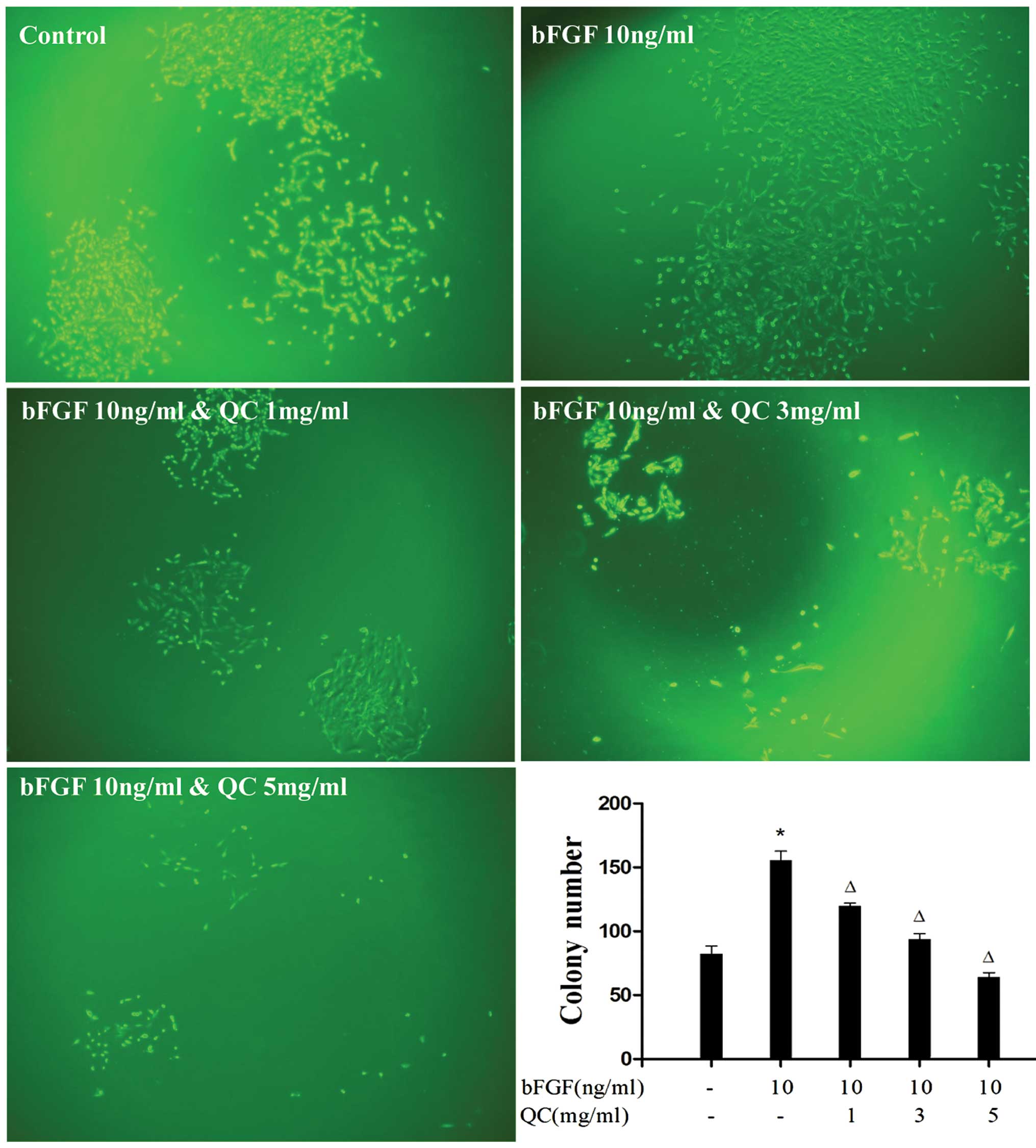
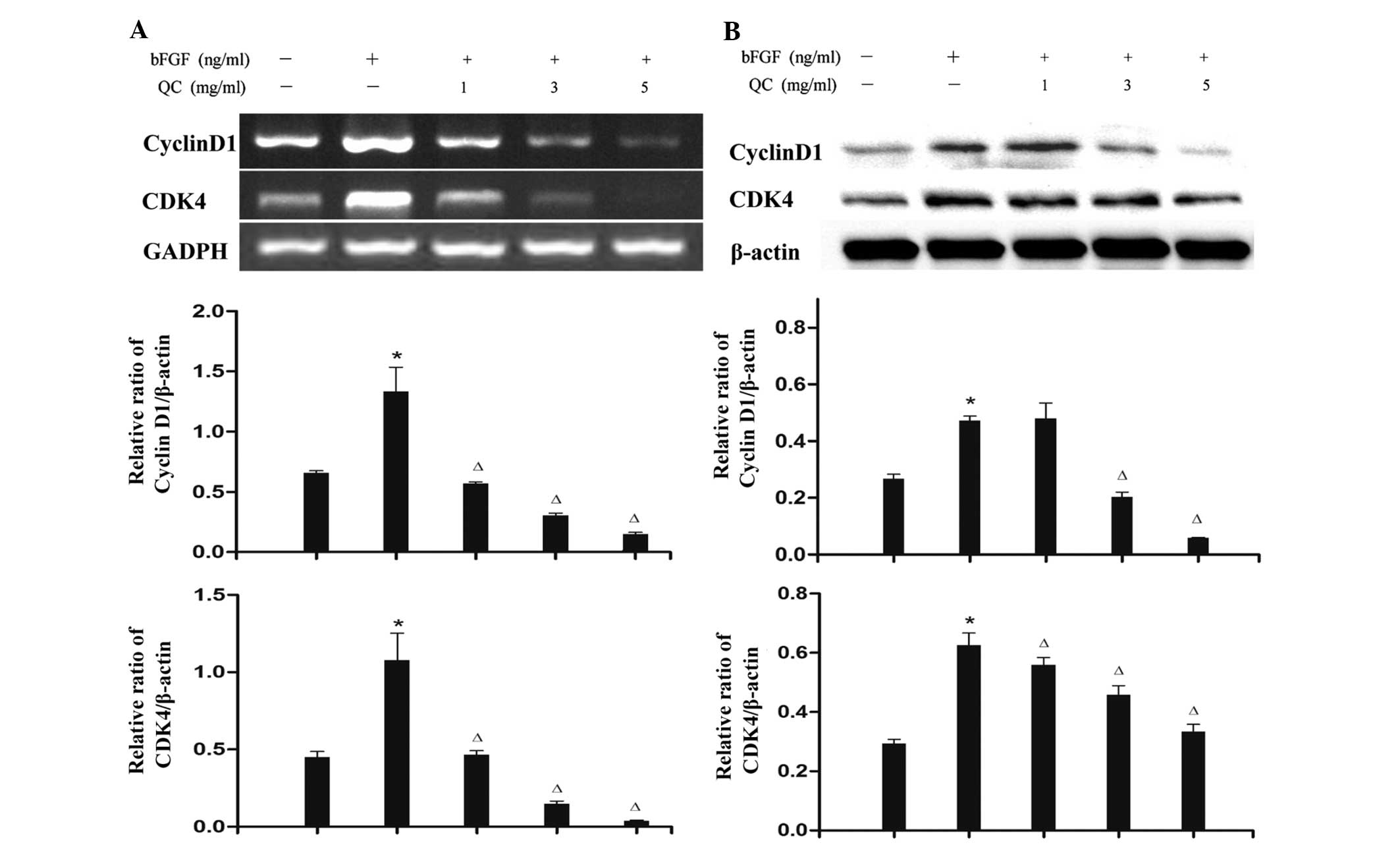
|
1
|
Kirby RS: The natural history of benign
prostatic hyperplasia: what have we learned in the last decade?
Urology. 56(Suppl 5): 3–6. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Djavan B: Lower urinary tract
symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia 1: fast control of the
patient’s quality of life. Urology. 62(Suppl 3): 6–14. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Lucia MS and Lambert JR: Growth factors in
benign prostatic hyperplasia: basic science implications. Curr Urol
Rep. 9:272–278. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Mori H, Maki M, Oishi K, et al: Increased
expression of genes for basic fibroblast growth factor and
transforming growth factor type beta 2 in human benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Prostate. 16:71–80. 1990. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Giri D and Ittmann M: Interleukin-8 is a
paracrine inducer of fibroblast growth factor 2, a stromal and
epithelial growth factor in benign prostatic hyperplasia. Am J
Pathol. 159:139–47. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Bartsch G, Brüngger A, Schweikert U,
Hintner H, Höpfl R and Rohr HP: Benign prostatic hyperplasia: a
stromal disease. Urologe A. 28:321–328. 1989.In German. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Djavan B, Remzi M, Erne B and Marberger M:
The pathophysiology of benign prostatic hyperplasia. Drugs Today
(Barc). 38:867–876. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Roehrborn CG: Pathology of benign
prostatic hyperplasia. Int J Impot Res. 20(Suppl 3): 11–18. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
9
|
Zhang MD, Zhao YN and An LW: B-cell
lymphoma/leukemia-2 and benign prostatic hyperplasia. Chin J
Androl. 15:452–454. 2009.In Chinese.
