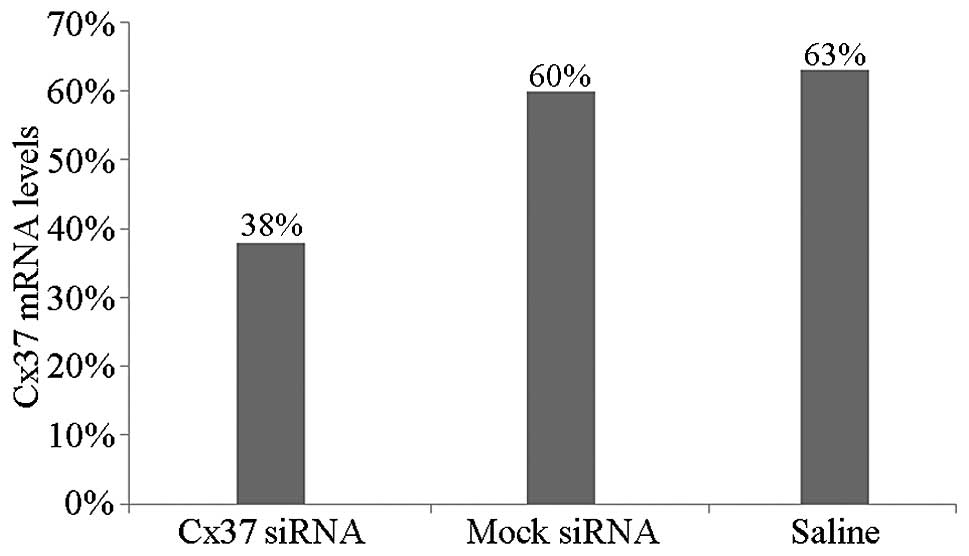
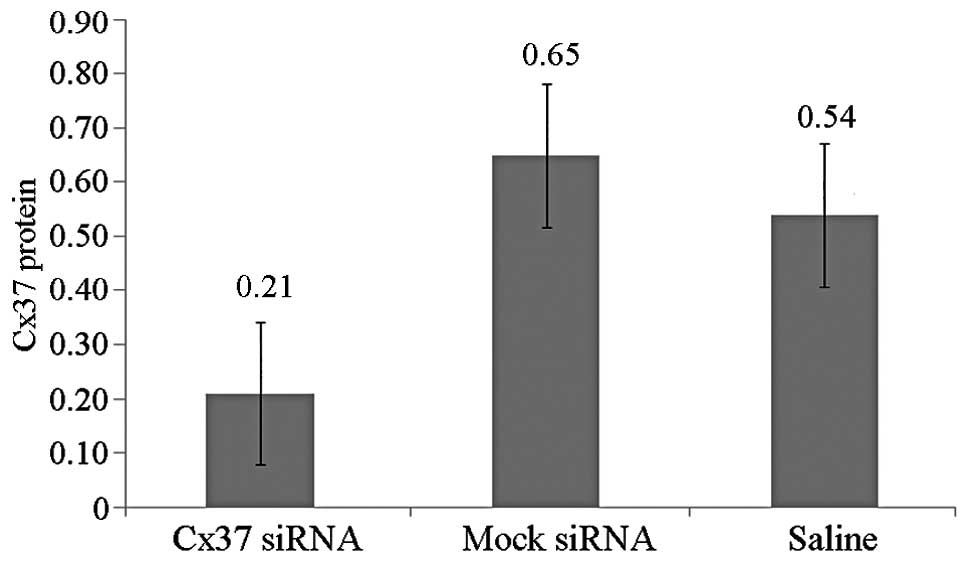
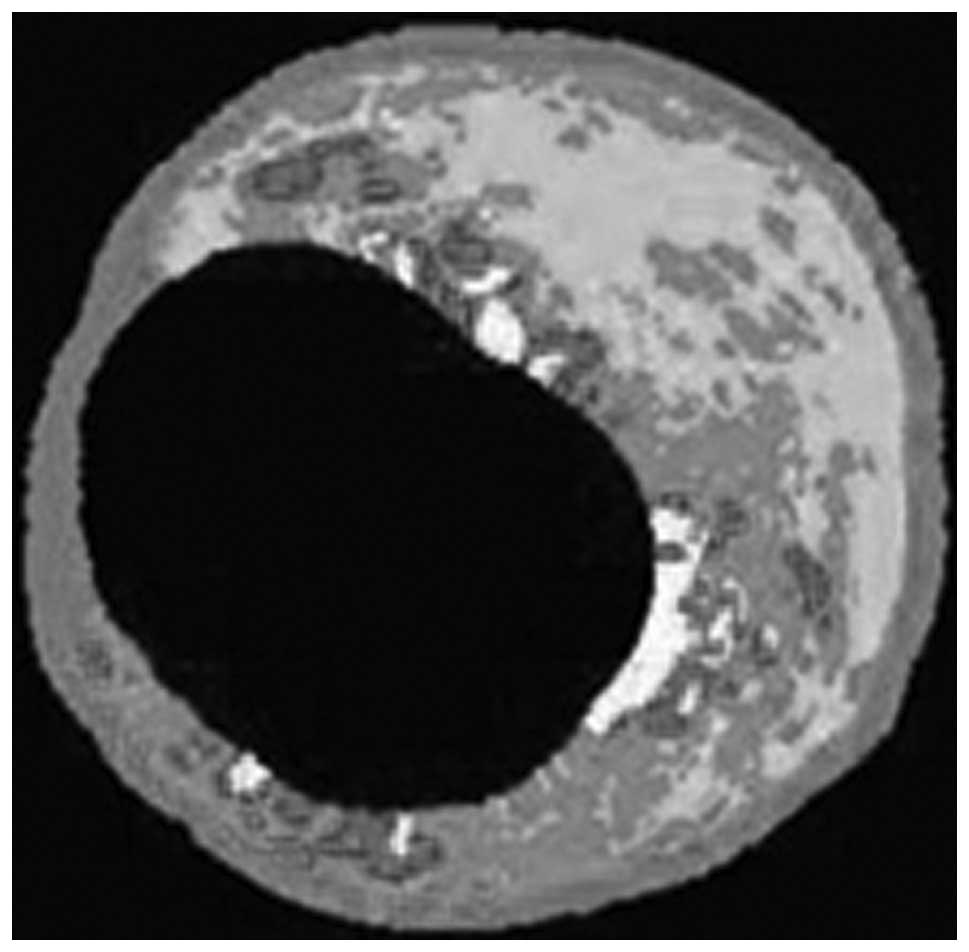
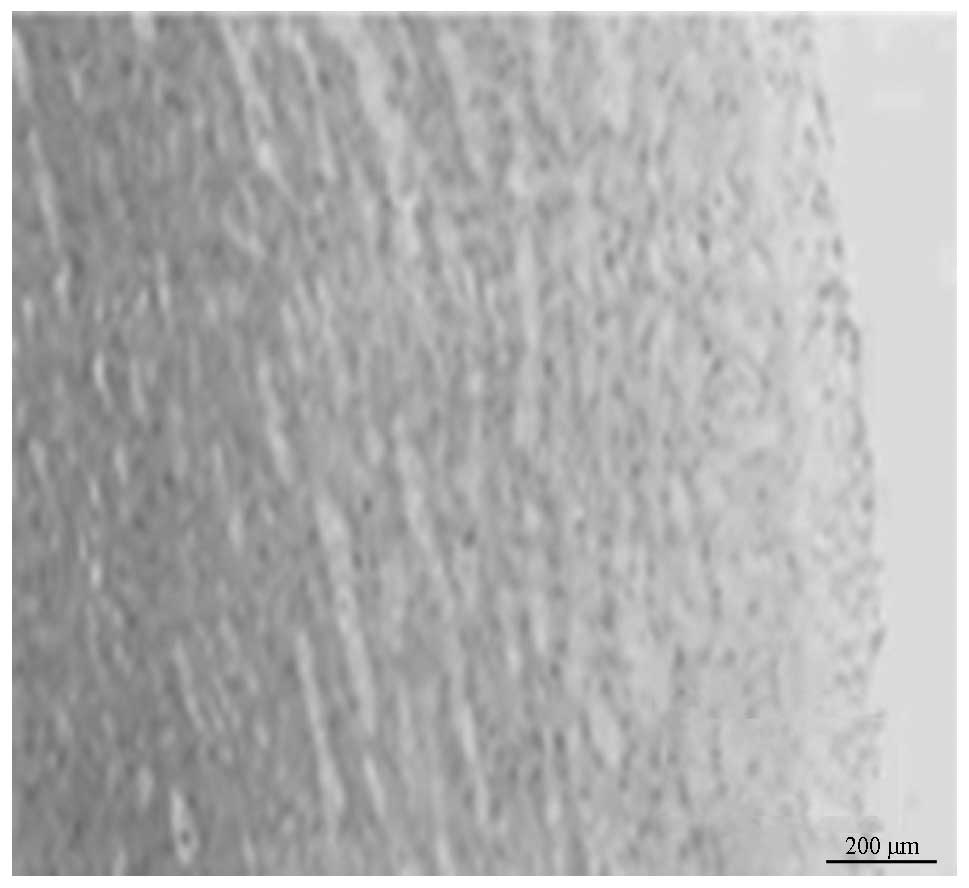
|
1
|
Pfenniger A, Chanson M and Kwak BR:
Connexins in atherosclerosis. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1828:157–166.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Otsuka F, Yahagi K, Sakakura K and Virmani
R: Why is the mammary artery so special and what protects it from
atherosclerosis. Ann Cardiothorac Surg. 2:519–526. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Steinberg D: In Celebration of the 100th
anniversary of the lipid hypothesis of atherosclerosis. J Lipid
Res. 54:2946–2949. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Xu Y, Liu Q, Xu Y, et al: Rutaecarpine
suppresses atherosclerosis in ApoE−/− mice through up-regulating
