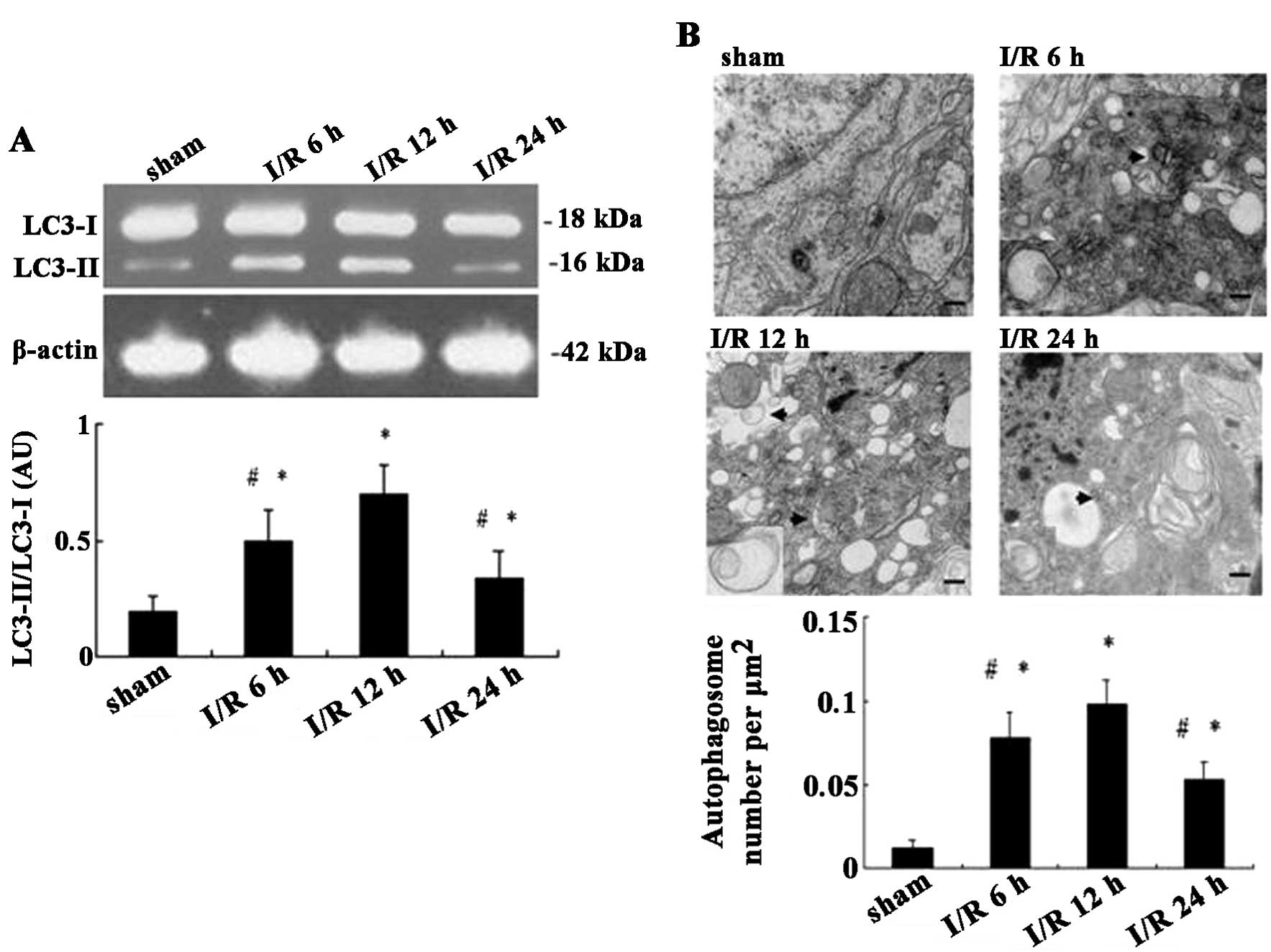
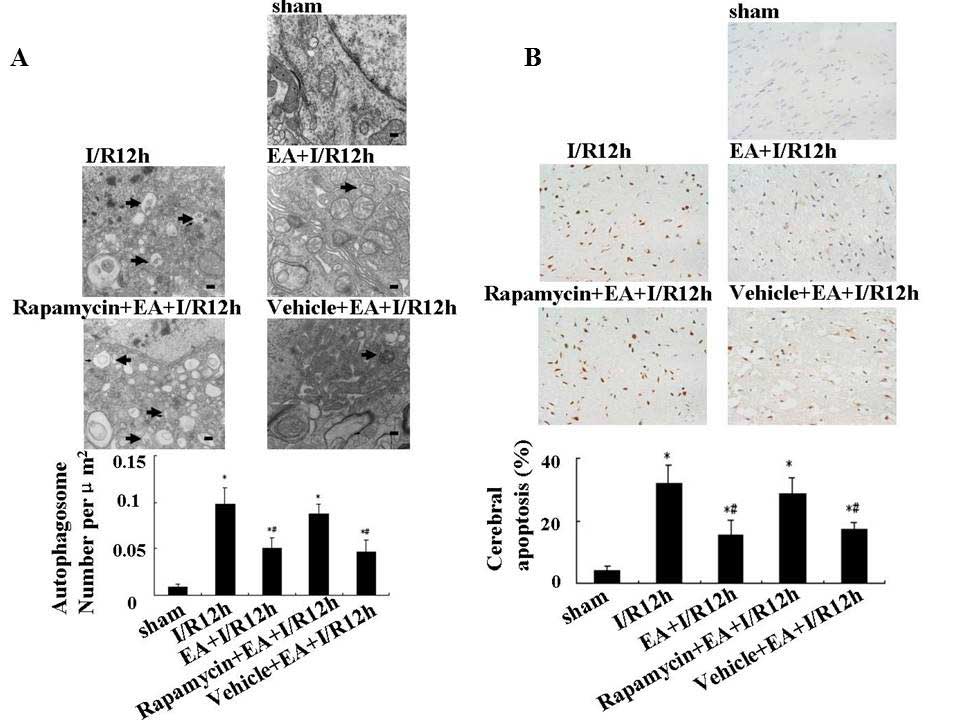
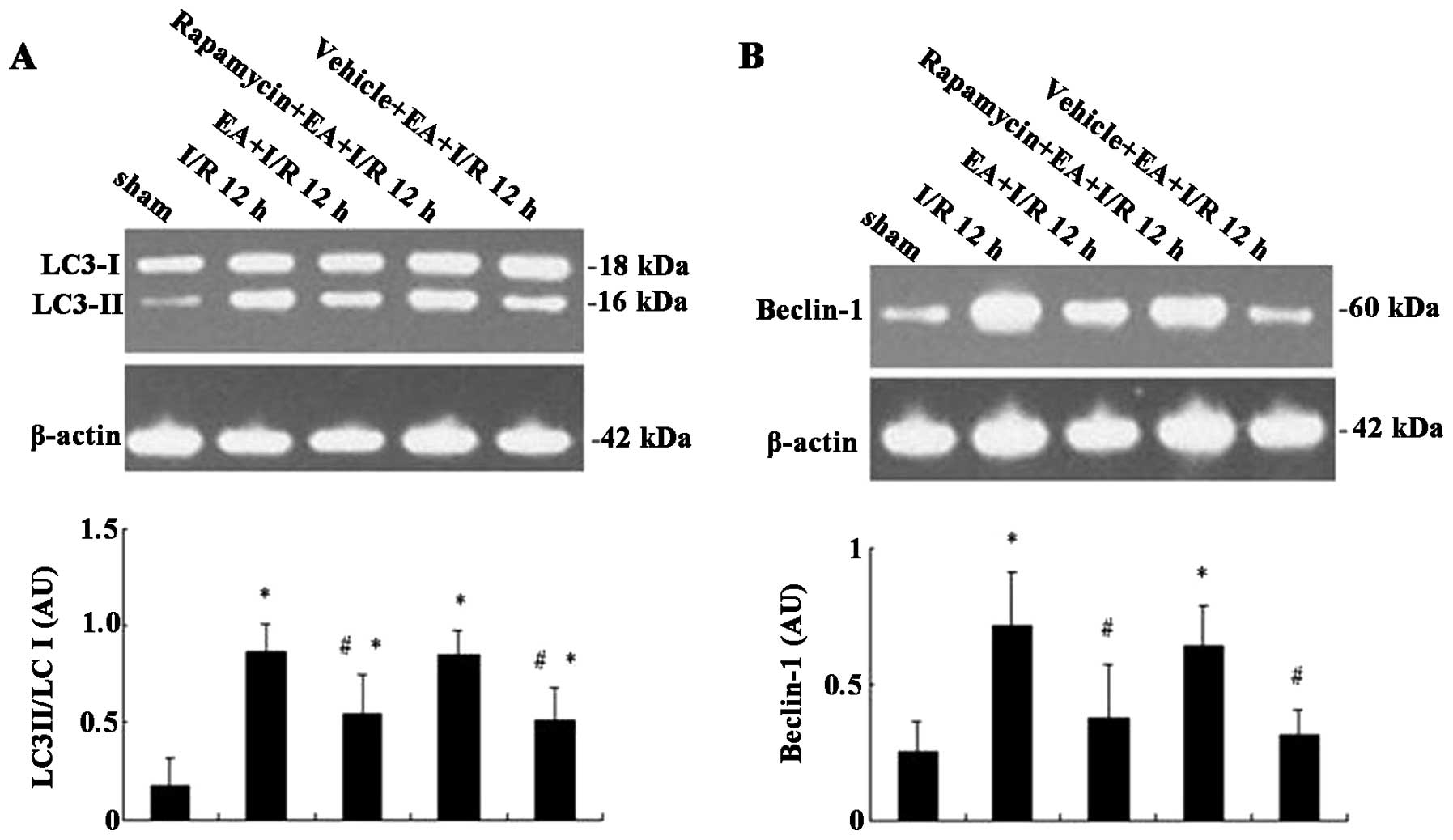
|
1
|
Donnan GA, Fisher M, Macleod M and Davis
SM: Stroke. Lancet. 371:1612–1623. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Zhao H, Sapolsky RM and Steinberg GK:
Interrupting reperfusion as a stroke therapy: ischemic
postconditioning reduces infarct size after focal ischemia in rats.
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 26:1114–1121. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Wang JK, Yu LN, Zhang FJ, Yang MJ, Yu J,
Yan M and Chen G: Postconditioning with sevoflurane protects
against focal cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury via PI3
