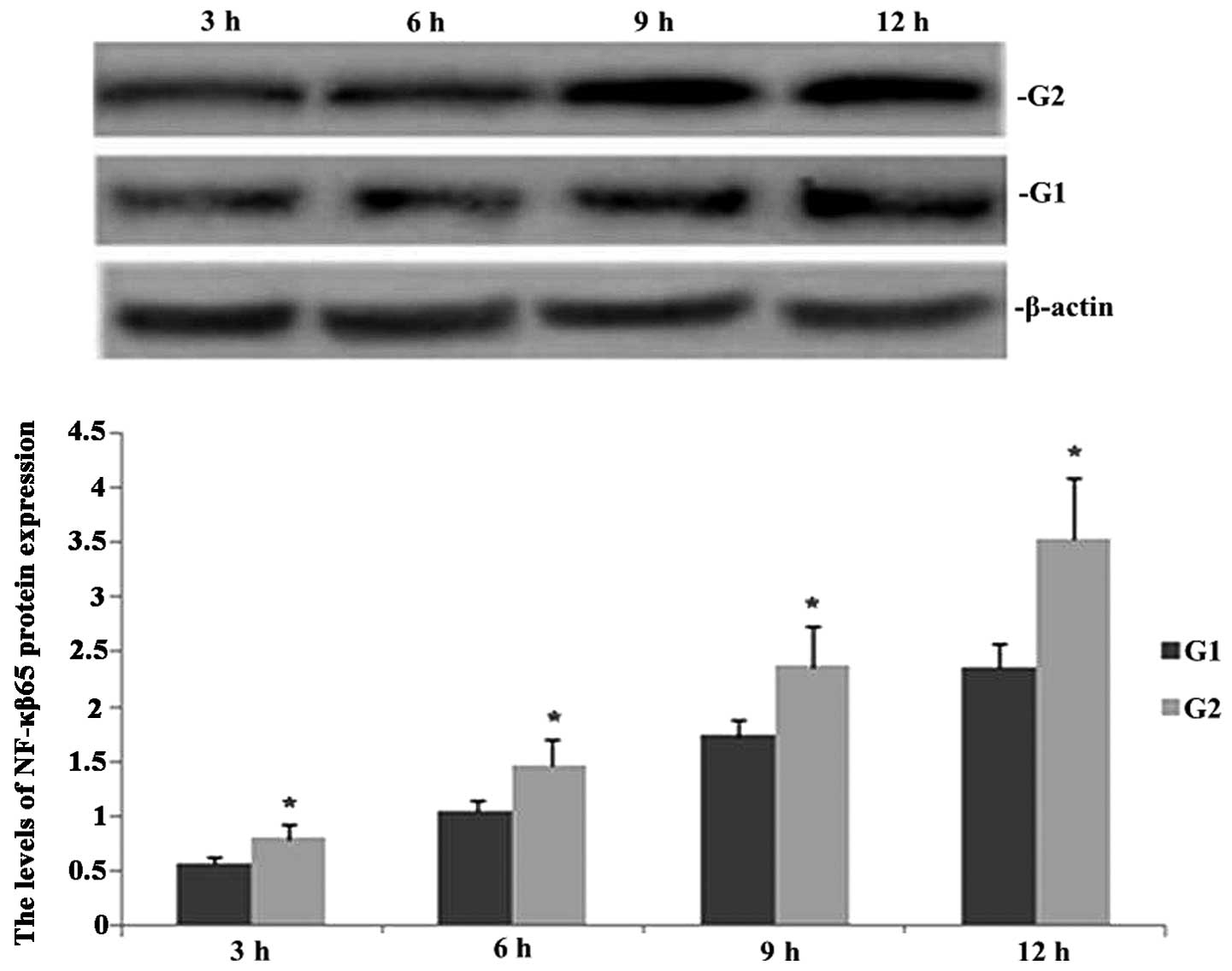
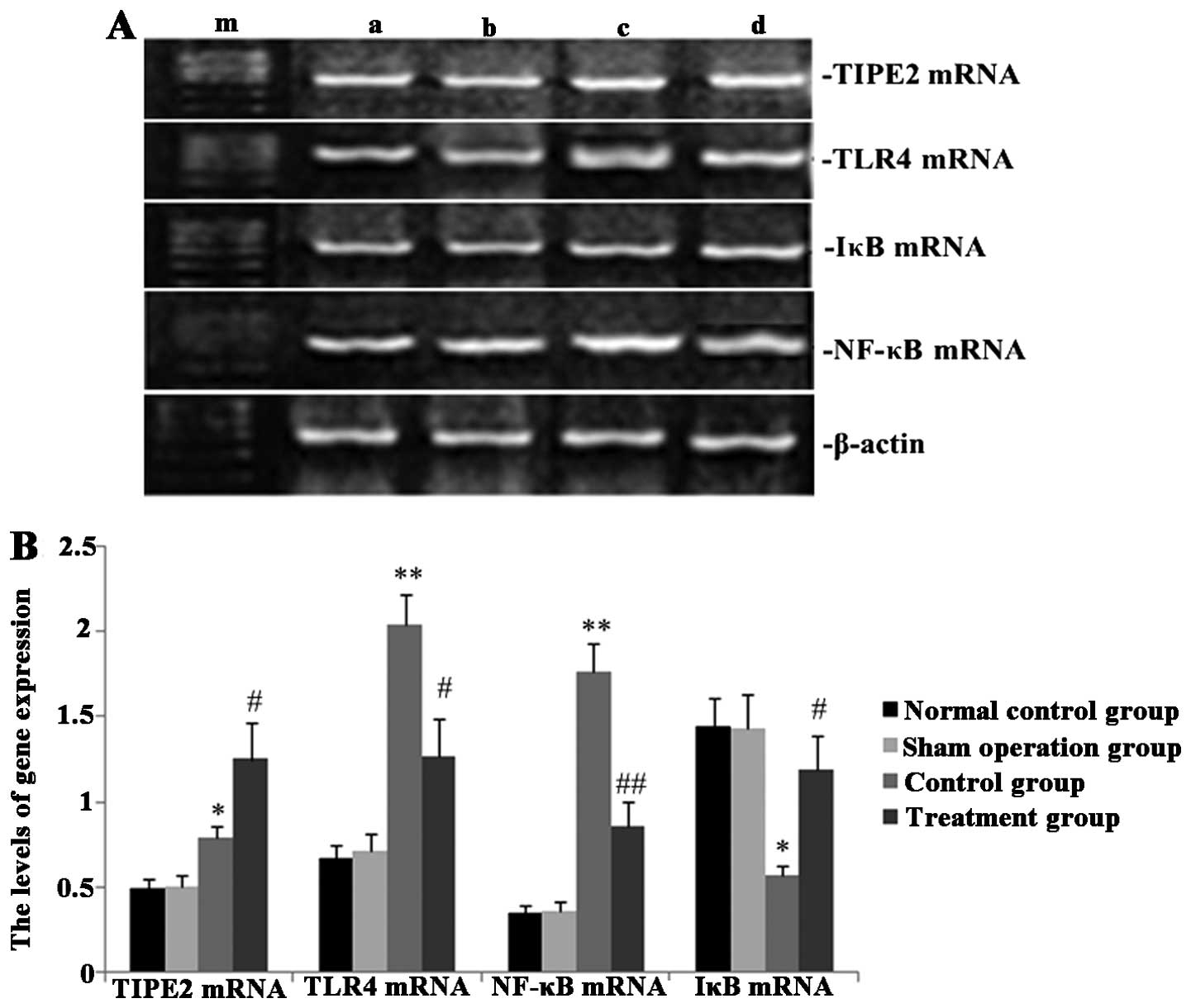
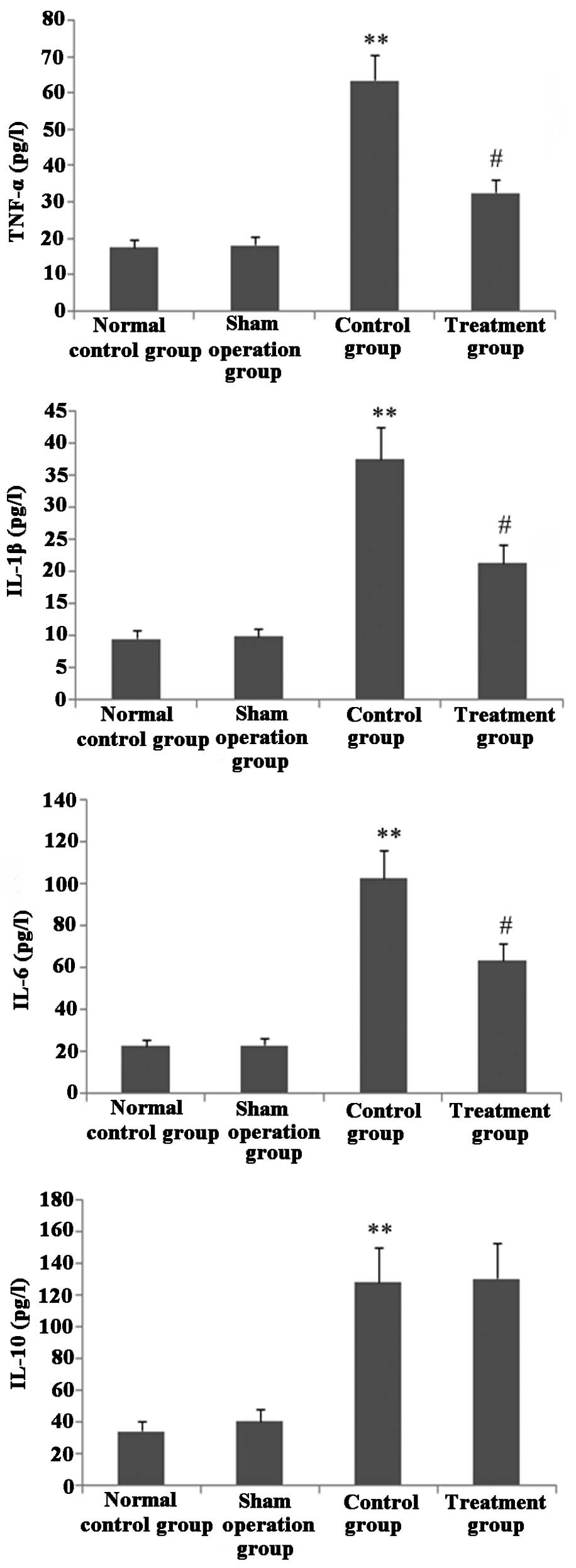
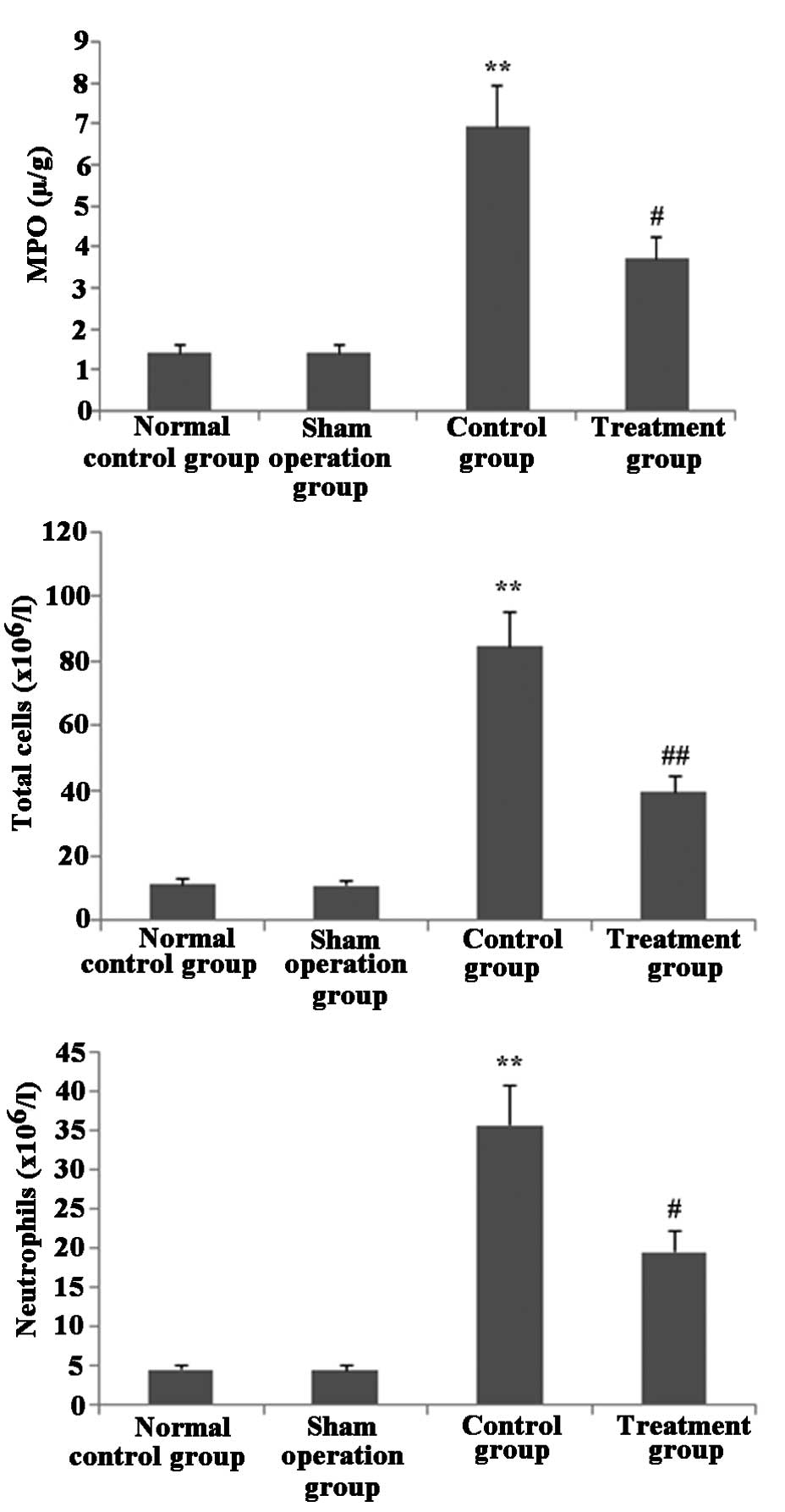
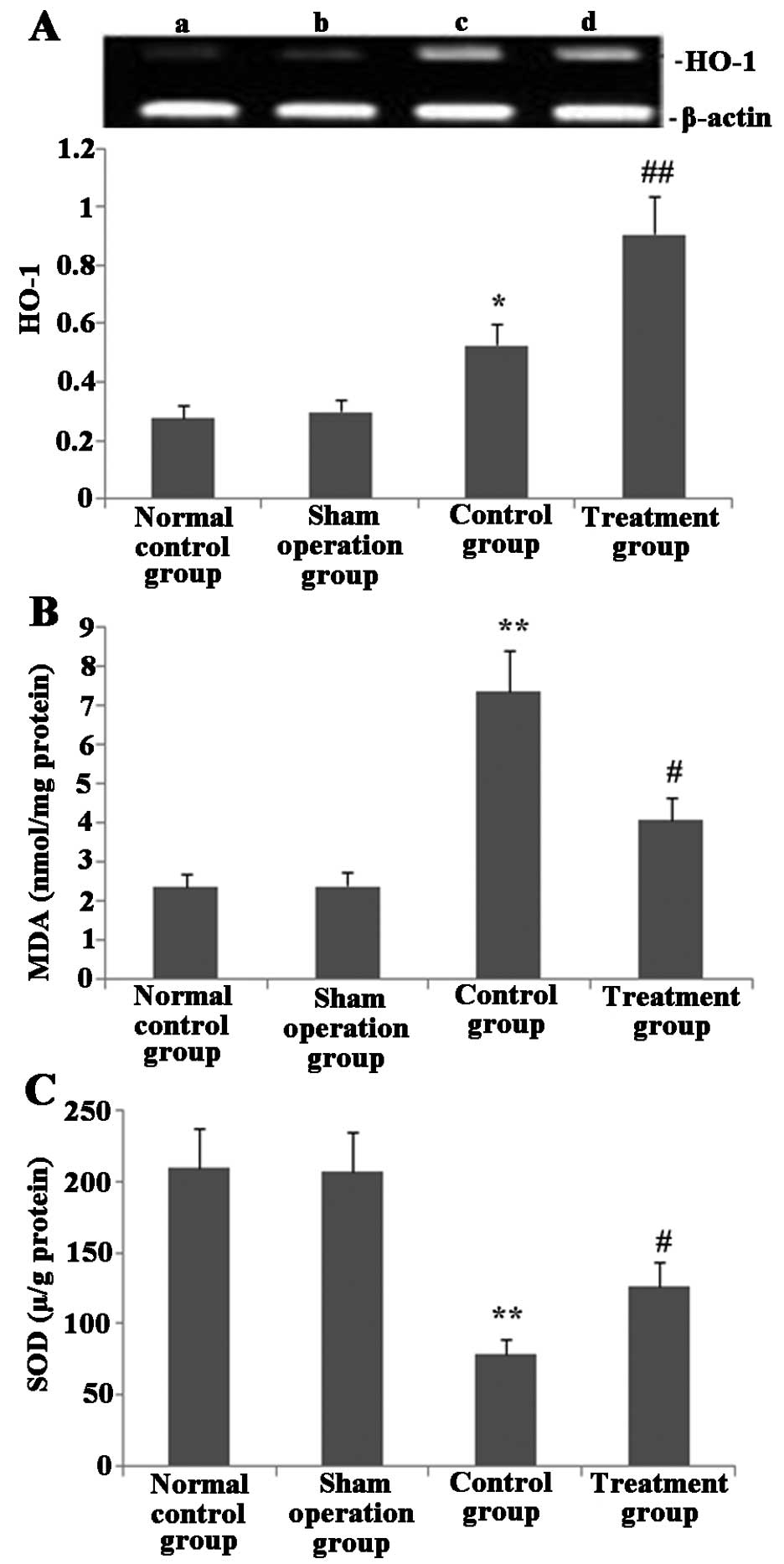
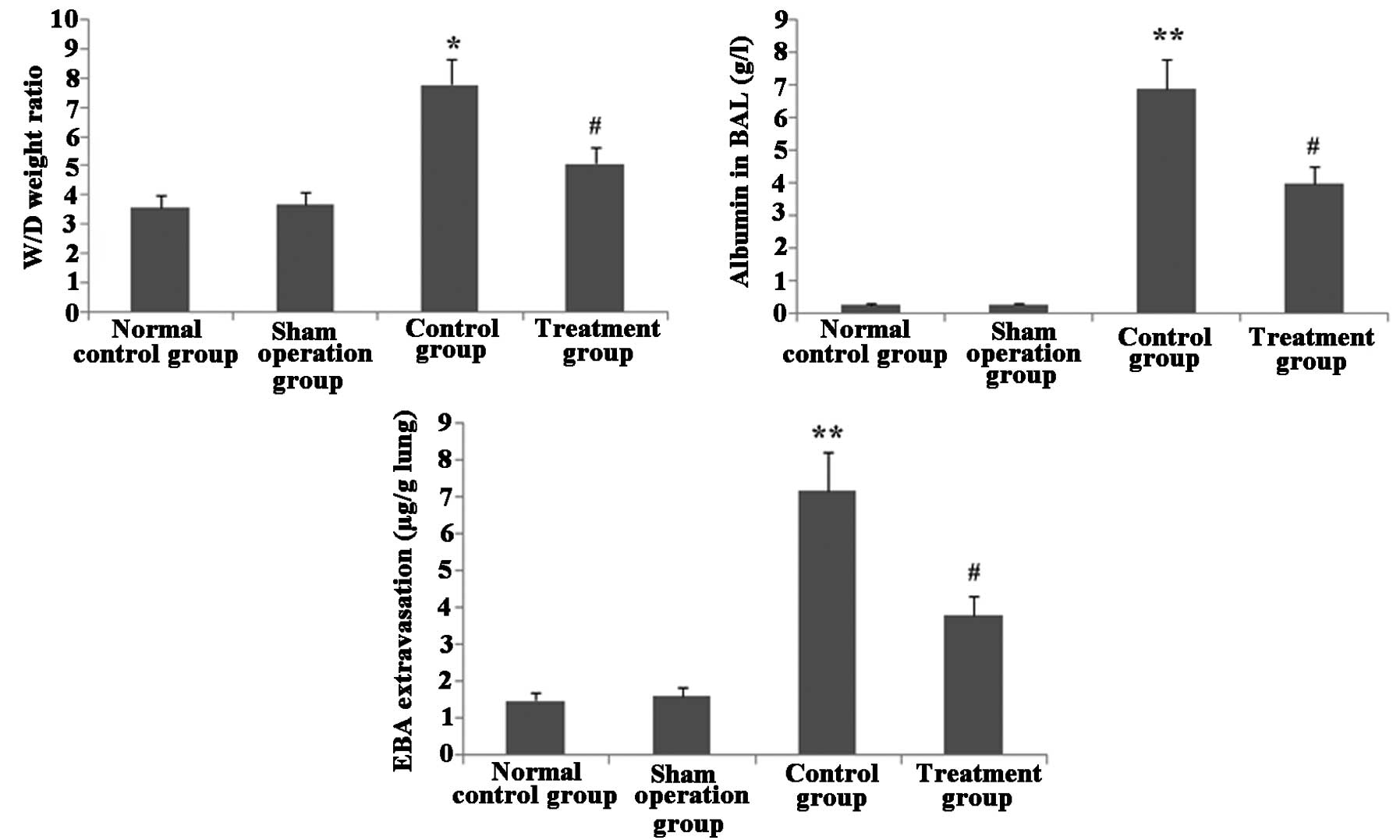
|
1
|
Seoane L, Winterbottom F, Nash T,
Behrhorst J, Chacko E, Shum L, Pavlov A, Briski D, Thibeau S,
Bergeron D, et al: Using quality improvement principles to improve
