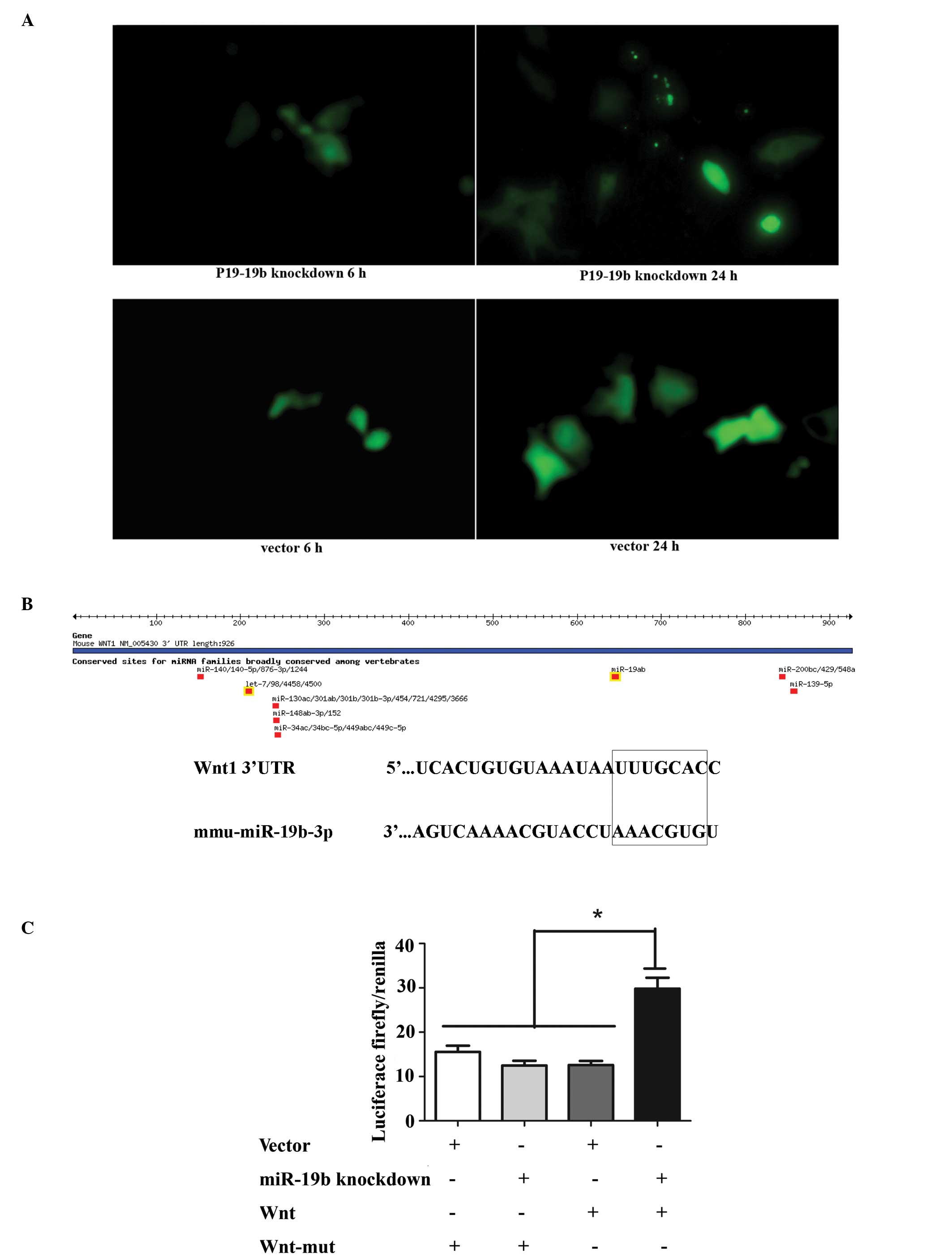
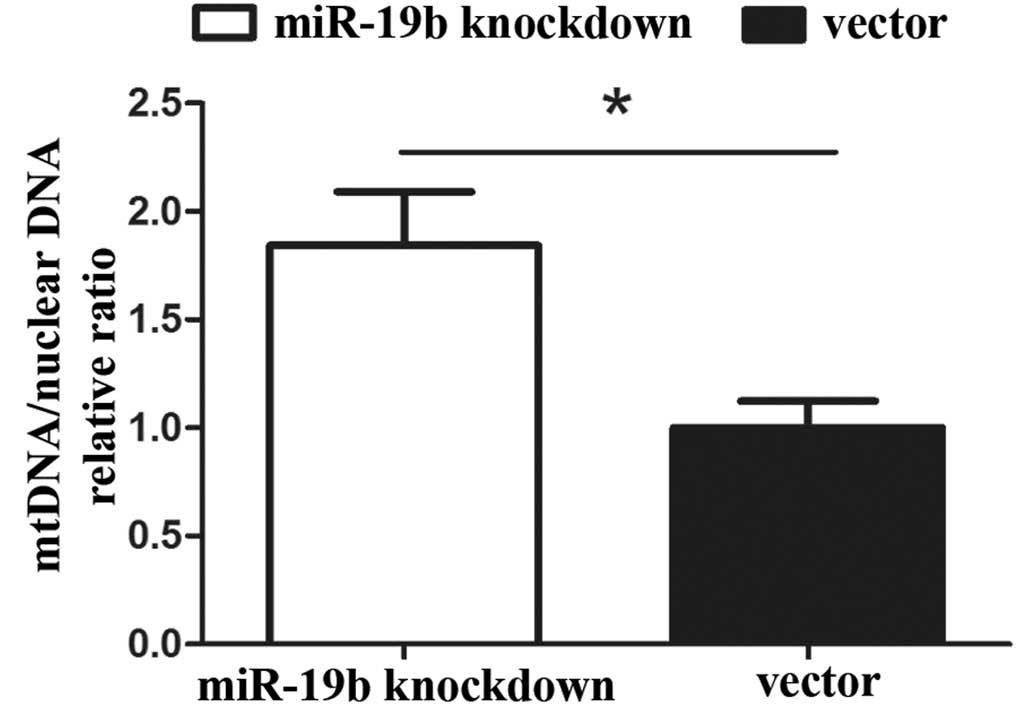
|
1
|
Capozzi G, Caputo S, Pizzuti R, Martina L,
Santoro M, Santoro G, et al: Congenital heart disease in live-born
children: incidence, distribution, and yearly changes in the
Campania Region. J Cardiovasc Med (Hagerstown). 9:368–374. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Thum T, Catalucci D and Bauersachs J:
MicroRNAs: novel regulators in cardiac development and disease.
Cardiovasc Res. 79:562–570. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wu C, Cao Y, He Z, He J, Hu C, Duan H and
Jiang J: Serum levels of miR-19b and miR-146a as prognostic
biomarkers for non-small cell lung cancer. Tohoku J Exp Med.
232:85–95. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Lu Y, Thomson JM, Wong HY, Hammond SM and
Hogan BL: Transgenic over-expression of the microRNA miR-17–92
cluster promotes proliferation and inhibits differentiation of lung
epithelial progenitor cells. Dev Biol. 310:442–453. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Boggs RM, Moody JA, Long CR, Tsai KL and
Murphy KE: Identification, amplification and characterization of
miR-17–92 from canine tissue. Gene. 404:25–30. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Hackl M, Brunner S, Fortschegger K,
Schreiner C, Micutkova L, Mück C, Laschober GT, et al: miR-17,
miR-19b, miR-20a, and miR-106a are down-regulated in human aging.
Aging Cell. 9:291–296. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Skerjanc IS: Cardiac and skeletal muscle
development in P19 embryonal carcinoma cells. Trends Cardiovasc
Med. 9:139–143. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
van der Heyden MA and Defize LH: Twenty
one years of P19 cells: what an embryonal carcinoma cell line
