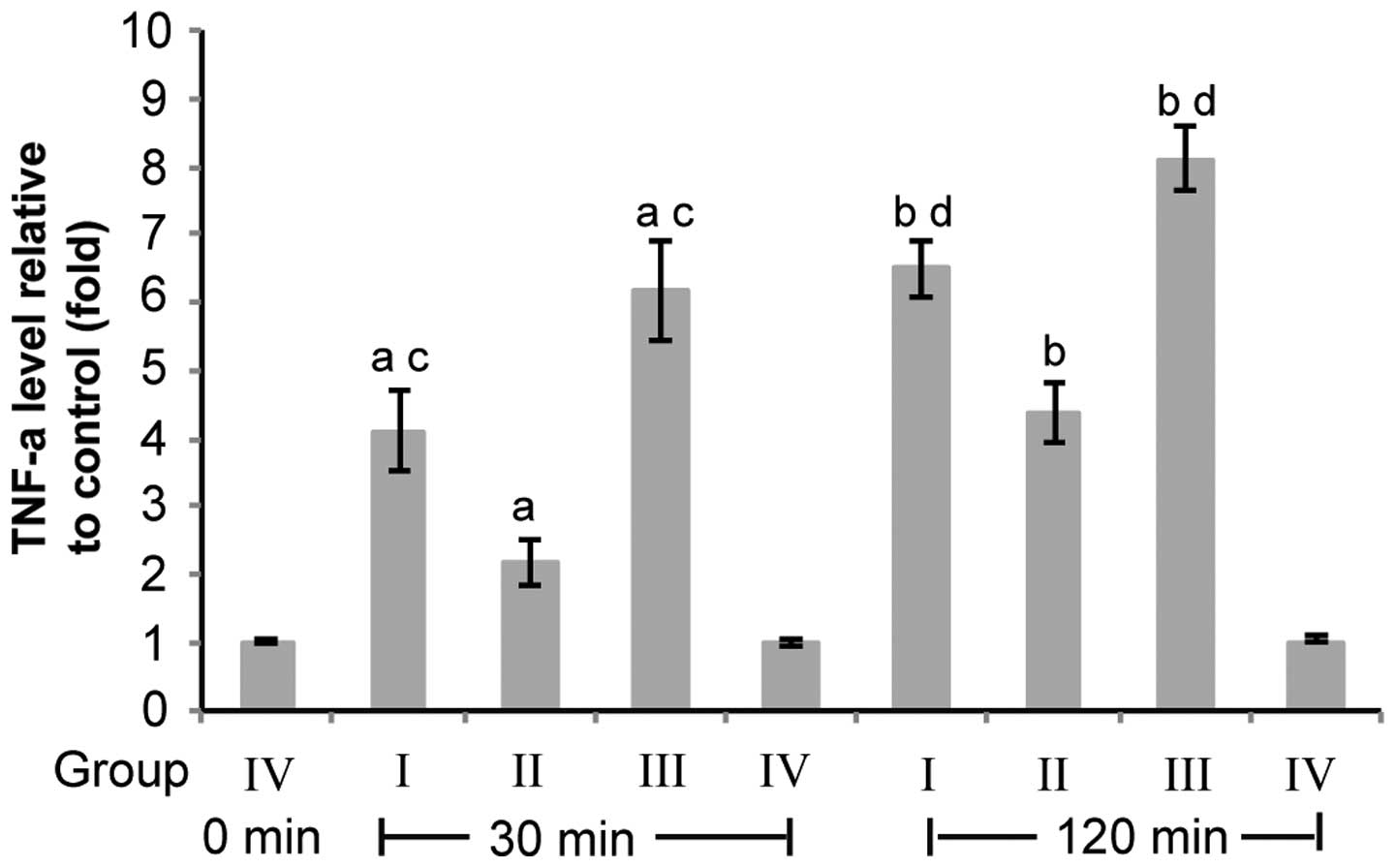
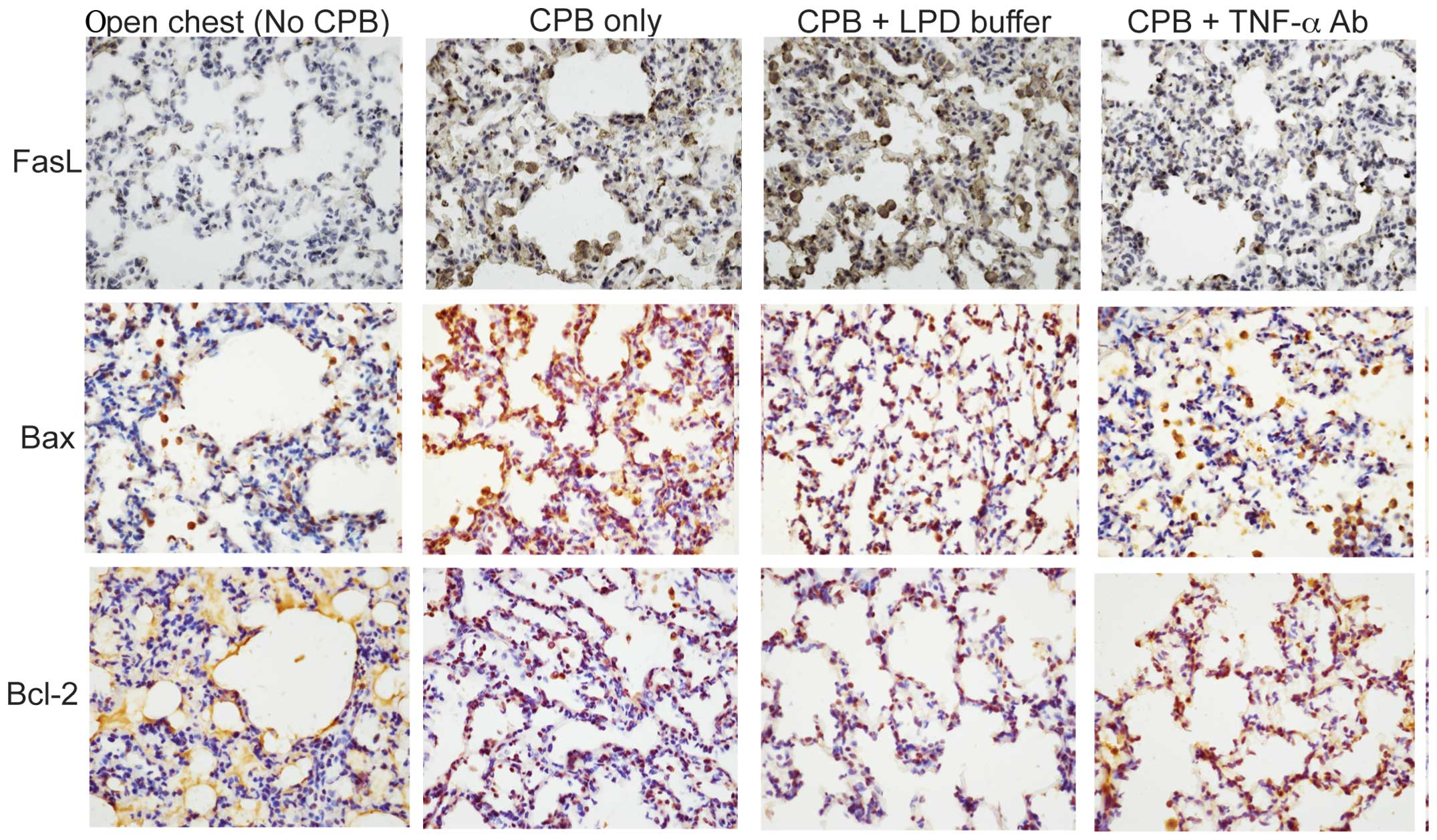
|
1
|
Stamou SC, Pfister AJ, Dangas G, et al:
Beating heart versus conventional single-vessel reoperative
coronary artery bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 69:1383–1387. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Asimakopoulos G, Smith PL, Ratnatunga CP
and Taylor KM: Lung injury and acute respiratory distress syndrome
after cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 68:1107–1115. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Hammermeister KE, Burchfiel C, Johnson R
and Grover FL: Identification of patients at greatest risk for
developing major complications at cardiac surgery. Circulation.
82:380–389. 1990.
|
|
4
|
Ng CS, Wan S, Yim AP and Arifi AA:
Pulmonary dysfunction after cardiac surgery. Chest. 121:1269–1277.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Taggart DP, el-Fiky M, Carter R, Bowman A
and Wheatley DJ: Respiratory dysfunction after uncomplicated
cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann Thorac Surg. 56:1123–1128. 1993.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wan S, LeClerc JL and Vincent JL:
Inflammatory response to cardiopulmonary bypass: mechanisms
involved and possible therapeutic strategies. Chest. 112:676–692.
