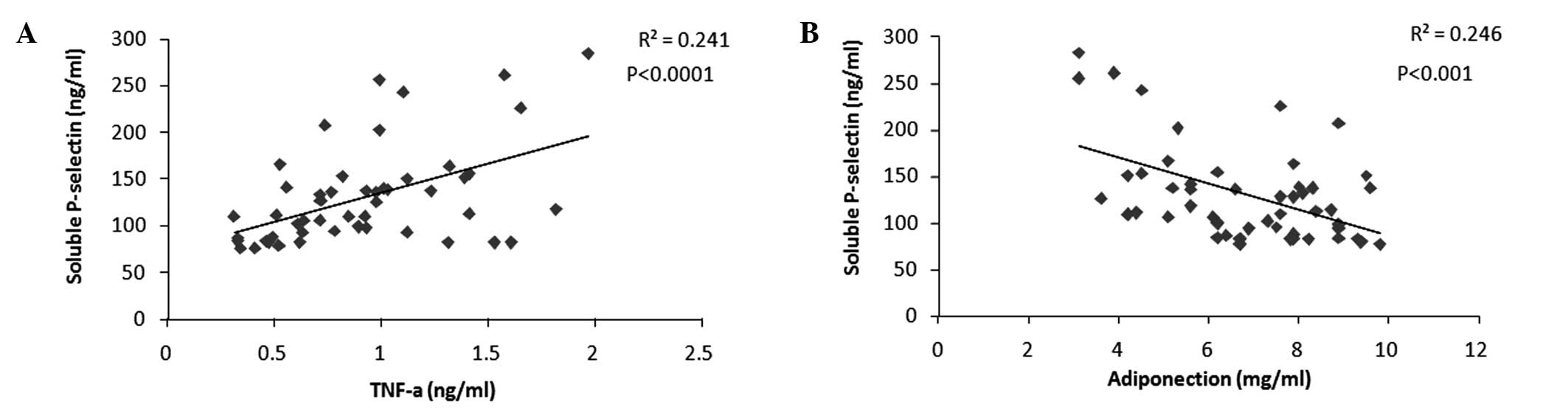
|
1
|
Geng JG, Chen M and Chou KC: P-selectin
cell adhesion molecule in inflammation, thrombosis, cancer growth
and metastasis. Curr Med Chem. 11:2153–2160. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Polek A, Sobiczewski W and Matowicka-Karna
J: P-selectin and its role in some diseases. Postepy Hig Med Dosw
(Online). 63:465–470. 2009.
|
|
3
|
Yang J, Furie BC and Furie B: The biology
of P-selectin glycoprotein ligand-1: its role as a selectin
counterreceptor in leukocyte-endothelial and leukocyte-platelet
interaction. Thromb Haemost. 81:1–7. 1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Blann AD, Nadar SK and Lip GY: The
adhesion molecule P-selectin and cardiovascular disease. Eur Heart
J. 24:2166–2179. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Ramacciotti E, Blackburn S, Hawley AE, et
al: Evaluation of soluble P-selectin as a marker for the diagnosis
of deep venous thrombosis. Clin Appl Thromb Hemost. 17:425–431.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Woollard KJ and Chin-Dusting J: P-selectin
antagonism in inflammatory disease. Curr Pharm Des. 16:4113–4118.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Burke AP and Virmani R: Pathophysiology of
acute myocardial infarction. Med Clin North Am. 91:553–572. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Woollard KJ and Chin-Dusting J:
Therapeutic targeting of p-selectin in atherosclerosis. Inflamm
Allergy Drug Targets. 6:69–74. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Aversano T, Aversano LT, Passamani E, et
al: Thrombolytic therapy vs primary percutaneous coronary
intervention for myocardial infarction in patients presenting to
hospitals without on-site cardiac surgery: a randomized controlled
trial. JAMA. 287:1943–1951. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ferroni P, Basili S, Martini F, et al:
Soluble P-selectin as a marker of platelet hyperactivity in
patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. J Investig
Med. 48:21–27. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Ertenli I, Kiraz S, Arici M, et al:
P-selectin as a circulating molecular marker in rheumatoid
arthritis with thrombocytosis. J Rheumatol. 25:1054–1058.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Tamagawa-Mineoka R, Katoh N, Ueda E,
Masuda K and Kishimoto S: Platelet-derived microparticles and
soluble P-selectin as platelet activation markers in patients with
atopic dermatitis. Clin Immunol. 131:495–500. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Konishi M, Sugiyama S, Sugamura K, et al:
Association of pericardial fat accumulation rather than abdominal
obesity with coronary atherosclerotic plaque formation in patients
with suspected coronary artery disease. Atherosclerosis.
209:573–578. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Zhou J, Lhotak S, Hilditch BA and Austin
RC: Activation of the unfolded protein response occurs at all
stages of atherosclerotic lesion development in apolipoprotein
E-deficient mice. Circulation. 111:1814–1821. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Johnson JL and Jackson CL: Atherosclerotic
plaque rupture in the apolipoprotein E knockout mouse.