K/Akt pathway. Brain Res. 1357:142–151. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Chou P, Chu H and Lin JG: Effects of
electroacupuncture treatment on impaired cognition and quality of
life in Taiwanese stroke patients. J Altern Complement Med.
15:1067–1073. 2009.
|
|
5
|
Wang Q, Xiong L, Chen S, Liu Y and Zhu X:
Rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia in rats is induced by
preconditioning with electroacupuncture: window of protection and
the role of adenosine. Neurosci Lett. 381:158–162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wang Q, Peng Y, Chen S, Gou X, Hu B, Du J,
Lu Y and Xiong L: Pretreatment with electroacupuncture induces
rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia through regulation of
endocannabinoid system. Stroke. 40:2157–2164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Wang Q, Wang F, Li X, Yang Q, Xu N, Huang
Y, Zhang Q, Gou X, Chen S and Xiong L: Electroacupuncture
pretreatment attenuates cerebral ischemic injury through alpha7
nicotinic acetylcholine receptor-mediated inhibition of
high-mobility group box 1 release in rats. J Neuroinflammation.
9:242012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Mizushima N: Autophagy: process and
function. Genes Dev. 21:2861–2873. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Yorimitsu T, Nair U, Yang Z and Klionsky
DJ: Endoplasmic reticulum stress triggers autophagy. J Biol Chem.
