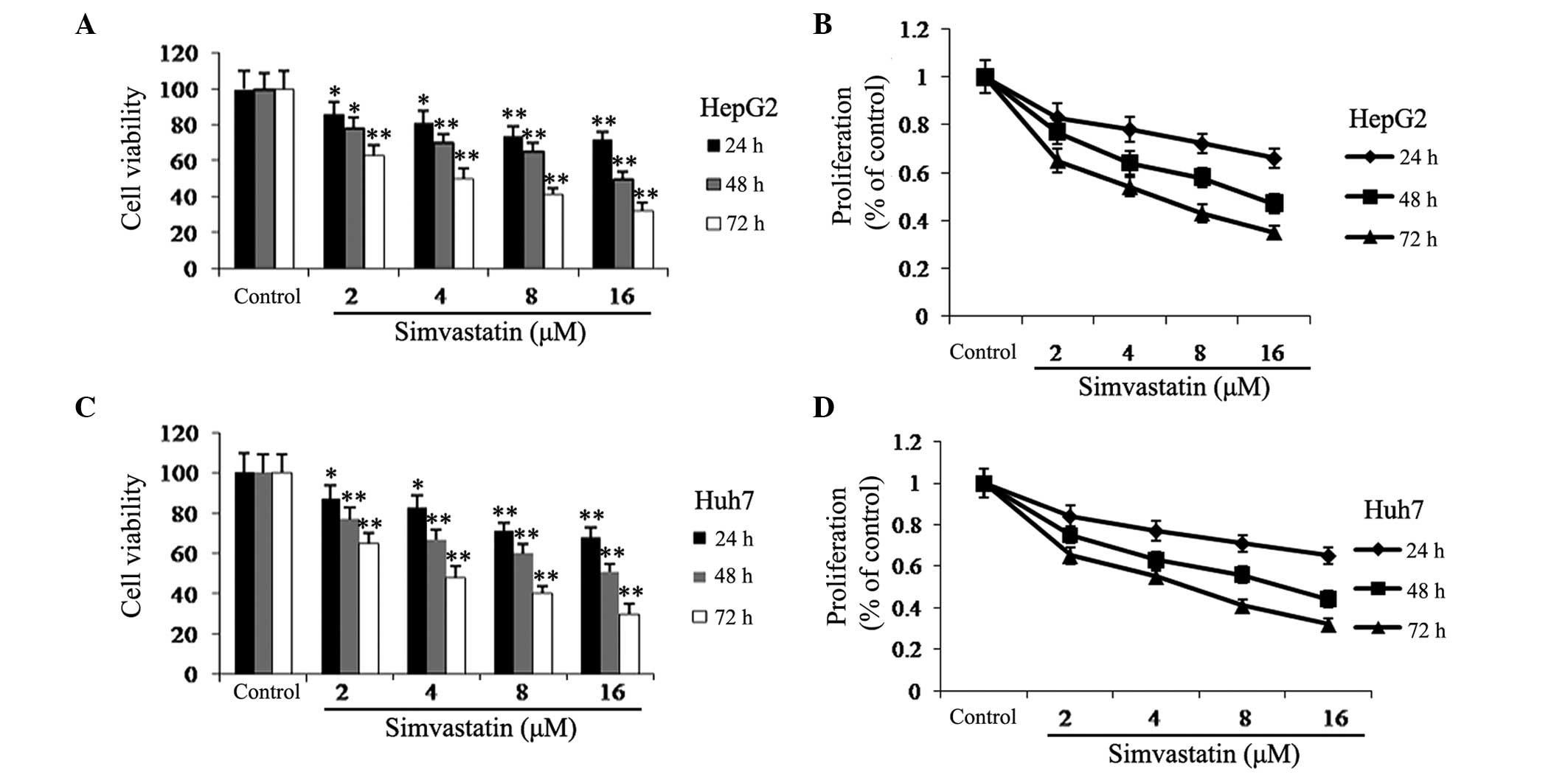
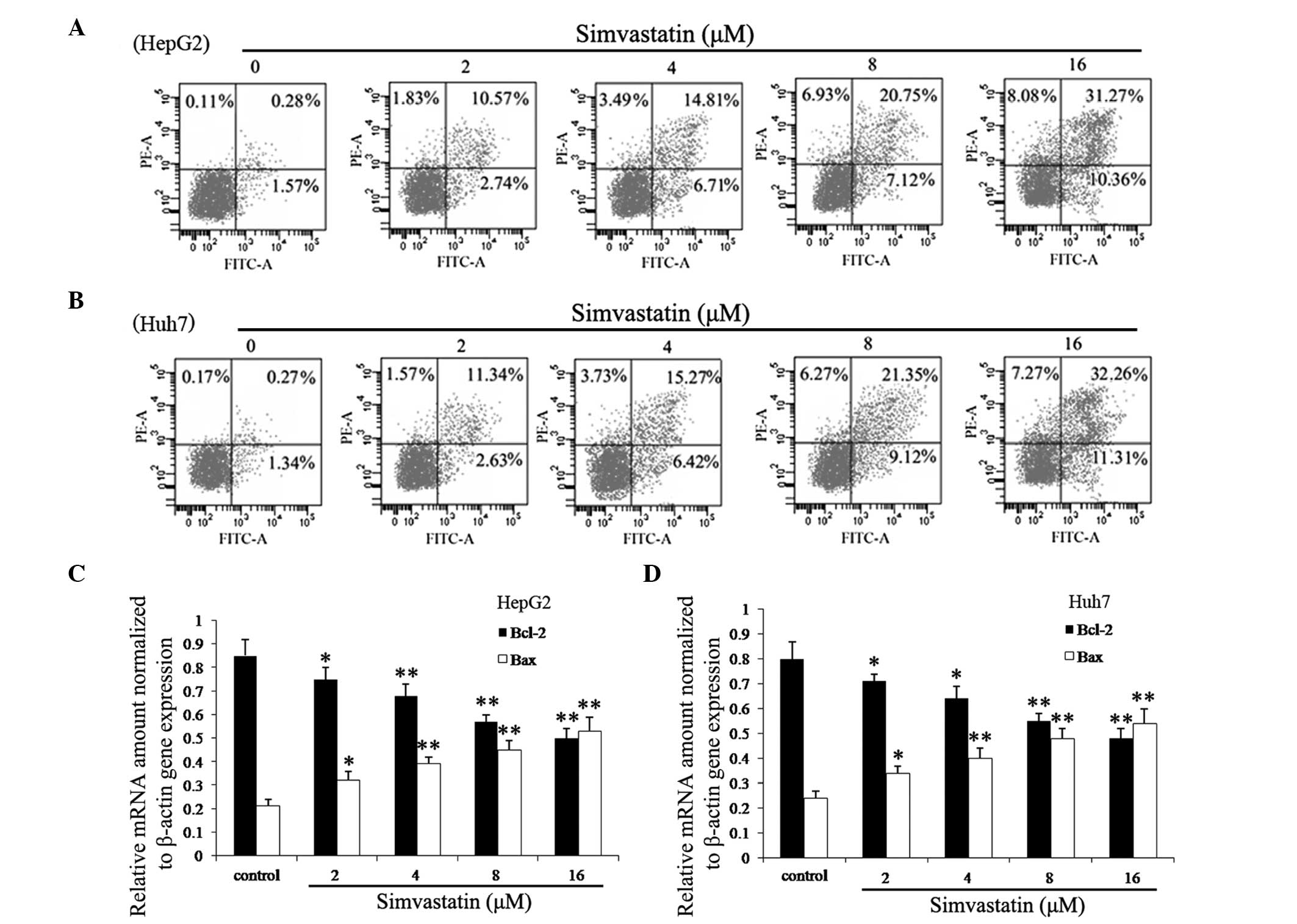
