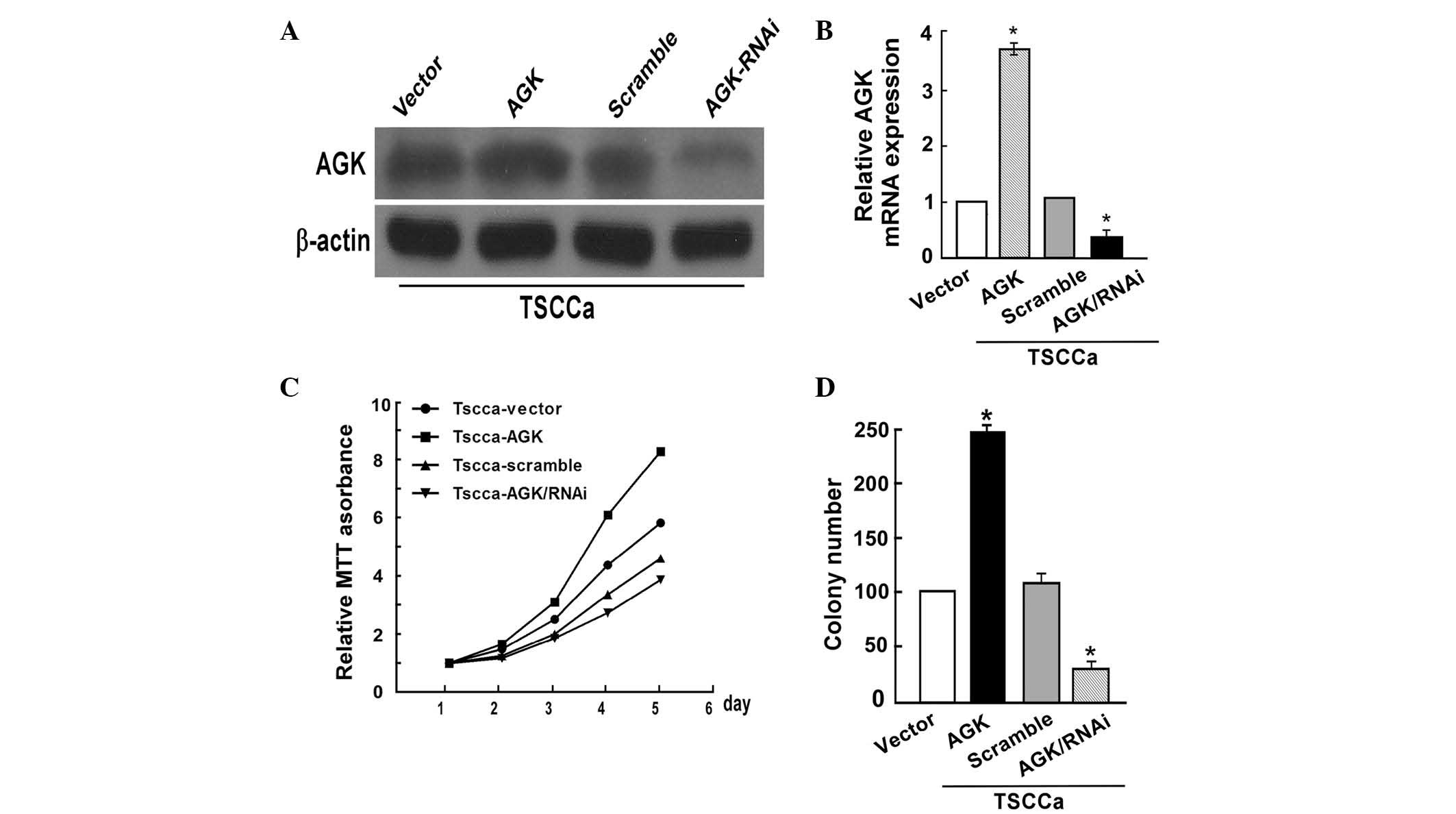
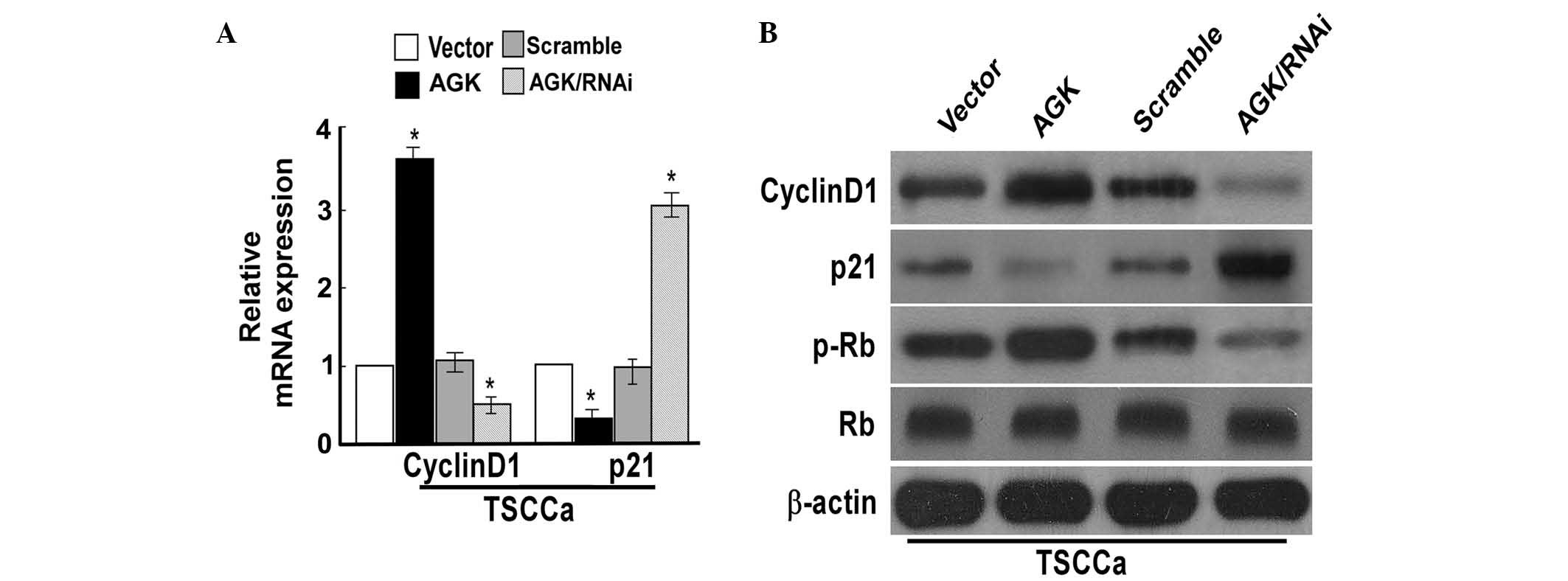
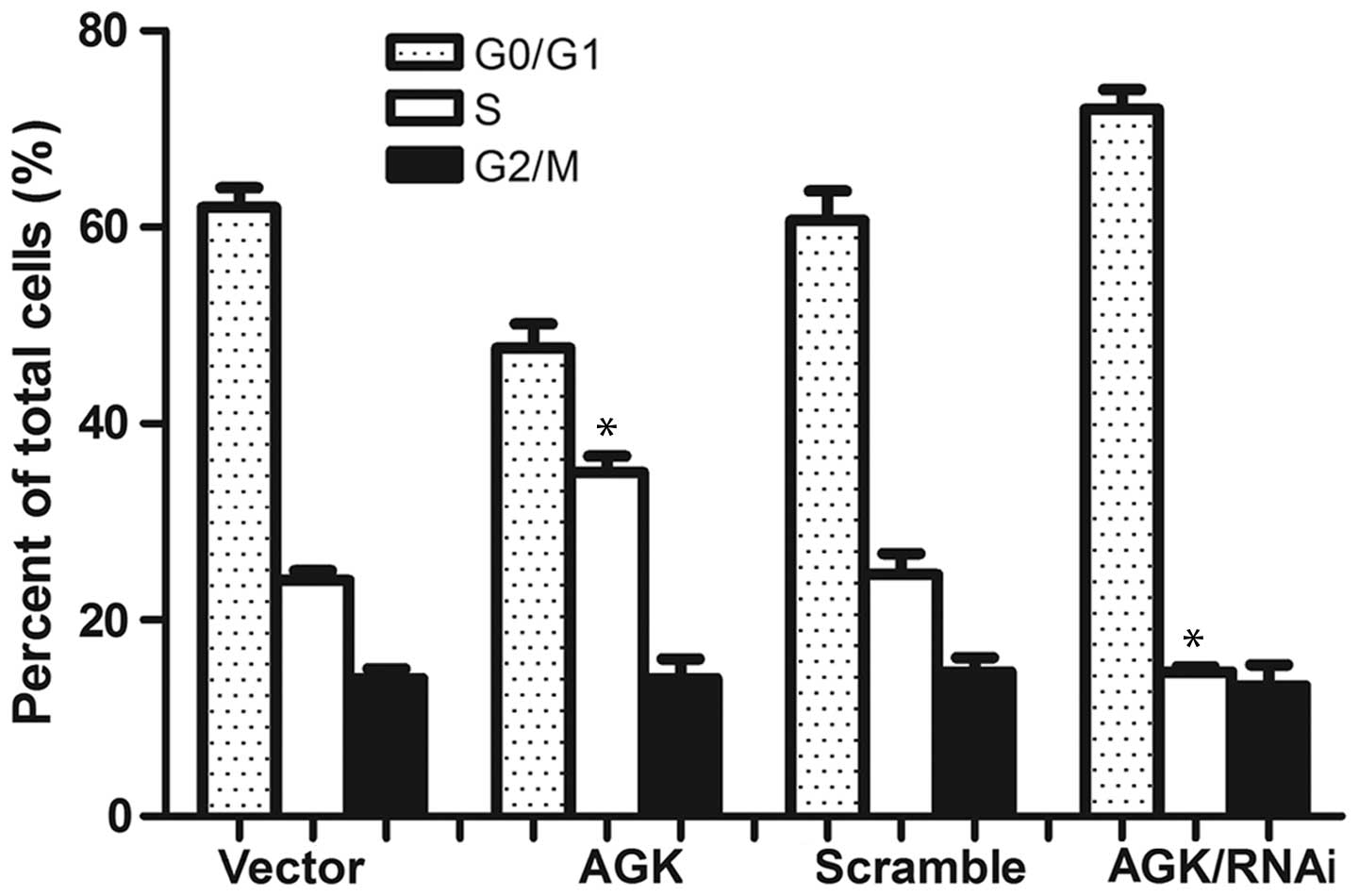
|
1
|
Jiang Q, Yu YC, Ding XJ, Luo Y and Ruan H:
Bioinformatics analysis reveals significant genes and pathways to
target for oral squamous cell carcinoma. Asian Pac J Cancer Prev.
15:2273–2278. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Rigual NR, Shafirstein G, Frustino J, et
al: Adjuvant intraoperative photodynamic therapy in head and neck
cancer. JAMA Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 139:706–711. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Epand RM, Shulga YV, Timmons HC, et al:
Substrate chirality and specificity of diacylglycerol kinases and
the multisubstrate lipid kinase. Biochemistry. 46:14225–14231.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Bektas M, Payne SG, Liu H, Goparaju S,
Milstien S and Spiegel S: A novel acylglycerol kinase that produces
lysophosphatidic acid modulates cross talk with EGFR in prostate
cancer cells. J Cell Biol. 169:801–811. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Spiegel S and Milstien S: Critical role of
acylglycerol kinase in epidermal growth factor-induced mitogenesis
of prostate cancer cells. Biochem Soc Trans. 33:1362–1365. 2005.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sherr CJ and Roberts JM: CDK inhibitors:
Positive and negative regulators of G1-phase progression. Genes
Dev. 13:1501–1512. 1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yong ST and Wang XF: A novel,
non-apoptotic role for Scythe/BAT3: A functional switch between the
pro- and anti-proliferative roles of p21 during the cell cycle.
