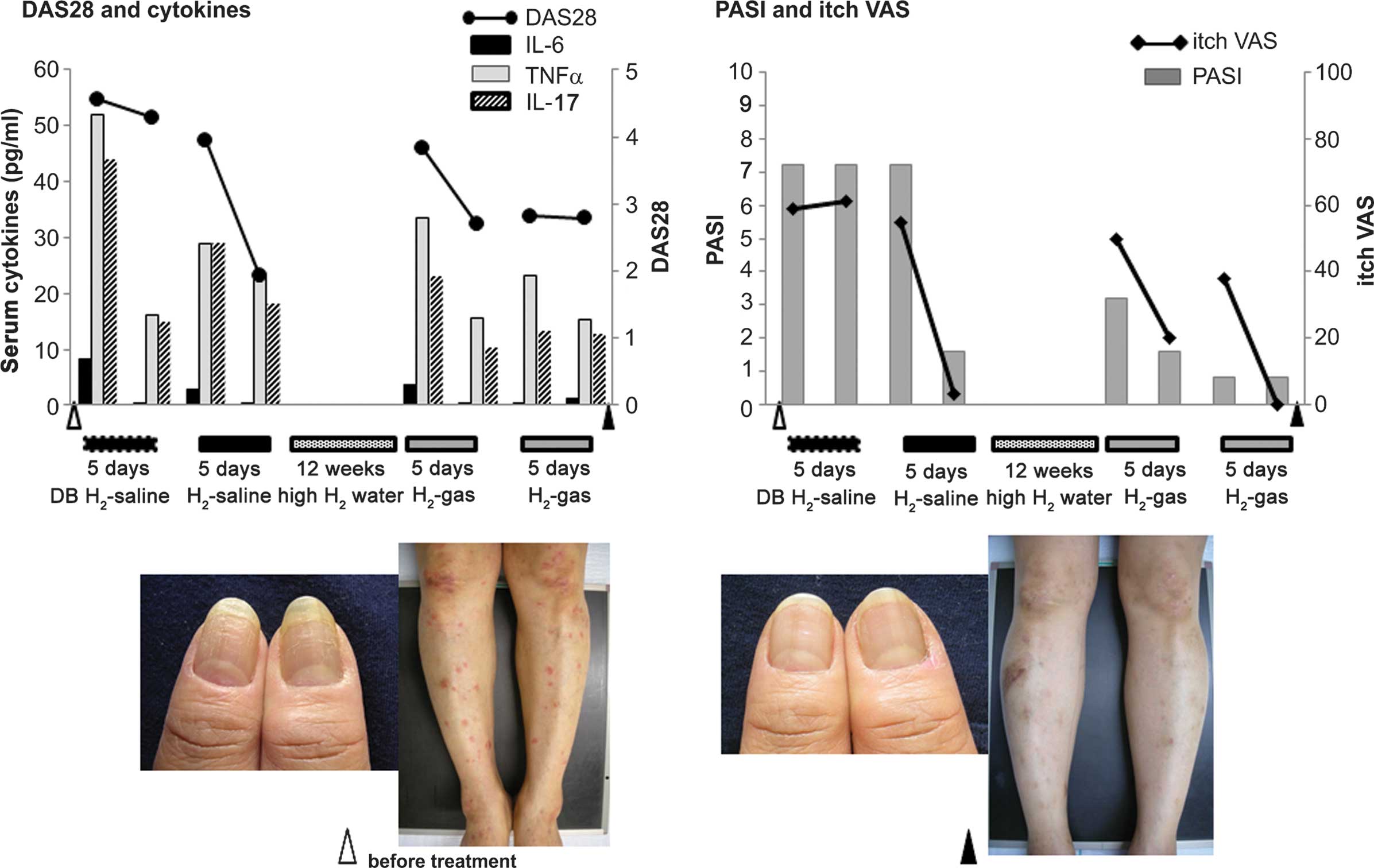
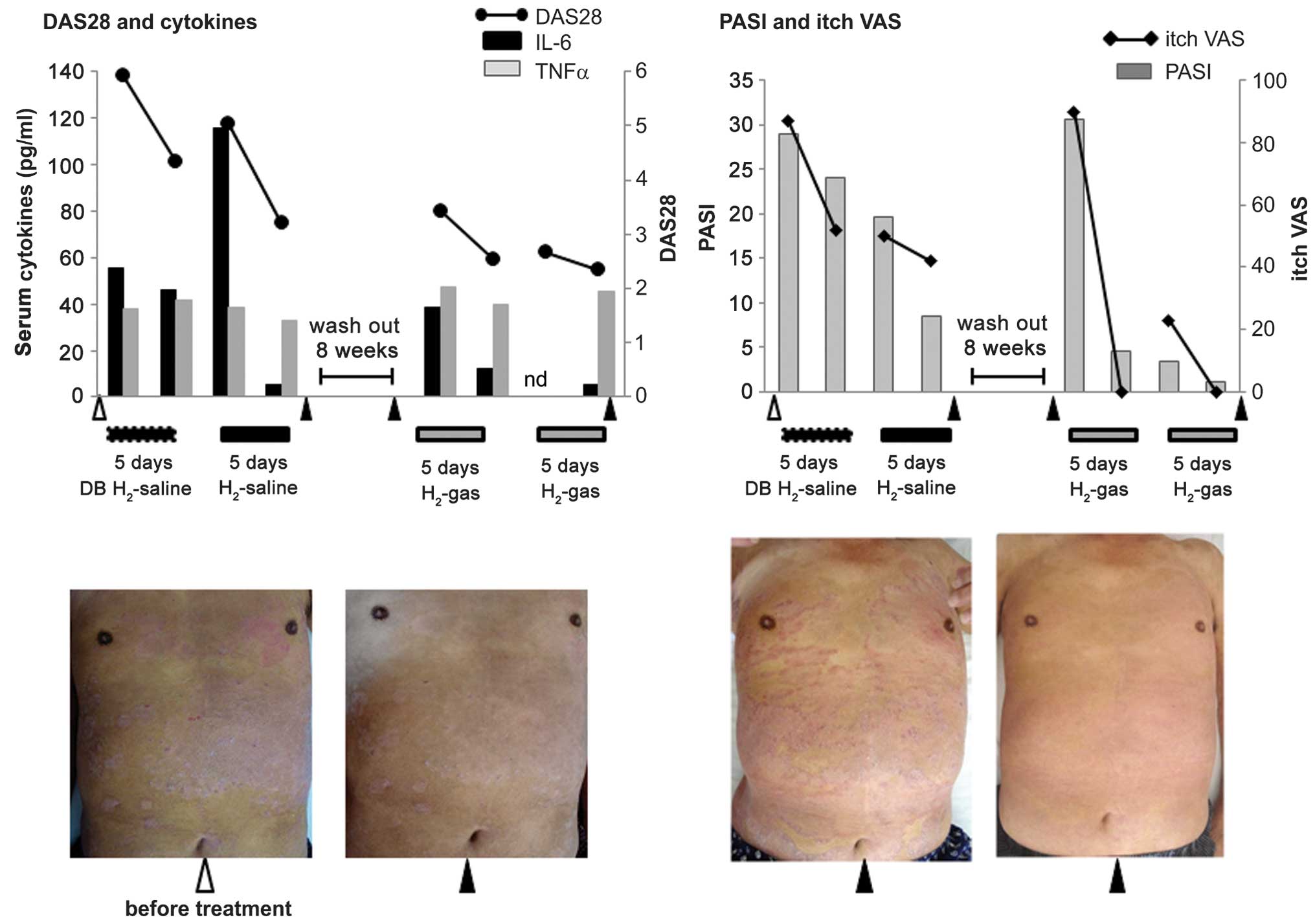
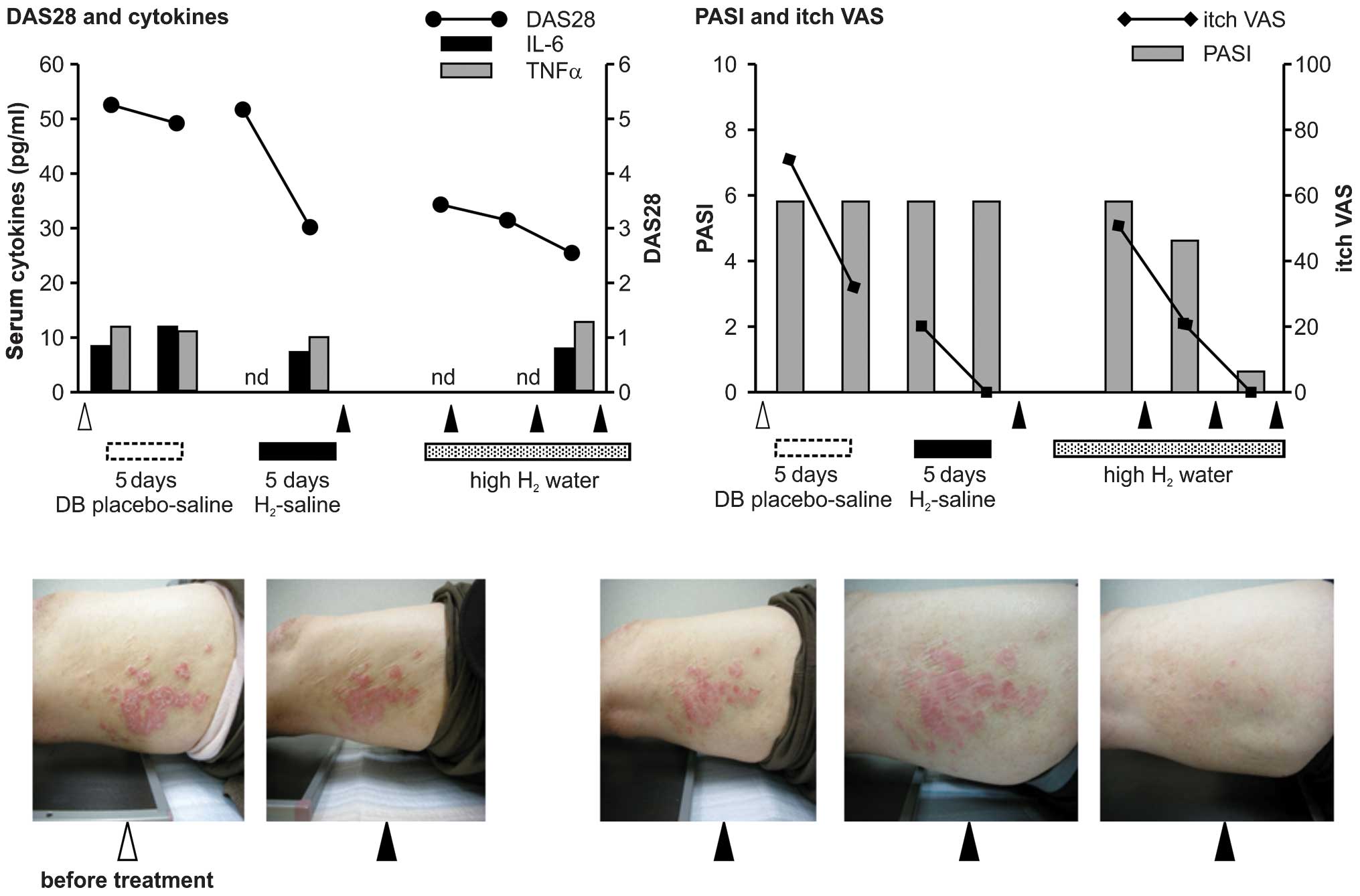
|
1
|
Schon MP and Boehncke WH: Psoriasis. N
Engl J Med. 352:1899–1912. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
2
|
Nestle FO, Kaplan DH and Barker J:
Psoriasis. N Engl J Med. 361:496–509. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
3
|
Goodman WA, Levine AD, Massari JV, et al:
IL-6 signaling in psoriasis prevents immune suppression by
regulatory T cells. J Immunol. 183:3170–3176. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
4
|
Arican O, Aral M, Sasmaz S and Ciragil P:
Serum levels of TNF-alpha, IFN-gamma, IL-6, IL-8, IL-12, IL-17 and
IL-18 in patients with active psoriasis and correlation with
disease severity. Mediators Inflamm. 2005:273–279. 2005. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
5
|
Mizutani H, Ohmoto Y, Mizutani T, Murata M
and Shimizu M: Role of increased production of monocytes TNF-alpha,
IL-1beta and IL-6 in psoriasis: relation to focal infection,
disease activity and responses to treatments. J Dermatol Sci.