281:30299–30304. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Sarkar S, Perlstein EO, Imarisio S, Pineau
S, Cordenier A, Maglathlin RL, Webster JA, Lewis TA, et al: Small
molecules enhance autophagy and reduce toxicity in Huntington’s
disease models. Nat Chem Biol. 3:331–338. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Shintani T and Klionsky DJ: Autophagy in
health and disease: a double-edged sword. Science. 306:990–995.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Mizushima N: The pleiotropic role of
autophagy: from protein metabolism to bactericide. Cell Death
Differ 12 Suppl. 2:1535–1541. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Kabeya Y, Mizushima N, Ueno T, Yamamoto A,
Kirisako T, Noda T, Kominami E, Ohsumi Y and Yoshimori T: LC3, a
mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome
membranes after processing. EMBO J. 19:5720–5728. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Liang XH, Jackson S, Seaman M, Brown K,
Kempkes B, Hibshoosh H and Levine B: Induction of autophagy and
inhibition of tumorigenesis by beclin 1. Nature. 402:672–676. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Pattingre S, Tassa A, Qu X, Garuti R,
Liang XH, Mizushima N, Packer M, Schneider MD and Levine B: Bcl-2
antiapoptotic proteins inhibit Beclin 1-dependent autophagy. Cell.
122:927–939. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Qin ZH, Wang Y, Kegel KB, Kazantsev A,
Apostol BL, Thompson LM, Yoder J, Aronin N and Di Figlia M:
Autophagy regulates the processing of amino terminal huntingtin
fragments. Hum Mol Genet. 12:3231–3244. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Fujita E, Kouroku Y, Isoai A, Kumagai H,
Misutani A, Matsuda C, Hayashi YK and Momoi T: Two endoplasmic
reticulum-associated degradation (ERAD) systems for the novel
variant of the mutant dysferlin: ubiquitin/proteasome ERAD(I) and
autophagy/lysosome ERAD(II). Hum Mol Genet. 16:618–629. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Park HK, Chu K, Jung KH, Lee ST, Bahn JJ,
Kim M, Lee SK and Roh JK: Autophagy is involved in the ischemic
preconditioning. Neurosci Lett. 451:16–19. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Liu XQ, Gao B
and Qin ZH: Autophagy activation is associated with neuroprotection
in a rat model of focal cerebral ischemic preconditioning.
Autophagy. 6:482–494. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Lockshin RA and Zakeri Z: Apoptosis,
autophagy, and more. Int J Biochem Cell Biol. 36:2405–2419. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Wen YD, Sheng R, Zhang LS, Han R, Zhang X,
Zhang XD, Han F, Fukunaga K and Qin ZH: Neuronal injury in rat
model of permanent focal cerebral ischemia is associated with
activation of autophagic and lysosomal pathways. Autophagy.
4:762–769. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Koike M, Shibata M, Tadakoshi M, Gotoh K,
Komatsu M, Waguri S, Kawahara N, Kuida K, Nagata S, et al:
Inhibition of autophagy prevents hippocampal pyramidal neuron death
after hypoxic-ischemic injury. Am J Pathol. 172:454–469. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Rami A, Langhagen A and Steiger S: Focal
cerebral ischemia induces upregulation of Beclin 1 and
autophagy-like cell death. Neurobiol Dis. 29:132–141. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Sadoshima J: The role of autophagy during
ischemia/reperfusion. Autophagy. 4:402–403. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Zheng YQ, Liu JX, Li XZ, Xu L and Xu YG:
RNA interference-mediated downregulation of Beclin1 attenuates
cerebral ischemic injury in rats. Acta Pharmacol Sin. 30:919–927.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Hou X, Zhang R, Lv H, Cai X, Xie G and
Song X: Acupuncture at Baihui and Dazhui reduces brain cell
apoptosis in heroin readdicts. Neural Regen Res. 9:164–70. 2014.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Hirai K, Aliev G, Nunomura A, Fujioka H,
Russell RL, Atwood CS, Johnson AB, Kress Y, Vinters HV, et al:
Mitochondrial abnormalities in Alzheimer’s disease. J Neurosci.
21:3017–3023. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Qin ZH, Chen RW, Wang Y, Nakai M, Chuang
DM and Chase TN: Nuclear factor κB nuclear translocation
upregulates c-Myc and p53 expression during NMDA receptor-mediated
apoptosis in rat striatum. J Neurosci. 19:4023–4033.