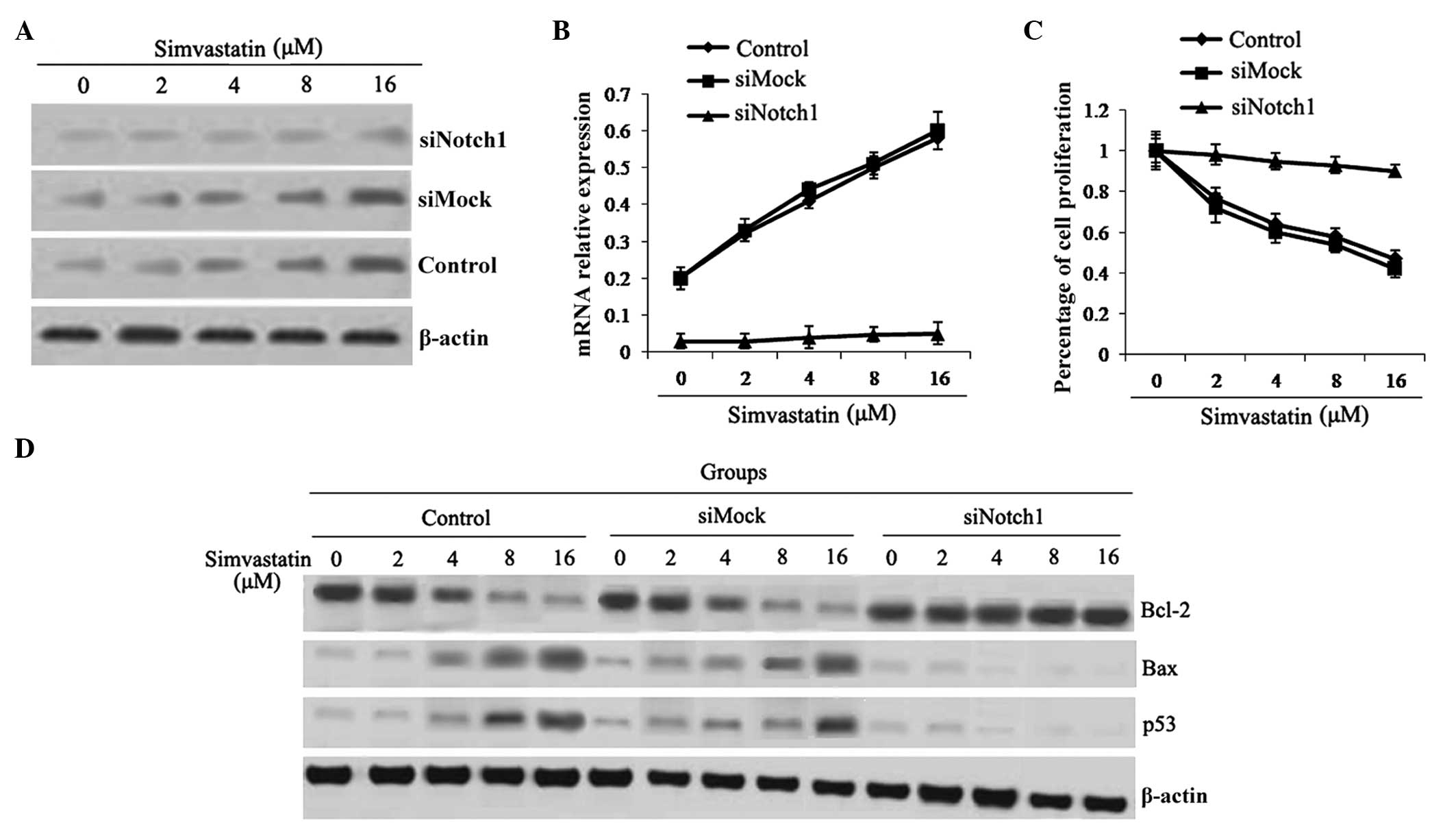
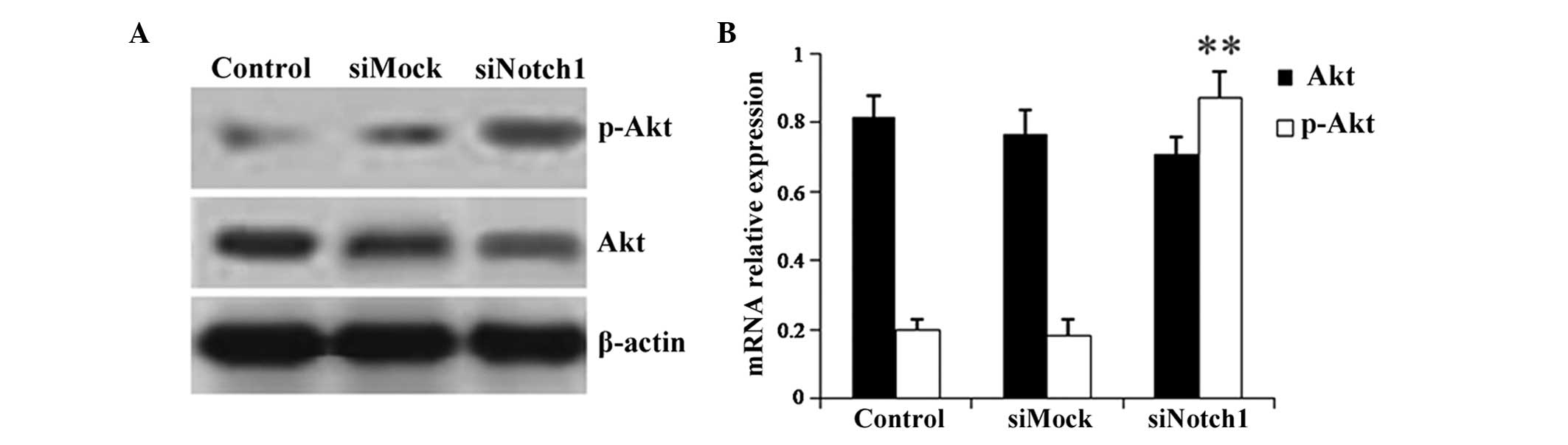
|
1
|
El-Serag HB and Rudolph KL: Hepatocellular
carcinoma: epidemiology and molecular carcinogenesis.
