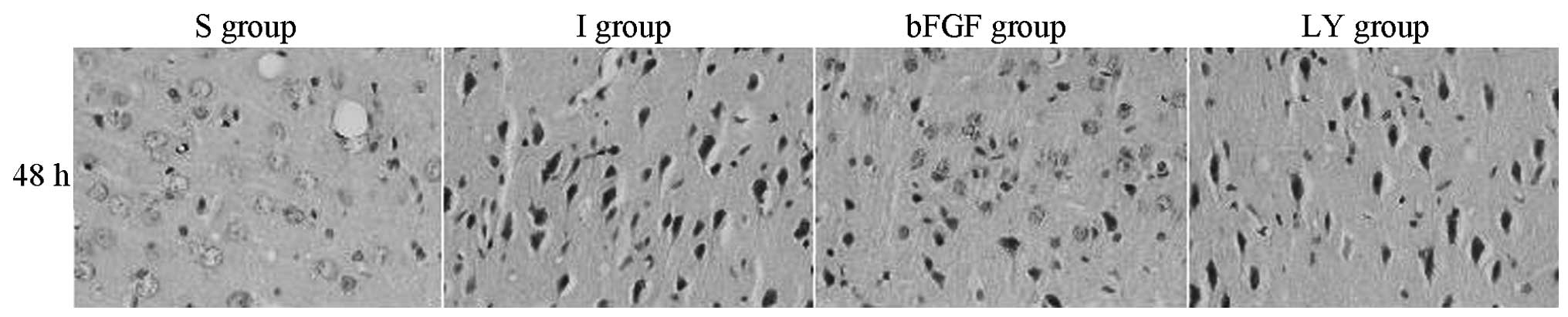
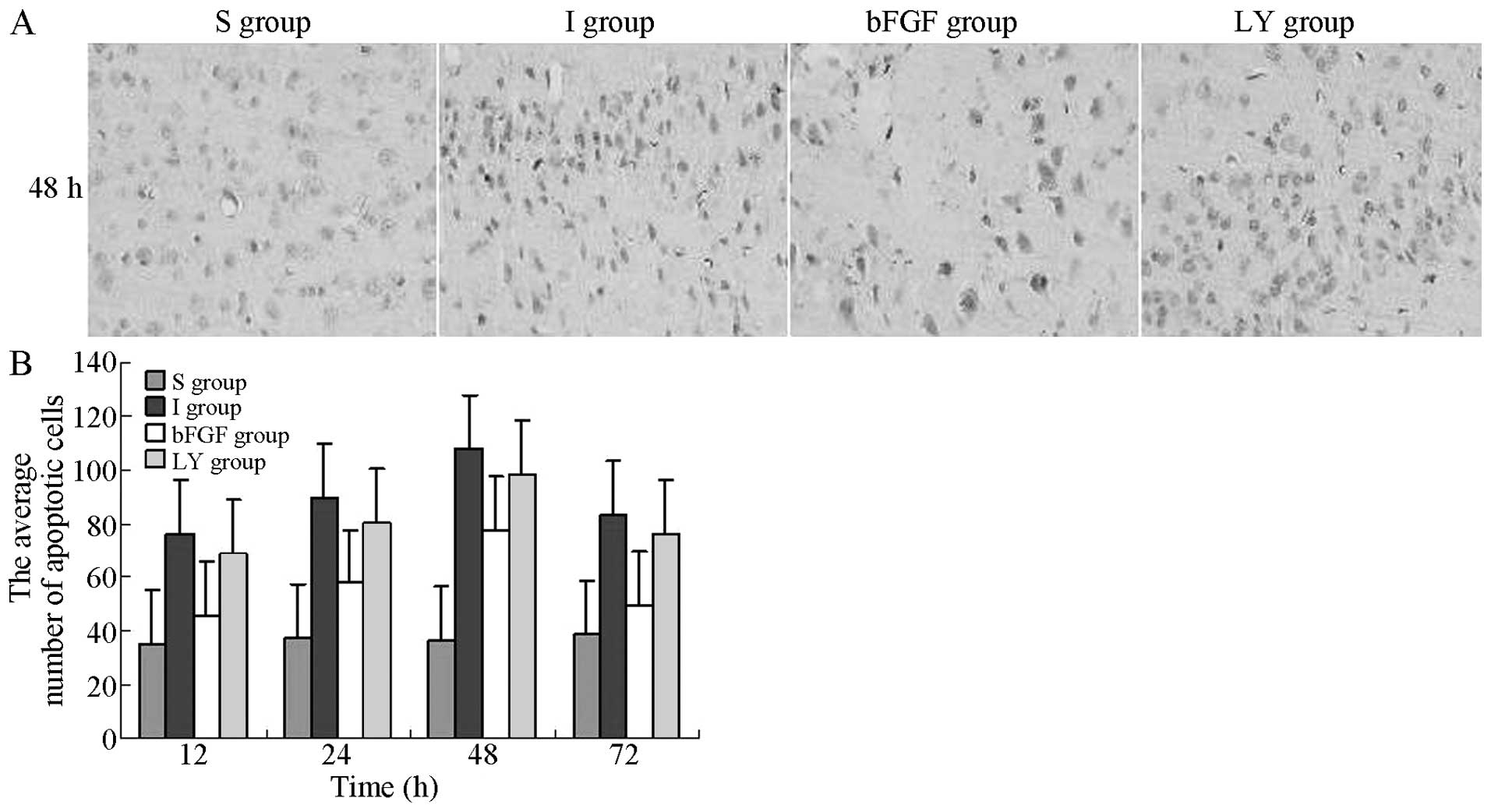
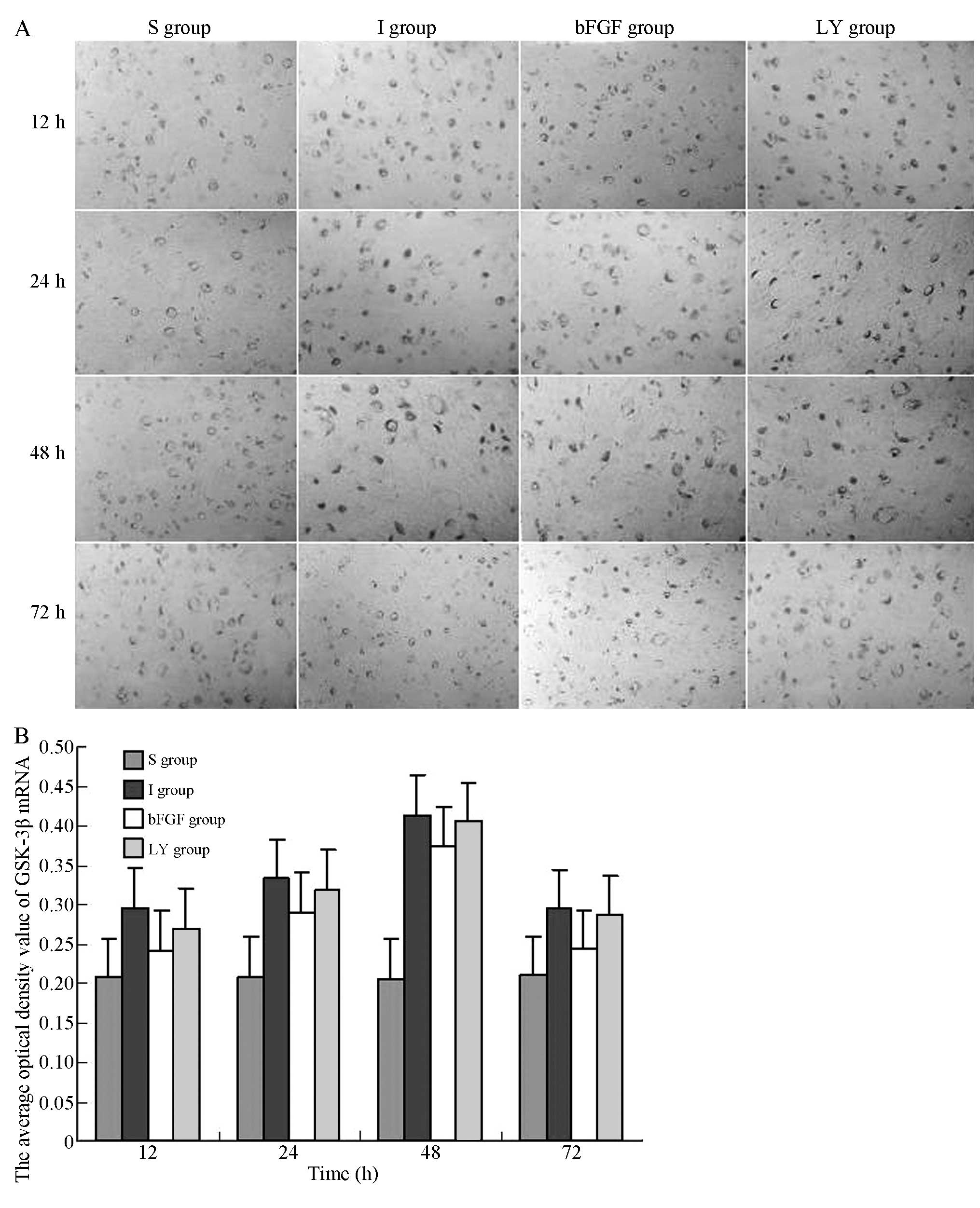
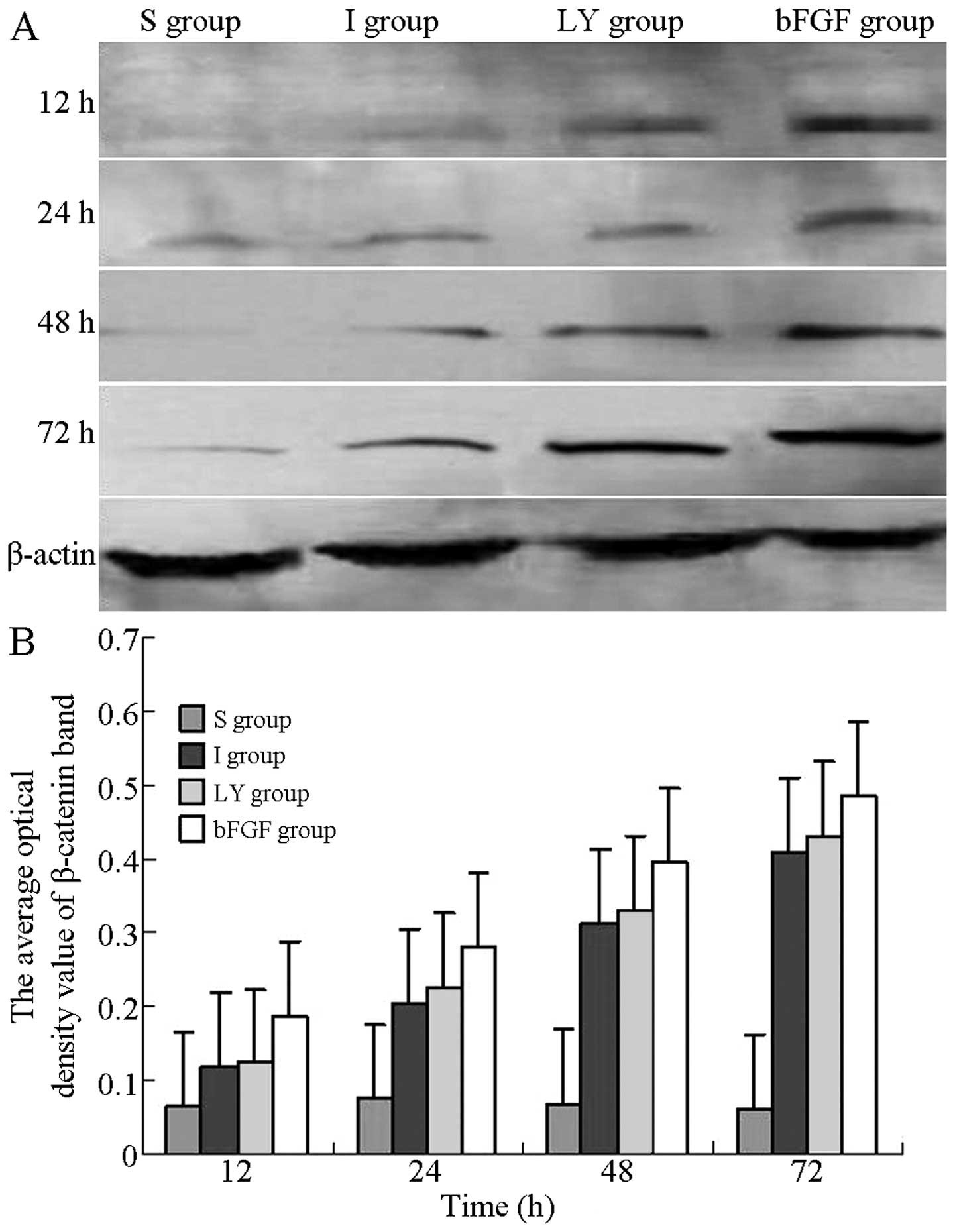
|
1
|
Guo WP, Fu XG, Jiang SM and Wu JZ:
Neuregulin-1 regulates the expression of Akt, Bcl-2, and Bad
signaling after focal cerebral ischemia in rats. Biochem Cell Biol.
88:649–654. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhu J, Shen W, Gao L, et al:
PI3K/Akt-independent negative regulation of JNK signaling by MKP-7
after cerebral ischemia in rat hippocampus. BMC Neurosci. 14:12013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Forde JE and Dale TC: Glycogen synthase
kinase 3: a key regulator of cellular fate. Cell Mol Life Sci.
64:1930–1944. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Ye Z, Guo Q, Xia P, Wang N, Wang E and
Yuan Y: Sevoflurane postconditioning involves an up-regulation of
HIF-1α and HO-1 expression via PI3K/Akt pathway in a rat model of
