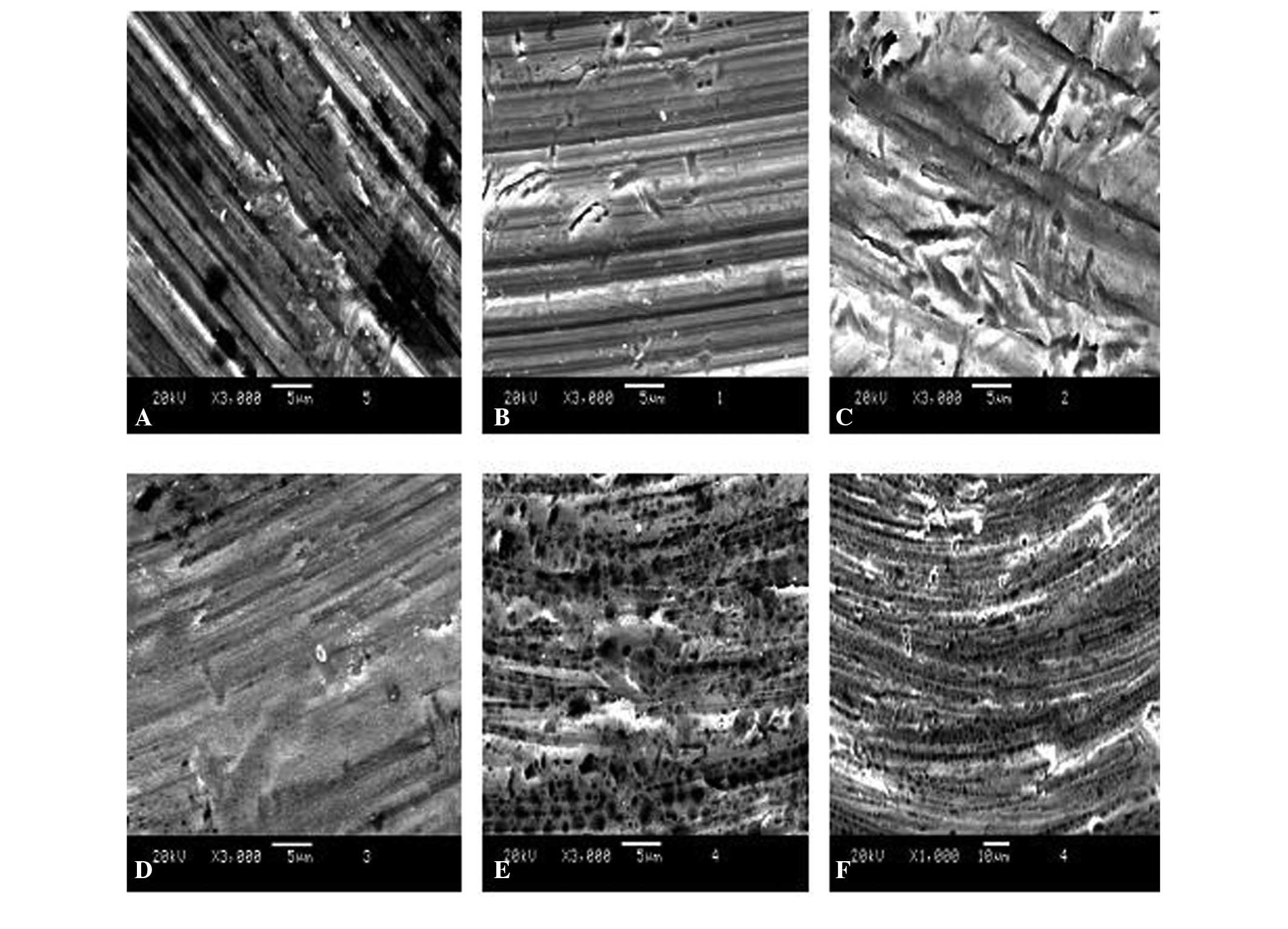
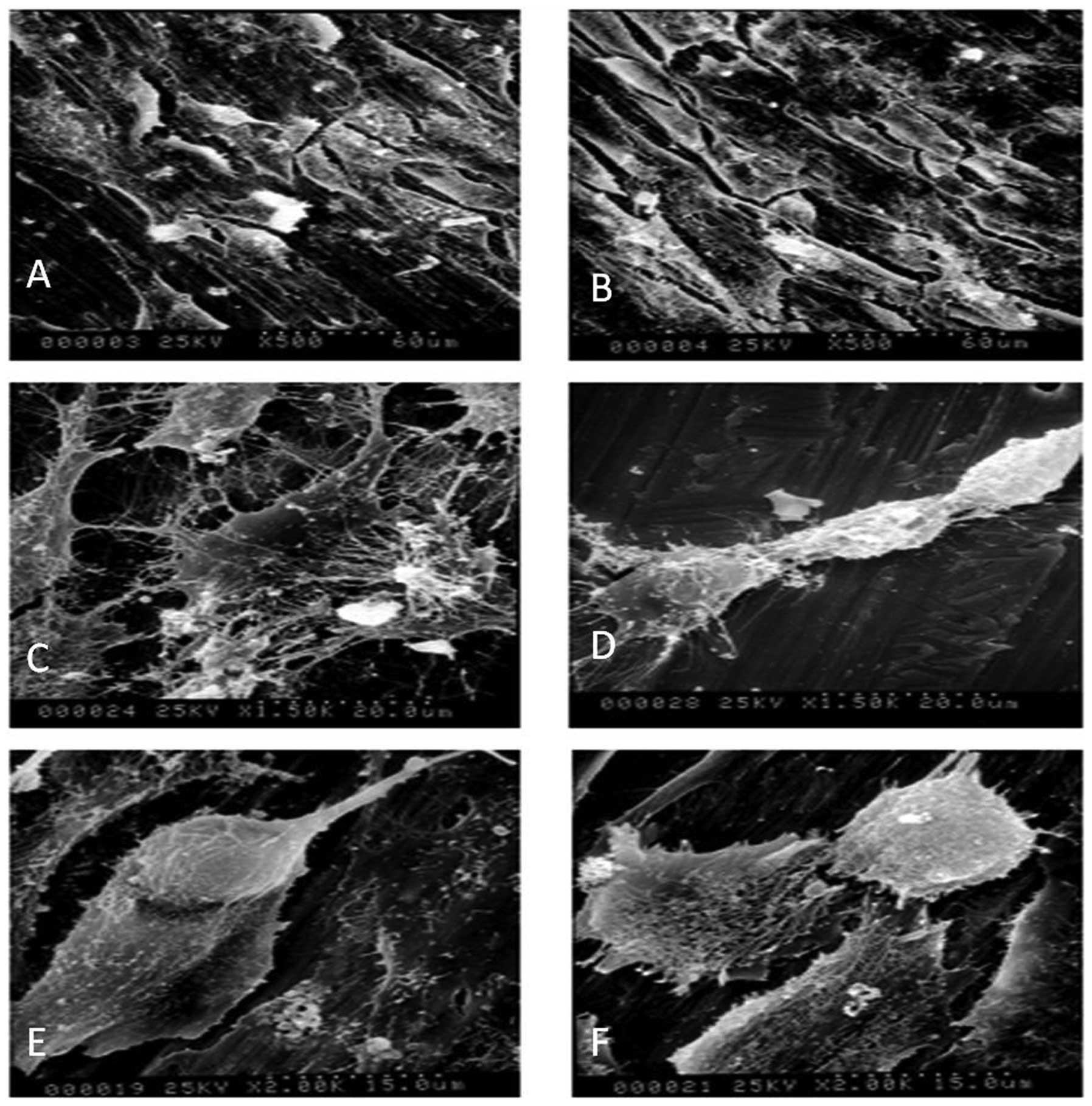
|
1
|
Rudy RJ, Levi PA, Bonacci FJ, Weisgold AS
and Engler-Hamm D: Intraosseous anchorage of dental prostheses: an
early 20th century contribution. Compend Contin Educ Dent.
29:220–222. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Elias CN, Oshida Y, Lima JH and Muller CA:
Relationship between surface properties (roughness, wettability and
morphology) of titanium and dental implant removal torque. J Mech
Behav Biomed Mater. 1:234–242. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
3
|
Condie R, Bose S and Bandyopadhyay A: Bone
cell-materials interaction on Si microchannels with bioinert
coatings. Acta Biomater. 3:523–530. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Hara T, Matsuoka K, Matsuzaka K, Yoshinari
M and Inoue T: Effect of surface roughness of titanium dental
implant placed under periosteum on gene expression of bone
morphogenic markers in rat. Bull Tokyo Dent Coll. 53:45–50. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Oga M, Arizono T and Sugioka Y: Bacterial
adherence to bioinert and bioactive materials studied in vitro.