PLoS One. 7:e380852012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Hong S, Li X, Zhao Y, Yang Q and Kong B:
53BP1 suppresses tumor growth and promotes susceptibility to
apoptosis of ovarian cancer cells through modulation of the Akt
pathway. Oncol Rep. 27:1251–1257. 2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Weinberg RA: The retinoblastoma protein
and cell cycle control. Cell. 81:323–330. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Wang X, Lin C, Zhao X, et al: Acylglycerol
kinase promotes cell proliferation and tumorigenicity in breast
cancer via suppression of the FOXO1 transcription factor. Mol
Cancer. 13:1062014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Cui Y, Lin C, Wu Z, et al: AGK enhances
angiogenesis and inhibits apoptosis via activation of the NF-κB
signaling pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncotarget.
5:12057–12069. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Chen X, Ying Z, Lin X, et al: Acylglycerol
kinase augments JAK2/STAT3 signaling in esophageal squamous cells.
J Clin Invest. 123:2576–2589. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Nouh MA, Wu XX, Okazoe H, et al:
Expression of autotaxin and acylglycerol kinase in prostate cancer:
Association with cancer development and progression. Cancer Sci.
100:1631–1638. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Knudsen KE, Diehl JA, Haiman CA and
Knudsen ES: Cyclin D1: polymorphism, aberrant splicing and cancer
risk. Oncogene. 25:1620–1628. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Bali A, O’Brien PM, Edwards LS, Sutherland
RL, Hacker NF and Henshall SM: Cyclin D1, p53 and p21Waf1/Cip1
expression is predictive of poor clinical outcome in serous
epithelial ovarian cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 10:5168–5177. 2004.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Ratschiller D, Heighway J, Gugger M, et
al: Cyclin D1 overexpression in bronchial epithelia of patients
with lung cancer is associated with smoking and predicts survival.
J Clin Oncol. 21:2085–2093. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Comstock CE, Augello MA, Goodwin JF, et
al: Targeting cell cycle and hormone receptor pathways in cancer.
Oncogene. 32:5481–5491. 2013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Baldin V, Lukas J, Marcote MJ, Pagano M
and Draetta G: Cyclin D1 is a nuclear protein required for cell
cycle progression in G1. Genes Dev. 7:812–821. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Motokura T and Arnold A: Cyclin D and
oncogenesis. Curr Opin Genet Dev. 3:5–10. 1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Carlos de Vicente J, Herrero-Zapatero A,
Fresno MF and Lόpez-Arranz JS: Expression of cyclin D1 and Ki-67 in
squamous cell carcinoma of the oral cavity: clinicopathological and
prognostic significance. Oral Oncol. 38:301–308. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Masamha CP and Benbrook DM: Cyclin D1
degradation is sufficient to induce G1 cell cycle arrest despite
constitutive expression of cyclin E2 in ovarian cancer cells.
Cancer Res. 69:6565–6572. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Seo JH, Jeong ES and Choi YK: Therapeutic
effects of lentivirus-mediated shRNA targeting of cyclin D1 in
human gastric cancer. BMC Cancer. 14:1752014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Wu J, Zhong D, Fu X, Liu Q, Kang L and
Ding Z: Silencing of Ether à go-go 1 by shRNA inhibits osteosarcoma
growth and cell cycle progression. Int J Mol Sci. 15:5570–5581.
2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Li W, Sun S, Chen Y, Yu H, Chen ZY and Li
H: Disrupting the interaction between retinoblastoma protein and
Raf-1 leads to defects in progenitor cell proliferation and
survival during early inner ear development. PLoS One.
8:e837262013. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Xu C, Wu C, Xia Y, et al: WT1 promotes
cell proliferation in non-small cell lung cancer cell lines through
up-regulating cyclin D1 and p-pRb in vitro and in vivo. PLoS One.
8:e688372013. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Nojiri S and Joh T: Albumin suppresses
human hepatocellular carcinoma proliferation and the cell cycle.
Int J Mol Sci. 15:5163–5174. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Rego MA, Harney JA, Mauro M, Shen M and
Howlett NG: Regulation of the activation of the Fanconi anemia
pathway by the p21 cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor. Oncogene.
31:366–375. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|