focal cerebral ischemia. Brain Res. 1463:63–74. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Dugo L, Collin M and Thiemermann C:
Glycogen synthase kinase 3beta as a target for the therapy of shock
and inflammation. Shock. 27:113–123. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Nishihara M, Miura T, Miki T, et al:
Modulation of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore
complex in GSK-3beta-mediated myocardial protection. J Mol Cell
Cardiol. 43:564–570. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM and Steinberg GK:
Phosphoinositide-3-kinase/akt survival signal pathways are
implicated in neuronal survival after stroke. Mol Neurobiol.
34:249–270. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Gao X, Zhang H, Takahashi T, et al: The
Akt signaling pathway contributes to postconditioning’s protection
against stroke; the protection is associated with the MAPK and PKC
pathways. J Neurochem. 105:943–955. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Peng B, Guo QL, He ZJ, et al: Remote
ischemic postconditioning protects the brain from global cerebral
ischemia/reperfusion injury by up-regulating endothelial nitric
oxide synthase through the PI3K/Akt pathway. Brain Res.
1445:92–102. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Chong ZZ, Li F and Maiese K: Cellular
demise and inflammatory microglial activation during beta-amyloid
toxicity are governed by Wnt1 and canonical signaling pathways.
Cell Signal. 19:1150–1162. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Murase S, Mosser E and Schuman EM:
Depolarization drives beta-catenin into neuronal spines promoting
changes in synaptic structure and function. Neuron. 35:91–105.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Zhang L, Zhang ZG, Liu XS, Hozeska-Solgot
A and Chopp M: The PI3K/Akt pathway mediates the neuroprotective
effect of atorvastatin in extending thrombolytic therapy after
embolic stroke in the rat. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol.
27:2470–2475. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Carmichael ST: Rodent models of focal
stroke: size, mechanism, and purpose. NeuroRx. 2:396–409. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Liu H, Liu X, Wei X, et al: Losartan, an
angiotensin II type 1 receptor blocker, ameliorates cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury via PI3K/Akt-mediated enos
phosphorylation. Brain Res Bull. 89:65–70. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bradford MM: A rapid and sensitive method
for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the
principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem. 72:248–254. 1976.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lu C, Liu L, Chen Y, et al: TLR2 ligand
induces protection against cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury via
activation of phosphoinositide 3-kinase/Akt signaling. J Immunol.
