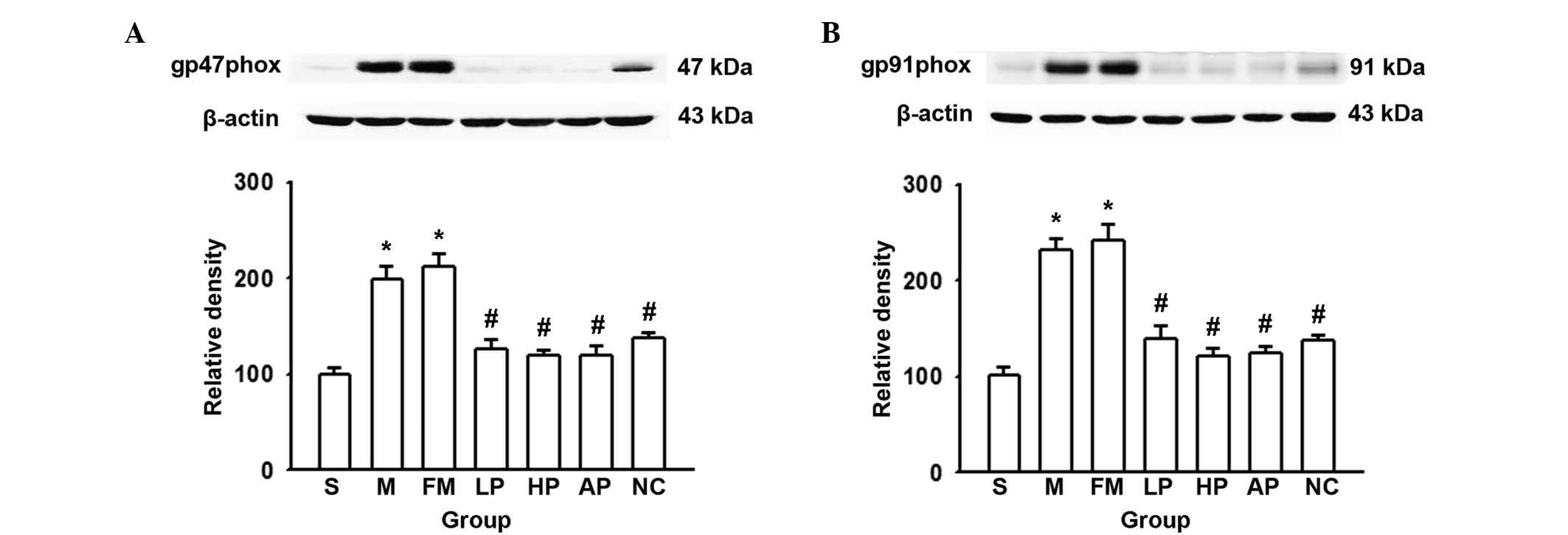
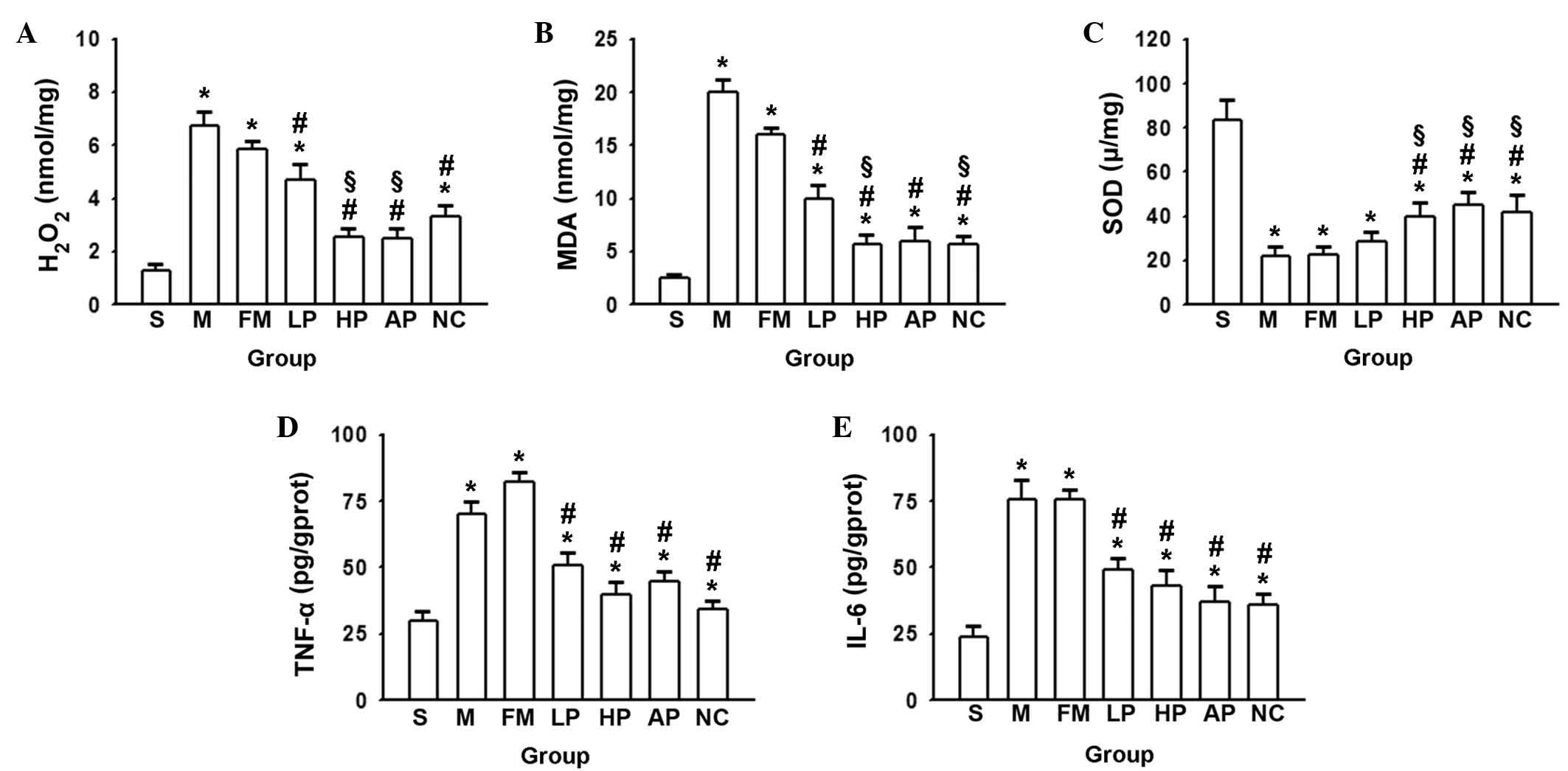
|
1
|
Hong SK, Hwang S, Lee SG, et al: Pulmonary
complications following adult liver transplantation. Transplantat
Proc. 38:2979–2981. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Hirsch J, Niemann CU, Hansen KC, et al:
Alterations in the proteome of pulmonary alveolar type II cells in
the rat after hepatic ischemia-reperfusion. Crit Care Med.
36:1846–1854. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Bellingan GJ: The pulmonary physician in
critical care * 6: The pathogenesis of ALI/ARDS. Thorax.
57:540–546. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Jiang A, Liu C, Song Y, et al: NF-κB
induced the donor liver cold preservation related acute lung injury
in rat liver transplantation model. PloS One. 6:e249602011.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Hei Z, Chi X, Cheng N, Luo G and Li S:
Upregulation of TLR2/4 expression in mononuclear cells in
postoperative systemic inflammatory response syndrome after liver
transplantation. Mediators Inflamm. 2010:5195892010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Altintas ND, Atilla P, Iskit AB and Topeli
A: Long-term simvastatin attenuates lung injury and oxidative
stress in murine acute lung injury models induced by oleic Acid and
endotoxin. Respir Care. 56:1156–1163. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Ramonaite R, Skieceviciene J, Kiudelis G,
et al: Influence of NADPH oxidase on inflammatory response in
primary intestinal epithelial cells in patients with ulcerative
colitis. BMC Gastroenterol. 13:1592013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Murphy PG, Myers DS, Davies MJ, Webster NR
and Jones JG: The antioxidant potential of propofol
(2,6-diisopropylphenol). Br J Anaesth. 68:613–618. 1992. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Jin C, Zhang PJ, Wu XM, et al: Impact of
hypoxic preconditioning on apoptosis and its possible mechanism in
orthotopic liver autotransplantation in rats. Hepatobiliary
Pancreat Dis Int. 8:40–45. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chi X, Zhang A, Luo G, et al: Knockdown of
myeloid differentiation protein-2 reduces acute lung injury
following orthotopic autologous liver transplantation in a rat
model. Pulm Pharmacol Ther. 26:380–387. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Liu KX, Chen SQ, Huang WQ, Li YS, Irwin MG
and Xia Z: Propofol pretreatment reduces ceramide production and
attenuates intestinal mucosal apoptosis induced by intestinal