ABCA1 and SR-BI within RCT. J Lipid Res. 55:1634–1647. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Saez JC, Berthoud VM, Branes MC, Martinez
AD and Beyer EC: Plasma membrane channels formed by connexins:
their regulation and functions. Physiol Rev. 83:1359–1400.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Fang JS, Angelov SN, Simon AM and Burt JM:
Cx37 deletion enhances vascular growth and facilitates ischemic
limb recovery. Am J Physiol Heart Circ Physiol. 301:H1872–H1881.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Kanady JD, Dellinger MT, Munger SJ, Witte
MH and Simon AM: Connexin37 and Connexin43 deficiencies in mice
disrupt lymphatic valve development and result in lymphatic
disorders including lymphedema and chylothorax. Dev Biol.
354:253–266. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Morel S and Kwak BR: Roles of connexins in
atherosclerosis and ischemia-reperfusion injury. Curr Pharm
Biotechnol. 13:17–26. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Guo SX, Yang ZY, Wang RX, Yang Y, Cao HM
and Zhang T: Association between C1019T polymorphism of the
connexin37 gene and coronary heart disease in patients with
in-stent restenosis. Exp Ther Med. 5:539–544. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Boerma M, Forsberg L, Van Zeijl L, et al:
A genetic polymorphism in connexin 37 as a prognostic marker for
atherosclerotic plaque development. J Intern Med. 246:211–218.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Yeh HI, Chou Y, Liu HF, Chang SC and Tsai
CH: Connexin37 gene polymorphism and coronary artery disease in
Taiwan. Int J Cardiol. 81:251–255. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Han YL, Xi SY, Zhang XL, Yan CH, Yang Y
and Kang J: Association of C1019T polymorphism in the Connexin37
gene and coronary artery disease in Chinese Han population.
