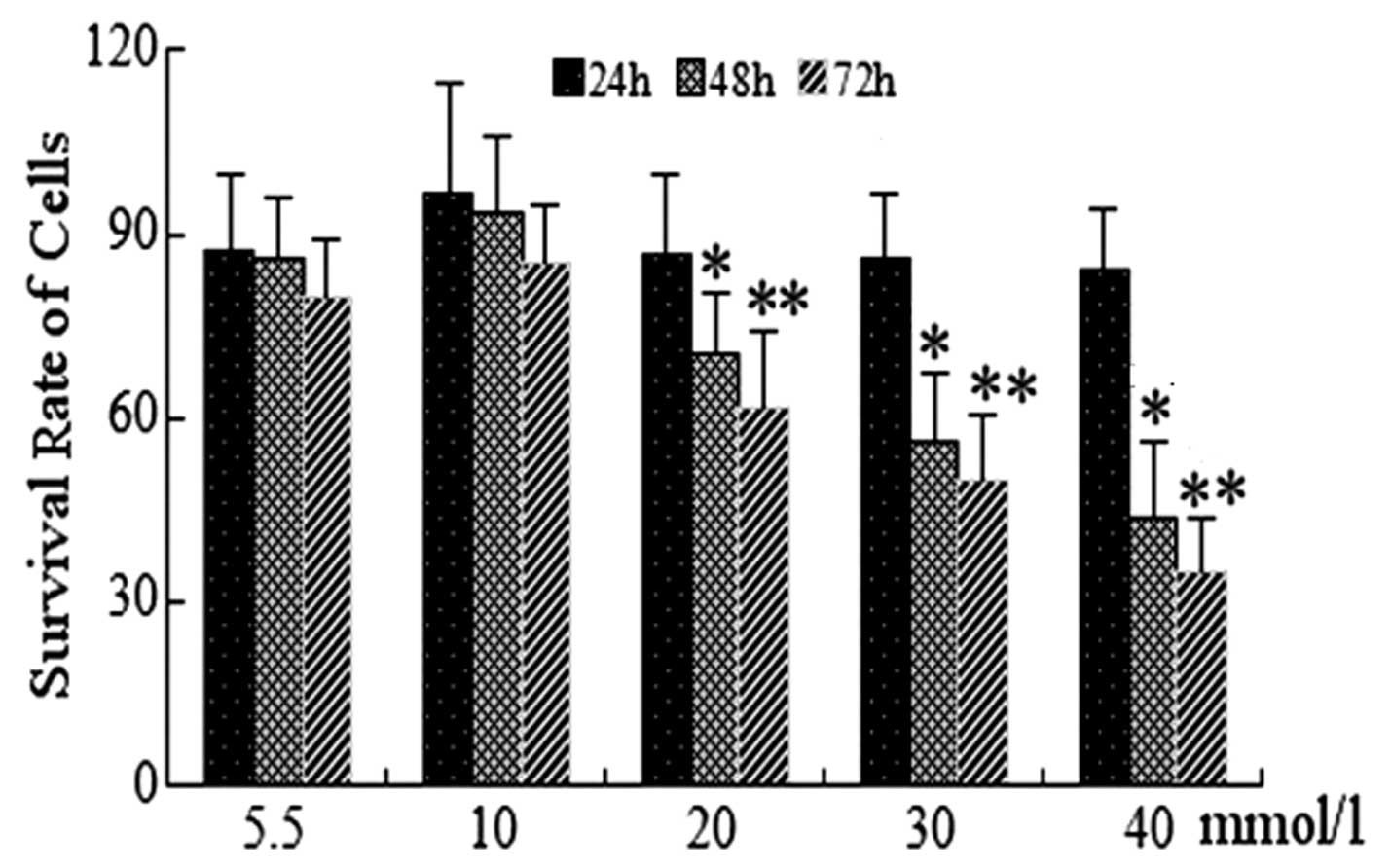
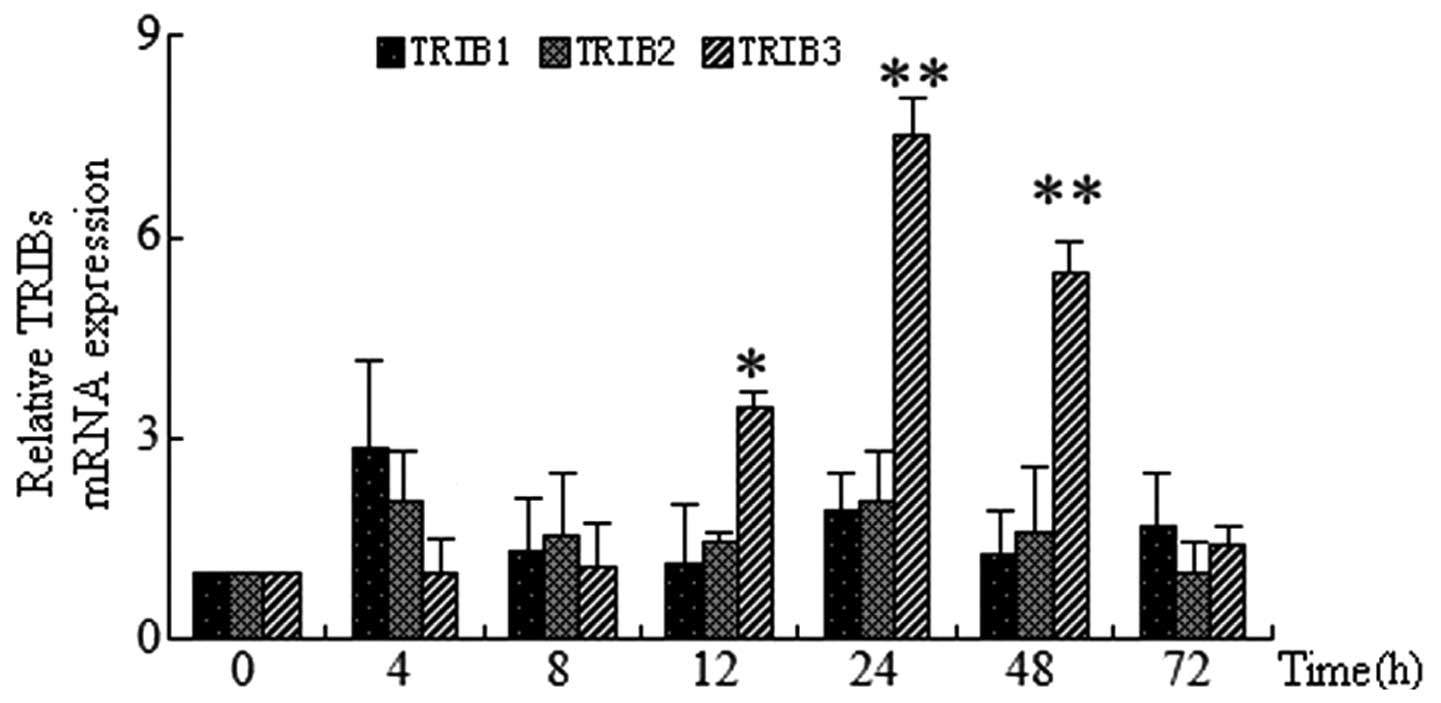
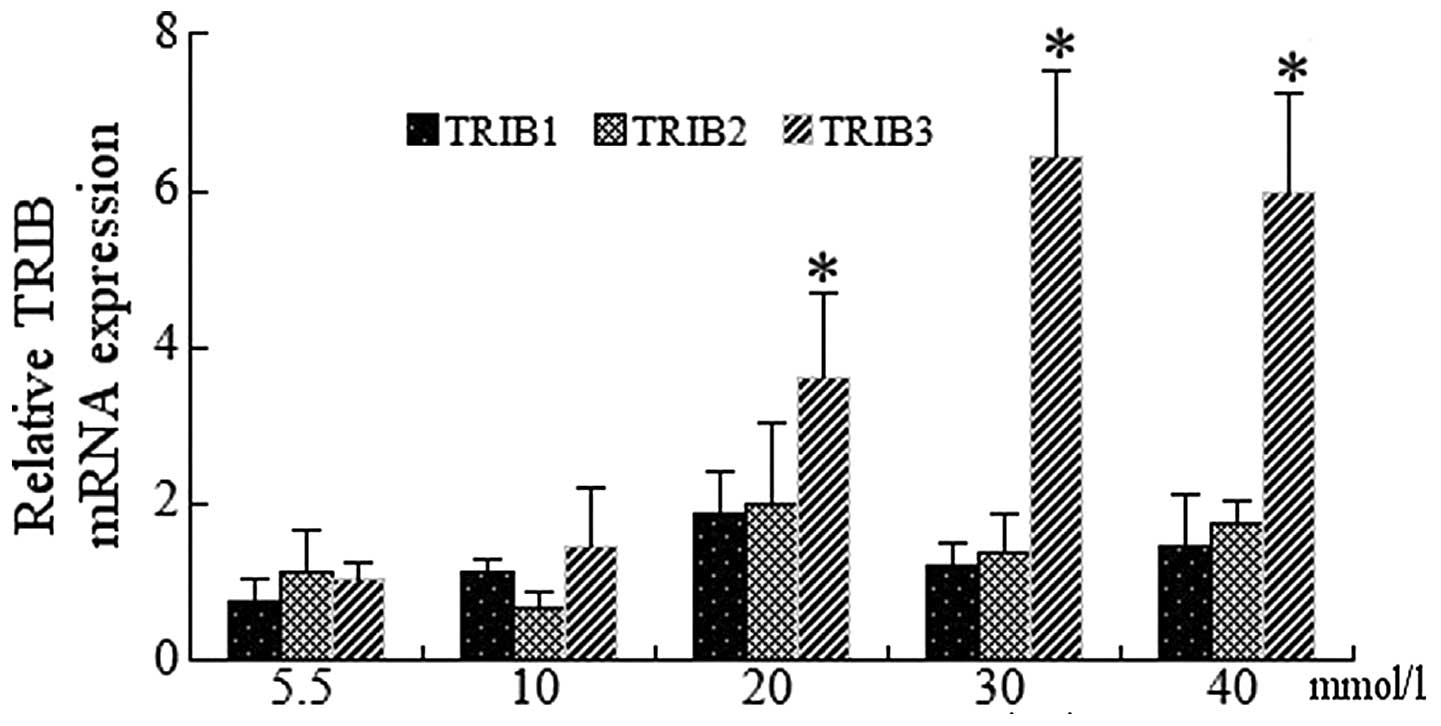
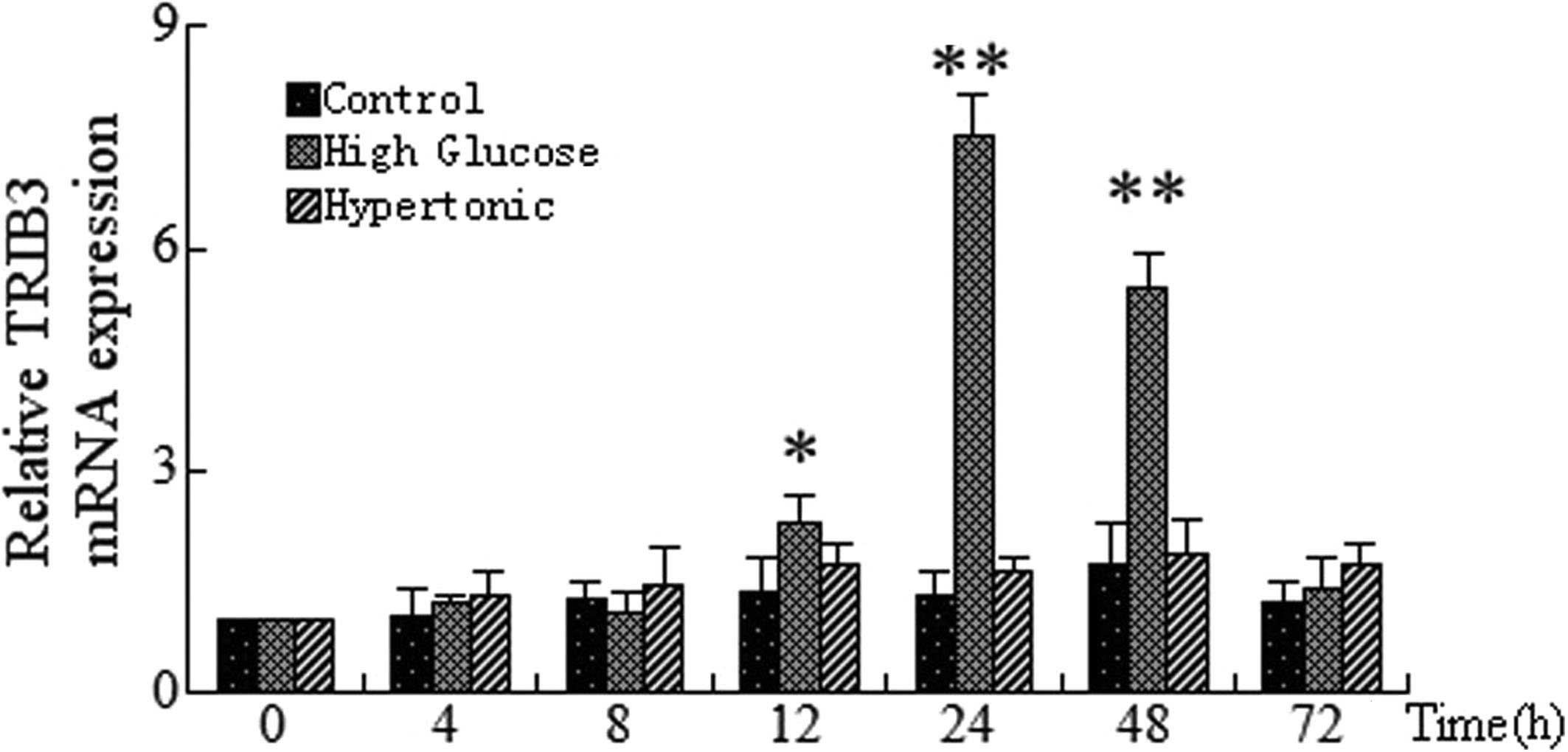
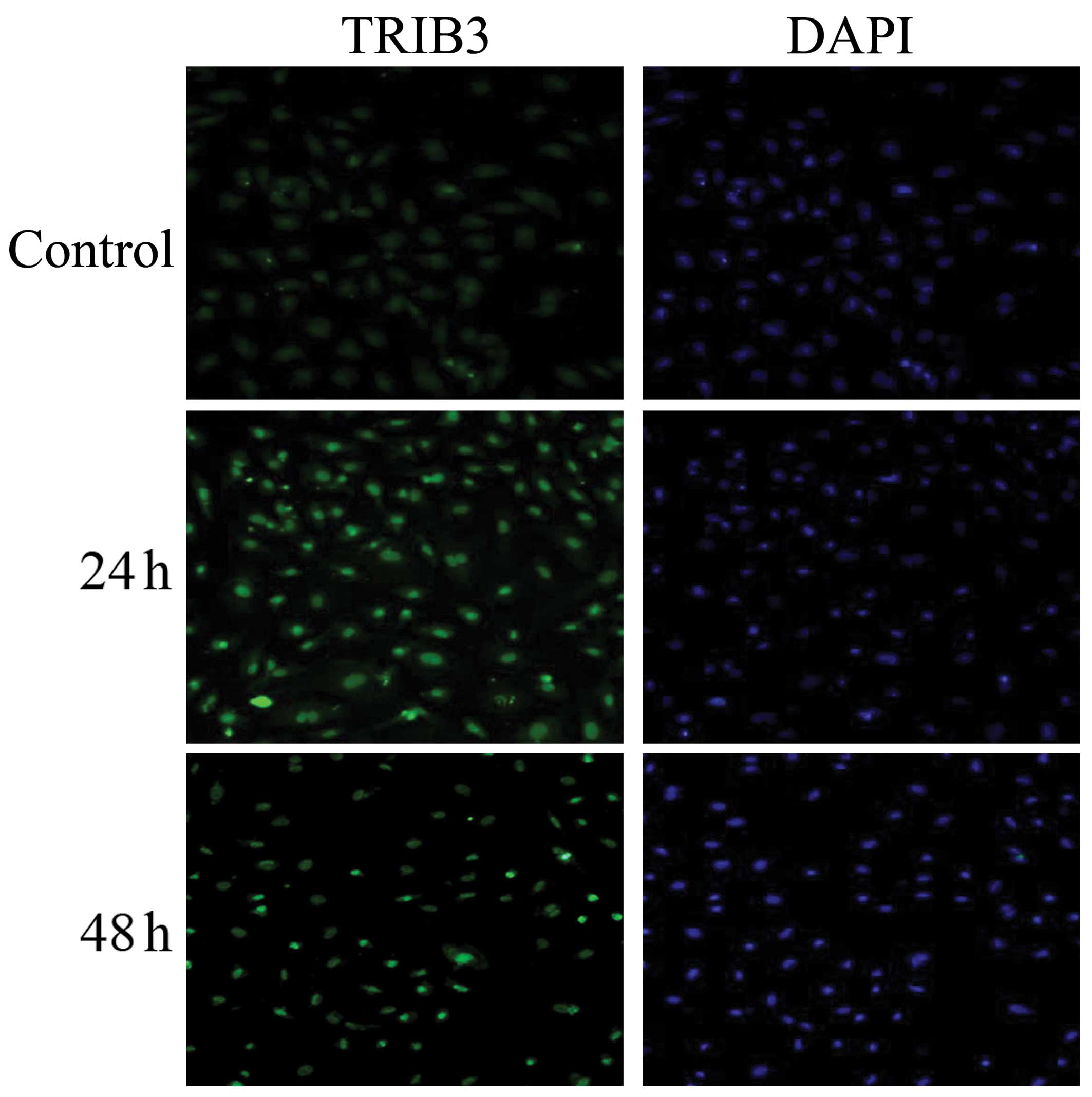
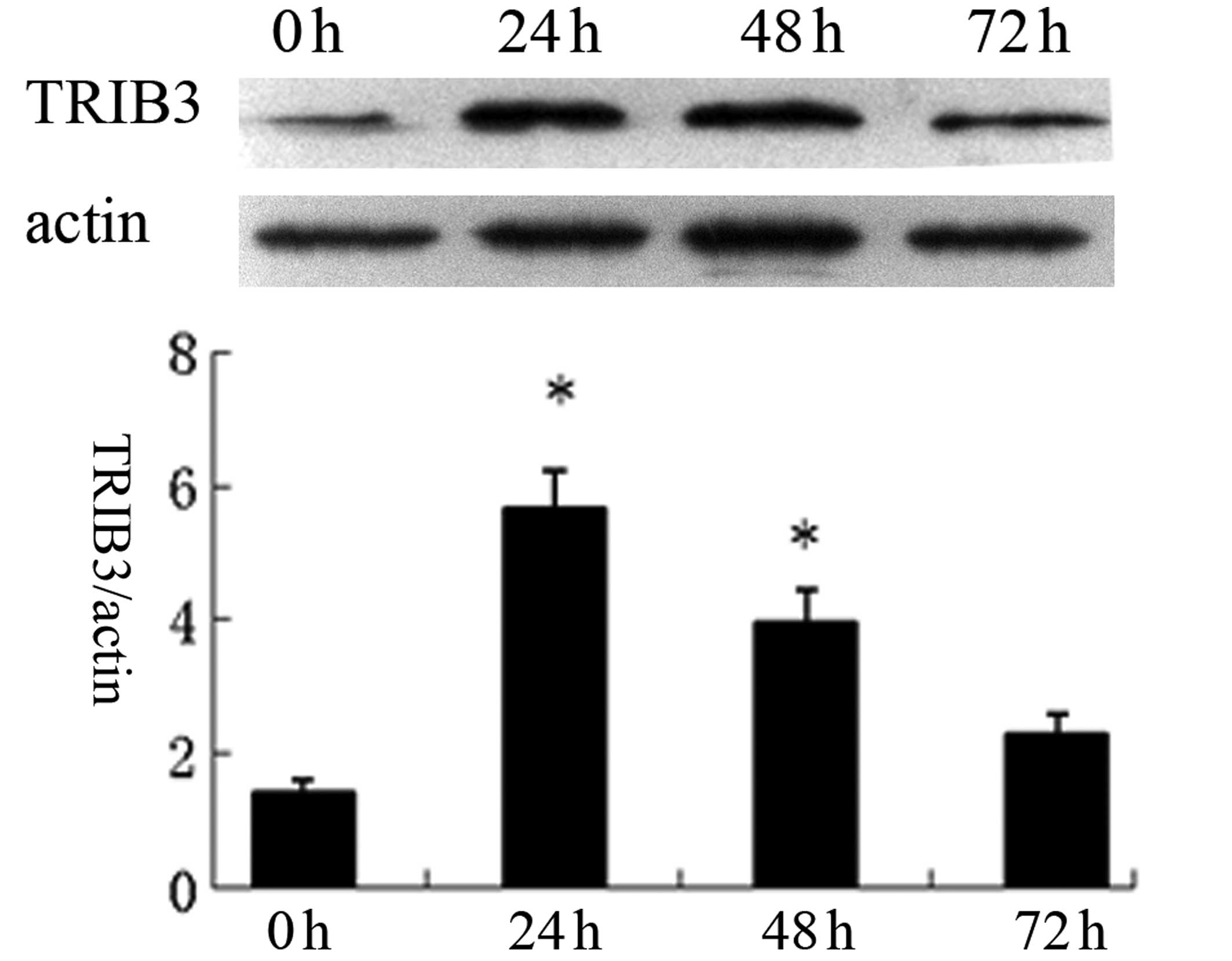
|
1
|
O’Neill MS, Veves A, Zanobetti A, et al:
Diabetes enhances vulnerability to particulate air
