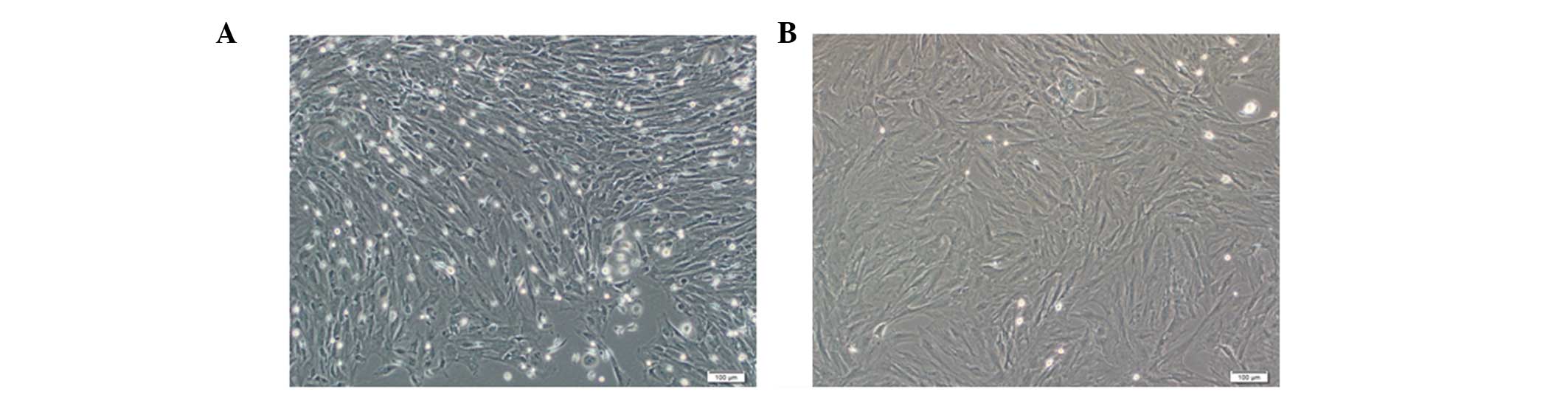
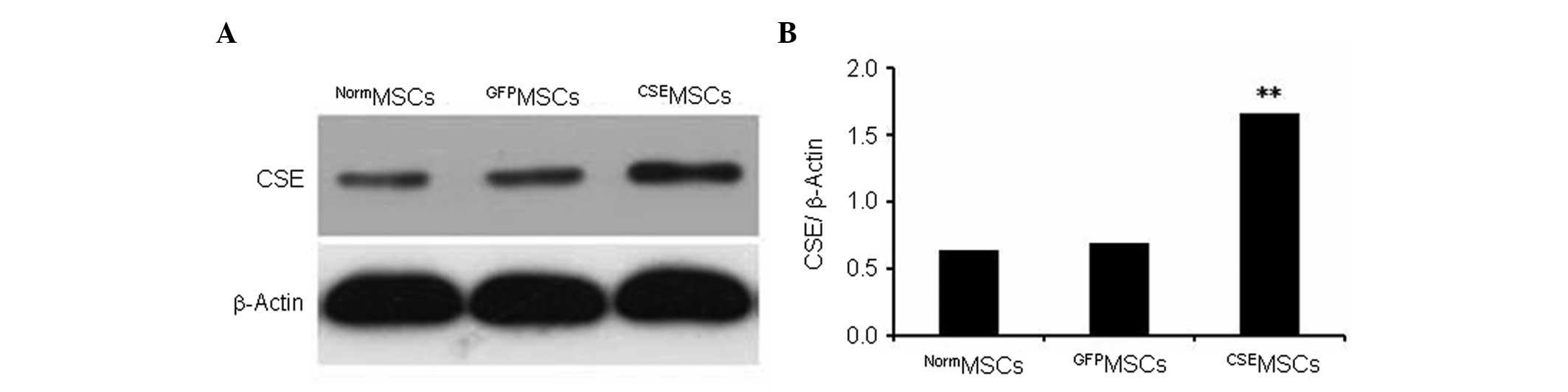
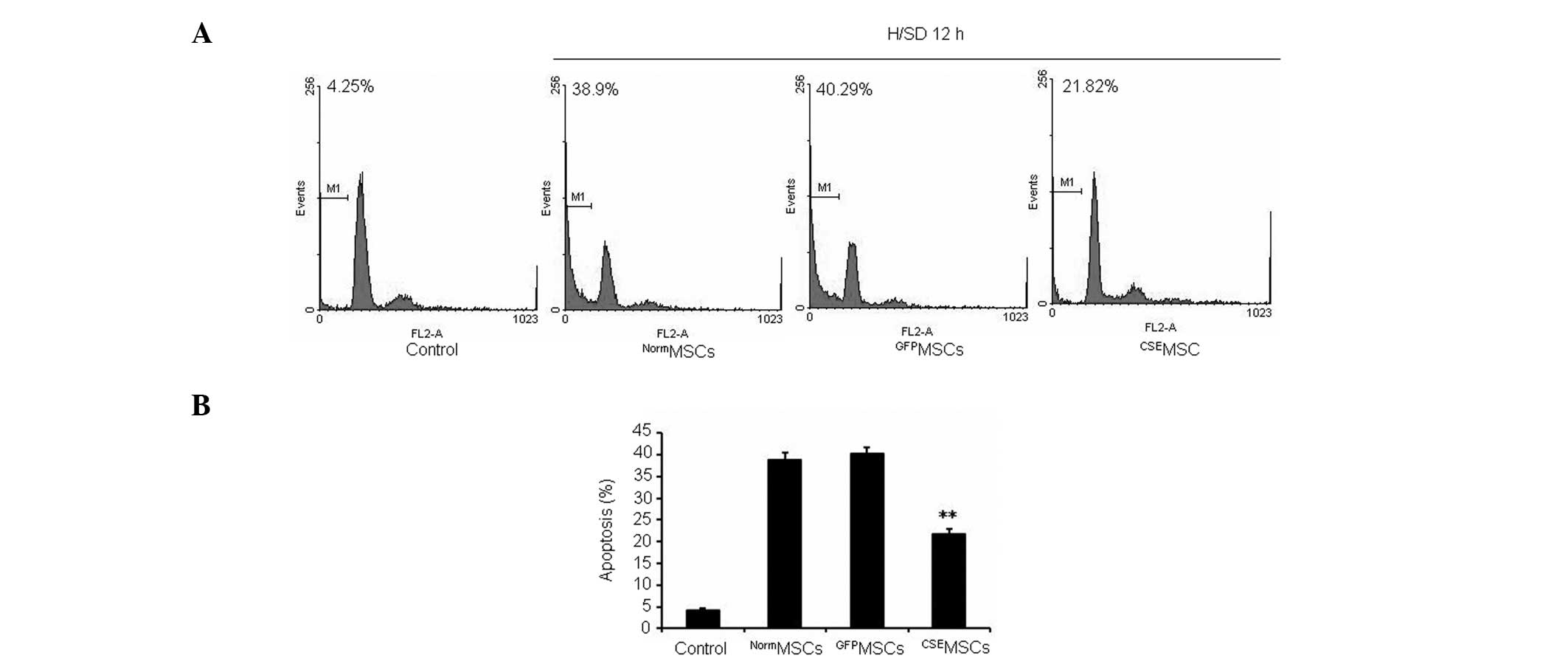
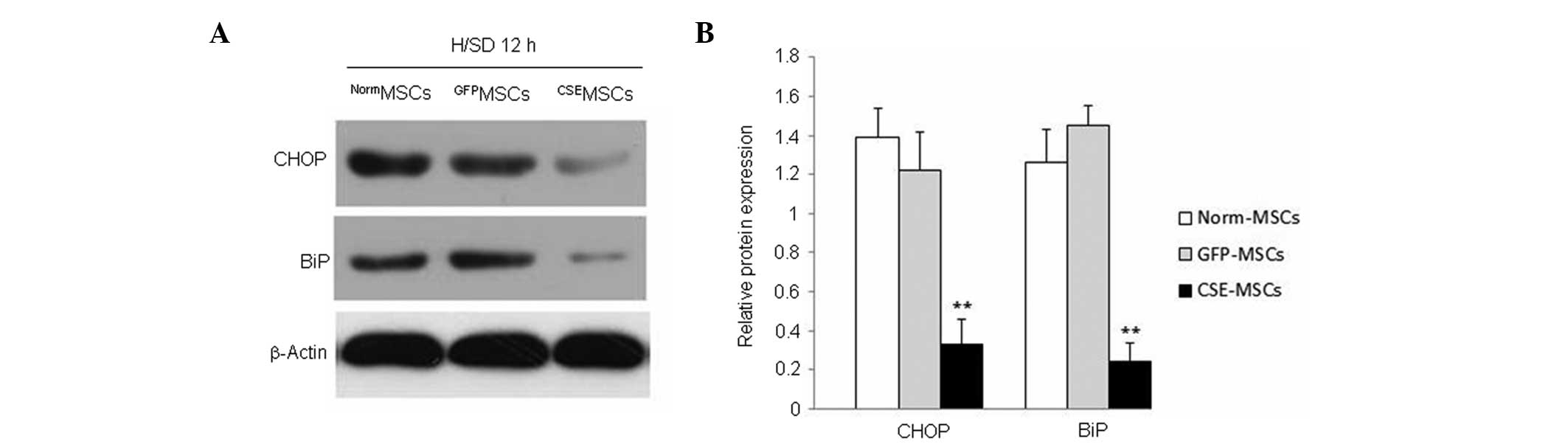
|
1
|
Miyahara Y, Nagaya N, Kataoka M, et al:
Monolayered mesenchymal stem cells repair scarred myocardium after
myocardial infarction. Nat Med. 12:459–465. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Mathur A and Martin JF: Stem cells and
repair of the heart. Lancet. 364:183–192. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Amado LC, Saliaris AP, Schuleri KH, et al:
Cardiac repair with intramyocardial injection of allogeneic
mesenchymal stem cells after myocardial infarction. Proc Natl Acad
Sci USA. 102:11474–11479. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Gyongyosi M, Lang I, Dettke M, et al:
Combined delivery approach of bone marrow mononuclear stem cells
early and late after myocardial infarction: the MYSTAR prospective,
randomized study. Nat Clin Pract Cardiovasc Med. 6:70–81. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
5
|
Zhang M, Methot D, Poppa V, Fujio Y, Walsh
K and Murry CE: Cardiomyocyte grafting for cardiac repair: graft
cell death and anti-death strategies. J Mol Cell Cardiol.