1999.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Rosen GD and Harry JD: Brain volume
estimation from serial section measurements: a comparison of
methodologies. J Neurosci Methods. 35:115–124. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Napadow V, Makris N, Liu J, Kettner NW,
Kwong KK and Hui KK: Effects of electroacupuncture versus manual
acupuncture on the human brain as measured by fMRI. Hum Brain Mapp.
24:193–205. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xiong LZ, Yang J, Wang Q and Lu ZH:
Involvement of delta- and mu-opioid receptors in the delayed
cerebral ischemic tolerance induced by repeated electroacupuncture
preconditioning in rats. Chin Med J (Engl). 120:394–399. 2007.
|
|
33
|
Talha S, Bouitbir J, Charles AL, Zoll J,
Goette-Di Marco P, Meziani F, Piquard F and Geny B: Pretreatment
with brain natriuretic peptide reduces skeletal muscle
mitochondrial dysfunction and oxidative stress after
ischemia-reperfusion. J Appl Physiol (1985). 114:172–179. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Wu XD, Du LN, Wu GC and Cao XD: Effects of
electroacupuncture on blood-brain barrier after cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion in rat. Acupunct Electrother Res. 26:1–9.
2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Zhao J, Xu H, Tian Y, Hu M and Xiao H:
Effect of electroacu-puncture on brain-derived neurotrophic factor
mRNA expression in mouse hippocampus following cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. J Tradit Chin Med. 33:253–257. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
36
|
Cui D, Wang L, Qi A, Zhou Q, Zhang X and
Jiang W: Propofol prevents autophagic cell death following oxygen
and glucose deprivation in PC12 cells and cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury in rats. PLoS One. 7:e353242012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Liu L, Fang YQ, Xue ZF, He YP, Fang RM and
Li L: β-asarone attenuates ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy
in rat brains via modulating JNK, p-JNK, Bcl-2 and Beclin 1. Eur J
Pharmacol. 680:34–40. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
38
|
Xia DY, Li W, Qian HR, Yao S, Liu JG and
Qi XK: Ischemia preconditioning is neuroprotective in a rat
cerebral ischemic injury model through autophagy activation and
apoptosis inhibition. Braz J Med Biol Res. 46:580–588. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
39
|
Wang JY, Xia Q, Chu KT, Pan J, Sun LN,
Zeng B, Zhu YJ, Wang Q, Wang K and Luo BY: Severe global cerebral
ischemia-induced programmed necrosis of hippocampal CA1 neurons in
rat is prevented by 3-methyladenine: a widely used inhibitor of
autophagy. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 70:314–22. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
40
|
Liu C, Gao Y, Barrett J and Hu B:
Autophagy and protein aggregation after brain ischemia. J
Neurochem. 115:68–78. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
41
|
Xu F, Li J, Ni W, Shen YW and Zhang XP:
Peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor-gamma agonist
15d-prostaglandin J2 mediates neuronal autophagy after cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion injury. PLoS One. 8:e550802013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
42
|
Xie R, Li X, Ling Y, Shen C, Wu X, Xu W
and Gao X: α-lipoic acid pre- and post-treatments provide
protection against in vitro ischemia-reperfusion injury in cerebral
endothelial cells via Akt/mTOR signaling. Brain Res. 1482:81–90.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
43
|
Puyal J, Vaslin A, Mottier V and Clarke
PG: Postischemic treatment of neonatal cerebral ischemia should
target autophagy. Ann Neurol. 66:378–389. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
44
|
Zhang X, Yan H, Yuan Y, Gao J, Shen Z,
Cheng Y, Shen Y, Wang RR, Wang X, et al: Cerebral
ischemia-reperfusion-induced autophagy protects against neuronal
injury by mitochondrial clearance. Autophagy. 9:1321–1333. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
45
|
Zhu C, Wang X, Xu F, Bahr BA, Shibata M,
Uchiyama Y, Hagberg H and Blomgren K: The influence of age on
apoptotic and other mechanisms of cell death after cerebral
hypoxia-ischemia. Cell Death Differ. 12:162–176. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|