14:145–153. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
6
|
Martin DA, Towne JE, Kricorian G, et al:
The emerging role of IL-17 in the pathogenesis of psoriasis:
preclinical and clinical findings. J Invest Dermatol. 133:17–26.
2013. View Article : Google Scholar :
|
|
7
|
Canavese M, Altruda F, Ruzicka T and
Schauber J: Vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF) in the
pathogenesis of psoriasis-a possible target for novel therapies? J
Dermatol Sci. 58:171–176. 2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
8
|
Zaba LC, Suárez-Fariñas M, Fuentes-Duculan
J, et al: Effective treatment of psoriasis with etanercept is
linked to suppression of IL-17 signaling, not immediate response
TNF genes. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 124:1022–1010. PubMed/NCBI
|
|
9
|
Chaudhari U, Romano P, Mulcahy LD, et al:
Efficacy and safety of infliximab monotherapy for plaque-type
psoriasis: a randomised trial. Lancet. 357:1842–1847. 2001.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
10
|
Ulmer A, Wölbing F, Metzler G, et al:
Severe exacerbation of chronic plaque psoriasis following initially
effective therapy with efalizumab: clinical characterization and
therapeutic management. Br J Dermatol. 158:867–869. 2008.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
11
|
Zhou Q, Mrowietz U and Rostami-Yazdi M:
Oxidative stress in the pathogenesis of psoriasis. Free Radic Biol
Med. 47:891–905. 2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
12
|
Gabr SA and Al-Ghadir AH: Role of cellular
oxidative stress and cytochrome c in the pathogenesis of psoriasis.
Arch Dermatol Res. 304:451–457. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
13
|
Lowes MA, Bowcock AM and Krueger JG:
Pathogenesis and therapy of psoriasis. Nature. 445:866–873. 2007.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
14
|
Ishibashi T: Molecular hydrogen: new
antioxidant and anti-inflammatory therapy for rheumatoid arthritis
and related diseases. Curr Pharm Des. 19:6375–6381. 2013.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
15
|
Arbiser JL: Fumarate esters as
angiogenesis inhibitors: key to action in psoriasis? J Invest
Dermatol. 131:1189–1191. 2011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
16
|
Lee DH, Gold R and Linker RA: Mechanisms
of oxidative damage in multiple sclerosis and neurodegenerative
diseases: therapeutic modulation via fumaric acid esters. Int J Mol
Sci. 13:11783–11803. 2012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
17
|
Ohsawa I, Ishikawa M, Takahashi K, et al:
Hydrogen acts as a therapeutic antioxidant by selectively reducing
cytotoxic oxygen radicals. Nat Med. 13:688–694. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
18
|
Gharib B, Hanna S, Abdallahi OM, et al:
Anti-inflammatory properties of molecular hydrogen: investigation
on parasite-induced liver inflammation. C R Acad Sci III.
324:719–724. 2001. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
19
|
Ohno K, Ito M and Ichihara M: Molecular
hydrogen as an emerging therapeutic medical gas for
neurodegenerative and other diseases. Oxid Med Cell Longev.
