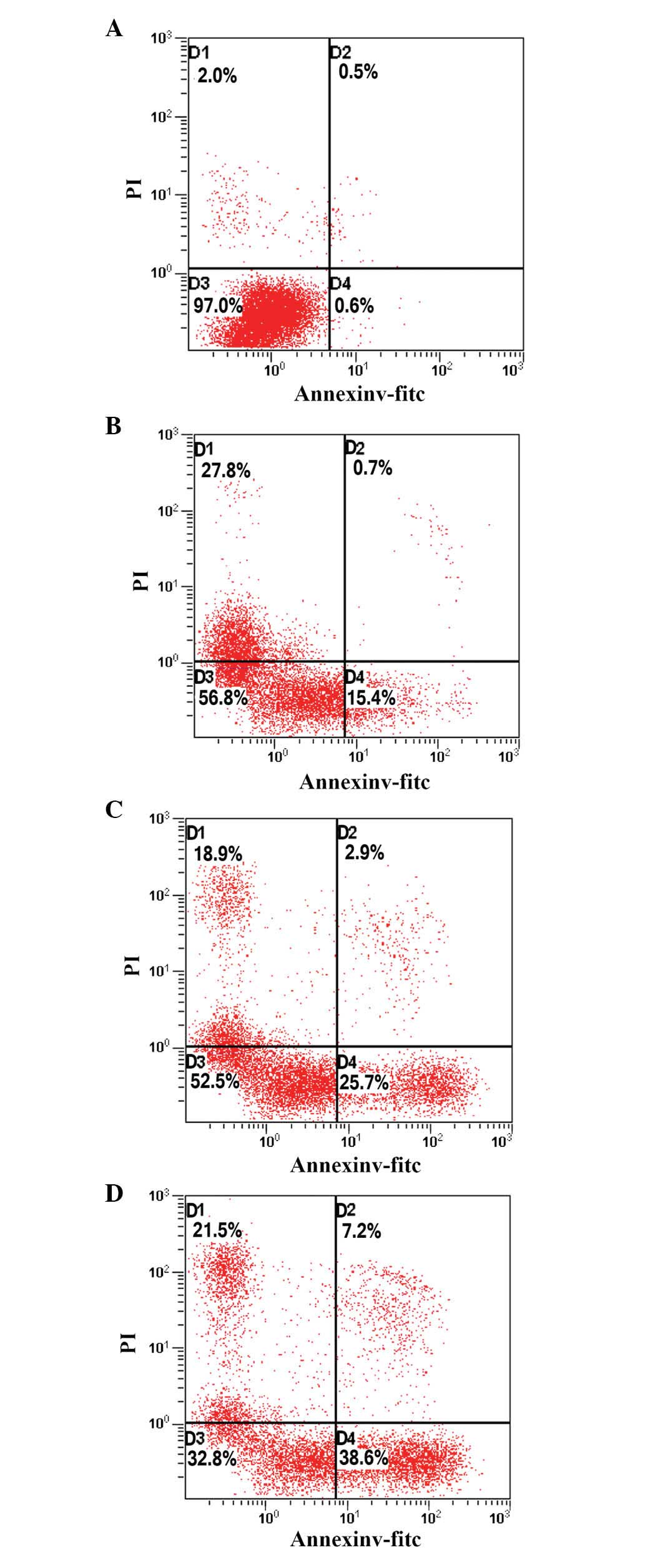
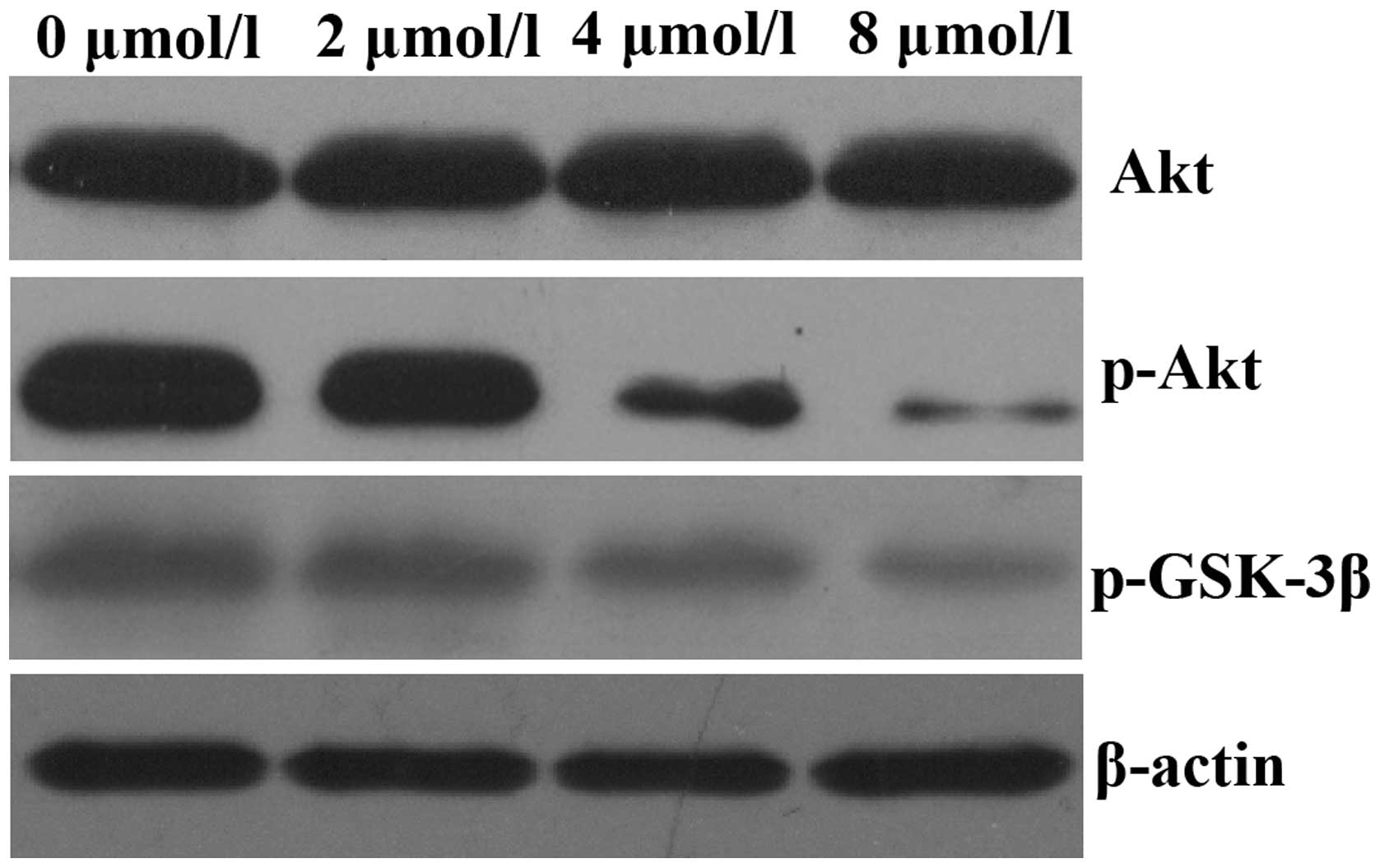
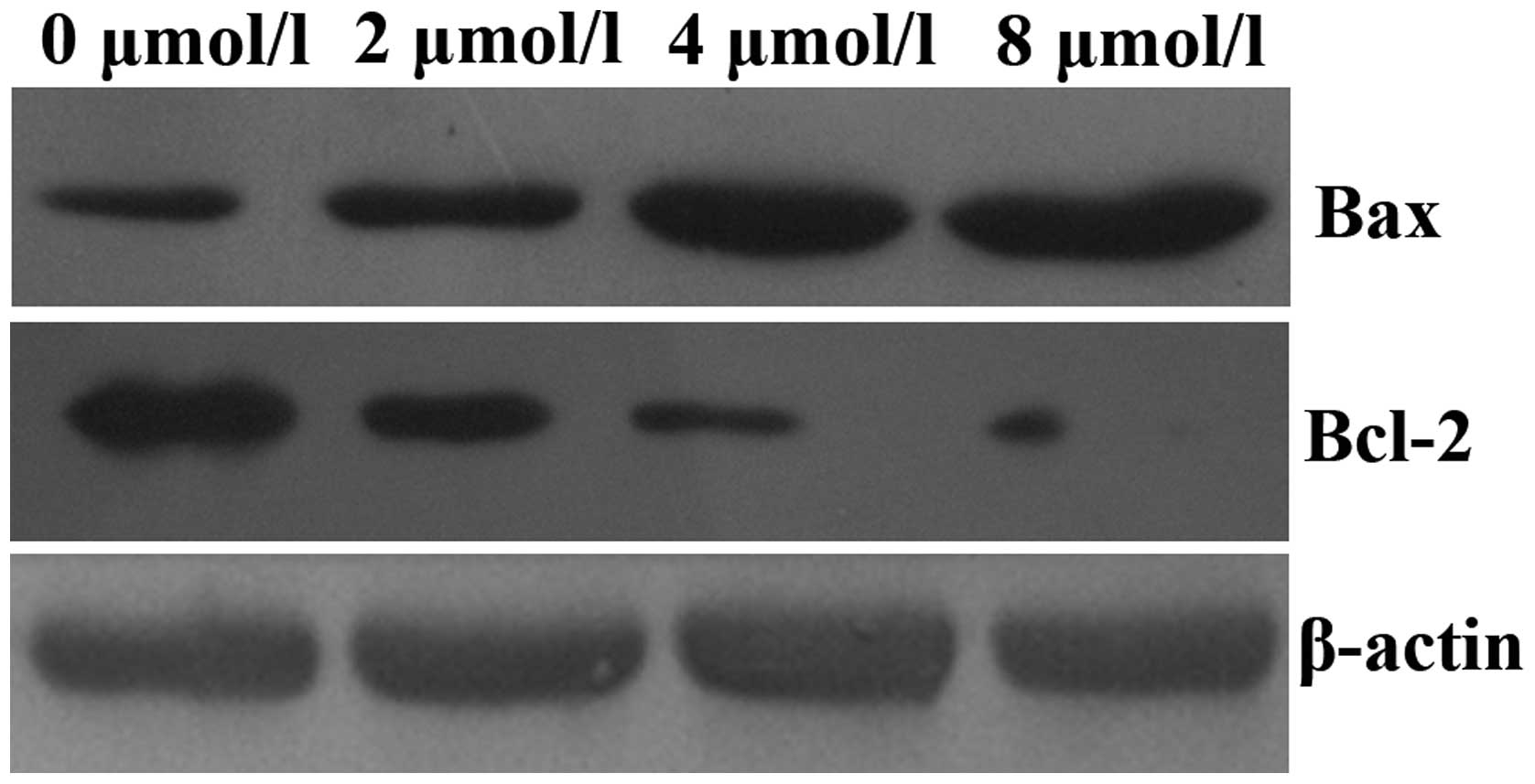
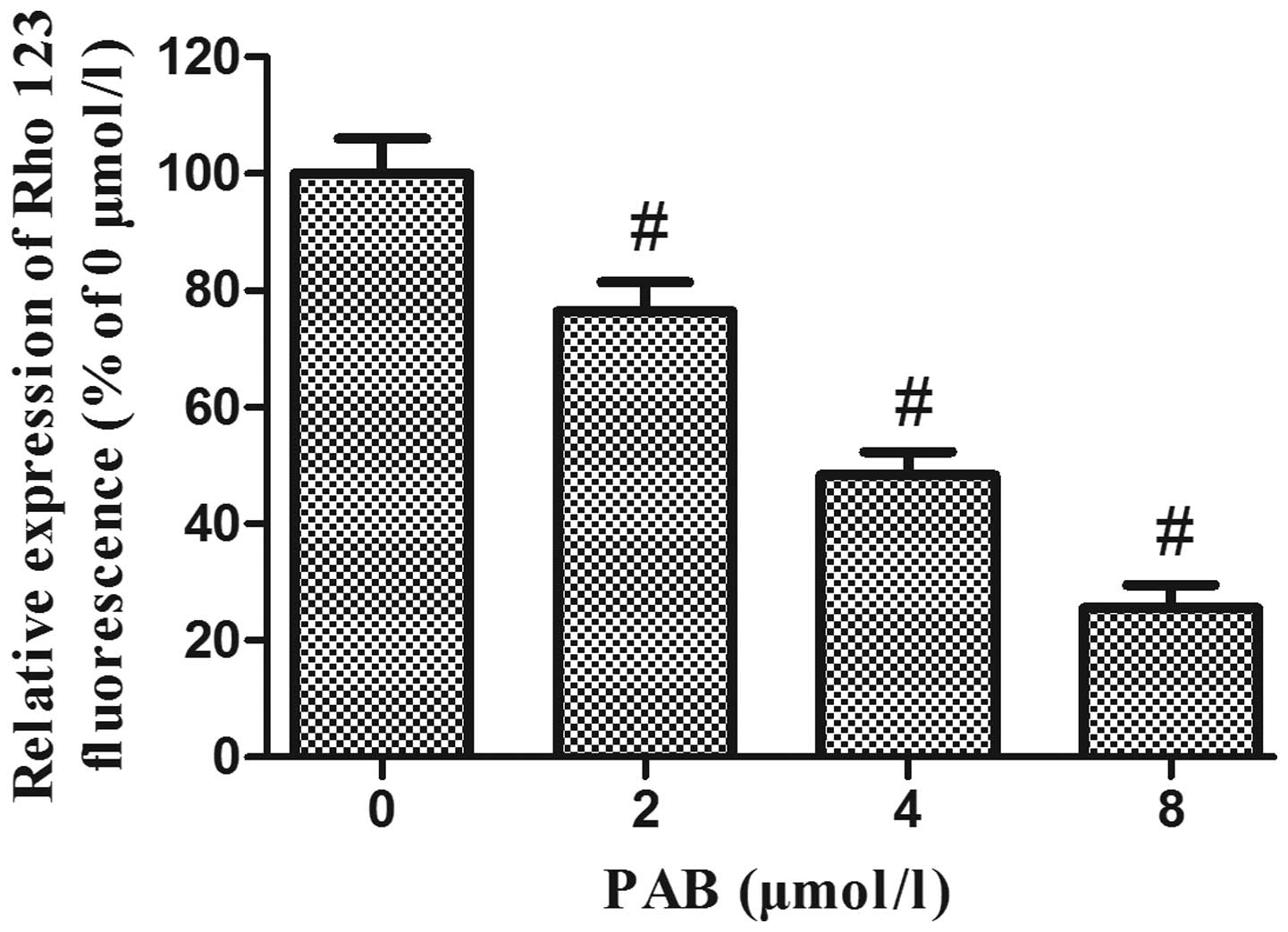
|
1
|
Jemal A, Bray F, Center MM, Ferlay J, Ward
E and Forman D: Global cancer statistics. CA Cancer J Clin.
61:69–90. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Tewari KS, Sill MW, Long HJ III, et al:
Improved survival with bevacizumab in advanced cervical cancer. N
Engl J Med. 370:734–743. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Yan Z, Hua H, Xu Y and Samaranayake LP:
Potent antifungal activity of pure compounds from Traditional
Chinese Medicine extracts against six oral Candida species and the
synergy with fluconazole against azole-resistant Candida albicans.
Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2012:1065832012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Zhang J, Yan LT, Yuan EL, et al:
Antifungal activity of compounds extracted from cortex
Pseudolaricis against Colletotrichum gloeosporioides. J Agric Food
Chem. 62:4905–4910. 2014. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Chiu P, Leung LT and Ko BC: Pseudolaric
acids: isolation, bioactivity and synthetic studies. Nat Prod Rep.
27:1066–1083. 2010. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Sarkar T, Nguyen TL, Su ZW, et al:
Interaction of pseudolaric acid B with the colchicine site of
tubulin. Biochem Pharmacol. 84:444–450. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
7
|
Yu B, Yue DM, Shu LH, Li NJ and Wang JH:
Pseudolaric acid B induces caspase-dependent cell death in human
ovarian cancer cells. Oncol Rep. 31:849–857. 2014.
|
|
8
|
Miao ZH, Feng JM and Ding J: Newly
discovered angiogenesis inhibitors and their mechanisms of action.
Acta Pharmacol Sin. 33:1103–1111. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Guan T and Yang Y: Role of pseudolaric
acid B in A549 lung cancer cell proliferation and apoptosis. Mol
Med Rep. 9:144–148. 2014.
|
|
10
|
Ma G, Chong L, Li XC, Khan IA, Walker LA
and Khan SI: Selective inhibition of human leukemia cell growth and
induction of cell cycle arrest and apoptosis by pseudolaric acid B.