33:907–921. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Calvert JW, Coetzee WA and Lefer DJ: Novel
insights into hydrogen sulfide-mediated cytoprotection. Antioxid
Redox Signal. 12:1203–1217
|
|
7
|
Dong XB, Yang CT, Zheng DD, et al:
Inhibition of ROS-activated ERK1/2 pathway contributes to the
protection of H2S against chemical hypoxia-induced
injury in H9c2 cells. Mol Cell Biochem. 362:149–157. 2012.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
8
|
Biermann J, Lagrèze WA, Schallner N,
Schwer CI and Goebel U: Inhalative preconditioning with hydrogen
sulfide attenuated apoptosis after retinal ischemia/reperfusion
injury. Mol Vis. 17:1275–1286. 2011.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Taniguchi S, Kang L, Kimura T and Niki I:
Hydrogen sulphide protects mouse pancreatic β-cells from cell death
induced by oxidative stress, but not by endoplasmic reticulum
stress. Br J Pharmacol. 162:1171–1178. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
10
|
Sivarajah A, Collino M, Yasin M, et al:
Anti-apoptotic and anti-inflammatory effects of hydrogen sulfide in
a rat model of regional myocardial I/R. Shock. 31:267–274. 2009.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
11
|
Li C, Guo Z and Guo B: Inhibition of
endogenous CSE/H2S system contributes to hypoxia and
serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells. Mol
Med Rep. 9:2467–2472. 2014.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Wang A, Shen F, Liang Y and Wang J:
Marrow-derived MSCs and atorvastatin improve cardiac function in
rat model of AMI. Int J Cardiol. 150:28–32. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
13
|
Zhu W, Chen J, Cong X, Hu S and Chen X:
Hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem
cells. Stem Cells. 24:416–425. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
14
|
Ferri KF and Kroemer G: Organelle-specific
initiation of cell death pathways. Nat Cell Biol. 3:E255–E263.
2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Oyadomari S and Mori M: Roles of
CHOP/GADD153 in endoplasmic reticulum stress. Cell Death Differ.
11:381–389. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Li Z, Wei H, Liu X, Hu S, Cong X and Chen
X: LPA rescues ER stress-associated apoptosis in hypoxia and serum
deprivation-stimulated mesenchymal stem cells. J Cell Biochem.