Acta Orthop Scand. 64:273–276. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Li F and Zhu L: Effect of
surfactant-induced cell surface modifications on electron transport
system and catechol 1,2-dioxygenase activities and phenanthrene
biodegradation by Citrobacter sp. SA01. Bioresour Technol.
123:42–48. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Nieciecka D, Nawara K, Kijewska K, et al:
Solid-core and hollow magnetic nanostructures: Synthesis, surface
modifications and biological applications. Bioelectrochemistry.
93:2–14. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Yamaguchi H, Ino S, Hamano N, Okada S and
Teranaka T: Examination of bond strength and mechanical properties
of Y-TZP zirconia ceramics with different surface modifications.
Dent Mater J. 31:472–480. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Iwai Y, Matsuda Y, Nakatsuka M, Mikami Y
and Kumabe S: A preliminary study of the dental implant therapy -
initial osteogenesis of human mesenchymal stem (HMS0014) cells on
titanium discs with different surface modifications. Okajimas Folia
Anat Jpn. 88:133–140. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Qin Z, Huang Y, Liao Q, Zhang Z and Zhang
Y: Effect of surface modifications on ZnO nanorod arrays electrode
for dye-sensitized solar cells. J Nanosci Nanotechnol. 12:463–468.
2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Wang L, Huang L, Xie Z, Wang X and Tang B:
Fourth-generation plasma immersion ion implantation and deposition
facility for hybrid surface modification layer fabrication. Rev Sci
Instrum. 79:0233062008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Kwok SC, Yang P, Wang J, Liu X and Chu PK:
Hemocompatibility of nitrogen-doped, hydrogen-free diamond-like
carbon prepared by nitrogen plasma immersion ion
implantation-deposition. J Biomed Mater Res A. 70:107–114. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Yang P, Huang N, Leng YX, et al:
Activation of platelets adhered on amorphous hydrogenated carbon
(a-C:H) films synthesized by plasma immersion ion
implantation-deposition (PIII-D). Biomaterials. 24:2821–2829. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Xua JA, Ding G, Li JL, et al: Zinc-ion
implanted and deposited titanium surfaces reduce adhesion of
Streptococccus mutans. Appl Surf Sci. 256:7540–7544. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
15
|
Anna K, Nina P, Yuri K, et al: Coating
zinc oxide submicron crystals on poly(methyl methacrylate) chips
and spheres via ultrasound irradiation. Ultrason Sonochem.
15:839–845. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Le Guéhennec L, Soueidan A, Layrolle P and
Amouriq Y: Surface treatments of titanium dental implants for rapid
osseointegration. Dent Mater. 23:844–854. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Chung SH, Kim HK, Shon WJ and Park YS:
Peri-implant bone formations around (Ti,Zr)O(2)-coated zirconia
implants with different surface roughness. J Clin Peridontol.
40:404–411. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
18
|
Sul YT: Electrochemical growth behavior,
surface properties, and enhanced in vivo bone response of
TiO2 nanotubes on microstructured surfaces of blasted,
screw-shaped titanium implants. Int J Nanomedicine. 5:87–100. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Triplett RG, Frohberg U, Sykaras N and
Woody RD: Implant materials, design and surface topographies: their
influence on osseointegration of dental implants. J Long Term Eff
Med Implants. 13:485–501. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
20
|
Sosa NE, Chen C, Liu J, et al: Nanoscale
structure, composition and charge transport analysis of transparent
conducting oxide nanowires written by focused ion beam
implantation. J Am Chem Soc. 132:7347–7354. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Minagar S, Berndt CC, Wang J, Ivanova E
and Wen C: A review of the application of anodization for the
fabrication of nanotubes on metal implant surfaces. Acta Biomater.
8:2875–2888. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Saksø M, Jakobsen SS, Saksø H, et al: Acid
etching and plasma sterilization fail to improve osseointegration
of grit blasted titanium implants. Open Orthop J. 6:376–382. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Hempel U, Hefti T, Dieter P and Schlottig
F: Response of human bone marrow stromal cells, MG-63 and SaOS-2 to
titanium-based dental implant surfaces with different topography
and surface energy. Clin Oral Implants Res. 24:174–182. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Cosar M, Ozer AF, Iplikcioglu AC, et al:
The results of beta-tricalcium phosphate coated hydroxyapatite
(beta‑TCP/HA) grafts for interbody fusion after anterior cervical
discectomy. J Spinal Disord Tech. 21:436–441. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|