|
|
10
|
Kyprianou N, Tu H and Jacobs SC: Apoptotic
versus proliferative activities in human benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Hum Pathol. 27:668–675. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Claus S, Berges R, Senge T and Schulze H:
Cell kinetic in epithelium and stroma of benign prostatic
hyperplasia. J Urol. 158:217–221. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen Y, Robles AI, Martinez LA, Liu F,
Gimenez-Conti IB and Conti CJ: Expression of G1 cyclins,
cyclin-dependent kinases and cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors in
androgen-induced prostate proliferation in castrated rats. Cell
Growth Differ. 7:1571–1578. 1996.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Graña X and Reddy EP: Cell cycle control
in mammalian cells: role of cyclins, cyclin dependent kinases
(CDKs), growth suppressor genes and cyclin-dependent kinase
inhibitors (CKIs). Oncogene. 11:211–219. 1995.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Zhong W, Peng J, He H, et al: Ki-67 and
PCNA expression in prostate cancer and benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Clin Invest Med. 31:E8–E15. 2008.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
McVary KT: A review of combination therapy
in patients with benign prostatic hyperplasia. Clin Ther.
29:387–398. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Schulman CC: Lower urinary tract
symptoms/benign prostatic hyperplasia: minimizing morbidity caused
by treatment. Urology. 62(3 Suppl 1): 24–33. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Lieber MM: Pharmacologic therapy for
prostatism. Mayo Clin Proc. 73:590–596. 1998. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Wilt T, Ishani A, Stark G, MacDonald R,
Mulrow C and Lau J: Serenoa repens for benign prostatic
hyperplasia. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. CD0014232000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
McPartland JM and Pruitt PL: Benign
prostatic hyperplasia treated with saw palmetto: a literature
search and an experimental case study. J Am Osteopath Assoc.
100:89–96. 2000.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Peng CC, Liu JH, Chang CH, et al: Action
mechanism of Ginkgo biloba Leaf extract intervened by exercise
therapy in treatment of benign prostate hyperplasia. Evid Based
Complement Alternat Med. 2013:4087342013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hong ZF, Lin JM, Zhong XY, et al:
Qianliening capsule inhibits human prostate cell growth via
induction of mitochondrion-dependent cell apoptosis. Chin J Integr
Med. 18:824–830. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Lin J, Zhou J, Xu W, Zhong X, Hong Z and
Peng J: Qianliening capsule treats benign prostatic hyperplasia via
suppression of the EGF/STAT3 signaling pathway. Exp Ther Med.
5:1293–1300. 2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Zheng H, Xu W, Lin J, Peng J and Hong Z:
Qianliening capsule treats benign prostatic hyperplasia via
induction of prostatic cell apoptosis. Mol Med Rep. 7:848–854.
2013.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Zhou J, Lin J, Wei X, Zhong X, Zheng Y,
Hong Z and Peng J: Qianliening capsule treats benign prostatic
hyperplasia through regulating the expression of sex hormones,
estrogen receptor and androgen receptor. Afr J Pharm Pharmacol.
6:173–180. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu W, Li H, Lin J, et al: Optimization of
the chitosan purification process of Qianleining capsule by
orthogonal test. J Zhejiang Univ Trad Chin Med. 35:571–574.
2011.
|
|
26
|
Shin IS, Lee MY, Ha HK, Seo CS and Shin
HK: Inhibitory effect of Yukmijihwangtang, a traditional herbal
formula against testosterone-induced benign prostatic hyperplasia
in rats. BMC Complement Altern Med. 12:482012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Wang Y, Shao JC and Zhang SW:
Histomorphological studies on hyperplastic prostate of castrated
rat caused by androgen. Zhonghua Nan Ke Xue. 8:190–193. 2002.In
Chinese.
|
|
28
|
Wang Y, Shao JC and Zhang SW:
Histomorphological studies on hyperplastic prostate of castrated
rat caused by androgen. Chin J Androl. 3:190–193. 2002.In
Chinese.
|
|
29
|
Nurse P, Masui Y and Hartwell L:
Understanding the cell cycle. Nat Med. 4:1103–1106. 1998.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Morgan DO: Principles of CDK regulation.
Nature. 374:131–134. 1995. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Nurse P: A long twentieth century of the
cell cycle and beyond. Cell. 100:71–78. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Day PJ, Cleasby A, Tickle IJ, et al:
Crystal structure of human CDK4 in complex with a D-type cyclin.
Proc Natl Acad Sci USA. 106:4166–4170. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Sridhar J, Akula N and Pattabiraman N:
Selectivity and potency of cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitors. AAPS
J. 8:E204–221. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Park KI, Park HS, Kang SR, et al: Korean
Scutellaria baicalensis water extract inhibits cell cycle G1/S
transition by suppressing cyclin D1 expression and
matrix-metalloproteinase-2 activity in human lung cancer cells. J
Ethnopharmacol. 133:634–641. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Bantis A, Giannopoulos A, Gonidi M, et al:
Expression of p120, Ki-67 and PCNA as proliferation biomarkers in
imprint smears of prostate carcinoma and their prognostic value.
Cytopathology. 15:25–31. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|