Gastroenterology. 132:2557–2576. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tsochatzis E, Meyer T, O’Beirne J and
Burroughs AK: Transarterial chemoembolisation is not superior to
embolisation alone: The recent European Association for the Study
of the Liver (EASL)-European Organisation for Research and
Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) guidelines. Eur J Cancer. 49:1509–1510.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Cabibbo G, Rolle E, De Giorgio M, et al:
Management of cirrhotic patients with hepatocellular carcinoma
treated with sorafenib. Expert Rev Anticancer Ther. 11:1807–1816.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Parkin DM: Global cancer statistics in the
year 2000. Lancet Onco. 2:533–543. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Jakobisiak M and Golab J: Statins can
modulate effectiveness of antitumor therapeutic modalities. Med Res
Rev. 30:102–135. 2010.
|
|
6
|
Jakobisiak M and Golab J: Potential
antitumor effects of statins (Review). Int J Oncol. 23:1055–1069.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Graaf MR, Richel DJ, van Noorden CJ and
Guchelaar HJ: Effects of statins and farnesyltransferase inhibitors
on the development and progression of cancer. Cancer Treat Rev.
30:609–641. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liao JK and Laufs U: Pleiotropic effects
of statins. Annu Rev Pharmacol Toxicol. 45:89–118. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Freed-Pastor WA, Mizuno H, Zhao X, et al:
Mutant p53 disrupts mammary tissue architecture via the mevalonate
pathway. Cell. 148:244–258. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Kochuparambil ST, Al-Husein B, Goc A,
Soliman S and Somanath PR: Anticancer efficacy of simvastatin on
prostate cancer cells and tumor xenografts is associated with
inhibition of Akt and reduced prostate-specific antigen expression.
J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 336:496–505. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Wang Y, Xu SL, Wu YZ, et al: Simvastatin
induces caspase-dependent apoptosis and activates p53 in OCM-1
cells. Exp Eye Res. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Xu J, Liu X, Chen J, et al: Simvastatin
enhances bone marrow stromal cell differentiation into endothelial
cells via notch signaling pathway. Am J Physiol Cell Physiol.
296:C535–C543. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
13
|
Zacharek A, Chen J, Cui X, Yang Y and
Chopp M: Simvastatin increases notch signaling activity and
promotes arteriogenesis after stroke. Stroke. 40:254–260. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Aster JC, Xu L, Karnell FG, et al:
Essential roles for ankyrin repeat and transactivation domains in
induction of T-cell leukemia by notch1. Mol Cell Biol.
20:7505–7515. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bresnick EH, Chu J, Christensen HM, Lin B
and Norton J: Linking Notch signaling, chromatin remodeling, and
T-cell leukemogenesis. J Cell Biochem Suppl. 35(Suppl): 46–53.
2000. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Wael H, Yoshida R, Kudoh S, et al: Notch
signaling controls cell proliferation, apoptosis and
differentiation in lung carcinoma. Lung Cancer. 85:131–140. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ramdass B, Maliekal TT, Lakshmi S, et al:
Coexpression of Notch1 and NF-κB signaling pathway components in
human cervical cancer progression. Gynecol Oncol. 104:352–361.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Wang Z, Banerjee S, Li Y, et al:
Down-regulation of notch-1 inhibits invasion by inactivation of
nuclear factor-κB, vascular endothelial growth factor, and matrix
metalloproteinase-9 in pancreatic cancer cells. Cancer Res.
66:2778–2784. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J, Fu L, Gu F and Ma Y: Notch1 is
involved in migration and invasion of human breast cancer cells.
Oncol Rep. 26:1295–1303. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Qi R, An H, Yu Y, et al: Notch1 signaling
inhibits growth of human hepatocellular carcinoma through induction
of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Cancer Res. 63:8323–8329.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Yu Y, Zhou XD, Liu YK, et al: Platelets
promote the adhesion of human hepatoma cells with a highly
metastatic potential to extracellular matrix protein: involvement
of platelet P-selectin and GP IIb-IIIa. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol.