2012:3531522012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
20
|
Hukuda S, Minami M, Saito T, et al:
Spondyloarthropathies in Japan: nationwide questionnaire survey
performed by the Japan Ankylosing Spondylitis Society. J Rheumatol.
28:554–559. 2001.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
21
|
Ishibashi T, Sato B, Rikitake M, et al:
Consumption of water containing a high concentration of molecular
hydrogen reduces oxidative stress and disease activity in patients
with rheumatoid arthritis: an open-label pilot study. Med Gas Res.
2:272012. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
22
|
Ono H, Nishijima Y, Adachi N, et al: A
basic study on molecular hydrogen (H2) inhalation in acute cerebral
ischemia patients for safety check with physiological parameters
and measurement of blood H2 level. Med Gas Res. 2:212012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
23
|
Ono H, Nishijima Y, Adachi N, et al:
Improved brain MRI indices in the acute brain stem infarct sites
treated with hydroxyl radical scavengers, Edaravone and hydrogen,
as compared to Edaravone alone. A non-controlled study. Med Gas
Res. 1:122011. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
24
|
Ono H, Nishijima Y, Adachi N, Sakamoto M,
et al: Hydrogen (H2) treatment for acute erythematous
skin diseases. A report of 4 patients with safety data and a
non-controlled feasibility study with H2 concentration
measurement on two volunteers. Med Gas Res. 2:142012. View Article : Google Scholar
|
|
25
|
Abraini JH, Gardette-Chauffour MC,
Martinez E, Rostain JC and Lemaire C: Psychophysiological reactions
in humans during an open sea dive to 500 m with a
hydrogen-helium-oxygen mixture. J Appl Physiol (1985).
76:1113–1118. 1994.
|
|
26
|
Seo T, Kurokawa R and Sato B: A convenient
method for determining the concentration of hydrogen in water: use
of methylene blue with colloidal platinum. Med Gas Res. 2:12012.
View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
27
|
van de Kerkhof PC: The psoriasis area and
severity index and alternative approaches for the assessment of
severity: persisting areas of confusion. Br J Dermatol.
137:661–662. 1997. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
28
|
Mabuchi T, Yamaoka H, Kojima T, Ikoma M,
et al: Psoriasis affects patient’s quality of life more seriously
in female than in male in Japan. Tokai J Exp Clin Med. 37:84–88.
2012.PubMed/NCBI
|
|
29
|
Prevoo ML, van’t Hof MA and Kuper HH:
Modified disease activity scores that include twenty-eight-joint
counts. Development and validation in a prospective longitudinal
study of patients with rheumatoid arthritis. Arthritis Rheum.
38:44–48. 1995. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
30
|
Levin RW, Park J, Ostrov B, Reginato A, et
al: Clinical assessment of the 1987 American College of
Rheumatology criteria for rheumatoid arthritis. Scand J Rheumatol.
25:277–281. 1996. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
31
|
Reich A, Hrehorów E and Szepietowski JC:
Pruritus is an important factor negatively influencing the
well-being of psoriatic patients. Acta Derm Venereol. 90:257–263.
2010. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
32
|
Verhoeven EW, Kraaimaat FW, van de Kerkhof
PC, et al: Prevalence of physical symptoms of itch, pain and
fatigue in patients with skin diseases in general practice. Br J
Dermatol. 156:1346–1349. 2007. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
33
|
Raychaudhuri SK and Raychaudhuri SP: NGF
and its receptor system: a new dimension in the pathogenesis of
psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. Ann NY Acad Sci. 1173:470–477.
2009. View Article : Google Scholar : PubMed/NCBI
|
|
34
|
Zegarska B, Lelińska A and Tyrakowski T:
Clinical and experimental aspects of cutaneous neurogenic
inflammation. Pharmacol Rep. 58:13–21. 2006.PubMed/NCBI
|