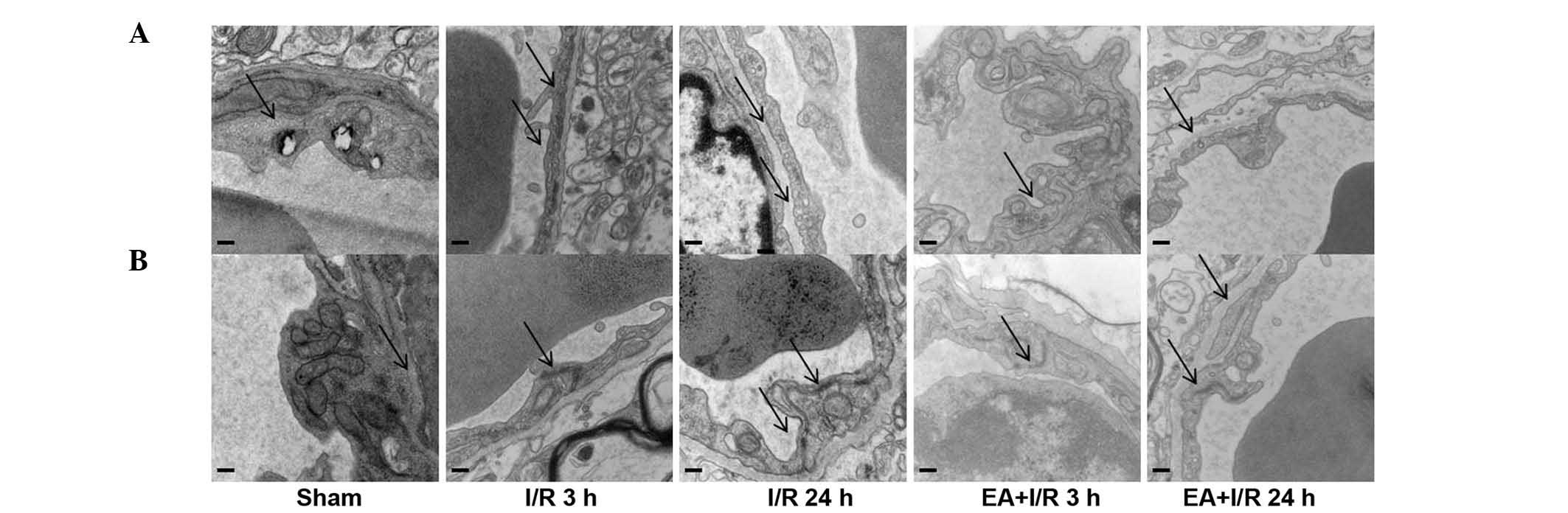
|
1
|
Lo EH, Dalkara T and Moskowitz MA:
Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev
Neurosci. 4:399–415. 2003. View
Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Jung JE, Kim GS, Chen H, et al:
Reperfusion and neurovascular dysfunction in stroke: from basic
mechanisms to potential strategies for neuroprotection. Mol
Neurobiol. 41:172–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Rubin LL and Staddon JM: The cell biology
of the blood-brain barrier. Annu Rev Neurosci. 22:11–28. 1999.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Saunders NR, Ek CJ, Habgood MD and
Dziegielewska KM: Barriers in the brain: a renaissance? Trends
Neurosci. 31:279–286. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Zlokovic BV: The blood-brain barrier in
health and chronic neurodegenerative disorders. Neuron. 57:178–201.
2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Wolburg H and Lippoldt A: Tight junctions
of the blood-brain barrier: development, composition and
regulation. Vascul Pharmacol. 38:323–337. 2002. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
7
|
Forster C: Tight junctions and the
modulation of barrier function in disease. Histochem Cell Biol.
130:55–70. 2008. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Liu W, Hendren J, Qin XJ, Shen J and Liu
KJ: Normobaric hyperoxia attenuates early blood-brain barrier
disruption by inhibiting MMP-9-mediated occludin degradation in
focal cerebral ischemia. J Neurochem. 108:811–820. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
ElAli A, Doeppner TR, Zechariah A and
Hermann DM: Increased blood-brain barrier permeability and brain
edema after focal cerebral ischemia induced by hyperlipidemia: role
of lipid peroxidation and calpain-1/2, matrix metalloproteinase-2/9
and RhoA overactivation. Stroke. 42:3238–3244. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Minshall RD, Sessa WC, Stan RV, Anderson
RG and Malik AB: Caveolin regulation of endothelial function. Am J
Physiol Lung Cell Mol Physiol. 285:L1179–L1183. 2003. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Jasmin JF, Malhotra S, Singh Dhallu M,
Mercier I, Rosenbaum DM and Lisanti MP: Caveolin-1 deficiency
increases cerebral ischemic injury. Circ Res. 100:721–729. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Li S, Seitz R and Lisanti MP:
Phosphorylation of caveolin by src tyrosine kinases. The
alpha-isoform of caveolin is selectively phosphorylated by v-Src. J
Biol Chem. 271:3863–3868. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lee H, Volonte D, Galbiati F, et al:
Constitutive and growth factor-regulated phosphorylation of
caveolin-1 occurs at the same site (Tyr-14) in vivo: Identification
of a c-Src/Cav-1/Grb7 signalling cassette. Mol Endocrinol.