1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Diegeler A, Doll N, Rauch T, Haberer D,
Walther T, Falk V, Gummert J, Autschbach R and Mohr FW: Humoral
immune response during coronary artery bypass grafting: a
comparison of limited approach, ‘off-pump’ technique, and
conventional cardiopulmonary bypass. Circulation. 102(Suppl):
III95–III100. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Ascione R, Lloyd CT, Underwood MJ, Lotto
AA, Pitsis AA and Angelini GD: Inflammatory response after coronary
revascularization with or without cardiopulmonary bypass. Ann
Thorac Surg. 69:1198–1204. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Matata BM, Sosnowski AW and Galiñanes M:
Off-pump bypass graft operation significantly reduces oxidative
stress and inflammation. Ann Thorac Surg. 69:785–791. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Zhang Z, Wu Y, Zhao Y, Xiao X, Liu J and
Zhou X: Dynamic changes in HMGB1 levels correlate with inflammatory
responses during cardiopulmonary bypass. Exp Ther Med. 5:1523–1527.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Qi D, Gao MX and Yu Y: Intratracheal
antitumor necrosis factor-α antibody attenuates lung tissue damage
following cardiopulmonary bypass. Artif Organs. 37:142–149. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Yu Y, Gao M, Li H, Zhang F and Gu C:
Pulmonary artery perfusion with anti-tumor necrosis factor alpha
antibody reduces cardiopulmonary bypass-induced inflammatory lung
injury in a rabbit model. PLoS One. 8:e832362013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Wan S, LeClerc JL and Vincent JL: Cytokine
responses to cardiopulmonary bypass: lessons learned from cardiac
transplantation. Ann Thorac Surg. 63:269–276. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Welters ID, Feurer MK, Preiss V, Müller M,
Scholz S, Kwapisz M, Mogk M and Neuhäuser C: Continuous
S-(+)-ketamine administration during elective coronary artery
bypass graft surgery attenuates pro-inflammatory cytokine response
during and after cardiopulmonary bypass. Br J Anaesth. 106:172–179.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Martínez-Comendador JM, Alvarez JR,
Mosquera I, Sierra J, Adrio B, Carro JG, Fernández A and Bengochea
J: Preoperative statin treatment reduces systemic inflammatory
response and myocardial damage in cardiac surgery. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 36:998–1005. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Boehm J, Hauner K, Grammer J, Dietrich W,
Wagenpfeil S, Braun S, Lange R and Bauernschmitt R: Tumor necrosis
factor-α-863 C/A promoter polymorphism affects the inflammatory
response after cardiac surgery. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg.
40:e50–e54. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Yoon SZ, Jang IJ, Choi YJ, Kang MH, Lim
HJ, Lim YJ, Lee HW, Chang SH and Yoon SM: Association between tumor
necrosis factor alpha 308G/A polymorphism and increased
proinflammatory cytokine release after cardiac surgery with
cardiopulmonary bypass in the Korean population. J Cardiothorac
Vasc Anesth. 23:646–650. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Galiñanes M, James M, Codd V, Baxi A and
Hadjinikolaou L: TNF-alpha gene promoter polymorphism at nucleotide
-308 and the inflammatory response and oxidative stress induced by
cardiac surgery: role of heart failure and medical treatment. Eur J
Cardiothorac Surg. 34:332–337. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Yewei X, Liya D, Jinghao Z, Rufang Z and
Li S: Study of the mechanism of pulmonary protection strategy on
pulmonary injury with deep hypothermia low flow. Eur Rev Med
Pharmacol Sci. 17:879–885. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Shen Y, Wu H, Wang C, Shao H, Huang H,
Jing H and Li D: Simvastatin attenuates cardiopulmonary
bypass-induced myocardial inflammatory injury in rats by activating
peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor γ. Eur J Pharmacol.
649:255–262. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Dauber IM, Parsons PE, Welsh CH, Giclas
PC, Whitman GJ, Wheeler GS, Horwitz LD and Weil JV: Peripheral
bypass-induced pulmonary and coronary vascular injury. Association
with increased levels of tumor necrosis factor. Circulation.
88:726–735. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Worrall NK, Chang K, LeJeune WS, Misko TP,
Sullivan PM, Ferguson TB Jr and Williamson JR: TNF-alpha causes
reversible in vivo systemic vascular barrier dysfunction via
NO-dependent and -independent mechanisms. Am J Physiol.
273:H2565–H2574. 1997.
|
|
23
|
Petrache I, Verin AD, Crow MT, Birukova A,
Liu F and Garcia JG: Differential effect of MLC kinase in
TNF-alpha-induced endothelial cell apoptosis and barrier
dysfunction. Am J Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 280:L1168–L1178.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang R, Alam G, Zagariya A, Gidea C,
Pinillos H, Lalude O, Choudhary G, Oezatalay D and Uhal BD:
Apoptosis of lung epithelial cells in response to TNF-alpha
requires angiotensin II generation de novo. J Cell Physiol.