the care of patients with severe sepsis and septic shock. Ochsner
J. 13:359–366. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Lee JW, Kwon JH, Lim MS, Lee HJ, Kim SS,
Lim SY and Chun W: 3,4,5-Trihydroxycinnamic acid increases
heme-oxygenase-1 (HO-1) and decreases macrophage infiltration in
LPS-induced septic kidney. Mol Cell Biochem. 397:109–116. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Koch A, Meesters MI, Scheller B, Boer C
and Zacharowski K: Systemic endotoxin activity correlates with clot
formation: an observational study in patients with early systemic
inflammation and sepsis. Crit Care. 17:R1982013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Brichon PY, Poquet C, Arvieux C and Pison
C: Successful treatment of a life-threatening air leakage,
complicating severe abdominal sepsis, with a one-way endobronchial
valve. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 15:779–780. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Rivers EP, Katranji M, Jaehne KA, Brown S,
Abou Dagher G, Cannon C and Coba V: Early interventions in
severesepsis and septic shock: a review of the evidence one decade
later. Minerva Anestesiol. 78:712–724. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lou Y and Liu S: The TIPE (TNFAIP8) family
in inflammation, immunity, and cancer. Mol Immunol. 49:4–7. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Luan YY, Yao YM, Zhang L, Dong N, Zhang
QH, Yu Y and Sheng ZY: Expression of tumor necrosis factor-α
induced protein 8 like-2 contributes to the immunosuppressive
property of CD4(+) CD25(+) regulatory T cells in mice. Mol Immunol.