111:811–820. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Wei H, Li Z, Hu S, Chen X and Cong X:
Apoptosis of mesenchymal stem cells induced by hydrogen peroxide
concerns both endoplasmic reticulum stress and mitochondrial death
pathway through regulation of caspases, p38 and JNK. J Cell
Biochem. 111:967–978. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Harding HP and Ron D: Endoplasmic
reticulum stress and the development of diabetes: a review.
Diabetes. 51(Suppl 3): 455–461. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
19
|
Franke TF, Kaplan DR and Cantley LC: PI3K:
Downstream AKTion blocks apoptosis. Cell. 88:435–437. 1997.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Datta SR, Brunet A and Greenberg ME:
Cellular survival: A play in three Akts. Genes Dev. 13:2905–2927.
1999. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Liao Y and Hung MC: Regulation of the
activity of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase by Akt in cancer
and adenoviral protein E1A-mediated sensitization to apoptosis. Mol
Cell Biol. 23:6836–6848. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Chen J, Baydoun AR, Xu R, et al:
Lysophosphatidic acid protects mesenchymal stem cells against
hypoxia and serum deprivation-induced apoptosis. Stem Cells.
26:135–145. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
23
|
Dong Q, Yang Y, Song L, et al:
Atorvastatin prevents mesen-chymal stem cells from hypoxia and
serum-free injury through activating AMP-activated protein kinase.
Int J Cardiol. 153:311–316. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
24
|
Nie Y, Han BM, Liu XB, et al:
Identification of MicroRNAs involved in hypoxia- and serum
deprivation-induced apoptosis in mesenchymal stem cells. Int J Biol
Sci. 7:762–768. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
25
|
Gao F, Hu XY, Xie XJ, et al: Heat shock
protein 90 protects rat mesenchymal stem cells against hypoxia and
serum deprivation-induced apoptosis via the PI3K/Akt and ERK1/2
pathways. J Zhejiang Univ Sci B. 11:608–617. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
26
|
Wang R: Two’s company, three’s a crowd:
Can H2S be the third endogenous gaseous transmitter. FASEB J.
6:1792–1798. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
27
|
Yang C, Yang Z, Zhang M, et al: Hydrogen
sulfide protects against chemical hypoxia-induced cytotoxicity and
inflammation in HaCaT cells through inhibition of ROS/NF-κB/COX-2
pathway. PLoS One. 6:e219712011. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
28
|
Yao LL, Huang XW, Wang YG, Cao YX, Zhang
CC and Zhu YC: Hydrogen sulfide protects cardiomyocytes from
hypoxia/reoxygenation-induced apoptosis by preventing
GSK-3beta-dependent opening of mPTP. Am J Physiol Heart Circ
Physiol. 298:H1310–H1319. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Hu Y, Chen X, Pan TT, et al:
Cardioprotection induced by hydrogen sulfide preconditioning
involves activation of ERK and PI3K/Akt pathways. Pflugers Arch.
455:607–616. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
30
|
Elrod JW, Calvert JW, Morrison J, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide attenuates myocardial ischemia-reperfusion injury
by preservation of mitochondrial function. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA.
104:15560–15565. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Guan Q, Zhang Y, Yu C, Liu Y, Gao L and
Zhao J: Hydrogen sulfide protects against high-glucose-induced
apoptosis in endo-thelial cells. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol.
59:188–193. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
32
|
Xie X, Sun A, Zhu W, et al:
Transplantation of mesenchymal stem cells preconditioned with
hydrogen sulfide enhances repair of myocardial infarction in rats.
Tohoku J Exp Med. 226:29–36. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
33
|
Kumar S: Caspase function in programmed
cell death. Cell Death Differ. 14:32–43. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
34
|
Berridge MJ: The endoplasmic reticulum: a
multifunctional signaling organelle. Cell Calcium. 32:235–249.
2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
35
|
Wang XY, Yang CT, Zheng DD, et al:
Hydrogen sulfide protects H9c2 cells against doxorubicin-induced
cardiotoxicity through inhibition of endoplasmic reticulum stress.
Mol Cell Biochem. 363:419–426. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Mangi AA, Noiseux N, Kong D, et al:
Mesenchymal stem cells modified with Akt prevent remodeling and
restore performance of infarcted hearts. Nat Med. 9:1195–1201.
2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|