185:253–259. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Faymonville ME, Pincemail J, Duchateau J,
Paulus JM, Adam A, Deby-Dupont G, Deby C, Albert A, Larbuisson R,
Limet R, et al: Myeloperoxidase and elastase as markers of
leukocyte activation during cardiopulmonary bypass in humans. J
Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 102:309–317. 1991.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Tsai CS, Chen DL, Lin SJ, Tsai JC, Lin TC,
Lin CY, Chen YH, Huang GS, Tsai HY, Lin FY and Li CY: TNF-alpha
inhibits toll-like receptor 4 expression on monocytic cells via
tristetraprolin during cardiopulmonary bypass. Shock. 32:40–48.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Lee JC and Young PR: Role of CSB/p38/RK
stress response kinase in LPS and cytokine signaling mechanisms. J
Leukoc Biol. 59:152–157. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Dong X, Liu Y, Du M, Wang Q, Yu CT and Fan
X: P38 mitogen-activated protein kinase inhibition attenuates
pulmonary inflammatory response in a rat cardiopulmonary bypass
model. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 30:77–84. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Szlosarek PW, Grimshaw MJ, Kulbe H, Wilson
JL, Wilbanks GD, Burke F and Balkwill FR: Expression and regulation
of tumor necrosis factor alpha in normal and malignant ovarian
epithelium. Mol Cancer Ther. 5:382–390. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Lisby S, Faurschou A and Gniadecki R: The
autocrine TNFalpha signalling loop in keratinocytes requires
atypical PKC species and NF-kappaB activation but is independent of
cholesterol-enriched membrane microdomains. Biochem Pharmacol.
73:526–533. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
31
|
Imai Y, Kawano T, Iwamoto S, Nakagawa S,
Takata M and Miyasaka K: Intratracheal anti-tumor necrosis
factor-alpha antibody attenuates ventilator-induced lung injury in
rabbits. J Appl Physiol (1985). 87:510–515. 1999.
|
|
32
|
Torre-Amione G, Kapadia S, Lee J, Bies RD,
Lebovitz R and Mann DL: Expression and functional significance of
tumor necrosis factor receptors in human myocardium. Circulation.
92:1487–1494. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Katsura K, Park M, Gatanaga M, Yu EC,
Takishima K, Granger GA and Gatanaga T: Identification of
proteolytic enzyme which cleaves human p75 TNF receptor in vitro.
Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 222:298–302. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Lantz M, Malik S, Slevin ML and Olsson I:
Infusion of tumor necrosis factor (TNF) causes an increase in
circulating TNF-binding protein in humans. Cytokine. 2:402–406.
1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Kapadia S, Torre-Amione G, Yokoyama T and
Mann DL: Soluble TNF binding proteins modulate the negative
inotropic properties of TNF-alpha in vitro. Am J Physiol.
268:H517–H525. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Wooley PH, Dutcher J, Widmer MB and Gillis
S: Influence of a recombinant human soluble tumor necrosis factor
receptor FC fusion protein on type II collagen-induced arthritis in
mice. J Immunol. 151:6602–6607. 1993.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Cain BS, Meldrum DR, Harken AH and
McIntyre RC Jr: The physiologic basis for anticytokine clinical
trials in the treatment of sepsis. J Am Coll Surg. 186:337–350.
1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Yamada H, Kudoh I, Hirose Y, Toyoshima M,
Abe H and Kurahashi K: Heparin-coated circuits reduce the formation
of TNF alpha during cardiopulmonary bypass. Acta Anaesthesiol
Scand. 40:311–317. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Schulze CJ, Han L, Ghorpade N, Etches WS,
Stang L, Koshal A and Wang SH: Phosphorylcholine-coated circuits
improve preservation of platelet count and reduce expression of
proinflammatory cytokines in CABG: a prospective randomized trial.
J Card Surg. 24:363–368. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Apostolakis EE, Koletsis EN, Baikoussis
NG, Siminelakis SN and Papadopoulos GS: Strategies to prevent
intraoperative lung injury during cardiopulmonary bypass. J
Cardiothorac Surg. 5:12010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Wiesner G, Braun SL, Gruber M, Gertler R,
Lange R, Tassani P and Martin K: Neither moxifloxacin nor
cefuroxime produces significant attenuation of inflammatory
mediator release in patients exposed to cardiopulmonary bypass: a
randomized controlled trial. J Antimicrob Chemother. 67:230–233.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Morgan C, Zappitelli M and Gill P: Statin
prophylaxis and inflammatory mediators following cardiopulmonary
bypass: a systematic review. Crit Care. 13:R1652009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|