187:1458–1466. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Shioda N, Ishigami T, Han F, et al:
Activation of phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase/protein kinase B
pathway by a vanadyl compound mediates its neuroprotective effect
in mouse brain ischemia. Neuroscience. 148:221–229. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Soshnikova N, Zechner D, Huelsken J, et
al: Genetic interaction between Wnt/beta-catenin and BMP receptor
signaling during formation of the AER and the dorsal-ventral axis
in the limb. Genes Dev. 17:1963–1968. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang J and Wynshaw-Boris A: The canonical
Wnt pathway in early mammalian embryogenesis and stem cell
maintenance/differentiation. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 14:533–539. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lickert H, Domon C, Huls G, et al:
Wnt/(beta)-catenin signaling regulates the expression of the
homeobox gene Cdx1 in embryonic intestine. Development.
127:3805–3813. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Monga SP, Pediaditakis P, Mule K, Stolz DB
and Michalopoulos GK: Changes in WNT/beta-catenin pathway during
regulated growth in rat liver regeneration. Hepatology.
33:1098–1109. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Reya T and Clevers H: Wnt signalling in
stem cells and cancer. Nature. 434:843–850. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Kamada H, Nito C, Endo H and Chan PH: Bad
as a converging signaling molecule between survival PI3-K/Akt and
death JNK in neurons after transient focal cerebral ischemia in
rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 27:521–533. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sun B, Chen L, Wei X, Xiang Y, Liu X and
Zhang X: The Akt/GSK-3β pathway mediates flurbiprofen-induced
neuroprotection against focal cerebral ischemia/reperfusion injury
in rats. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 409:808–813. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Chai YS, Hu J, Lei F, et al: Effect of
berberine on cell cycle arrest and cell survival during cerebral
ischemia and reperfusion and correlations with p53/cyclin D1 and
PI3K/Akt. Eur J Pharmacol. 708:44–55. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Zhan L, Li D, Liang D, et al: Activation
of Akt/FoxO and inactivation of MEK/ERK pathways contribute to
induction of neuroprotection against transient global cerebral
ischemia by delayed hypoxic postconditioning in adult rats.
Neuropharmacology. 63:873–882. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhang J, Deng Z, Liao J, et al: Leptin
attenuates cerebral ischemia injury through the promotion of energy
metabolism via the PI3K/Akt pathway. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab.
33:567–574. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ma YP, Ma MM, Cheng SM, et al: Intranasal
bFGF-induced progenitor cell proliferation and neuroprotection
after transient focal cerebral ischemia. Neurosci Lett. 437:93–97.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maric D, Fiorio Pla A, Chang YH and Barker
JL: Self-renewing and differentiating properties of cortical neural
stem cells are selectively regulated by basic fibroblast growth
factor (BFGF) signaling via specific FGF receptors. J Neurosci.
27:1836–1852. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Xing Y, Zhang X, Zhao K, et al: Beneficial
effects of sulindac in focal cerebral ischemia: a positive role in
Wnt/β-catenin pathway. Brain Res. 1482:71–80. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Cai L, Ye Z, Zhou BY, Mali P, Zhou C and
Cheng L: Promoting human embryonic stem cell renewal or
differentiation by modulating Wnt signal and culture conditions.
Cell Res. 17:62–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Endo H, Nito C, Kamada H, Nishi T and Chan
PH: Activation of the Akt/GSK3beta signaling pathway mediates
survival of vulnerable hippocampal neurons after transient global
cerebral ischemia in rats. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:1479–1489.
2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Spaccapelo L, Galantucci M, Neri L, et al:
Up-regulation of the canonical Wnt-3A and sonic hedgehog signaling
underlies melanocortin-induced neurogenesis after cerebral
ischemia. Eur J Pharmacol. 707:78–86. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|