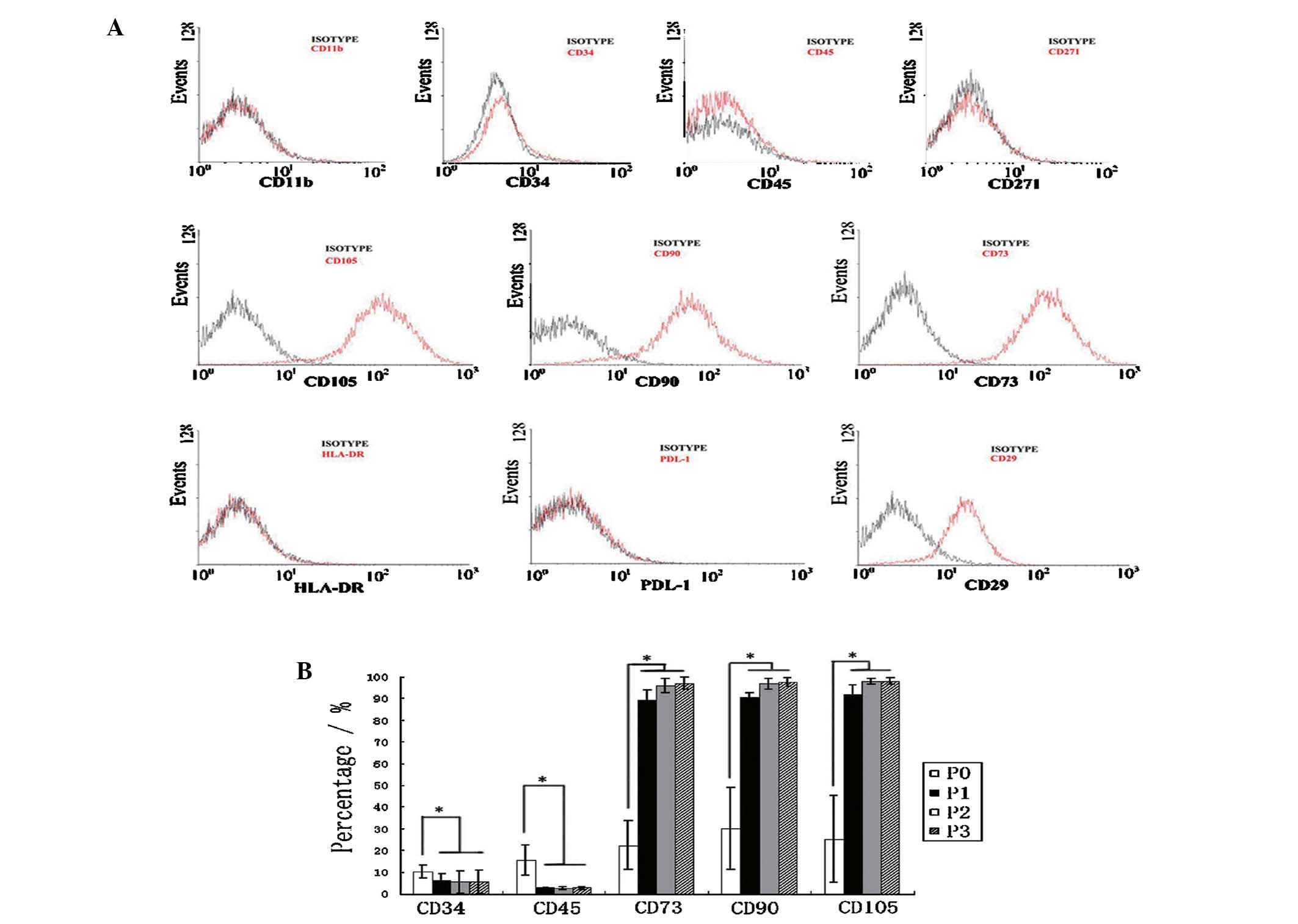
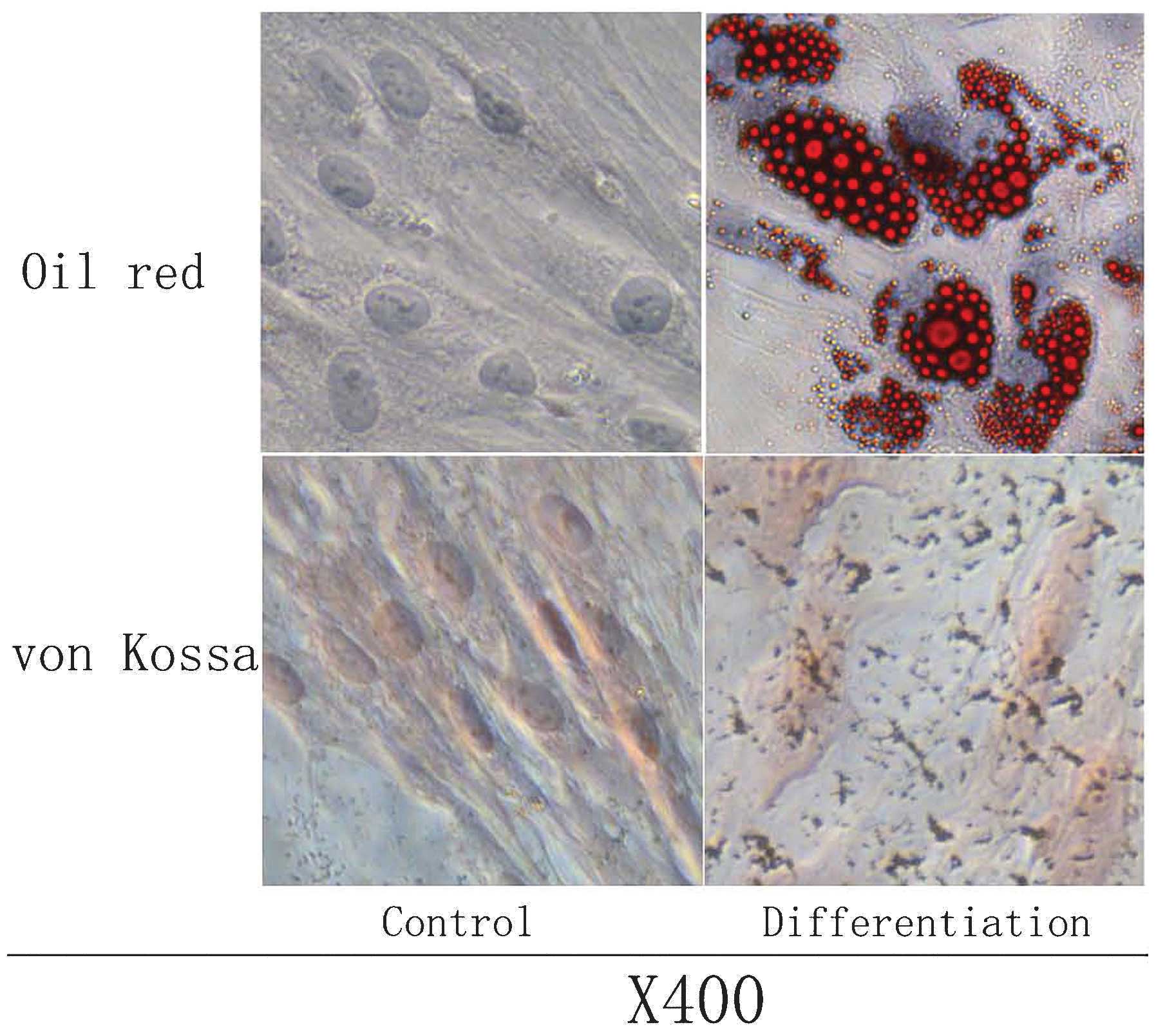
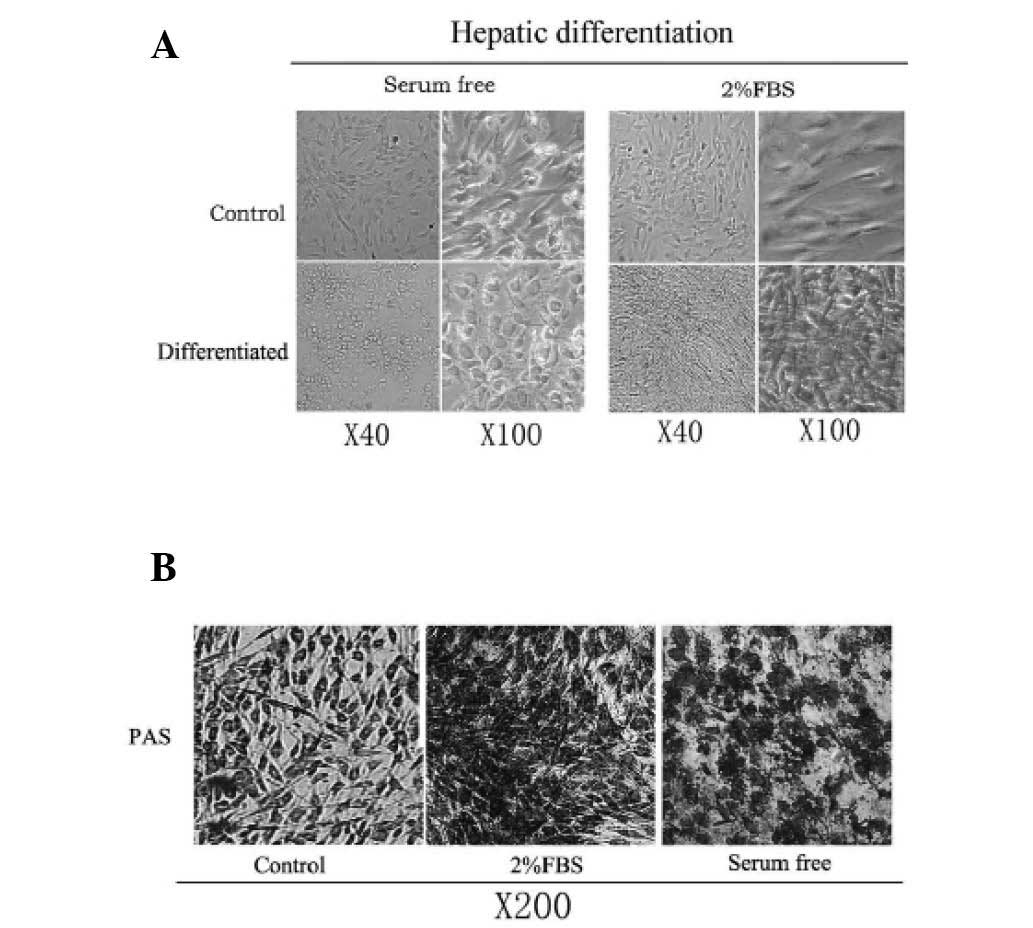