Atherosclerosis. 154:399–406. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Sata M, Maejima Y, Adachi F, et al: A
mouse model of vascular injury that induces rapid onset of medial
cell apoptosis followed by reproducible neointimal hyperplasia. J
Mol Cell Cardiol. 32:2097–2104. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Phillips JW, Barringhaus KG, Sanders JM,
et al: Single injection of P-selectin or P-selectin glycoprotein
ligand-1 monoclonal antibody blocks neointima formation after
arterial injury in apolipoprotein E-deficient mice. Circulation.
107:2244–2249. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin WY, Lee LT, Chen CY, et al: Optimal
cut-off values for obesity: using simple anthropometric indices to
predict cardiovascular risk factors in Taiwan. Int J Obes Relat
Metab Disord. 26:1232–1238. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Guo L, Ning W, Tan Z, Gong Z and Li X:
Mechanism of matrix metalloproteinase axis-induced neointimal
growth. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 66:116–125. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Konishi M, Sugiyama S, Sato Y, et al:
Pericardial fat inflammation correlates with coronary artery
disease. Atherosclerosis. 213:649–655. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hamminga EA, van der Lely AJ, Neumann HA
and Thio HB: Chronic inflammation in psoriasis and obesity:
implications for therapy. Med Hypotheses. 67:768–773. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hackam DG and Anand SS: Emerging risk
factors for atherosclerotic vascular disease: a critical review of
the evidence. JAMA. 290:932–940. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Quarck R, De Geest B, Stengel D, et al:
Adenovirus-mediated gene transfer of human platelet-activating
factor-acetylhydrolase prevents injury-induced neointima formation
and reduces spontaneous atherosclerosis in apolipoprotein
E-deficient mice. Circulation. 103:2495–2500. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Merten M and Thiagarajan P: P-selectin in
arterial thrombosis. Z Kardiol. 93:855–863. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Hong MK, Mintz GS, Lee CW, et al:
Comparison of coronary plaque rupture between stable angina and
acute myocardial infarction: a three-vessel intravascular
ultrasound study in 235 patients. Circulation. 110:928–933. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Lee SG, Lee CW, Hong MK, Kim JJ, Park SW
and Park SJ: Change of multiple complex coronary plaques in
patients with acute myocardial infarction: a study with coronary
angiography. Am Heart J. 147:281–286. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Finn AV, Nakano M, Narula J, Kolodgie FD
and Virmani R: Concept of vulnerable/unstable plaque. Arterioscler
Thromb Vasc Biol. 30:1282–1292. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Claeys MJ, Bosmans J, Veenstra L, Jorens
P, De Raedt H and Vrints CJ: Determinants and prognostic
implications of persistent ST-segment elevation after primary
angioplasty for acute myocardial infarction: importance of
microvascular reperfusion injury on clinical outcome. Circulation.
99:1972–1977. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Triant VA, Lee H, Hadigan C and Grinspoon
SK: Increased acute myocardial infarction rates and cardiovascular
risk factors among patients with human immunodeficiency virus
disease. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 92:2506–2512. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rosengren A, Wallentin L, Simoons M, et
al: Cardiovascular risk factors and clinical presentation in acute
coronary syndromes. Heart. 91:1141–1147. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kvasnicka T, Kvasnicka J, Ceska R, Grauova
B and Vrablik M: Increasing plasma levels of soluble cell adhesion
molecules (sE-selectin, sP-selectin and sICAM-1) in overweight
adults with combined hyperlipidemia. Sb Lek. 102:473–477. 2001.
|
|
32
|
De Pergola G, Pannacciulli N, Coviello M,
et al: sP-selectin plasma levels in obesity: association with
insulin resistance and related metabolic and prothrombotic factors.
Nutr Metab Cardiovasc Dis. 18:227–232. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Larsson PT, Hallerstam S, Rosfors S and
Wallen NH: Circulating markers of inflammation are related to
carotid artery atherosclerosis. Int Angiol. 24:43–51.
2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Yngen M, Ostenson CG, Hu H, Li N, Hjemdahl
P and Wallen NH: Enhanced P-selectin expression and increased
soluble CD40 Ligand in patients with Type 1 diabetes mellitus and
microangiopathy: evidence for platelet hyperactivity and chronic
inflammation. Diabetologia. 47:537–540. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gokulakrishnan K, Deepa R, Mohan V and
Gross MD: Soluble P-selectin and CD40L levels in subjects with
prediabetes, diabetes mellitus, and metabolic syndrome - the
Chennai Urban Rural Epidemiology Study. Metabolism. 55:237–242.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Xu DY, Zhao SP and Peng WP: Elevated
plasma levels of soluble P-selectin in patients with acute
myocardial infarction and unstable angina. An inverse link to
lipoprotein(a). Int J Cardiol. 64:253–258. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Atalar E, Aytemir K, Haznedaroglu I, et
al: Increased plasma levels of soluble selectins in patients with
unstable angina. Int J Cardiol. 78:69–73. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Eberini I, Gianazza E, Breghi L, et al:
Apolipoprotein A-I breakdown is induced by thrombolysis in coronary
patients. Ann Med. 39:306–311. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|