49:219–226. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Lou Y, Sun H, Morrissey S, Porturas T, Liu
S, Hua X and Chen YH: Critical roles of TIPE2 protein in murine
experimental colitis. J Immunol. 193:1064–1070. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang Q, Huber N, Noel G, Haar L, Shan Y,
Pritts TA and Ogle CK: NF-κB inhibition is ineffective in blocking
cytokine-induced IL-8 production but P38 and STAT1 inhibitors are
effective. Inflamm Res. 61:977–985. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Li X, Wu G, Wu M, Chen W and Liu X: In
vitro study of inhibitory millimeter wave treatment effects on the
TNF-α-induced NF-κB signal transduction pathway. Int J Mol Med.
27:71–78. 2011.
|
|
11
|
Sun X, Lv Z, Peng H, Fung M, Yang L, Yang
J, Zheng H, Liang J and Wu Z: Effects of a recombinant
schistosomal-derived anti-inflammatory molecular (rSj16) on the
lipopolysaccharide (LPS)-induced activated RAW264.7. Parasitol Res.
110:2429–2437. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Xu F, Zeng W, Mao X and Fan GK: The
efficacy of Melilotus extract in the management of postoperative
ecchymosis and edema after simultaneous rhinoplasty and
blepharoplasty. Aesthetic Plast Surg. 32:599–603. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Pleşca-Manea L, Pârvu AE, Pârvu M, Taămaş
M, Buia R and Puia M: Effects of Melilotus officinalis on acute
inflammation. Phytother Res. 16:316–319. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Namsa ND, Tag H, Mandal M, Kalita P and
Das AK: An ethnobotanical study of traditional anti-inflammatory
plants used by the Lohit community of Arunachal Pradesh. India J
Ethnopharmacol. 125:234–245. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Pang R, Zhang SL, Zhao L, Liu SL, Dong JH
and Tao JY: Effect of petroleum ether extract from Melilotus
suaveolens Ledeb on the expression of NF-kappaB and Heme oxygenase
1. Xi Bao Yu Fen Zi Mian Yi Xue Za Zhi. 24:861–863. 2008.(In
Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Asres K, Gibbons S, Hana E and Bucar F:
Anti-inflammatory activity of extracts and a saponin isolated from
Melilotus elegans. Pharmazie. 60:310–312. 2005.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zhang XY, Tao JY, Zhao L, Huang ZJ, Xiong
FL, Zhang SL, Li CM and Xiao F: In vitro anti-inflammatory effects
of different solution fractions of ethanol extract from Melilotus
suaveolens Ledeb. Chin Med J (Engl). 120:1992–1998. 2007.
|
|
18
|
Cataldi A, Gasbarro V, Viaggi R, Soverini
R, Gresta E and Mascoli F: Effectiveness of the combination of
alpha tocopherol, rutin, melilotus, and centella asiatica in the
treatment of patients with chronic venous insufficiency. Minerva
Cardioangiol. 49:159–163. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Forte R, Cennamo G, Finelli ML,
Bonavolontà P, de Crecchio G and Greco GM: Combination of
flavonoids with Centella asiatica and Melilotus for diabetic
cystoid macular edema without macular thickening. J Ocul Pharmacol
Ther. 27:109–113. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Yu Z, Zhou X, Yu S, Xie H and Zheng S:
IL-15 is decreased upon CsA and FK506 treatment of acute rejection
following heart transplantation in mice. Mol Med Rep. 11:37–42.
2015.
|
|
21
|
Wang LY, Fan YC, Zhao J, Gao S, Sun FK,
Han J, Yang Y and Wang K: Elevated expression of tumour necrosis
factor-α-induced protein 8 (TNFAIP8)-like 2 mRNA in peripheral
blood mononuclear cells is associated with disease progression of
acute-on-chronic hepatitis B liver failure. J Viral Hepat.
21:64–73. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Bradford MM: Rapid and sensitive method
for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing
the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254.