taught us about cardiomyocyte differentiation. Cardiovasc Res.
58:292–302. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
van der Heyden MA, van Kempen MJ, Tsuji Y,
Rook MB, Jongsma HJ and Opthof T: P19 embryonal carcinoma cells: a
suitable model system for cardiac electrophysiological
differentiation at the molecular and functional level. Cardiovasc
Res. 58:410–422. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Han SP, Pan Y, Peng YZ, Gu XQ, Chen RH and
Guo XR: Folbp1 promotes embryonic myocardial cell proliferation and
apoptosis through the WNT signal transduction pathway. Int J Mol
Med. 23:321–330. 2009.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Hu DL, Chen FK, Liu YQ, Shen YH, Yang R,
et al: GATA-4 promotes the differentiation of P19 cells into
cardiac myocytes. Int J Mol Med. 26:365–372. 2010.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Cohen ED, Tian Y and Morrisey EE: Wnt
signaling: an essential regulator of cardiovascular
differentiation, morphogenesis and progenitor self-renewal.
Development. 135:789–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Ueno S, Weidinger G, Osugi T, Kohn AD,
Golob JL, et al: Biphasic role for Wnt/beta-catenin signaling in
cardiac specification in zebrafish and embryonic stem cells. Proc
Natl Acad Sci USA. 104:9685–9690. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhu S, Cao L, Zhu J, Kong L, Jin J, Qian
L, Zhu C, Hu X, Li M, Guo X, Han S and Yu Z: Identification of
maternal serum microRNAs as novel non-invasive biomarkers for
prenatal detection of fetal congenital heart defects. Clin Chim
Acta. 424:66–72. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
van Almen GC, Verhesen W, van Leeuwen RE,
van de Vrie M, Eurlings C, et al: MicroRNA-18 and microRNA-19
regulate CTGF and TSP-1 expression in age-related heart failure.