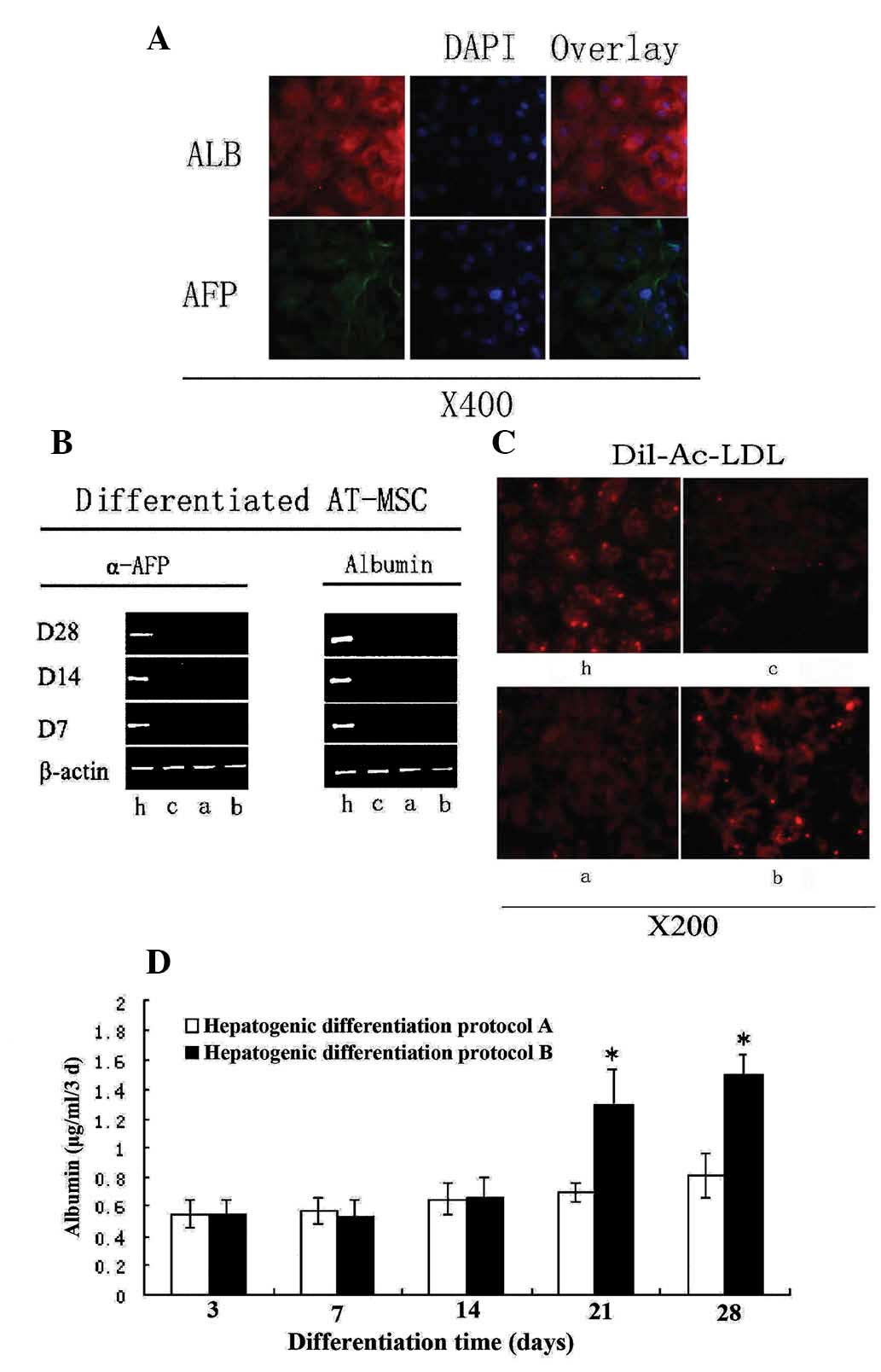
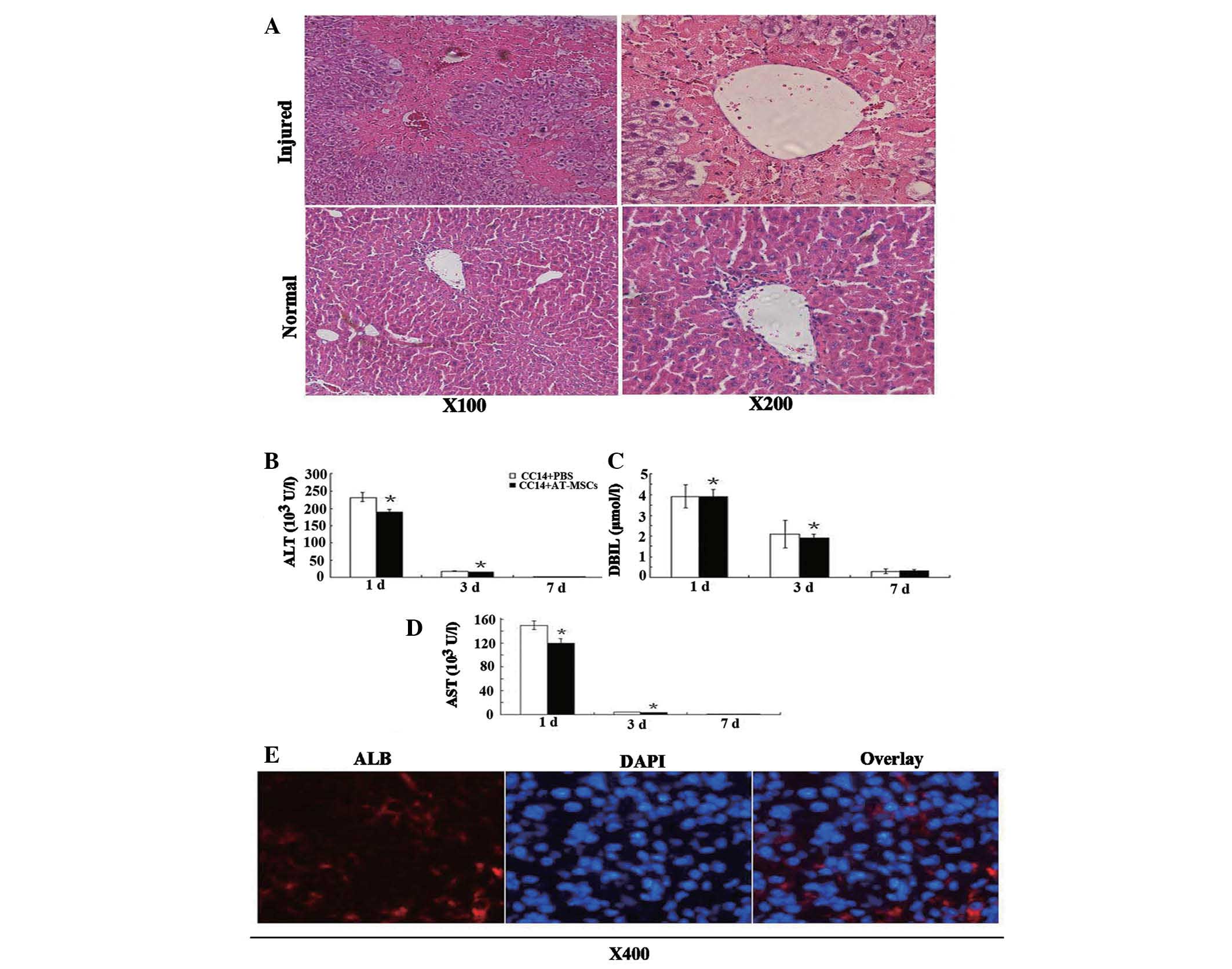
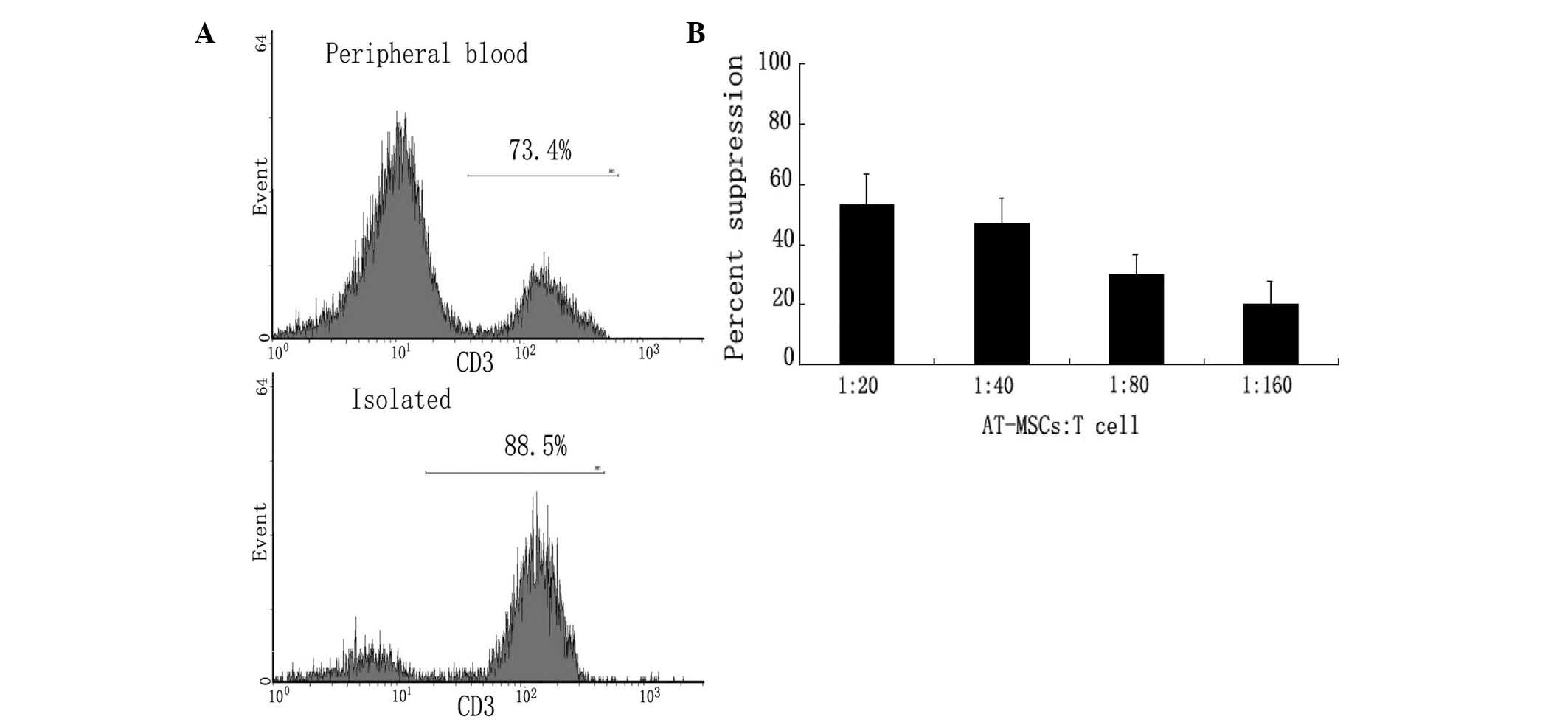
|
1
|
van Poll D, Parekkadan B, Cho CH, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cell-derived molecules directly modulate
hepatocellular death and regeneration in vitro and in vivo.
Hepatology. 47:1634–1643. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Kashofer K and Bonnet D: Gene therapy
progress and prospects: stem cell plasticity. Gene Ther.
12:1229–1234. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Kern S, Eichler H, Stoeve J, Klüter H and
Bieback K: Comparative analysis of mesenchymal stem cells from bone
marrow, umbilical cord blood, or adipose tissue. Stem Cells.