14:1750–1775. 2000. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Labrecque L, Nyalendo C, Langlois S, et
al: Src-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation of caveolin-1 induces its
association with membrane type 1 matrix metalloproteinase. J Biol
Chem. 279:52132–52140. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Nag S, Manias JL and Stewart DJ:
Expression of endothelial phosphorylated caveolin-1 is increased in
brain injury. Neuropath Appl Neuro. 35:417–426. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
16
|
Chou P, Chu H and Lin JG: Effects of
electroacupuncture treatment on impaired cognition and quality of
life in Taiwanese stroke patients. J Altern Complement Med.
15:1067–1073. 2009.
|
|
17
|
Xiong L, Lu Z, Hou L, Zheng H, Zhu Z, Wang
Q and Chen S: Pretreatment with repeated electroacupuncture
attenuates transient focal cerebral ischemic injury in rats. Chin
Med J (Engl). 116:108–111. 2003.
|
|
18
|
Wang Q, Xiong L, Chen S, Liu Y and Zhu X:
Rapid tolerance to focal cerebral ischemia in rats is induced by
preconditioning with electroacupuncture: window of protection and
the role of adenosine. Neurosci Lett. 381:158–162. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Wang Q, Peng Y, Chen S, et al:
Pretreatment with electroacupuncture induces rapid tolerance to
focal cerebral ischemia through regulation of endocannabinoid
system. Stroke. 40:2157–2164. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
National Research Council (US) Committee
for the Update of the Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory
Animals: Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals. 8th
edition. National Academies Press (US); Washington, DC: 2011
|
|
21
|
Longa EZ, Weinstein PR, Carlson S and
Cummins R: Reversible middle cerebral artery occlusion without
craniectomy in rats. Stroke. 20:84–91. 1989. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Hu Q, Ma Q, Zhan Y, He Z, Tang J, Zhou C
and Zhang J: Isoflurane enhanced hemorrhagic transformation by
impairing antioxidant enzymes in hyperglycemic rats with middle
cerebral artery occlusion. Stroke. 42:1750–1756. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Tsubokawa T, Jadhav V, Solaroglu I,
Shiokawa Y, Konishi Y and Zhang JH: Lecithinized superoxide
dismutase improves outcomes and attenuates focal cerebral ischemic
injury via anti-apoptotic mechanisms in rats. Stroke. 38:1057–1062.
2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Swanson RA, Morton MT, Tsao-Wu GJ, Savalos
RA, Davidson C and Sharp FR: A semiautomated method for measuring
brain infarct volume. Cereb Blood Flow Metab. 10:290–293. 1990.
View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Zhang C: The brain-resuscitation
acupuncture method for treatment of post wind-stroke mental
depression - a report of 45 cases. J Tradit Chin Med. 25:243–246.
2005.
|
|
26
|
Zhang H, Zhao L, He CQ, Hu KM and Liu J:
Clinically multi-central randomized controlled study on scalp
electroacupuncture for treatment of vascular dementia. Zhongguo
Zhen Jiu. 28:783–787. 2008.In Chinese. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
Zhou Y, Zhou GY, Li SK and Jin J: Clinical
observation on the therapeutic effect of electroacupuncture
combined with cupping on post-stroke fatigue. Zhen Ci Yan Jiu.
35:380–383. 2010.In Chinese.
|
|
28
|
Jung JE, Kim GS, Chen H, et al:
Reperfusion and neurovascular dysfunction in stroke: from basic
mechanisms to potential strategies for neuroprotection. Mol
Neurobiol. 41:172–179. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Ballabh P, Braun A and Nedergaard M: The
blood-brain barrier: an overview: structure, regulation and
clinical implications. Neurobiol Dis. 16:1–13. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Bazzoni G and Dejana E: Endothelial
cell-to-cell junctions: molecular organization and role in vascular
homeostasis. Physiol Rev. 84:869–901. 2004. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Schubert W, Frank PG, Razani B, Park DS,
Chow CW and Lisanti MP: Caveolae-deficient endothelial cells show
defects in the uptake and transport of albumin in vivo. J Biol
Chem. 276:48619–48622. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Furuse M, Hirase T, Itoh M, Nagafuchi A,
Yonemura S and Tsukita S: Occludin: a novel integral membrane
protein localizing at tight junctions. J Cell Biol. 123:1777–1788.
1993. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Nitta T, Hata M, Gotoh S, et al:
Size-selective loosening of the blood-brain barrier in
claudin-5-deficient mice. J Cell Biol. 161:653–660. 2003.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Shen J, Ma S, Chan P, et al: Nitric oxide
down-regulates caveolin-1 expression in rat brains during focal
cerebral ischemia and reperfusion injury. J Neurochem.
96:1078–1089. 2006. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
35
|
Gu Y, Zheng G, Xu M, et al: Caveolin-1
regulates nitric oxide-mediated matrix metalloproteinases activity
and blood-brain barrier permeability in focal cerebral ischemia and
reperfusion injury. J Neurochem. 120:147–156. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
36
|
Huang P, Zhou CM, Qin Hu, et al:
Cerebralcare Granule attenuates blood-brain barrier disruption
after middle cerebral artery occlusion in rats. Exp Neurol.
237:453–463. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
37
|
Zhang S, Liu Y, Zhao Z and Xue Y: Effects
of green tea polyphenols on Caveolin-1 of microvessel fragments in
rats with cerebral ischemia. Neurol Res. 32:963–970. 2010.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|