Aging Cell. 10:769–779. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Gao S, Liu TW, Wang Z, Jiao ZY, Cai J, Chi
HJ and Yang XC: Downregulation of microRNA-19b contributes to
angiotensin II-induced overexpression of connective tissue growth
factor in cardiomyocytes. Cardiology. 127:114–120. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Jung YJ, Kim JW, Park SJ, Min BY, Jang ES,
Kim NY, Jeong SH, Shin CM, Lee SH, Park YS, Hwang JH, Kim N and Lee
DH: c-Myc-mediated overexpression of miR-17–92 suppresses
replication of hepatitis B virus in human hepatoma cells. J Med
Virol. 85:969–978. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Qin DN, Qian L, Hu DL, Yu ZB, Han SP, Zhu
C, Wang X and Hu X: Effects of miR-19b overexpression on
proliferation, differentiation, apoptosis and Wnt/β-catenin
signaling pathway in P19 cell model of cardiac differentiation in
vitro. Cell Biochem Biophys. 66:709–722. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Fiorina P, Corradi D, Pinelli S, Maestri
R, Lagrasta C, Buscaglia M, et al: Apoptotic/mytogenic pathways
during human heart development. Int J Cardiol. 96:409–417. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lévy M, Maurey C, Celermajer DS, Vouhé PR,
Danel C, Bonnet D and Israël-Biet D: Impaired apoptosis of
pulmonary endothelial cells is associated with intimal
proliferation and irreversibility of pulmonary hypertension in
congenital heart disease. J Am Coll Cardiol. 49:803–810. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Gittenberger-de Groot GA, Bartelings MM,
Deruiter MC and Poelmann RE: Basics of cardiac development for the
understanding of congenital heart malformations. Pediatr Res.
57:169–176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Yan HL, Xue G, Mei Q, Wang YZ, Ding FX,
Liu MF, et al: Repression of the miR-17–92 cluster by p53 has an
important function in hypoxia-induced apoptosis. EMBO J.
28:2719–2732. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Sharifi M, Salehi R, Gheisari Y and Kazemi
M: Inhibition of MicroRNA miR-92a inhibits cell proliferation in
human acute promyelocytic leukemia. Turk J Hematol. 30:157–162.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Crow MT, Mani K, Nam YJ and Kitsis RN: The
mitochondrial death pathway and cardiac myocyte apoptosis. Circ
Res. 95:957–970. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Brooks C and Dong Z: Regulation of
mitochondrial morphological dynamics during apoptosis by Bcl-2
family proteins: a key in Bak? Cell Cycle. 6:3043–3047. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Cohen ED, Tian Y and Morrisey EE: Wnt
signaling: an essential regulator of cardiovascular
differentiation, morphogenesis and progenitor self-renewal.
Development. 135:789–798. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Olson EN and Schneider MD: Sizing up the
heart: development redux in disease. Genes Dev. 17:1937–1956. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Hurlstone AF, Haramis AP, Wienholds E,
Begthel H, Korving J, Van Eeden F, et al: The Wnt/beta-catenin
pathway regulates cardiac valve formation. Nature. 425:633–637.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Verhoeven MC, Haase C, Christoffels VM,
Weidinger G and Bakkers J: Wnt Signaling Regulates Atrioventricular
Canal Formation Upstream of BMP and Tbx2. Birth Defect Res A Clin
Mol Teratol. 91:435–440. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Ai D, Fu X, Wang J, Lu MF, Chen L, Baldini
A, et al: Canonical Wnt signaling functions in second heart field
to promote right ventricular growth. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:9319–9324. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Kwon C, Arnold J, Hsiao EC, Taketo MM,
Conklin BR and Srivastava D: Canonical Wnt signaling is a positive
regulator of mammalian cardiac progenitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:10894–10899. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Cai X, Zhang W, Hu J, Zhang L, Sultana N,
Wu B, Cai W, Zhou B and Cai CL: Tbx20 acts upstream of Wnt
signaling to regulate endocardial cushion formation and valve
remodeling during mouse cardiogenesis. Development. 140:3176–3187.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Gantier MP, Stunden HJ, McCoy CE, Behlke
MA, Wang D, Kaparakis-Liaskos M, Sarvestani ST, Yang YH, Xu D, Corr
SC, Morand EF and Williams BR: A miR-19 regulon that controls NF-iB
signaling. Nucleic Acids Res. 40:8048–8058. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lakner AM, Steuerwald NM, Walling TL,
Ghosh S, Li T, McKillop IH, Russo MW, Bonkovsky HL and Schrum LW:
Inhibitory effects of microRNA 19b in hepatic stellate
cell-mediated fibrogenesis. Hepatology. 56:300–310. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Song DW, Ryu JY, Kim JO, Kwon EJ and Kim
do H: The miR-19a/bfamily positively regulates cardiomyocyte
hypertrophy by targeting atrogin-1 and MuRF-1. Biochem J.
457:151–162. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar
|