128:283–287. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Yu H, Zhao X, Huang S, et al: Blocking
Notch1 signaling by RNA interference can induce growth inhibition
in HeLa cells. Int J Gynecol Cancer. 17:511–516. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Singh L, Pushker N, Saini N, et al:
Expression of pro-apoptotic Bax and anti-apoptotic Bcl-2 proteins
in human retinoblastoma. Clin Experiment Ophthalmol. Jul
31–2014.(Epud ahead of print). View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Gao J, Yan Q, Liu S and Yang X: Knockdown
of EpCAM enhaces the chemosensitivity of breast cancer cells to
5-fluorouracil by downregulating the antiapoptotic factor Bcl-2.
PLoS One. 9:e1025902014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Ekström L, Johansson M, Monostory K, et
al: Simvastatin inhibits the core promoter of the TXNRD1 gene and
lowers cellular TrxR activity in HepG2 cells. Biochem Biophys Res
Commun. 430:90–94. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Liao JK: Isoprenoids as mediators of the
biological effects of statins. J Clin Invest. 110:285–288. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Shimada T, Takeshita Y, Murohara T, et al:
Angiogenesis and vasculogenesis are impaired in the
precocious-aging klotho mouse. Circulation. 110:1148–1155. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Seeger H, Wallwiener D and Mueck A:
Statins can inhibit proliferation of human breast cancer cells in
vitro. Exp Clin Endocrinol Diabetes. 111:47–48. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Mandal CC and Ghosh-Choudhury N, Yoneda T,
Choudhury GG and Ghosh-Choudhury N: Simvastatin prevents skeletal
metastasis of breast cancer by an antagonistic interplay between
p53 and CD44. J Biol Chem. 286:11314–11327. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Hwang KE, Na KS, Park DS, et al: Apoptotic
induction by simvastatin in human lung cancer A549 cells via Akt
signaling dependent down-regulation of survivin. Invest New Drugs.
29:945–952. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Hussain B, Saleh GM, Sivaprasad S and
Hammond CJ: Changing from Snellen to LogMAR: debate or delay? Clin
Experimental Ophthalmol. 34:6–8. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Sriuranpong V, Borges MW, Ravi RK, et al:
Notch signaling induces cell cycle arrest in small cell lung cancer
cells. Cancer Res. 61:3200–3205. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Shou J, Ross S, Koeppen H, de Sauvage FJ
and Gao WQ: Dynamics of notch expression during murine prostate
development and tumorigenesis. Cancer Res. 61:7291–7297.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Talora C, Sgroi DC, Crum CP and Dotto GP:
Specific down-modulation of Notch1 signaling in cervical cancer
cells is required for sustained HPV-E6/E7 expression and late steps
of malignant transformation. Genes Dev. 16:2252–2263. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Nicolas M, Wolfer A, Raj K, et al: Notch1
functions as a tumor suppressor in mouse skin. Nature Genet.
33:416–421. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Ahn S, Hyeon J and Park CK: Notch1 and
Notch4 are markers for poor prognosis of hepatocellular carcinoma.
Hepatobiliary Pancreat Dis Int. 12:286–294. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhou L, Zhang N, Song W, et al: The
significance of Notch1 compared with Notch3 in high metastasis and
poor overall survival in hepatocellular carcinoma. PLoS One.
8:e574822013.
|
|
38
|
Masaki T, Shiratori Y, Rengifo W, et al:
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases: Comparative study of
hepatocellular carcinoma versus cirrhosis. Hepatology. 37:534–543.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Basu A and Haldar S: The relationship
between BcI2, Bax and p53: consequences for cell cycle progression
and cell death. Mol Hum Reprod. 4:1099–1109. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
40
|
Somanath P, Vijai J, Kichina J, Byzova T
and Kandel E: The role of PAK-1 in activation of MAP kinase cascade
and oncogenic transformation by Akt. Oncogene. 28:2365–2369. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Goc A, Al-Husein B, Kochuparambil ST, et
al: PI3 kinase integrates Akt and MAP kinase signaling pathways in
the regulation of prostate cancer. Int J Oncol. 38:267–277.
2011.
|
|
42
|
Crowell JA, Steele VE and Fay JR:
Targeting the AKT protein kinase for cancer chemoprevention. Mol
Cancer Ther. 6:2139–2148. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Davies MA: Regulation, role, and targeting
of Akt in cancer. J Clin Oncol. 29:4715–4717. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Amaravadi R and Thompson CB: The survival
kinases Akt and Pim as potential pharmacological targets. J Clin
Invest. 115:2618–2624. 2005. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Vaira V, Lee CW, Goel HL, et al:
Regulation of survivin expression by IGF-1/mTOR signaling.
Oncogene. 26:2678–2684. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|