1976. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kakkar P, Das B and Viswanathan PN: A
modified spectrophotometric assay of superoxide dismutase. Indian J
Biochem Biophys. 21:130–132. 1984.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Farooq MA, Ali S, Hameed A, Ishaque W,
Mahmood K and Iqbal Z: Alleviation of cadmium toxicity by silicon
is related to elevated photosynthesis, antioxidant enzymes;
suppressed cadmium uptake and oxidative stress in cotton.
Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. 96:242–249. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Dada L, Gonzalez AR, Urich D, Soberanes S,
Manghi TS, Chiarella SE, Chandel NS, Budinger GR and Mutlu GM:
Alcohol worsens acute lung injury by inhibiting alveolar sodium
transport through the adenosine A1 receptor. PLoS One.
7:e304482012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Li Z and Jin ZQ: Ischemic preconditioning
enhances integrity of coronary endothelial tight junctions. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 425:630–635. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Luna LG: Routine staining procedures
Hematoxylin and eosin stains. Manual of Histologic Staining Methods
of the Armed Forces Institute of Pathology. 3rd edition.
McGraw-Hill; New York, NY: pp. 32–39. 1968
|
|
28
|
Seely KA, Holthoff JH, Burns ST, Wang Z,
Thakali KM, Gokden N, Rhee SW and Mayeux PR: Hemodynamic changes in
the kidney in a pediatric rat model of sepsis-induced acute kidney
injury. Am J Physiol Renal Physiol. 301:F209–F217. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Iba T, Okamoto K, Kawasaki S, Nakarai E
and Miyasho T: Effect of hemoperfusion using polymyxin
B-immobilized fibers on non-shock rat sepsis model. J Surg Res.
171:755–761. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Chihara R, Nakamoto H, Arima H, Moriwaki
K, Kanno Y, Sugahara S, Okada H and Suzuki H: Systemic capillary
leak syndrome. Intern Med. 41:953–956. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Miliauskas G, Venskutonis PR and Beek TA:
Screening of radical scavenging activity of some medicinal and
aromatic plant extracts. Food Chem. 85:231–237. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Trouillas P, Calliste CA, Allais DP, Simon
A, Marfak A, Delage C and Duroux JL: An tioxidant,
anti-inflammatory and an tip roliferative properties of sixteen
water plant extracts used in the Limousin countryside as herbal
teas. Food Chem. 80:399–407. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Parejo I, Viladomat F, Bastida J,
Schmeda-Hirschmann G, Burillo J and Codina C: Bioguided isolation
and identification of the nonvolatile antioxidant compounds from
fennel(Foeniculum vulgare Mill) waste. Agric Food Chem.
52:1890–1897. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Pabst HW and Klemm H: Effect of extracts
of Melilotus officinalis. Med Monatsschr. 4:589–591. 1960.(In
German).
|
|
35
|
Kang SS, Lee YS and Lee EB: Isolation of
azukisaponin V possessing leucocyte migration inhibitory activity
from Melilotus officinalis. Natural Products. 18:89–93. 1987.
|
|
36
|
Zhang XY, Tao JY, Zhao L, Huang ZJ, Xiong
FL, Zhang SL, Li CM and Xiao F: In vitro anti-inflammatory effects
of different solution fractions of ethanol extract from Melilotus
suaveolens Ledeb. Chin Med J (Engl). 120:1992–1998. 2007.
|
|
37
|
Wang TY, Li J, Jin Z, Wu F and Zhou Q:
Inhibitory effect of TGF-β1 on no production in peritoneal
macrophages from collagen-induced arthritis rats involving the
LPS-TLR4 pathway. Mol Med Rep. 8:1143–1148. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Black KE, Collins SL, Hagan RS, Hamblin
MJ, Chan-Li Y, Hallowell RW, Powell JD and Horton MR: Hyaluronan
fragments induce IFNbeta via a novel TLR4-TRIF-TBK1-IRF3-dependent
pathway. Inflamm (Lond). 10:23–29. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
39
|
Ren W, Hu L, Hua F, Jin J, Wang Y and Zhu
L: Myeloid differentiation protein 2 silencing decreases
LPS-induced cytokine production and TLR4/MyD88 pathway activity in
alveolar macrophages. Immunol Lett. 141:94–101. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Kannan Y, Sundaram K, Aluganti Narasimhulu
C, Parthasarathy S and Wewers MD: Oxidatively modified low density
lipoprotein (LDL) inhibits TLR2 and TLR4 cytokine responses in
human monocytes but not in macrophages. J Biol Chem.