ischemia/reperfusion in rats. Anesth Analg. 107:1884–1891. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Jin X, Wang L, Wu HS, et al:
N-acetylcysteine inhibits activation of toll-like receptor 2 and 4
gene expression in the liver and lung after partial hepatic
ischemia-reperfusion injury in mice. Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis
Int. 6:284–289. 2007.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Sonta T, Inoguchi T, Tsubouchi H, et al:
Evidence for contribution of vascular NAD(P)H oxidase to increased
oxidative stress in animal models of diabetes and obesity. Free
Radic Biol Med. 37:115–123. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Sadowska AM: N-Acetylcysteine mucolysis in
the management of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease. Ther Adv
Respir Dis. 6:127–135. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Dodd-o JM, Welsh LE, Salazar JD, et al:
Effect of NADPH oxidase inhibition on cardiopulmonary
bypass-induced lung injury. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
287:H927–H936. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Franco-Gou R, Roselló-Catafau J and
Peralta C: Protection against lung damage in reduced-size liver
transplantation. Crit Care Med. 34:1506–1513. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fan J, Frey RS and Malik AB: TLR4
signaling induces TLR2 expression in endothelial cells via
neutrophil NADPH oxidase. J Clin Invest. 112:1234–1243. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Poinas A, Gaillard J, Vignais P and
Doussiere J: Exploration of the diaphorase activity of neutrophil
NADPH oxidase. Eur J Biochem. 269:1243–1252. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Auten RL, Richardson RM, White JR, Mason
SN, Vozzelli MA and Whorton MH: Nonpeptide CXCR2 antagonist
prevents neutrophil accumulation in hyperoxia-exposed newborn rats.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 299:90–95. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Auten RL, Whorton MH and Nicholas Mason S:
Blocking neutrophil influx reduces DNA damage in hyperoxia-exposed
newborn rat lung. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol. 26:391–397. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hõrak P, Sild E, Soomets U, Sepp T and
Kilk K: Oxidative stress and information content of black and
yellow plumage coloration: an experiment with greenfinches. J Exp
Biol. 213:2225–2233. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Manni ML, Epperly MW, Han W, et al:
Leukocyte-derived extracellular superoxide dismutase does not
contribute to airspace EC-SOD after interstitial pulmonary injury.
Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302:L160–L166. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Keegan MT and Pickering BW: Critical care
issues following orthotopic liver transplantation. Minerva
Gastroenterol Dietol. 56:305–330. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Yamaoka S, Kim HS, Ogihara T, et al:
Severe Vitamin E deficiency exacerbates acute hyperoxic lung injury
associated with increased oxidative stress and inflammation. Free
Radic Res. 42:602–612. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Weng TI, Wu HY, Kuo CW and Liu SH:
Honokiol rescues sepsis-associated acute lung injury and lethality
via the inhibition of oxidative stress and inflammation. Intensive
Care Med. 37:533–541. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Compton CN, Franko AP, Murray MT, Diebel
LN and Dulchavsky SA: Signaling of apoptotic lung injury by lipid
hydroperoxides. J Trauma. 44:783–788. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Kupatt C, Habazettl H, Goedecke A, et al:
Tumor necrosis factor-alpha contributes to ischemia- and
reperfusion-induced endothelial activation in isolated hearts. Circ
Res. 84:392–400. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Kennedy TP, Rao NV, Hopkins C, Pennington
L, Tolley E and Hoidal JR: Role of reactive oxygen species in
reperfusion injury of the rabbit lung. J Clin Invest. 83:1326–1335.
1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
den Hengst WA, Gielis JF, Lin JY, Van
Schil PE, De Windt LJ and Moens AL: Lung ischemia-reperfusion
injury: a molecular and clinical view on a complex
pathophysiological process. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol.
299:H1283–H1299. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Adkins WK and Taylor AE: Role of xanthine
oxidase and neutrophils in ischemia-reperfusion injury in rabbit
lung. J Appl Physiol (1985). 69:2012–2018. 1990.
|
|
31
|
Al-Mehdi AB, Zhao G, Dodia C, et al:
Endothelial NADPH oxidase as the source of oxidants in lungs
exposed to ischemia or high K+. Circ Res. 83:730–737.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Zulueta JJ, Yu FS, Hertig IA, Thannickal
VJ and Hassoun PM: Release of hydrogen peroxide in response to
hypoxia-reoxygenation: role of an NAD(P)H oxidase-like enzyme in
endothelial cell plasma membrane. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol.
12:41–49. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Bernard GR, Wheeler AP, Arons MM, et al: A
trial of antioxidants N-acetylcysteine and procysteine in ARDS. The
Antioxidant in ARDS Study Group. Chest. 112:164–172. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Takao Y, Mikawa K, Nishina K and Obara H:
Attenuation of acute lung injury with propofol in endotoxemia.
Anesth Analg. 100:810–816. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Shao H, Li J, Zhou Y, et al:
Dose-dependent protective effect of propofol against mitochondrial
dysfunction in ischaemic/reperfused rat heart: role of cardiolipin.
Br J Pharmacol. 153:1641–1649. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wang B, Shravah J, Luo H, Raedschelders K,
Chen DD and Ansley DM: Propofol protects against hydrogen
peroxide-induced injury in cardiac H9c2 cells via Akt activation
and Bcl-2 up-regulation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 389:105–111.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Ware LB: Pathophysiology of acute lung
injury and the acute respiratory distress syndrome. Semin Respir
Crit Care Med. 27:337–349. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Park HR, Kamau PW and Loch-Caruso R:
Involvement of reactive oxygen species in brominated diphenyl
ether-47-induced inflammatory cytokine release from human
extravillous trophoblasts in vitro. Toxicol Appl Pharmacol.
274:283–292. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Luo C, Yuan D, Li X, et al: Propofol
Attenuated Acute Kidney Injury after Orthotopic Liver
Transplantation via Inhibiting Gap Junction Composed of Connexin
32. Anesthesiology. Sept 24–2014.(Epub ahead of print). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Ma L, Wu X, Chen W and Fujino Y: Propofol
has anti-inflammatory effects on alveolar type II epithelial cells.
Acta anaesthesiologica Scandinavica. 54:362–369. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|