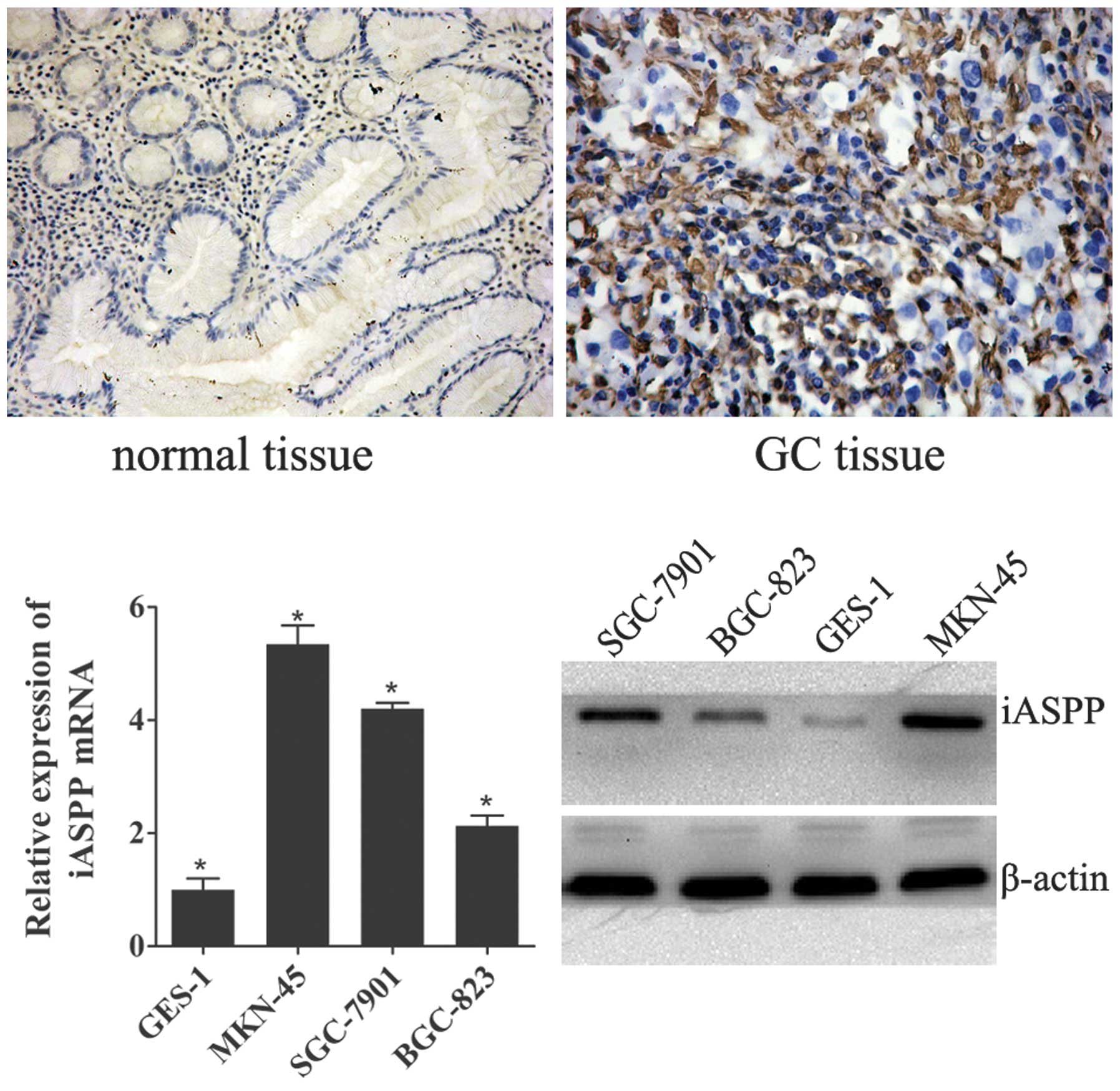
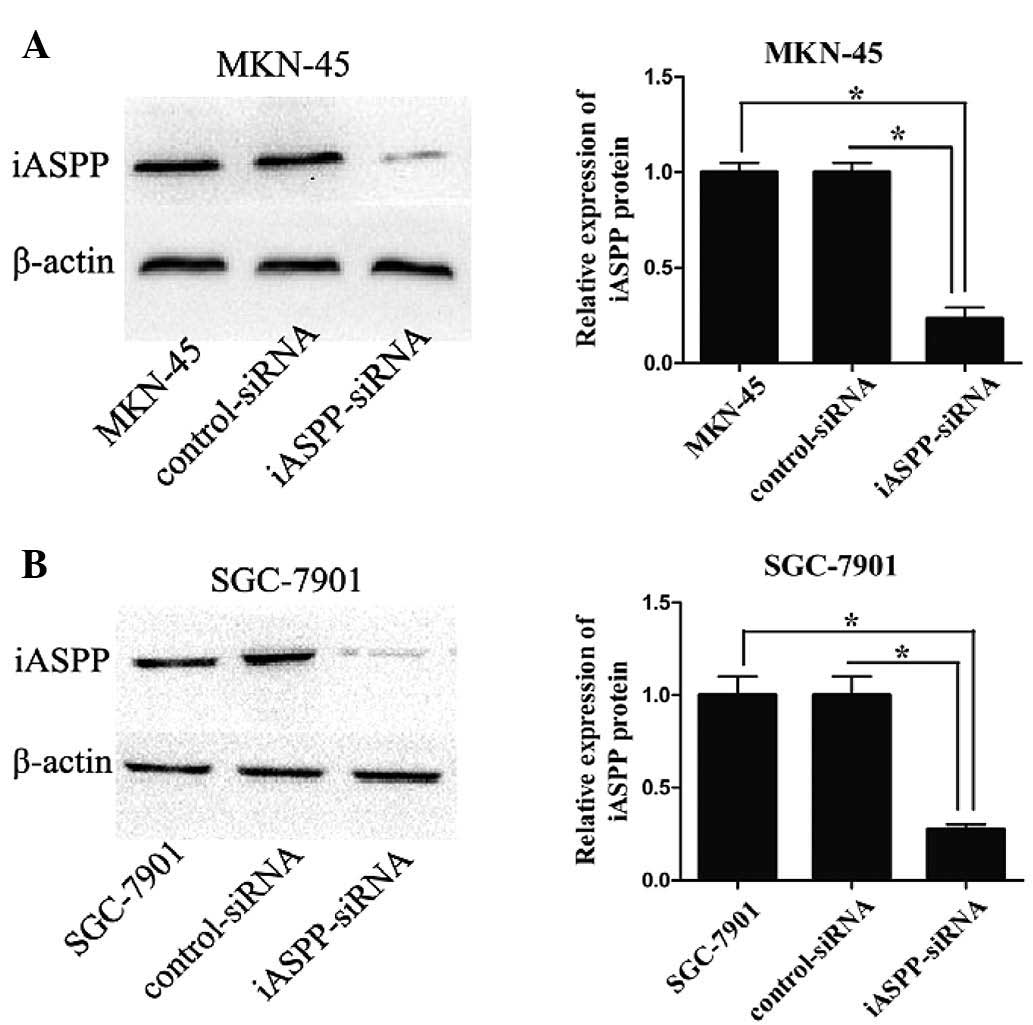
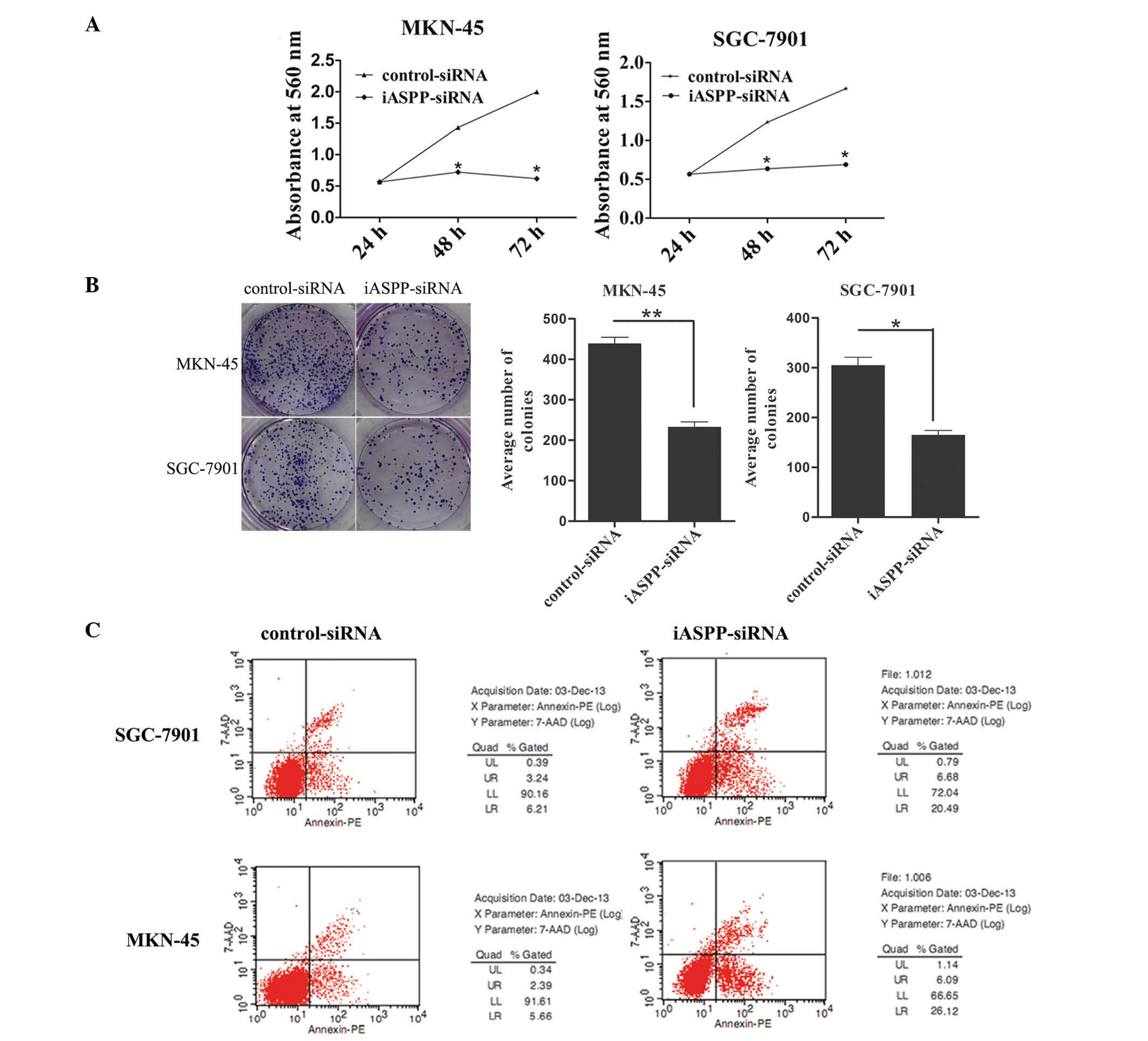
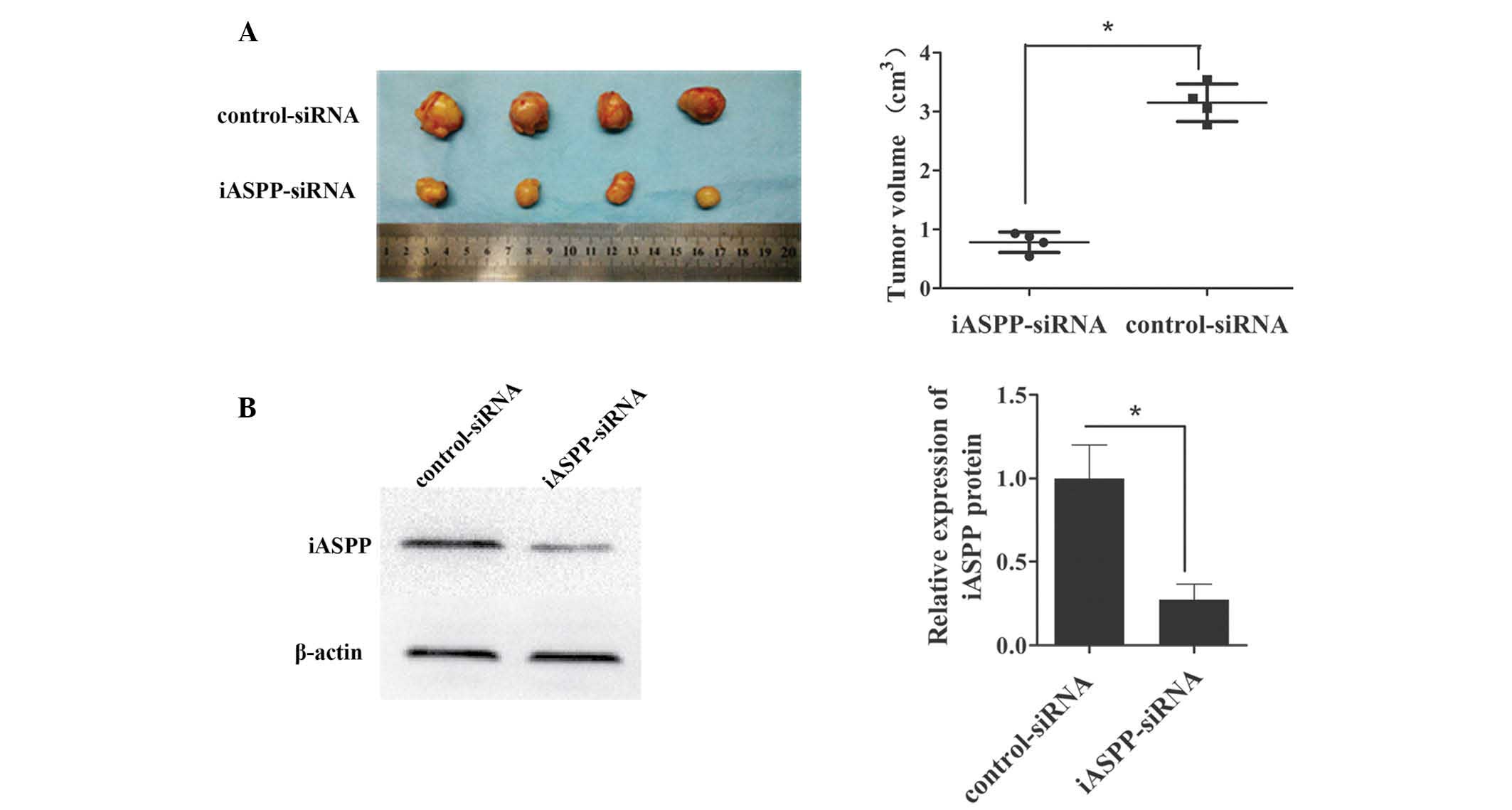
|
1
|
Takahashi T, Saikawa Y and Kitagawa Y:
Gastric cancer: current status of diagnosis and treatment. Cancers
(Basel). 5:48–63. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
2
|
Samuels-Lev Y, O’Connor DJ, Bergamaschi D,
et al: ASPP proteins specifically stimulate the apoptotic function
of p53. Mol Cell. 8:781–794. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Laska MJ, Vogel UB, Jensen UB and Nexø BA:
p53 and PPP1R13L (alias iASPP or RAI) form a feedback loop to
regulate genotoxic stress responses. Biochim Biophys Acta.
1800:1231–1240. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Murray-Zmijewski F, Lane DP and Bourdon
JC: p53/p63/p73 isoforms: an orchestra of isoforms to harmonise
cell differentiation and response to stress. Cell Death Differ.