24:1294–1301. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Devine SM, Cobbs C, Jennings M,
Bartholomew A and Hoffman R: Mesenchymal stem cells distribute to a
wide range of tissues following systemic infusion into nonhuman
primates. Blood. 101:2999–3001. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Tepliashin AS, Chupikova NI, Korzhikova
SV, et al: Comparative analysis of cell populations with a
phenotype similar to that of mesenchymal stem cells derived from
subcutaneous fat. Tsitologiia. 47:637–643. 2005.(in Russian).
|
|
6
|
Malhi H, Irani AN, Gagandeep S and Gupta
S: Isolation of human progenitor liver epithelial cells with
extensive replication capacity and differentiation into mature
hepatocytes. J Cell Sci. 115:2679–2688. 2002.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Young HE, Steele TA, Bray RA, et al: Human
reserve pluripotent mesenchymal stem cells are present in the
connective tissues of skeletal muscle and dermis derived from
fetal, adult, and geriatric donors. Anat Rec. 264:51–62. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lowes KN, Croager EJ, Olynyk JK, Abraham
LJ and Yeoh GC: Oval cell-mediated liver regeneration: Role of
cytokines and growth factors. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 18:4–12.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Zuk PA, Zhu M, Ashjian P, et al: Human
adipose tissue is a source of multipotent stem cells. Mol Biol
Cell. 13:4279–4295. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Lagasse E, Connors H, Al-Dhalimy M, et al:
Purified hematopoietic stem cells can differentiate into
hepatocytes in vivo. Nat Med. 6:1229–1234. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Alison MR, Poulsom R, Jeffery R, et al:
Hepatocytes from non-hepatic adult stem cells. Nature. 406:2572000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Herzog EL, Chai L and Krause DS:
Plasticity of marrow-derived stem cells. Blood. 102:3483–3493.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Vassilopoulos G, Wang PR and Russell DW:
Transplanted bone marrow regenerates liver by cell fusion. Nature.
422:901–904. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Wang X, Willenbring H, Akkari Y, et al:
Cell fusion is the principal source of bone-marrow-derived
hepatocytes. Nature. 422:897–901. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Wagner W, Wein F, Seckinger A, et al:
Comparative characteristics of mesenchymal stem cells from human
bone marrow, adipose tissue, and umbilical cord blood. Exp Hematol.
33:1402–1416. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Snykers S, Vanhaecke T, De Becker A, et
al: Chromatin remodeling agent trichostatin A: a key-factor in the
hepatic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells derived of
adult bone marrow. BMC Dev Biol. 7:242007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yamamoto H, Quinn G, Asari A, et al:
Differentiation of embryonic stem cells into hepatocytes:
biological functions and therapeutic application. Hepatology.
37:983–993. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kim JW, Kim SY, Park SY, et al:
Mesenchymal progenitor cells in the human umbilical cord. Ann
Hematol. 83:733–738. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Reyes M, Lund T, Lenvik T, et al:
Purification and ex vivo expansion of postnatal human marrow
mesodermal progenitor cells. Blood. 98:2615–2625. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Teratani T, Yamamoto H, Aoyagi K, et al:
Direct hepatic fate specification from mouse embryonic stem cells.
Hepatology. 41:836–846. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yamamoto Y, Teratani T, Yamamoto H, et al:
Recapitulation of in vivo gene expression during hepatic
differentiation from murine embryonic stem cells. Hepatology.
42:558–567. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Baertschiger RM, Serre-Beinier V, Morel P,
et al: Fibrogenic potential of human multipotent mesenchymal
stromal cells in injured liver. PLoS One. 4:e66572009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Chien CC, Yen BL, Lee FK, et al: In vitro
differentiation of human placenta-derived multipotent cells into
hepatocyte-like cells. Stem Cells. 24:1759–1768. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Herold C, Ganslmayer M, Ocker M, et al:
The histone-deacetylase inhibitor Trichostatin A blocks
proliferation and triggers apoptotic programs in hepatoma cells. J
Hepatol. 36:233–240. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Vinken M, Henkens T, Vanhaecke T, et al:
Trichostatin a enhances gap junctional intercellular communication
in primary cultures of adult rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Sci.
