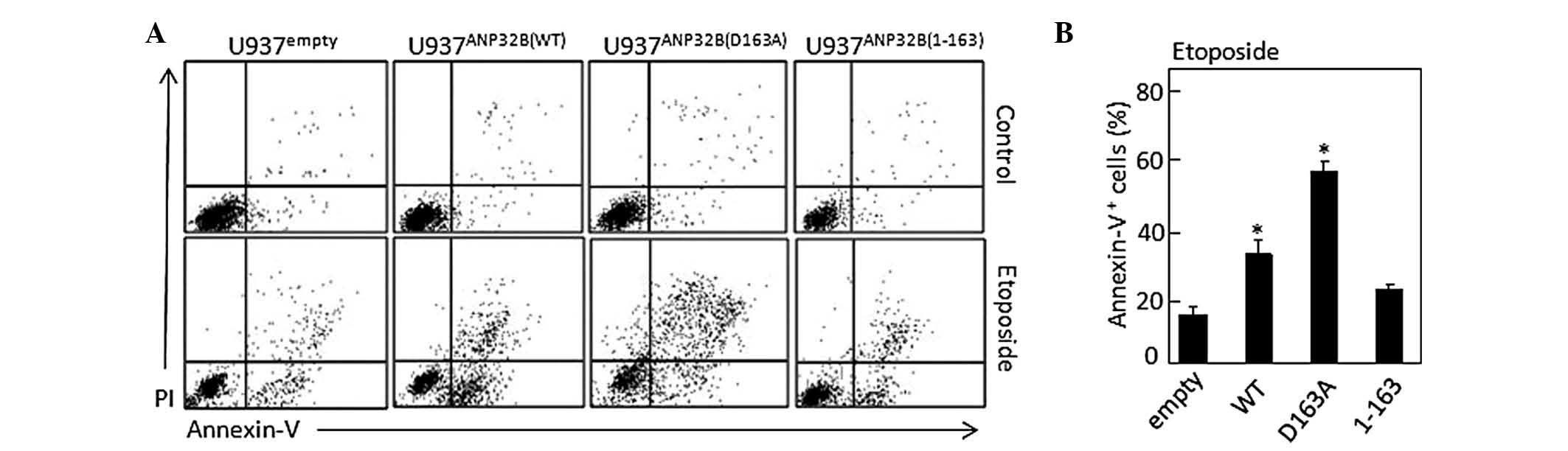
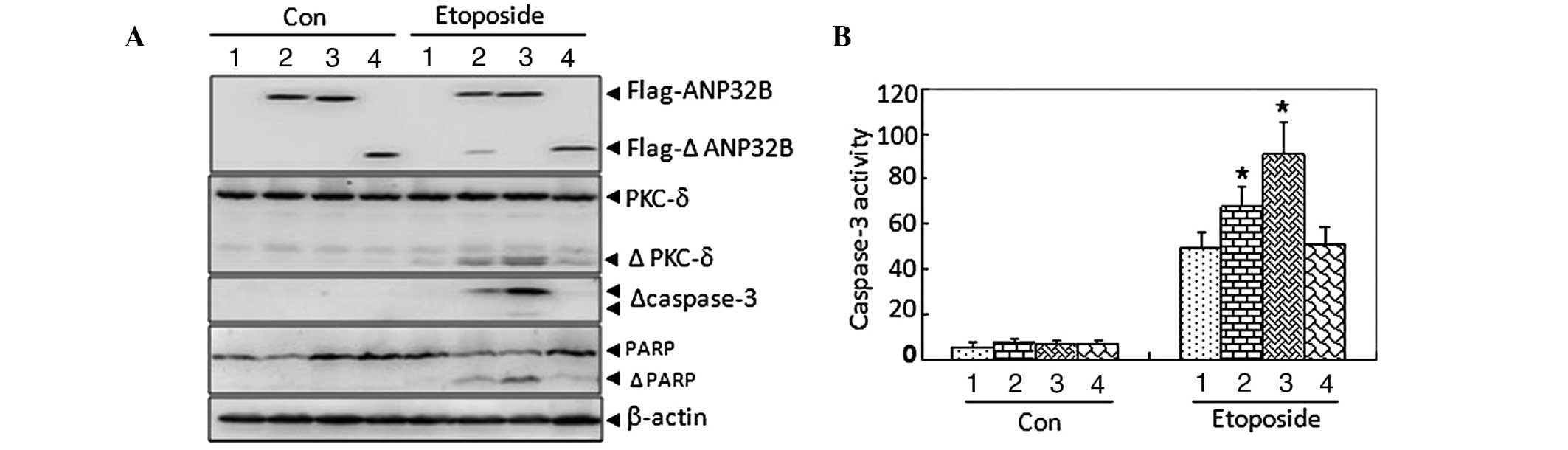
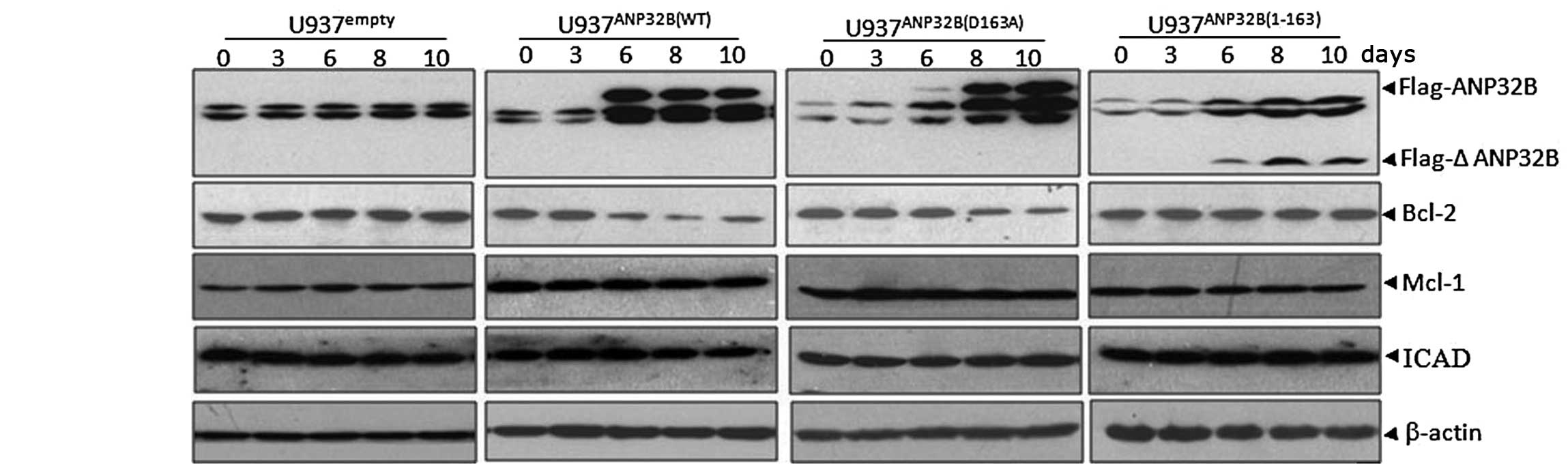
|
1
|
Fuchs Y and Steller H: Programmed cell
death in animal development and disease. Cell. 147:742–758. 2011.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Thornberry NA and Lazebnik Y: Caspases:
enemies within. Science. 281:1312–1316. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Utz PJ and Anderson P: Life and death
decisions: regulation of apoptosis by proteolysis of signaling
molecules. Cell Death Differ. 7:589–602. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Johnson CE and Kornbluth S: Caspase
cleavage is not for everyone. Cell. 134:720–721. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Timmer JC and Salvesen GS: Caspase
substrates. Cell Death Differ. 14:66–72. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
6
|
Matilla A and Radrizzani M: The Anp32
family of proteins containing leucine-rich repeats. Cerebellum.
4:7–18. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Adegbola O and Pasternack GR:
Phosphorylated retinoblastoma protein complexes with pp32 and
inhibits pp32-mediated apoptosis. J Biol Chem. 280:15497–15502.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hoffarth S, Zitzer A, Wiewrodt R, et al:
pp32/PHAPI determines the apoptosis response of non-small-cell lung
cancer. Cell Death Differ. 15:161–170. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Jiang X, Kim HE, Shu H, et al: Distinctive
roles of PHAP proteins and prothymosin-alpha in a death regulatory
pathway. Science. 299:223–226. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Pan W, da Graca LS, Shao Y, et al:
PHAPI/pp32 suppresses tumorigenesis by stimulating apoptosis. J
Biol Chem. 284:6946–6954. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Schafer ZT, Parrish AB, Wright KM, et al:
Enhanced sensitivity to cytochrome c-induced apoptosis mediated by
PHAPI in breast cancer cells. Cancer Res. 66:2210–2218. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Shen SM, Yu Y, Wu YL, et al:
Downregulation of ANP32B, a novel substrate of caspase-3, enhances
caspase-3 activation and apoptosis induction in myeloid leukemic
cells. Carcinogenesis. 31:419–426. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Brody JR, Kadkol SS, Hauer MC, et al: pp32
reduction induces differentiation of TSU-Pr1 cells. Am J Pathol.