Zhonghua Yi Xue Za Zhi. 87:100–104. 2007.(In Chinese). PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Wong CW, Christen T, Pfenniger A, James RW
and Kwak BR: Do allelic variants of the connexin37 1019 gene
polymorphism differentially predict for coronary artery disease and
myocardial infarction? Atherosclorosis. 191:355–361. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yamada Y, Izawa H, Ichihara S, et al:
Prediction of the risk of myocardial infarction from polymorphisms
in candidate genes. N Engl J Med. 347:1916–1923. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Listi F, Candore G, Lio D, et al:
Association between C1019T polymorphism of connexin37 and acute
myocardial infarction: a study in patients from Sicily. Int J
Cardiol. 102:269–271. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Seifi M, Fallah S, Ghasemi A, Aghajani H,
Razaghi M and Danaei N: Mutations of the connexin 37 and 40
gap-junction genes in patients with acute myocardial infarction.
Clin Lab. 59:343–348. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Pfenniger A, Wong C, Sutter E, et al:
Shear stress modulates the expression of the atheroprotective
protein Cx37 in endothelial cells. J Mol Cell Cardiol. 53:299–309.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kumari SS, Varadaraj K, Valiunas V, et al:
Functional expression and biophysical properties of polymorphic
variants of the human gap junction protein connexin37. Biochem
Biophys Res Commun. 274:216–224. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Schecter AD, Rollins BJ, Zhang YJ, et al:
Tissue factor is induced by monocyte chemoattractant protein-1 in
human aortic smooth muscle and THP-1 cells. J Biol Chem.
272:28568–28573. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Moghadasian MH: Experimental
atherosclerosis: a historical overview. Life Sci. 70:855–865. 2002.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Reinhard K, Rougier JS, Ogrodnik J and
Abriel H: Electrophysiological properties of mouse and
epitope-tagged human cardiac sodium channel Na v1.5 expressed in
HEK293 cells. F1000Res. 2:482013.
|
|
22
|
Yang JM, Wang Y, Qi LH, et al:
Combinatorial interference of toll-like receptor 2 and 4
synergistically stabilizes atherosclerotic plaque in apolipoprotein
E-knockout mice. J Cell Mol Med. 15:602–611. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Chapman MJ, Mills GL and Ledford JH: The
distribution and partial characterization of the serum
apolipoproteins in the guinea pig. Biochem J. 149:423–436.
1975.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Qi LH, Wang Y, Gao F, et al: Enhanced
stabilization of atherosclerotic plaques in apolipoprotein
E-knockout mice by combinatorial Toll-like receptor-1 and -2 gene
silencing. Hum Gene Ther. 20:739–750. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Thompson PL, Nidorf SM and Eikelboom J:
Targeting the unstable plaque in acute coronary syndromes. Clin
Ther. 35:1099–1107. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Mallavia B, Recio C, Oguiza A, et al:
Peptide inhibitor of NF-κB translocation ameliorates experimental
atherosclerosis. Am J Pathol. 182:1910–1921. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zaina S and Lund G: Atherosclerosis: cell
biology and lipoproteins - panoramic views of DNA methylation
landscapes of atherosclerosis. Curr Opin Lipidol. 24:369–370. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Menghini R, Casagrande V and Federici M:
MicroRNAs in endothelial senescence and atherosclerosis. J
Cardiovasc Transl Res. 6:924–930. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Maraghechi P, Hiripi L, Toth G, Bontovics
B, Bosze Z and Gocza E: Discovery of pluripotency-associated
microRNAs in rabbit preimplantation embryos and embryonic stem-like
cells. Reproduction. 145:421–437. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Reed KE, Westphale EM, Larson DM, Wang HZ,
Veenstra RD and Beyer EC: Molecular cloning and functional
expression of human connexin37, an endothelial cell gap junction
protein. J Clin Invest. 91:997–1004. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|