91:484–492. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Henkens T, Papeleu P, Elaut G, et al:
Trichostatin A, a critical factor in maintaining the functional
differentiation of primary cultured rat hepatocytes. Toxicol Appl
Pharmacol. 218:64–71. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Bochev I, Elmadjian G, Kyurkchiev D, et
al: Mesenchymal stem cells from human bone marrow or adipose tissue
differently modulate mitogen-stimulated B-cell immunoglobulin
production in vitro. Cell Biol Int. 32:384–393. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
McIntosh K, Zvonic S, Garrett S, et al:
The immunogenicity of human adipose-derived cells: temporal changes
in vitro. Stem Cells. 24:1246–1253. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Battiwalla M and Hematti P: Mesenchymal
stem cells in hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Cytotherapy.
11:503–515. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Dinarello CA: The interleukin-1 family: 10
years of discovery. FASEB J. 8:1314–1325. 1994.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Ortiz LA, Dutreil M, Fattman C, et al:
Interleukin 1 receptor antagonist mediates the anti-inflammatory
and antifibrotic effect of mesenchymal stem cells during lung
injury. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:11002–11007. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Ponte AL, Marais E, Gallay N, et al: The
in vitro migration capacity of human bone marrow mesenchymal stem
cells: comparison of chemokine and growth factor chemotactic
activities. Stem Cells. 25:1737–1745. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Potian JA, Aviv H, Ponzio NM, Harrison JS
and Rameshwar P: Veto-like activity of mesenchymal stem cells:
functional discrimination between cellular responses to
alloantigens and recall antigens. J Immunol. 171:3426–3434. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Tang J, Wang J, Yang J, et al: Mesenchymal
stem cells over-expressing SDF-1 promote angiogenesis and improve
heart function in experimental myocardial infarction in rats. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 36:644–650. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Greco SJ and Rameshwar P:
Microenvironmental considerations in the application of human
mesenchymal stem cells in regenerative therapies. Biologics.
2:699–705. 2008.
|
|
36
|
Mouiseddine M, François S, Semont A, et
al: Human mesenchymal stem cells home specifically to
radiation-injured tissues in a non-obese diabetes/severe combined
immunodeficiency mouse model. Br J Radiol. 80(Spec 1): S49–55.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Oyagi S, Hirose M, Kojima M, et al:
Therapeutic effect of transplanting HGF-treated bone marrow
mesenchymal cells into CCl4-injured rats. J Hepatol.
44:742–748. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Pan MX, Hou WL, Zhang QJ, et al: Infusion
of autologous mesenchymal stem cells prolongs the survival of dogs
receiving living donor liver transplantation. J South Med Univ. (in
Chinese).
|
|
39
|
Kuo YR, Goto S, Shih HS, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells prolong composite tissue allotransplant
survival in a swine model. Transplantation. 87:1769–1777. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Matsuda Y, Matsumoto K, Ichida T and
Nakamura T: Hepatocyte growth factor suppresses the onset of liver
cirrhosis and abrogates lethal hepatic dysfunction in rats. J
Biochem. 118:643–649. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Silva GV, Litovsky S, Assad JA, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells differentiate into an endothelial phenotype,
enhance vascular density, and improve heart function in a canine
chronic ischemia model. Circulation. 111:150–156. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Phinney DG and Prockop DJ: Concise review:
mesenchymal stem/multipotent stromal cells: the state of
transdifferentiation and modes of tissue repair - current views.
Stem Cells. 25:2896–2902. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Krampera M, Cosmi L, Angeli R, et al: Role
for interferon-gamma in the immunomodulatory activity of human bone
marrow mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells. 24:386–398. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Rasmusson I, Uhlin M, Le Blanc K and
Levitsky V: Mesenchymal stem cells fail to trigger effector
functions of cytotoxic T lymphocytes. J Leukoc Biol. 82:887–893.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|