287:23479–23488. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Zhang Y, Wei X, Liu L, Liu S, Wang Z,
Zhang B, Fan B, Yang F, Huang S, Jiang F, Chen YH and Yi F: TIPE2,
a novel regulator of immunity, protects against experimental
stroke. J Biol Chem. 287:32546–32555. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
42
|
Li D, Song L, Fan Y, Li X, Li Y, Chen J,
Zhu F, Guo C, Shi Y and Zhang L: Down-regulation of TIPE2mRNA
expression in peripheral blood mononuclear cells from patients with
systemic lupus erythematosus. Clin Immunol. 133:422–427. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Zhang X, Wang J, Fan C, Li H, Sun H, Gong
S, Chen YH and Shi Y: Crystal structure of TIPE2 provides insights
into immune homeostasis. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 16:89–90. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
44
|
Liu MW, Su MX, Zhang W, Wang L and Qian
CY: Atorvastatin increases lipopolysaccharide-induced expression of
tumour necrosis factor-α-induced protein 8-like 2 in RAW264.7
cells. Exp Ther Med. 8:219–228. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Gus-Brautbar Y, Johnson D, Zhang L, Sun H,
Wang P, Zhang S, Zhang L and Chen YH: The anti-inflammatory TIPE2
is an inhibitor of the oncogenic Ras. Mol Cell. 45:610–618. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
46
|
Sun H, Gong S, Carmody RJ, Hilliard A, Li
L, Sun J, Kong L, Xu L, Hilliard B, Hu S, Shen H, Yang X and Chen
YH: TIPE2, a negative regulator of innate and adaptive immunity
that maintain immune Homeostasis. Cell. 133:415–426. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
47
|
Xi W, Hu Y, Liu Y, Zhang J, Wang L, Lou Y,
Qu Z, Cui J, Zhang G, et al: Roles of TIPE2 in hepatitis B
virus-induced hepatic inflammation in humans and mice. Mol Immunol.
48:1203–1208. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
48
|
Freundt EC, Bidere N and Lenardo MJ: A
different TIPE2 of immune homeostasis. Cell. 133:401–402. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
49
|
Wang HT, Liu CF, Tsai TH, Chen YL, Chang
HW, Tsai CY, Leu S, Zhen YY, Chai HT, et al: Effect of obesity
reduction on preservation of heart function and attenuation of left
ventricular remodeling, oxidative stress and inflammation in obese
mice. J Transl Med. 10:145–148. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
50
|
Lv R, Zheng J, Ye Z, Sun X, Tao H, Liu K,
Li R, Xu W, Liu W and Zhang R: Advances in the therapy of
hyperoxia-induced lung injury: findings from animal models.
Undersea Hyperb Med. 41:183–202. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
51
|
Su ZQ, Mo ZZ, Liao JB, Feng XX, Liang YZ,
Zhang X, Liu YH, Chen XY, Chen ZW, Su ZR and Lai XP: Usnic acid
protects LPS-induced acute lung injury in mice through attenuating
inflammatory responses and oxidative stress. Int Immunopharmacol.
22:371–378. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
52
|
Wu KL, Chan SH and Chan JY:
Neuroinflammation and oxidative stress in rostral ventrolateral
medulla contribute to neurogenic hypertension induced by systemic
inflammation. J Neuroinflammation. 9:212–218. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
53
|
Lino-dos-Santos-Franco A, Correa-Costa M,
Durão AC, de Oliveira AP, Breithaupt-Faloppa AC, de Bertoni JA,
Oliveira-Filho RM, Câmara NO, Marcourakis T and Tavares-de-Lima W:
Formaldehyde induces lung inflammation by an oxidant and
antioxidant enzymes mediated mechanism in the lung tissue. Toxicol
Lett. 207:278–285. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
54
|
de Sousa Oliveira Vanderlei E, de Araújo
IW, Quinderé AL, Fontes BP, Eloy YR, Rodrigues JA, e Silva AA,
Chaves HV, Jorge RJ, et al: The involvement of the HO-1 pathway in
the anti-inflammatory action of a sulfated polysaccharide isolated
from the red seaweed Gracilaria birdiae. Inflamm Res. 60:1121–1130.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
55
|
Yeligar SM, Machida K and Kalra VK:
Ethanol-induced HO-1 and NQO1 are differentially regulated by
HIF-1alpha and Nrf2 to attenuate inflammatory cytokine expression.
J Biol Chem. 285:35359–35373. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
56
|
Hu ZF and Sun HC: The mechanism of
inflammatory mediators of vascular endothelial cells in acute lung
injury. Traum Surg. 11:281–290. 2009.
|
|
57
|
Campos R, Shimizu MH, Volpini RA, de
Bragança AC, Andrade L, Lopes FD, Olivo C, Canale D and Seguro AC:
N-acetylcysteine prevents pulmonary edema and acute kidney injury
in rats with sepsis submitted to mechanical ventilation. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 302:L640–L650. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|