pollution-associated impairment in vascular reactivity and
endothelial function. Circulation. 111:2913–2920. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Davignon J and Ganz P: Role of endothelial
dysfunction in atherosclerosis. Circulation. 109(21 Suppl 1):
III27–III32. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Norata GD, Tonti L, Roma P and Catapano
AL: Apoptosis and proliferation of endothelial cells in early
atherosclerotic lesions: possible role of oxidised LDL. Nutr Metab
Cardiovasc Dis. 12:297–305. 2002.
|
|
4
|
Guangda X and Yuhua W: Apolipoprotein e4
allele and endothelium-dependent arterial dilation in Type 2
diabetes mellitus without angiopathy. Diabetologia. 46:514–519.
2003.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Lorenzi M, Cagliero E and Toledo S:
Glucose toxicity for human endothelial cells in culture. Delayed
replication, disturbed cell cycle, and accelerated death. Diabetes.
34:621–627. 1985. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Lorenzi M, Montisano DF, Toledo S and
Barrievx A: High glucose induces DNA damage in cultured human
endothelial cells. J Clin Invest. 77:322–325. 1986. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Lorenzi M, Nordberg JA and Toledo S: High
glucose prolongs cell-cycle traversal of cultured human endothelial
cells. Diabetes. 36:1261–1267. 1987. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Kageyama S, Yokoo H, Tomita K, et al: High
glucose-induced apoptosis in human coronary artery endothelial
cells involves up-regulation of death receptors. Cardiovasc
Diabetol. 10:732011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Sheu ML, Ho FM, Yang RS, et al: High
glucose induces human endothelial cell apoptosis through a
phosphoinositide 3-kinase-regulated cyclooxygenase-2 pathway.
Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 25:539–545. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Du K, Herzig S, Kulkarni RN and Montminy
M: TRIB3: a tribbles homolog that inhibits Akt/PKB activation by
insulin in liver. Science. 300:1574–1577. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Radovits T, Lin LN, Zotkina J, et al:
Poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase inhibition improves endothelial
dysfunction induced by reactive oxidant hydrogen peroxide in vitro.
Eur J Pharmacol. 564:158–166. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Prudente S, Hribal ML, Flex E, et al: The
functional Q84R polymorphism of mammalian Tribbles homolog TRIB3 is
associated with insulin resistance and related cardiovascular risk
in Caucasians from Italy. Diabetes. 54:2807–2811. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Qi L, Heredia JE, Almrejos JY, et al: TRB3
links the E3 ubiquitin ligase COP 1 to lipid metabolism. Science.
312:1763–1766. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Gong HP, Wang ZH, Jiang H, et al: TRIB3
functional Q84R polymorphism is a risk factor for metabolic
syndrome and carotid atherosclerosis. Diabetes Care. 32:1311–1313.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Baumgartner-Parzer SM, Wagner L,
Pettermann M, et al: High-glucose-triggered apoptosis in cultured
endothelial cells. Diabetes. 44:1323–1327. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Nakagami H, Morishita R, Yamamoto K, et
al: Phosphorylation of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase
downstream of bax-caspase-3 pathway leads to cell death induced by
high D-glucose in human endothelial cells. Diabetes. 50:1472–1481.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Zou MH, Shi C and Cohen RA: High glucose
via peroxynitrite causes tyrosine nitration and inactivation of
prostacyclin synthase that is associated with
thromboxane/prostaglandin H(2) receptor-mediated apoptosis and
adhesion molecule expression in cultured human aortic endothelial
cells. Diabetes. 51:198–203. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Kiss-Toth E, Wyllie DH, Holland K, et al:
Functional mapping of Toll/interleukin-1 signalling networks by
expression cloning. Biochem Soc Trans. 33(Pt 6): 1405–1406. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Mata J, Curado S, Ephrussi A and Rørth P:
Tribbles coordinates mitosis and morphogenesis in Drosophila by
regulating string/CDC25 proteolysis. Cell. 101:511–522. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Grosshans J and Wieschaus EA: A genetic
link between morphogenesis and cell division during formation of
the ventral furrow in Drosophila. Cell. 101:523–531. 2000.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Hegedus Z, Czibula A and Kiss-Toth E:
Tribbles: a family of kinase-like proteins with potent signalling
regulatory function. Cell Signal. 19:238–250. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Sung HY, Francis SE, Crossman DC and
Kiss-Toth E: Regulation of expression and signalling modulator
function of mammalian tribbles is cell-type specific. Immunol Lett.
104:171–177. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Ord D and Ord T: Mouse NIPK interacts with
ATF4 and affects its transcriptional activity. Exp Cell Res.
286:308–320. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Okamoto H, Latres E, Liu R, et al: Genetic
deletion of Trb3, the mammalian Drosophila tribbles homolog,
displays normal hepatic insulin signaling and glucose homeostasis.
Diabetes. 56:1350–1356. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Schwarzer R, Dames S, Tondera D, et al:
TRB3 is a PI 3-kinase dependent indicator for nutrient starvation.
Cell Signal. 18:899–909. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Yacoub Wasef SZ, Robinson KA, Berkaw MN
and Buse MG: Glucose, dexamethasone and the unfolded protein
response regulate TRB3 mRNA expression in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and L6
myotubes. Am J Physiol Endocrinol Metab. 291:E1274–E1280. 2006.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Ord D, Meerits K and Ord T: TRB3 protects
cells against the growth inhibitory and cytotoxic effect of ATF4.
Exp Cell Res. 313:3556–3567. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Ohoka N, Hattori T, Kitagawa M, et al:
Critical and functional regulation of CHOP (C/EBP homologous
protein) through the N-terminal portion. J Biol Chem.
282:35687–35694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Agrawal N, Dasaradhi PV, Mohmmed A, et al:
RNA interference: biology, mechanism, and applications. Microbiol
Mol Biol Rev. 67:657–685. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|