J Cancer Res Clin Oncol. 136:1333–1340. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Tong J, Yin S, Dong Y, Guo X, Fan L, Ye M
and Hu H: Pseudolaric acid B induces caspase-dependent apoptosis
and autophagic cell death in prostate cancer cells. Phytother Res.
27:885–891. 2013. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
12
|
Brazil DP, Yang ZZ and Hemmings BA:
Advances in protein kinase B signalling: AKTion on multiple fronts.
Trends Biochem Sci. 29:233–242. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Manning BD and Cantley LC: AKT/PKB
signaling: navigating downstream. Cell. 129:1261–1274. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Vivanco I and Sawyers CL: The
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase AKT pathway in human cancer. Nat Rev
Cancer. 2:489–501. 2002. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Huang B, Meng N, Zhao B, Zhao J, Zhang Y,
Zhang S and Miao J: Protective effects of a synthesized
butyrolactone derivative against chloroquine-induced autophagic
vesicle accumulation and the disturbance of mitochondrial membrane
potential and Na+, K+-ATPase activity in vascular endothelial
cells. Chem Res Toxicol. 22:471–475. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Galluzzi L, Vitale I, Abrams JM, et al:
Molecular definitions of cell death subroutines: Recommendations of
the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2012. Cell Death Differ.
19:107–120. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
17
|
Vandenabeele P, Galluzzi L, Vanden Berghe
T and Kroemer G: Molecular mechanisms of necroptosis: An ordered
cellular explosion. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 11:700–714. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Ferlay J, Shin HR, Bray F, Forman D,
Mathers C and Parkin DM: Estimates of worldwide burden of cancer in
2008: GLOBOCAN 2008. Int J Cancer. 127:2893–2917. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Green JA, Kirwan JM, Tierney JF, Symonds
P, Fresco L, Collingwood M and Williams CJ: Survival and recurrence
after concomitant chemotherapy and radiotherapy for cancer of the
uterine cervix: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet.
358:781–786. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Rogers L, Siu SS, Luesley D, Bryant A and
Dickinson HO: Radiotherapy and chemoradiation after surgery for
early cervical cancer. Cochrane Database Syst Rev.
5:CD0075832012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Tang D, Lotze MT, Kang R and Zeh HJ:
Apoptosis promotes early tumorigenesis. Oncogene. 30:1851–1854.
2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
22
|
Youle RJ and Strasser A: The BCL-2 protein
family: opposing activities that mediate cell death. Nat Rev Mol
Cell Biol. 9:47–59. 2008. View
Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Coffer PJ, Jin J and Woodgett JR: Protein
kinase B (c-Akt): a multifunctional mediator of
phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase activation. Biochem J. 335:1–13.
1998.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Wang Z, Yang J, Fisher T, Xiao H, Jiang Y
and Yang C: Akt activation is responsible for enhanced migratory
and invasive behavior of arsenic-transformed human bronchial
epithelial cells. Environ Health Perspect. 120:92–97. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
25
|
Mosca E, Barcella M, Alfieri R, Bevilacqua
A, Canti G and Milanesi L: Systems biology of the metabolic network
regulated by the Akt pathway. Biotechnol Adv. 30:131–141. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
26
|
Wang R, Cong WH, Guo G, Li XX, Chen XL, Yu
XN and Li H: Synergism between carnosic acid and arsenic trioxide
on induction of acute myeloid leukemia cell apoptosis is associated
with modulation of PTEN/Akt signaling pathway. Chin J Integr Med.
18:934–941. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Lindsley CW: The Akt/PKB family of protein
kinases: a review of small molecule inhibitors and progress towards
target validation: a 2009 update. Curr Top Med Chem. 10:458–477.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Oki E, Baba H, Tokunaga E, et al: Akt
phosphorylation associates with LOH of PTEN and leads to
chemoresistance for gastric cancer. Int J Cancer. 117:376–380.
2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Song L, Xiong H, Li J, et al: Sphingosine
kinase-1 enhances resistance to apoptosis through activation of
PI3K/Akt/NF-κB pathway in human non-small cell lung cancer. Clin
Cancer Res. 17:1839–1849. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|