13:962–972. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Cai Y, Qiu S, Gao X, Gu SZ and Liu ZJ:
iASPP inhibits p53-independent apoptosis by inhibiting
transcriptional activity of p63/p73 on promoters of proapoptotic
genes. Apoptosis. 17:777–783. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Yang JP, Hori M, Sanda T and Okamoto T:
Identification of a novel inhibitor of nuclear factor-kappaB,
RelA-associated inhibitor. J Biol Chem. 274:15662–15670. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Notari M, Hu Y, Koch S, et al: Inhibitor
of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 (iASPP) prevents senescence
and is required for epithelial stratification. Proc Natl Acad Sci
USA. 108:16645–16650. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, O’Neil NJ, et
al: iASPP oncoprotein is a key inhibitor of p53 conserved from worm
to human. Nat Genet. 33:162–167. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Wang C, Gao CF, Chen Y, Yin J, Wang P and
Lv X: Expression pattern of the apoptosis-stimulating protein of
p53 family in p53+ human breast cancer cell lines.
Cancer Cell Int. 13:1162013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
10
|
Liu ZJ, Zhang Y, Zhang XB and Yang X:
Abnormal mRNA expression of ASPP members in leukemia cell lines.
Leukemia. 18:8802004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Chen J, Xie F, Zhang L and Jiang WG: iASPP
is over-expressed in human non-small cell lung cancer and regulates
the proliferation of lung cancer cells through a p53 associated
pathway. BMC Cancer. 10:6942010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Lu B, Guo H, Zhao J, et al: Increased
expression of iASPP, regulated by hepatitis B virus X
protein-mediated NF-κB activation, in hepatocellular carcinoma.
Gastroenterology. 139:2183–2194. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Meng WD, Chu RX, Wang BZ, et al:
Helicobacter pylori infection and expressions of apoptosis-related
proteins p53, ASPP2 and iASPP in gastric cancer and precancerous
lesions. Pathol Biol (Paris). 61:199–202. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Yokozaki H: Molecular characteristics of
eight gastric cancer cell lines established in Japan. Pathol Int.
50:767–777. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Xue Z, Yan H, Li J, et al: Identification
of cancer stem cells in vincristine preconditioned SGC7901 gastric
cancer cell line. J Cell Biochem. 113:302–312. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li GL, Wang RZ, Gao J, et al: RNA
interference-mediated silencing of iASPP induces cell proliferation
inhibition and G0/G1 cell cycle arrest in U251 human glioblastoma
cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 350:193–200. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
17
|
Zhang B, Xiao HJ, Chen J, Tao X and Cai
LH: Inhibitory member of the apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53
(ASPP) family promotes growth and tumorigenesis in human
p53-deficient prostate cancer cells. Prostate Cancer Prostatic Dis.
14:219–224. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Lin BL, Xie DY, Xie SB, Xie JQ, Zhang XH,
Zhang YF and Gao ZL: Down-regulation of iASPP in human
hepatocellular carcinoma cells inhibits cell proliferation and
tumor growth. Neoplasma. 58:205–210. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Liu ZJ, Cai Y, Hou L, et al: Effect of RNA
interference of iASPP on the apoptosis in MCF-7 breast cancer
cells. Cancer Invest. 26:878–882. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carmeliet P and Jain RK: Angiogenesis in
cancer and other diseases. Nature. 407:249–257. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Lu X: p53: a heavily dictated dictator of
life and death. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 15:27–33. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Suzuki K and Matsubara H: Recent advances
in p53 research and cancer treatment. J Biomed Biotechnol.
2011:9783122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Patel S, George R, Autore F, Fraternali F,
Ladbury JE and Nikolova PV: Molecular interactions of ASPP1 and
ASPP2 with the p53 protein family and the apoptotic promoters PUMA
and Bax. Nucleic Acids Res. 36:5139–5151. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Bergamaschi D, Samuels Y, Jin B,
Duraisingham S, Crook T and Lu X: ASPP1 and ASPP2: common
activators of p53 family members. Mol Cell Biol. 24:1341–1350.
2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|