164:273–283. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Kular RK, Cvetanovic M, Silferd S, et al:
Neuronal differentiation is regulated by leucine-rich acidic
nuclear protein (LANP), a member of the inhibitor of histone
acetyltransferase complex. J Biol Chem. 284:7783–7792. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Puente LG, Carrière JF, Kelly JF and
Megeney LA: Comparative analysis of phosphoprotein-enriched myocyte
proteomes reveals widespread alterations during differentiation.
FEBS Lett. 574:138–144. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Yu Y, Shen SM, Zhang FF, et al: Acidic
leucine-rich nuclear phosphoprotein 32 family member B (ANP32B)
contributes to retinoic acid-induced differentiation of leukemic
cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 423:721–725. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Amasaki H, Ogawa M, Nagasao J, et al:
Distributional changes of BrdU, PCNA, E2F1 and PAL31 molecules in
developing murine palatal rugae. Ann Anat. 185:517–523. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sun W, Hattori N, Mutai H, et al: PAL31, a
nuclear protein required for progression to the S phase. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 280:1048–1054. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fukukawa C, Tanuma N, Okada T, et al:
pp32/ I-1(PP2A) negatively regulates the Raf-1/MEK/ERK pathway.
Cancer Lett. 226:155–160. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Opal P, Garcia JJ, McCall AE, et al:
Generation and characterization of LANP/pp32 null mice. Mol Cell
Biol. 24:3140–3149. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reilly PT, Afzal S, Gorrini C, et al:
Acidic nuclear phosphoprotein 32kDa (ANP32)B-deficient mouse
reveals a hierarchy of ANP32 importance in mammalian development.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 108:10243–10248. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Boer J, Bonten-Surtel J and Grosveld G:
Overexpression of the nucleoporin CAN/NUP214 induces growth arrest,
nucleocytoplasmic transport defects, and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol.
18:1236–1247. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Boer J, Bonten-Surtel J and Grosveld G:
Overexpression of the nucleoporin CAN/NUP214 induces growth arrest,
nucleocytoplasmic transport defects, and apoptosis. Mol Cell Biol.
18:1236–1247. 1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Matassa AA, Carpenter L, Biden TJ, et al:
PKCdelta is required for mitochondrial-dependent apoptosis in
salivary epithelial cells. J Biol Chem. 276:29719–29728. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Qi X and Mochly-Rosen D: The PKCdelta -Abl
complex communicates ER stress to the mitochondria - an essential
step in subsequent apoptosis. J Cell Sci. 121:804–813. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Song MG, Gao SM, Du KM, et al: Nanomolar
concentration of NSC606985, a camptothecin analog, induces
leukemic-cell apoptosis through protein kinase Cdelta-dependent
mechanisms. Blood. 105:3714–3721. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Munemasa Y, Suzuki T, Aizawa K, et al:
Promoter region-specific histone incorporation by the novel histone
chaperone ANP32B and DNA-binding factor KLF5. Mol Cell Biol.
28:1171–1181. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
28
|
Yu Y, Wang LS, Shen SM, et al: Subcellular
proteome analysis of camptothecin analogue NSC606985-treated acute
myeloid leukemic cells. J Proteome Res. 6:3808–3818. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hill MM, Adrain C, Duriez PJ, et al:
Analysis of the composition, assembly kinetics and activity of
native Apaf-1 apoptosomes. EMBO J. 23:2134–2145. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Mutai H, Toyoshima Y, Sun W, et al: PAL31,
a novel nuclear protein, expressed in the developing brain. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 274:427–433. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Karin M and Lin A: NF-kappaB at the
crossroads of life and death. Nat Immunol. 3:221–227. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|